Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Heterochromia Iridis - More Than Beautiful Eyes
Uploaded by
Johny Marquez TrochezOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Heterochromia Iridis - More Than Beautiful Eyes
Uploaded by
Johny Marquez TrochezCopyright:
Available Formats
Letter
Postgrad Med J: first published as 10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-137621 on 6 March 2020. Downloaded from http://pmj.bmj.com/ on May 15, 2020 at Uppsala Universitet BIBSAM Consortia.
Heterochromia iridis: More of age.4 Whereas in adults, on the other Jeyasakthy Saniasiaya
hand, eye hue changes are seen in about Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Hospital Tuanku
than beautiful eyes 15% of white population.5 Ja’afar Seremban, Seremban, Malaysia
Eye colour is determined by four Correspondence to Dr Jeyasakthy Saniasiaya,
elements: hereditary, sympathetic stim- Otorhinolaryngology, Hospital Tuanku Ja’afar Seremban,
The article on focal cortical dysplasia and ulation of iris melanocytes, melanocytic Seremban 70300, Malaysia; shakthy_18@yahoo.com
heterochromia of the iris in the ‘Images in stimulating hormone and biochemical Acknowledgements We would like to acknowledge
Medicine’ section reported an association factors of melanin metabolism.6 Heter- Dr Sarah Shafwan for the image taken.
between brain malformation and heter- ochomia attributed by congenital cause Contributors I am the sole contributor.
ochromia iridis.1 Although rare, this entity has three types: complete, sectoral and Funding The authors have not declared a specific
has drawn our attention to the often triv- central. In complete heterochromia, one grant for this research from any funding agency in the
ialised heterochromia iridis and its over- iris is different from the other, whereas public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
looked underlying pathology. in sectoral heterochromia, segment of Competing interests None declared.
Heterochromia iridis (HI) is defined as iris is of a different colour as compared Patient consent for publication Parental/guardian
variation in iris colour and structure. Aris- with the remaining iris. Spikes of various consent obtained.
totle called it heteroglaucos. Iris colour colours were noted to radiate from the Provenance and peer review Not commissioned;
is known to be derived in a Mendelian pupil.7 Despite being mostly sporadic and internally peer reviewed.
manner and is determined by concentra- benign, myriad syndromes are associated © Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2020. No commercial
tion of melanin.2 Iris may be hyperchromic with this entity. These include congen- re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
or hypochromic which occurs as a result of ital Horner’s syndrome, Sturge- Weber
a defect in the gene determining melanin syndrome, Waardenburg syndrome and
dispersal in the 8-HTP (hydroxyl trypto- Parry-Roomberg syndrome. Waarden-
burg syndrome is an autosomal-dominant To cite Saniasiaya J. Postgrad Med J Epub ahead of
phan) pathway.3 Blue-coloured iris occurs print: [please include Day Month Year]. doi:10.1136/
as a result of reflected light over scattered genetic condition that is evident at birth postgradmedj-2020-137621
melanin granules, whereas black-coloured characterised by pigmentation of hair,
Accepted 27 February 2020
skin, bilateral iris and congenital deafness
iris is following reflected light over the Postgrad Med J 2020;0:1.
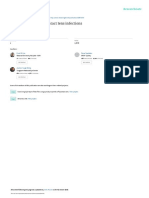
(figure 1).
black pigment of choroid. In addition to doi:10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-137621
Besides that, HI can occur following
that, iris has lipochrome—yellowish patch
Protected by copyright.
ocular trauma, foreign body, melanocytic ORCID iD
of fat pigment. Combination of pigments
infiltration and impaired sympathetic Jeyasakthy Saniasiaya http://orcid.org/0000-0003-
gives rise to various colours. For instance,
tone.8 HI associated with large malfor- 1974-4379
yellow and black pigment gives rise to
mation of the cortical development has
green iris. The Louisville Twin Study
also been reported.1 Iris colour can be References
revealed alteration in eye shade noted in 1 Reddy ST, Kalamangalam GP. Focal cortical dysplasia
affected by ageing, siderosis, metastatic
10% to 20% of children up until 6 years and heterochromia of the iris.. Postgrad Med J
carcinoma, juvenile xanthogranuloma,
2016;92:422.
acquired Horner syndrome and Fuchs 2 Wielgus AR, Sarna T. Melanin in human irides of
heterochromic iridocyclitis in addition different color and age of donors. Pigment Cell Res
to medication- induced pigmentation, 2005;18:454–64.
such as by latanoprost, a prostaglandin 3 Loewenstein J, Scott L. Ophthalmology: just the facts.
New York: McGraw-Hill, 2004.
analogue.9 10
4 Matheny AP, Dolan AB. Changes in eye colour during
Heterochromia warrants investigation early childhood: sex and genetic differences. Ann Hum
as myriad conditions have been reported Biol 1975;2:191–6.
to be associated with this entity. More- 5 Bito LZ, Matheny A, Cruickshanks KJ, et al. Eye color
over, thorough family history, notably changes past early childhood. The Louisville Twin
Study. Arch Ophthalmol 1997;115:659–63.
family pedigree, date and progression of 6 Gladstone RM. Development and significance
HI, history of ocular trauma as well as of heterochromia of the iris. Arch Neurol
head injury, is deemed necessary. Multidis- 1969;21:184–92.
ciplinary team evaluation should include 7 Tomar M, Dhiman R, Sharma G, et al. Artistic iris: a
ophthalmology team as a rule along with case of congenital sectoral heterochromia iridis. J
Ophthalmic Vis Res 2018;13:359–60.
other related teams based on history and 8 Ur Rehman H. Heterochromia. CMAJ 2008;179:447–8.
physical examination. Evaluation by 9 Eagle RC. Congenital, developmental and
ophthalmology team inevitably includes degenerative disorders of the iris and ciliary body.
slit-
lamp examination and intraocular In: Albert D, Jakobiec F, eds. Principles and practice
pressure measurement. Patients suspected of ophthalmology. Philadelphia: WB Saunders,
1994: 372.
with the syndrome requires audiological, 10 Selén G, Stjernschantz J, Resul B. Prostaglandin-
Figure 1 Heterochromia iridis with neurological and paediatric evaluation induced iridial pigmentation in primates. Surv
asymmetric colour. along with geneticist assessment. Ophthalmol 1997;41:S125–8.
Postgrad Med J Month 2020 Vol 0 No 0 1
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Drifters Game Workshop Hamund's Harvesting Handbook v1 02Document150 pagesDrifters Game Workshop Hamund's Harvesting Handbook v1 02João Nascimento75% (4)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Sample of JHA FormatDocument7 pagesSample of JHA Formatprince salangsangNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- OC Thinking-Sample-Explained-AnswersDocument8 pagesOC Thinking-Sample-Explained-AnswersSherry JiangNo ratings yet
- Electro Physiology of VisionDocument528 pagesElectro Physiology of VisionYazmin Peñaloza RoaNo ratings yet
- Iritis, Glaucoma and Corneal Decompensation Associated With BrightOcular Cosmetic Iris ImplantDocument5 pagesIritis, Glaucoma and Corneal Decompensation Associated With BrightOcular Cosmetic Iris ImplantJohny Marquez TrochezNo ratings yet
- A Review of Cosmetic Contact Lens Infections: Eye November 2018Document10 pagesA Review of Cosmetic Contact Lens Infections: Eye November 2018Johny Marquez TrochezNo ratings yet
- 10 1016@j Survophthal 2019 10 003Document26 pages10 1016@j Survophthal 2019 10 003judith cahuana aparcoNo ratings yet
- Pterygium: Surgical Techniques and ChoicesDocument2 pagesPterygium: Surgical Techniques and ChoicesJohny Marquez TrochezNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus Manifestaciones OcularesDocument6 pagesCoronavirus Manifestaciones OcularesJohny Marquez TrochezNo ratings yet
- Eye Care Surgery and Laser: Open Angle GlaucomaDocument2 pagesEye Care Surgery and Laser: Open Angle GlaucomaABDUL HADI ABD LATIFNo ratings yet
- Spectacle Non-Tolerance in Clinical Practice - A Systematic Review With Meta-AnalysisDocument14 pagesSpectacle Non-Tolerance in Clinical Practice - A Systematic Review With Meta-AnalysisjovanaNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: Hard Surface AntimicrobialDocument2 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Hard Surface AntimicrobialpNo ratings yet
- IncidenceDocument11 pagesIncidenceNenad ProdanovicNo ratings yet
- Neruda, Jan - VampireDocument3 pagesNeruda, Jan - VampireRicky Leonard PereiraNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Pupil, How To DoDocument8 pagesAbnormal Pupil, How To DoUNHAS OphthalmologyNo ratings yet
- @tonometryDocument49 pages@tonometryabhishek tNo ratings yet
- 8 Ppe PDFDocument18 pages8 Ppe PDFdeltacris1No ratings yet
- Choroidal Coloboma: Presenter:Dr. Rahul Moderator: Dr. ArchisDocument48 pagesChoroidal Coloboma: Presenter:Dr. Rahul Moderator: Dr. ArchisjihanNo ratings yet
- ODC Form 1ADocument11 pagesODC Form 1ADaphne MagsiNo ratings yet
- Facial Structure UnderstandingDocument9 pagesFacial Structure UnderstandingJose Maria Julian RoggenNo ratings yet
- CH 9 - Etiology of Heterophoria and Heterotropia, P. 134-152-EmailDocument19 pagesCH 9 - Etiology of Heterophoria and Heterotropia, P. 134-152-EmailAmi MisiciNo ratings yet
- Ocular ProstheticsDocument2 pagesOcular ProstheticsEshiramhe AugustineNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes - Ch10Document6 pagesRevision Notes - Ch10Hi hi ChanNo ratings yet
- MSDS Pertamina Radiator CoolantDocument4 pagesMSDS Pertamina Radiator CoolantMuhamad Hasbi100% (1)
- Dwnload Full Contemporary Auditing 10th Edition Knapp Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Contemporary Auditing 10th Edition Knapp Solutions Manual PDFfurmediatetbpwnk100% (16)
- The Client With Health Problems of The Eyes, Ears, Nose, and ThroatDocument13 pagesThe Client With Health Problems of The Eyes, Ears, Nose, and ThroatCiaraNo ratings yet
- Egs2022 Prog 0606Document67 pagesEgs2022 Prog 0606Natalia PalarieNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma NCPDocument4 pagesGlaucoma NCPChantal CaraganNo ratings yet
- Describing PeopleDocument4 pagesDescribing PeoplePalade Madalina-anaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22Document17 pagesChapter 22Jeferson Alexander Pabon RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Smartphone Use As A Possible Risk Factor For MyopiaDocument8 pagesSmartphone Use As A Possible Risk Factor For MyopialenniNo ratings yet
- Amblyopia - Httpsjamanetwork - Comjournalsjamafullarticle2775449Document1 pageAmblyopia - Httpsjamanetwork - Comjournalsjamafullarticle2775449Rael Rodrigues Dos SantosNo ratings yet
- JFF..H, .R) : B.'FT-F ......................Document1 pageJFF..H, .R) : B.'FT-F ......................rehanNo ratings yet
- Episcleral Brachytherapy For RetinoblastomaDocument6 pagesEpiscleral Brachytherapy For Retinoblastomamadimadi11No ratings yet
- PC 250 MTDocument36 pagesPC 250 MTTerrmosTerrmosNo ratings yet