0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3K views3 pagesCell References and Types of Cell References: Cell Address or Cell Reference
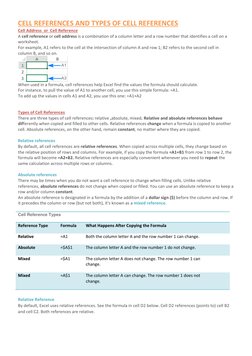
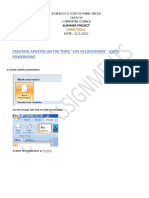
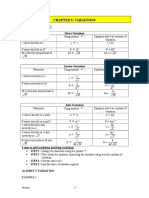
This document discusses different types of cell references in Excel formulas including relative, absolute, and mixed references. It provides examples of how each type of reference behaves when a formula is copied or filled to other cells. Relative references change when copied, absolute references remain constant, and mixed references keep either the row or column constant. The document demonstrates examples of each type of reference and how they can be used in formulas.
Uploaded by
swapnil sardarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3K views3 pagesCell References and Types of Cell References: Cell Address or Cell Reference
This document discusses different types of cell references in Excel formulas including relative, absolute, and mixed references. It provides examples of how each type of reference behaves when a formula is copied or filled to other cells. Relative references change when copied, absolute references remain constant, and mixed references keep either the row or column constant. The document demonstrates examples of each type of reference and how they can be used in formulas.
Uploaded by
swapnil sardarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Cell References Overview: Introduces the concept of cell references and how they identify specific locations in a spreadsheet.
- Types of Cell References: Describes different types of cell references such as relative, absolute, and mixed and their uses in formulas.
- Formula Application Examples: Illustrates practical applications of cell references in formulas to automate calculations across spreadsheet data.
- Important Notice and Email Contact: Provides important submission deadlines for assignments and includes a contact email for further communication.