Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Eye Position Distribution Depends On Hea PDF
Uploaded by
Alvaro ChacónOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Eye Position Distribution Depends On Hea PDF
Uploaded by
Alvaro ChacónCopyright:
Available Formats
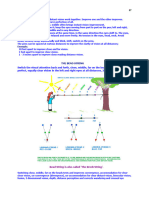
Eye Position Distribution Depends On Head Orientation
Yu Fang (fangyork@riec.tohoku.ac.jp)1, Ryoichi Nakashima2,3, Kazumichi Matsumiya2, Rumi Tokunaga2, Ichiro Kuriki2, Satoshi Shioiri2,3
1Graduate School of Information Sciences, Tohoku University 2Research Institute of Electrical Communication, Tohoku University 3Japan Science and Technology Agency, CREST
BACKGROUND RESULTS
Eye and head movement ※ The frequency of eye position in each head orientation and velocity was calculated (Data from all trials were analyzed).
Our visual field is limited, we need to move our head and body to The eyes oriented more in the direction of the head orientation.
obtain visual information from the word. Head orientation Head velocity The eyes oriented in the direction of the head motion.
Right/left of the head direction when the head directed right/left side.
Although the cooperation between eye and head movements has -27 ° -18 ° -9 ° 0° 9° 18 ° 27 ° -27 °/s -18 °/s -9 °/s 0 °/s 9 °/s 18 °/s 27 °/s
been reported(Zangmeister et al., 1982; Freedman et al., 2000; Cecala et al., 2008), in
Frequency (%)
Frequency (%)
which they studied with simple stimuli and/or without body
movements, there is only limited knowledge of how to move
cooperatively in the nature environment with the freely body
movements.
L ← → R L ← → R
Eye position (deg)
PURPOSE Eye position (deg)
R
R
To investigate the relationship between eye and head Head orientation and velocity
movements while searching for a target in a 360°visual The peak eye orientation is at right/left most, Evaluation of the eye position distributions
display with freely head and body movement. when the head orientation and velocity are both in right/left. by comparing the standard deviation of the distributions
**
MATERIALS AND METHODS 30
Standard Deviation (deg)
** p < .01
L
L
L R L R
→ R 15
**
Peak value of eye position
L distribution R
Head velocity (deg/s)
0 Head velocity Head orientation Head orientation and
velocity
Eight participants ran 4 blocks:
each block consisted of 48 trials. The standard deviation of eye position distribution classified based on both
The participant naturally moved R head orientation and velocity is significantly smaller than that classified
his head, eyes, and body to search -15 R based on either.
An example of head and eye movements
←
for the target and pressed a button L L → Eye position is correlated both with head orientation and velocity.
→ R
Head orientation
relative to body as soon as he found the target.
L
We measured participant’s eyes,
CONCLUSIONS
Degree
head and body movements.
-30
The distribution of the eye position tended to peak at right/left side of the head when the head
Eye position
oriented right/left and the head moved in right/left.
L ←
relative to head
When head oriented right/left,
eyes’ positions were biased to right/left. -30 -15 0 15 30 The gaze direction can be predicted as a distribution function with a standard deviation of less than
L ← Head orientation (deg) → R
Time (sec) 10 degrees by analyzing both head orientation and velocity.
You might also like
- Knapp and Turnbull ABA Curriculum PDFDocument426 pagesKnapp and Turnbull ABA Curriculum PDFBraile A100% (2)
- Abstract Reasoning - Test 1Document9 pagesAbstract Reasoning - Test 1Talal AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in H.O.P.E 3 Dance Traditional Dance I. ObjectivesDocument2 pagesLesson Plan in H.O.P.E 3 Dance Traditional Dance I. Objectivesrosemarie fortaleza100% (3)
- Employee EngagementDocument23 pagesEmployee EngagementMikha Jane MataNo ratings yet
- Reliability and ValidityDocument2 pagesReliability and ValidityDavid_belemNo ratings yet
- Clinical Skills Week 1Document3 pagesClinical Skills Week 1Aishah SiddiqahNo ratings yet
- Psychological Disorders Chapter OutlineDocument13 pagesPsychological Disorders Chapter OutlineCameron PhillipsNo ratings yet
- Facial Keys To Orthodontic Diagnosis and Treatment, Part IIDocument15 pagesFacial Keys To Orthodontic Diagnosis and Treatment, Part IIAlvaro Chacón100% (1)
- Shooting With Both Eyes Open The Correct MethodDocument2 pagesShooting With Both Eyes Open The Correct MethodAmmoLand Shooting Sports News100% (1)
- Vision Screening Form DepedDocument3 pagesVision Screening Form DepedAbigael Abac RiveraNo ratings yet
- The Pragmatic ApproachDocument5 pagesThe Pragmatic ApproachAnonymous 6rSv4gofkNo ratings yet
- 8 Answer Key A: GrammarDocument6 pages8 Answer Key A: GrammarFirstNameNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPJoshua DecenaNo ratings yet
- Stereoscopic VisionDocument4 pagesStereoscopic Visionsunleon31No ratings yet
- Vision ResearchDocument8 pagesVision Researchqq1309782250No ratings yet
- Head Pose EstimationDocument32 pagesHead Pose Estimationمسافر عابرNo ratings yet
- Kasus Rujukan MataDocument52 pagesKasus Rujukan MatadepihermawanNo ratings yet
- Marotta Neuropsychologia 2019Document7 pagesMarotta Neuropsychologia 2019Damián Baños SáezNo ratings yet
- Hough Pupil Detection0459Document10 pagesHough Pupil Detection0459ingrid.joraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Ocular Motor SystemDocument1 pageChapter 7 Ocular Motor SystemDeena Al NuaimiNo ratings yet
- The Coding and Updarting of Visuospatial Memory For Goal-Directed Reaching and PointingDocument8 pagesThe Coding and Updarting of Visuospatial Memory For Goal-Directed Reaching and PointingYUREINY DUCUARA GONZALEZNo ratings yet
- Squirting Exactly Squirting During: AngularDocument1 pageSquirting Exactly Squirting During: Angularfaizanmalik.znNo ratings yet
- Rodrigues 2015Document4 pagesRodrigues 2015Benjapol BenjapalakornNo ratings yet
- Beyond One 'S Body Parts: Remote Object Movement With Sense of Agency Involuntarily Biases Spatial AttentionDocument7 pagesBeyond One 'S Body Parts: Remote Object Movement With Sense of Agency Involuntarily Biases Spatial AttentiondaikuroitsukiNo ratings yet
- 30 June 2020 - Stereophotogrammetry by Dr. Poonam S. TiwariDocument36 pages30 June 2020 - Stereophotogrammetry by Dr. Poonam S. TiwariLiamNo ratings yet
- There Are 5 Types of Eye Movements. EachDocument1 pageThere Are 5 Types of Eye Movements. EachGASA1111No ratings yet
- AUTOLEVELDocument49 pagesAUTOLEVELChetan ChauhanNo ratings yet
- A Comparison of Tests For Quantifying Sensory Eye DominanceDocument10 pagesA Comparison of Tests For Quantifying Sensory Eye DominanceBONNo ratings yet
- Notetaking - CS3VRC1611Document10 pagesNotetaking - CS3VRC1611SazNo ratings yet
- Language of AnatomyDocument6 pagesLanguage of AnatomyGwen KimNo ratings yet
- Randot LEA InstructionsDocument2 pagesRandot LEA InstructionsKeerthana KumarNo ratings yet
- Visually Guided Eye Movements Reduce Postural Sway in Dyslexic ChildrenDocument6 pagesVisually Guided Eye Movements Reduce Postural Sway in Dyslexic ChildrenGabriella FigueiredoNo ratings yet
- Non Manuals in Sign LanguagesDocument34 pagesNon Manuals in Sign LanguagesClevis LimaNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Binocular VisionDocument28 pagesBasic Concepts of Binocular Visionhenok birukNo ratings yet
- 2016 - Tau G GuidanceDocument16 pages2016 - Tau G GuidanceMayankNo ratings yet
- Zoology BSCDocument60 pagesZoology BSCdeathisreal1331No ratings yet
- Binocular Vision With Rotationally Asymmetric Multifocal IOLs at Different OrientationsDocument1 pageBinocular Vision With Rotationally Asymmetric Multifocal IOLs at Different OrientationsTjundewo LawuNo ratings yet
- Stereoscopic Vision, Stereoscope, Selection of Stereo Pair and Its OrientationDocument6 pagesStereoscopic Vision, Stereoscope, Selection of Stereo Pair and Its OrientationrekhaNo ratings yet
- Week 24 - Day 3 - Reflection of LightDocument21 pagesWeek 24 - Day 3 - Reflection of Lightnouran alsaadanyNo ratings yet
- 3D TelevisionDocument8 pages3D TelevisionAlexander BokovNo ratings yet
- 1 GearsDocument27 pages1 GearsKhaled AlhamawiNo ratings yet
- Sim 1 PDFDocument27 pagesSim 1 PDFJhasmia MabayaNo ratings yet
- 01 Early Visual ProcessingDocument73 pages01 Early Visual ProcessingsethNo ratings yet
- Drowsy Detection System Using SVM Classifier: Email: Mprabukumar@vit - Ac.inDocument32 pagesDrowsy Detection System Using SVM Classifier: Email: Mprabukumar@vit - Ac.inDharmaNo ratings yet
- How Do We ReadDocument7 pagesHow Do We ReadRonnel Manilag AtienzaNo ratings yet
- SUT 171 Fundamentals of Surveying Unit # 4 "Measurement of Angles"Document7 pagesSUT 171 Fundamentals of Surveying Unit # 4 "Measurement of Angles"TsegishNo ratings yet
- Lets Try 2 - Yearly Instruction Plan - ENGDocument2 pagesLets Try 2 - Yearly Instruction Plan - ENGjuan25amarilloNo ratings yet
- LEA Symbols FLY 2017 User Manual ONLY 12212017 2Document2 pagesLEA Symbols FLY 2017 User Manual ONLY 12212017 2David VásquezNo ratings yet
- Photogeo 2Document17 pagesPhotogeo 2som ranaNo ratings yet
- VTX 1287519847538 402Document1 pageVTX 1287519847538 402Dominic FatinikunNo ratings yet
- Whats The Weather Like American English Teacher Ver2Document4 pagesWhats The Weather Like American English Teacher Ver2Alejandra VegaNo ratings yet
- Stereo FLY Instruction Manual 09 2018Document2 pagesStereo FLY Instruction Manual 09 2018Jennifer Andrea PardoNo ratings yet
- Academic Profile ExampleDocument11 pagesAcademic Profile ExampleMakiNo ratings yet
- Starting at Just: CoursesDocument25 pagesStarting at Just: CoursesAditiNo ratings yet
- Revista Dental Press de Ortodontia e Ortopedia FacialDocument27 pagesRevista Dental Press de Ortodontia e Ortopedia FacialGabriela BarbozaNo ratings yet
- Ergonomic Desin Study Nov 2010Document13 pagesErgonomic Desin Study Nov 2010Watson A. Gama JrNo ratings yet
- Signfer and Signfied - A Study of Ibin Jini's Linguistics ThoughtDocument12 pagesSignfer and Signfied - A Study of Ibin Jini's Linguistics ThoughtAchmad KusumahNo ratings yet
- Saúde Ocular TDR Parceiros FINAL1Document6 pagesSaúde Ocular TDR Parceiros FINAL1Jorge TaylorNo ratings yet
- Week 4-A Lecture Artheory1Document25 pagesWeek 4-A Lecture Artheory1Francis DavidNo ratings yet
- Hoya Nulux EPDocument4 pagesHoya Nulux EPevershineopticalNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.2-1.3 - Descrbing Motion & Technology For SafetyDocument32 pagesLesson 1.2-1.3 - Descrbing Motion & Technology For Safety- TheTrueMainCharacter -No ratings yet
- Coursebook: Track Your ProgressDocument5 pagesCoursebook: Track Your ProgressKrishaNo ratings yet
- Gerund PhraseDocument2 pagesGerund PhrasejezauroraaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 AnglesDocument14 pagesLecture 6 AnglesJEAN DE DIEU MUVARANo ratings yet
- Revolution Manual PDFDocument2 pagesRevolution Manual PDFKoukis PericlesNo ratings yet
- Whats The Weather Like American English Teacher Ver2 BWDocument3 pagesWhats The Weather Like American English Teacher Ver2 BWAlejandra González MartínezNo ratings yet
- Loads of Continuous Mechanics For Uprighting The Second Molar On The Second Molar and PremolarDocument8 pagesLoads of Continuous Mechanics For Uprighting The Second Molar On The Second Molar and PremolarAlvaro ChacónNo ratings yet
- Treatment Decisions On Molar-Incisor HypomineralizDocument8 pagesTreatment Decisions On Molar-Incisor HypomineralizAlvaro ChacónNo ratings yet
- Physical Mechanical and Flexural Properties of 3 Orthodontic Wires An in Vitro Study. DANIELA DLICANDocument8 pagesPhysical Mechanical and Flexural Properties of 3 Orthodontic Wires An in Vitro Study. DANIELA DLICANAlvaro ChacónNo ratings yet
- Systematic Review of Self-Ligating Brackets. ALVARO CHACONDocument18 pagesSystematic Review of Self-Ligating Brackets. ALVARO CHACONAlvaro ChacónNo ratings yet
- Role of Bone Screw (Izc & BSS) in Skeletal Anchorage System - A Review ArticleDocument5 pagesRole of Bone Screw (Izc & BSS) in Skeletal Anchorage System - A Review ArticleAlvaro ChacónNo ratings yet
- Virtual Setup in Orthodontics Planning and Evaluation - CLAUDIA GALLARDODocument9 pagesVirtual Setup in Orthodontics Planning and Evaluation - CLAUDIA GALLARDOAlvaro ChacónNo ratings yet
- Force Levels of Nickel Titanium Initial Archwires. LESLIE LOZANODocument7 pagesForce Levels of Nickel Titanium Initial Archwires. LESLIE LOZANOAlvaro ChacónNo ratings yet
- Up-to-Date Approach in The Treatment of Impacted MDocument10 pagesUp-to-Date Approach in The Treatment of Impacted MAlvaro ChacónNo ratings yet
- Setup 3DDocument8 pagesSetup 3DAlvaro ChacónNo ratings yet
- The Forsus Fatigue Resistant Device: Better Than Elastics For Class IIDocument5 pagesThe Forsus Fatigue Resistant Device: Better Than Elastics For Class IIAlvaro ChacónNo ratings yet
- 2018 Millett - Orthodontic Treatment For Deep Bite and Retroclined Upper Front Teeth in ChildrenDocument17 pages2018 Millett - Orthodontic Treatment For Deep Bite and Retroclined Upper Front Teeth in ChildrenAlvaro ChacónNo ratings yet
- Tanzo Classic 23L WosonDocument9 pagesTanzo Classic 23L WosonAlvaro ChacónNo ratings yet
- The Relationship Between Cranial Base Angle and Various Malocclusion TypesDocument5 pagesThe Relationship Between Cranial Base Angle and Various Malocclusion TypesAlvaro ChacónNo ratings yet
- The Skeletodental Adaptations in Deep Bite CorrectionDocument6 pagesThe Skeletodental Adaptations in Deep Bite CorrectionAlvaro ChacónNo ratings yet
- Angle 2005 Filtekvs MCIndirect BondDocument6 pagesAngle 2005 Filtekvs MCIndirect BondAlvaro ChacónNo ratings yet
- Juan Mondragon, 30.0 M: Report Generated by Oneceph Thu Aug 22 16:17:09 Gmt-05:00 2019Document2 pagesJuan Mondragon, 30.0 M: Report Generated by Oneceph Thu Aug 22 16:17:09 Gmt-05:00 2019Alvaro ChacónNo ratings yet
- Effects of Direct and Indirect Bonding Techniques PDFDocument9 pagesEffects of Direct and Indirect Bonding Techniques PDFAlvaro ChacónNo ratings yet
- 19-A Natural Head Position Technique For Radiographic CephalometryDocument3 pages19-A Natural Head Position Technique For Radiographic CephalometryAlvaro ChacónNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Shear Bond Strength of Orthodontic BDocument5 pagesComparison of Shear Bond Strength of Orthodontic BAlvaro ChacónNo ratings yet
- Indirect Bonding - A New Transfer MethodDocument9 pagesIndirect Bonding - A New Transfer MethodAlvaro ChacónNo ratings yet
- The Indirect Bonding Technique in Orthodontics-A Narrative Literature ReviewDocument9 pagesThe Indirect Bonding Technique in Orthodontics-A Narrative Literature ReviewAlvaro ChacónNo ratings yet
- The Measurement of Craniocervical Posture A Simple Method To EvaluateDocument5 pagesThe Measurement of Craniocervical Posture A Simple Method To EvaluateAlvaro ChacónNo ratings yet
- The Relationship Between Estimated and Registered PNCDocument6 pagesThe Relationship Between Estimated and Registered PNCAlvaro ChacónNo ratings yet
- Juan Mondragon, 30.0 M: Report Generated by Oneceph Thu Aug 22 16:22:26 Gmt-05:00 2019Document2 pagesJuan Mondragon, 30.0 M: Report Generated by Oneceph Thu Aug 22 16:22:26 Gmt-05:00 2019Alvaro ChacónNo ratings yet
- Three Dimensional Reproducibility of NHPDocument7 pagesThree Dimensional Reproducibility of NHPAlvaro ChacónNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Using Mobile Phone in The School Joseph Guevarra ResearchDocument3 pagesThe Effect of Using Mobile Phone in The School Joseph Guevarra ResearchTata Duero LachicaNo ratings yet
- Heutagogy and PeeragogyDocument5 pagesHeutagogy and PeeragogySilves VoIONo ratings yet
- 2017 Tasso PsychodynamicPsychotherapy PrimaryCareDocument8 pages2017 Tasso PsychodynamicPsychotherapy PrimaryCareWycliffe OtienoNo ratings yet
- Language Acquisition - Reporter'sDocument9 pagesLanguage Acquisition - Reporter'sBA ELSIWANG, PRECIOUS GAYLE T.No ratings yet
- Second Level-Learning English: "Institute Technical Language Military"Document3 pagesSecond Level-Learning English: "Institute Technical Language Military"Luis Romer Soliz AndiaNo ratings yet
- Teaching and Learning Cycle ProformaDocument3 pagesTeaching and Learning Cycle Proformaapi-264380514No ratings yet
- Two Poles of TheologyDocument1 pageTwo Poles of Theologynelle de leonNo ratings yet
- Developing Entrepreneurship Team and OrganisationDocument34 pagesDeveloping Entrepreneurship Team and OrganisationMuhammad SyahmiNo ratings yet
- Lost in Translation: Scene Analysis: Task 2Document3 pagesLost in Translation: Scene Analysis: Task 2Janelle Bianca GuanteroNo ratings yet
- Factors Influencing Training Effectiveness Among Employees: A Case of Sigma SDN BHDDocument13 pagesFactors Influencing Training Effectiveness Among Employees: A Case of Sigma SDN BHDShajith SudhakaranNo ratings yet
- OB Chapter 1: Controlling Planning Staffing OrganizingDocument10 pagesOB Chapter 1: Controlling Planning Staffing OrganizingApurvakc KcNo ratings yet
- Game Elements and ExamplesDocument3 pagesGame Elements and ExamplesEissej Dawn EchonNo ratings yet
- Class DojoDocument8 pagesClass DojoJelyn LapermeNo ratings yet
- 1 Presentation 208Document25 pages1 Presentation 208Yuki SeishiroNo ratings yet
- Customer Pyramid: A Proven CRM StrategyDocument6 pagesCustomer Pyramid: A Proven CRM StrategyRolandas Medžiūnas50% (2)
- Opd3e LP 02 04 1Document2 pagesOpd3e LP 02 04 1api-269352299No ratings yet
- DAGMARDocument6 pagesDAGMARraviNo ratings yet
- WEEK 13 - (DAY 1 To DAY 3) - MATH 1Document3 pagesWEEK 13 - (DAY 1 To DAY 3) - MATH 1Southwill learning centerNo ratings yet
- Statement of Research Philosophy - Genna Reeves - 11-21-15Document2 pagesStatement of Research Philosophy - Genna Reeves - 11-21-15api-240203048No ratings yet
- Notes On FoucaultDocument6 pagesNotes On FoucaultUrszula SzyszkaNo ratings yet
- How We RaiseDocument19 pagesHow We RaiseErickson ManaladNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 4 - About Me - Paragraph Structure 2Document3 pagesLesson Plan 4 - About Me - Paragraph Structure 2api-242370085No ratings yet