Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Modal Verbs-Must, Have To.
Modal Verbs-Must, Have To.
Uploaded by
pesek beatrice0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageModal verbs such as can, could, may, might, must, have to, and should are used before other verbs but do not take verb endings. They are followed by the short form of the verb without "to." Must expresses strong obligation, have to expresses obligation not from the speaker, and should expresses mild advice or recommendations. Should and must are used to give advice, with must being stronger, while have to/don't have to and mustn't refer to obligation and prohibition.
Original Description:
o fisa teoretica cu explicatii pentru utilizarea unor verbe modale , contine si exemple.
Original Title
Modal verbs-must, have to.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentModal verbs such as can, could, may, might, must, have to, and should are used before other verbs but do not take verb endings. They are followed by the short form of the verb without "to." Must expresses strong obligation, have to expresses obligation not from the speaker, and should expresses mild advice or recommendations. Should and must are used to give advice, with must being stronger, while have to/don't have to and mustn't refer to obligation and prohibition.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageModal Verbs-Must, Have To.
Modal Verbs-Must, Have To.
Uploaded by
pesek beatriceModal verbs such as can, could, may, might, must, have to, and should are used before other verbs but do not take verb endings. They are followed by the short form of the verb without "to." Must expresses strong obligation, have to expresses obligation not from the speaker, and should expresses mild advice or recommendations. Should and must are used to give advice, with must being stronger, while have to/don't have to and mustn't refer to obligation and prohibition.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
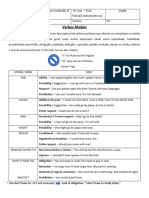
MODAL VERBS
-are auxiliaries
-come before other verbs
- do not take the verbal endings –s, -ing, -ed.
- are followed by the short infinitive (without TO)
Modal verbs: can, be able to, could, may, might, must, have to, should.
For requests, we use can, could, would. Could and would are usually a little more polite than
can.
Ex. Can I have a cup of coffee, please?
Could you say that again, please?
Would you lend me your phone, please?
HAVE TO, MUST, SHOULD
MUST – strong OBLIGATION /NECESSITY
- Shows that it is necessary to do something that comes from the speaker.
I must give up smoking.
MUSTN’T (the negative form) –PROHIBITION ( not to do things)
You mustn’t cross the street on red.
HAVE TO - strong OBLIGATION /NECESSITY
- obligation that doesn’t come from the speaker.
You have to pay to use Internet cafés.
DO NOT HAVE TO/DON’T HAVE TO – LACK OF OBLIGATION /NECESSITY
I don’t have to read this lesson.
SHOULD /SHOULDN’T –are used to make recommendations or to give advice
- Are used for giving mild advice You should prepare for your exam.
You shouldn’t eat so much bread.
MUST –for strong advice You must give up smoking!
You might also like
- Modal Verb ChartDocument4 pagesModal Verb ChartsarfarazNo ratings yet
- Infinitive or - Ing FormDocument2 pagesInfinitive or - Ing FormXantal Garcia100% (3)
- Giving DirectionDocument8 pagesGiving DirectionErina NiluhNo ratings yet
- Modals Semi-Modals: Always The Same Form. Change Form According To The SubjectDocument9 pagesModals Semi-Modals: Always The Same Form. Change Form According To The SubjectMaría RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Negatives Modals RaghdaaDocument12 pagesNegatives Modals RaghdaaAhmed Mohamed sSsNo ratings yet
- MODAL VERBS - Clasa A X ADocument11 pagesMODAL VERBS - Clasa A X ADumitruRalucaNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs BACHDocument26 pagesModal Verbs BACHZulcka TTVNo ratings yet
- Lessons 19th and 20th Productive, Receptive Skills and GrammarDocument7 pagesLessons 19th and 20th Productive, Receptive Skills and GrammarNaoaki ShiozawaNo ratings yet
- Modal Auxiliary VerbsDocument17 pagesModal Auxiliary VerbsEmmanuel PeralvilloNo ratings yet
- Modals HandoutDocument10 pagesModals Handoutjuliannaborbely7641No ratings yet
- MODAL VERBS (Simple Forms)Document3 pagesMODAL VERBS (Simple Forms)David Sánchez GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Modal VerbsDocument18 pagesModal VerbsInes BerriosNo ratings yet
- Session 09 - 10 Modal Verbs May, Might, Could, CouldntDocument18 pagesSession 09 - 10 Modal Verbs May, Might, Could, CouldntAlex Anthony Cruz VizcarraNo ratings yet
- Obligation-Permission in The PresentDocument9 pagesObligation-Permission in The PresentFelipe Mosquera BohorquezNo ratings yet
- Toeic Practice TestDocument17 pagesToeic Practice TestjoelNo ratings yet
- Here Is A List of Modal VerbsDocument2 pagesHere Is A List of Modal VerbsSarah EttaNo ratings yet
- Modal VerbsDocument2 pagesModal VerbsЕлвира ЧенковаNo ratings yet
- Modal VerbsDocument6 pagesModal VerbsbsanavalentinaNo ratings yet
- Should - Ought To AEF 2BDocument4 pagesShould - Ought To AEF 2BLi lyNo ratings yet
- MODALSDocument2 pagesMODALSMihaela MiricaNo ratings yet
- Exercícios Com Modal VerbsDocument1 pageExercícios Com Modal VerbsDoritos FxNo ratings yet
- Modal VerbsDocument5 pagesModal VerbsNataliaNo ratings yet
- 2.1.1. Form: 2. Sentence Types (By Functions) 2.1. Declarative SentencesDocument4 pages2.1.1. Form: 2. Sentence Types (By Functions) 2.1. Declarative SentencesthduyNo ratings yet
- Obligation and NecessityDocument3 pagesObligation and NecessityIsabel DobónNo ratings yet
- Modal VerbsDocument21 pagesModal VerbsIoana Margineanu100% (1)
- MustDocument3 pagesMustChiosa AdinaNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs GuideDocument10 pagesModal Verbs GuideDaniela Herrera Saboyá100% (1)
- Functions of Modal VerbsDocument2 pagesFunctions of Modal VerbsNare Britez100% (6)
- Auxiliary Verbs, Modal Auxiliaries) AreDocument3 pagesAuxiliary Verbs, Modal Auxiliaries) AreAijamal SartaevaNo ratings yet
- GrammarDocument3 pagesGrammarIlargi AnguloNo ratings yet
- Modals RephrasingDocument1 pageModals Rephrasingt89No ratings yet
- Modals in English GrammarDocument12 pagesModals in English GrammarUmmahUnity100% (1)
- English GrammarDocument16 pagesEnglish GrammarLyssia dfghjklNo ratings yet
- Modals and Semi-ModalsDocument11 pagesModals and Semi-Modalsmarinela100% (1)
- Forma Affermativa: NOTA BENE: Nella Forma Interrogativa Non Esistono Le ContrazioniDocument20 pagesForma Affermativa: NOTA BENE: Nella Forma Interrogativa Non Esistono Le ContrazioniGiulia CotugnoNo ratings yet
- Social Modals: Centro de Educación Integral CEDIDocument6 pagesSocial Modals: Centro de Educación Integral CEDIFundación CEDINo ratings yet
- Unit 2.modal VerbsDocument5 pagesUnit 2.modal VerbsjdaNo ratings yet
- Here Is A List of Modals With Examples:: Modal Verb Expressing ExampleDocument2 pagesHere Is A List of Modals With Examples:: Modal Verb Expressing ExampleNevena TrajkovicNo ratings yet
- Modal VerbsDocument16 pagesModal VerbsSoyun AnnayewNo ratings yet
- What Are Modal VerbsDocument2 pagesWhat Are Modal VerbsHasz Ronquillo100% (1)
- Mudul E4b2-20202121 OkeyDocument36 pagesMudul E4b2-20202121 OkeyAyu Dwi HapsariNo ratings yet
- Gerunds & Infinitives MasterclassDocument6 pagesGerunds & Infinitives MasterclassSusannaNo ratings yet
- Grammar: Auxiliary Verbs, Modal Auxiliaries) AreDocument4 pagesGrammar: Auxiliary Verbs, Modal Auxiliaries) AreVaishu UparkarNo ratings yet
- Modals With Activities For LearnersDocument26 pagesModals With Activities For LearnersJohn Jabez LuceroNo ratings yet
- Modal Auxiliary Part 1Document3 pagesModal Auxiliary Part 1Yeni HandayaniNo ratings yet
- Modals Choices Module6Document9 pagesModals Choices Module6cl0wn xyzNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris BisnisDocument4 pagesBahasa Inggris Bisniskura bearNo ratings yet
- MODALSDocument56 pagesMODALSMme. Jess PascualNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs, 11°Document6 pagesModal Verbs, 11°Manuel Esteban Ospina SanchezNo ratings yet
- Modals: Nur Laily Lupita Sari, M.PDDocument32 pagesModals: Nur Laily Lupita Sari, M.PDA LuckyNo ratings yet
- Verbos ModalesDocument3 pagesVerbos ModalesEsther GilNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs (1) Short NoteDocument7 pagesModal Verbs (1) Short NoteSelam TenayeNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs: Alida LindiaDocument16 pagesModal Verbs: Alida LindiaAlida Antonietta LindiaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 GramáticaDocument11 pagesUnit 4 GramáticaLILIAN DEL CARMEN RAMIREZ RIVASNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs-BatxDocument21 pagesModal Verbs-BatxMinhang Lin LinNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs 2Document7 pagesModal Verbs 2pepemusicaantequeraNo ratings yet
- Present TensesDocument15 pagesPresent TensesSmart TranslationNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs: Beatriz Jorge Isabbel Sandy PAUDocument31 pagesModal Verbs: Beatriz Jorge Isabbel Sandy PAUclara selene ojedaNo ratings yet
- Modals VerbsDocument2 pagesModals VerbsAbdennour BelarbiNo ratings yet
- Dictionary of English Idioms: Vocabulary BuildingFrom EverandDictionary of English Idioms: Vocabulary BuildingRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (4)