Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Language of Anatomy
Uploaded by
Gwen Kim0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views6 pages1) Anatomy studies the structure and shape of the body parts, their relationships, and positions. Gross anatomy looks at structures visible to the eye, while microscopic anatomy requires a microscope.
2) Physiology studies the functions of body parts and organs that sustain life, including at the systemic, cellular, and pathological levels.
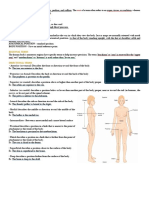
3) Special terminology is used in anatomy to avoid misunderstanding by referring to standardized anatomical position and terms for location, direction, and body regions. Precise anatomical language allows clear description of relationships between structures.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) Anatomy studies the structure and shape of the body parts, their relationships, and positions. Gross anatomy looks at structures visible to the eye, while microscopic anatomy requires a microscope.
2) Physiology studies the functions of body parts and organs that sustain life, including at the systemic, cellular, and pathological levels.
3) Special terminology is used in anatomy to avoid misunderstanding by referring to standardized anatomical position and terms for location, direction, and body regions. Precise anatomical language allows clear description of relationships between structures.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views6 pagesLanguage of Anatomy
Uploaded by
Gwen Kim1) Anatomy studies the structure and shape of the body parts, their relationships, and positions. Gross anatomy looks at structures visible to the eye, while microscopic anatomy requires a microscope.
2) Physiology studies the functions of body parts and organs that sustain life, including at the systemic, cellular, and pathological levels.
3) Special terminology is used in anatomy to avoid misunderstanding by referring to standardized anatomical position and terms for location, direction, and body regions. Precise anatomical language allows clear description of relationships between structures.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
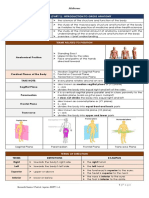
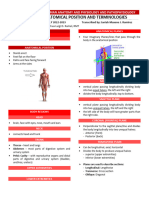
Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Language of Anatomy
→ The Human Body: An Introduction Special terminology is used to prevent
Anatomy misunderstanding
- Studies the structure, shape, form of the Exact terms are used for:
body parts and their relation → position
● Types of Anatomy → direction
Gross Anatomy → regions
- Body parts/structures that can be → structures
easily observed with the naked eye Anatomical Position
Microscopic Anatomy - Standard position used to avoid confusion
- Observed using a microscope - Terminology refers to this position
Physiology regardless of actual body position
- Studies the different functions of body → stand erect, feet parallel, arms hanging
parts/organs that help keep us alive at the side with palms facing forward and
● Subdivision of Physiology thumbs pointing away from the body
Systemic ● Supine
- Studies the different function of - Subject is lying down and
different organ systems facing up
Cellular ● Prone
- Studies the physiological process - Lying with face down
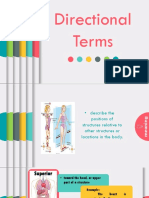
that cells undergo Directional terms
Pathological - Explain location of one body structure in
- Studies the disordered physiological relation to another
process during instances of - Allows to describe the relationship between
diseases and/or injuries two structures
● Superior (Cranial or Cephalic)
- Toward the head or upper
part of the structure/body;
above
● Inferior (Caudal)
- Away from the head or toad
the lower part of a structure
or the body; below
→ example: the nose is superior to
the mouth; the relation of the mouth
to the nose is inferior
● Anterior (Ventral)
- Toward or at the front of the
body; in front of
● Posterior (Dorsal)
- Toward or at the backside of
the body; behind
→ example: the breastbone is
anterior to the spine; the relation of
the kidney to the abdominal wall is
posterior
(clearer image on phone)
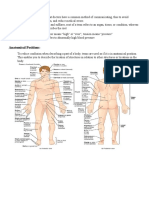
● Medial Regional terms
- Toward or at the midline of There are many visible landmarks on the
the body; on the inner side of surface of the body. Once you have
● Lateral knowledge of proper anatomical terms, you
- Away from the midline of the can be specific when referring to different
body; on the outer side of regions of the body.
● Intermediate ● Anterior Body Landmarks
- Between a more medial and
more lateral structure
→ example: The heart is located in
the middle of the left and right lung,
therefore the heart is medial to
the lungs. The lungs are located on
the sides of the heart, therefore the
lungs are lateral to the heart. The
eyes are located in the middle of the
nose and the ear, therefore the
eyes are intermediate to the nose
and the ear
● Proximal
- Close to the origin of the
body part or point of
attachment to a limb to the
body trunk
● Distal
- Farther from the origin of a
body part or the point of
attachment of a limb to the
❖ Cephalic
body trunk
➔ Frontal - forehead
→ example: the knee is proximal to
➔ Orbital - eye area
the ankle since the knee is nearer to
➔ Nasal - nose area
the hip or the point of attachment
➔ Buccal - cheek area
compared to the ankle. The wrist is
➔ Oral - mouth
distal to the elbow since the wrist is
➔ Mental - chin
farther to the shoulder than the
❖ Cervical - neck region
elbow
❖ Thoracic - area between the neck and
● Superficial (external)
abdomen, supported by the ribs and
- Toward or at the body
sternum and costal cartilages
surface
➔ Sternal - breastbone
● Deep (internal)
➔ Axillary - armpit
- Away from the body surface;
➔ Pectoral - relating to or occurring in
more internal
or on the chest
→ example: the skin is superficial to
❖ Abdominal - anterior body trunk inferior to
the skeleton since the skin is found
the ribs
outside of the body and the skeleton
➔ Umbilical - navel
is inside. The lungs are deep to the
❖ Pelvic - area overlying the pelvis anteriorly
rib cage because the lungs are
➔ Inguinal (groin) - area where thigh
found inside of the rib cage.
meets the body trunk
❖ Pubic (genital) ❖ Back (dorsal)
❖ Upper limb ➔ Scapular- the shoulder blade region
➔ Acromial - point of the shoulder ➔ Vertebral - pertaining to the area of
➔ Deltoid - curve of the shoulder the spinal column
formed by large deltoid muscle ➔ Lumbar- area of the back between
➔ Brachial (arm) the lips on the hips or this is also
➔ Antecubital - anterior surface of the known as colloid
elbow ➔ Sacral - area between the hips at the
➔ Antebrachial (forearms) base of the spine and
➔ carpal (wrist) ➔ Gluteal - the bottom area now
❖ Manus (hand) ❖ Upper limb
➔ Digital - fingers ➔ Acromial - points of the shoulder
❖ Lower limb ➔ brachial arm
➔ Coxal (hip) ➔ Olecranal - posterior surface of the
➔ Femoral (thigh) that applies to both elbow
anterior and posterior ➔ antebrachial (forearm)
➔ Patellar - anterior knee ❖ Manus (hand)
➔ Crural (leg) - anterior leg or shin ➔ Digital (fingers)
➔ Fibular - lateral part of the leg ❖ Lower limb
❖ Pedal (foot) ➔ Femoral (thigh)
➔ Tarsal (ankle) ➔ Popliteal - posterior knee area
➔ Digital - toes ➔ Sural (calf) - posterior surface of the
leg
● Posterior Body Landmarks ➔ Fibular - lateral part of leg
❖ Pedal (foot)
➔ Calcaneal - heel of foot
➔ Plantar - sole of the foot actually on
the inferior body surface
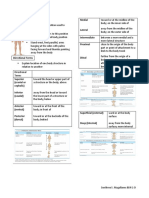
Body Planes and Sections
Sections
- are cuts along imaginary lines known as
planes
To better understand the structure or
function sections are made to see the
internal structure of the body or organ
three types of planes or sections exist as
right angles to one another
● Sagittal section
- divides the body or organ into left
and right parts
- Cutting body into left and right
portions regardless of its size and
❖ Cephalic volume on each side
➔ Occipital - posterior surface of the ● Median or Midsagittal
head or base of the skull - divides the body or organ into equal
❖ Cervical - posterior portion of the neck left and right parts
region
● Frontal section > the central region
- is a cut along a lengthwise plane > houses heart, trachea, and
divides the body or organ into other visceral organs
anterior and posterior parts > separate the lungs into the
● Transverse or Cross section right and left cavities in the
- it is a cut along a horizontal plane thoracic cavity
dividing the body or organ into - Protected by the rib cage
superior and inferior parts → Abdominopelvic cavity
- Cavity inferior to the
2 Internal Body Cavities diaphragm
- Superior abdominal cavity
> contains the stomach, liver,
and other organs
> Protected only by trunk
muscles
- Inferior pelvic cavity
> contains reproductive
organs, bladder, and rectum
> protected somewhat by
bony pelvis
- No physical structure
separates abdominal from
pelvic cavities
- The pelvic cavity is not
immediately inferior to the
abdominal cavity but rather,
this tips away from the
abdominal cavity in the
posterior direction
● Dorsal - Abdominopelvic cavity
- Has 2 subdivisions subdivisions
→ Cranial Cavity > 4 Quadrants of Abdominopelvic Cavity (Subd.)
- Houses the brain
- Protected by the skull
→ Spinal cavity
- Houses the spinal cord
- Protected by the vertebrae
● Ventral
- Has 2 subdivision separated by the
diaphragm
- Contains all the structures within the
chest and abdomen
→ Thoracic cavity
- Cavity superior to the
diaphragm
- Houses the heart, lungs, and - Named according to their relative location
other organs with respect to anatomical position
- Mediastinum
● RUQ ● Hypochondriac Region
- Contains the liver, right kidney, ➔ Right hypochondriac region
gallbladder, portion of the colon and - Liver, right kidney and the
pancreas large small intestine
● LUQ ➔ Left hypochondriac region
- Contains stomach, left kidney, - Liver’s tip, stomach
spleen, portion of the colon and pancreas, left kidney, spleen,
pancreas large and small intestine
● RLQ ● Epigastric Region
- Appendix, colon, small intestine, - Superior to the umbilical region
ureter, major vein and artery to the - Contains the liver, stomach, spleen,
right leg duodenum, adrenal glands, and
● LLQ pancreas
- Contains colon, small intestine, ● Lumbar Region
ureter, major vein and artery to the - Lateral to the umbilical region and
left leg spinal column between the bottom
Midline contains the aorta, pancreas small ribs and the hip bone
intestine, bladder and the spine ➔ Right Lumbar Region
- Ascending colon, small
> 9 Regions of Abdominopelvic Cavity (Subd.) intestine, and right kidney
➔ Left
- Descending colon, small
intestine, left kidney
● Umbilical Region
- Center most region
- Deep to and surrounding the
umbilicus
- Contains the duodenum, small
intestine, transverse colon
● Iliac Region
- Lateral to the hypogastric region
➔ Right Iliac (Inguinal) Region
- Appendix, secum, ascending
colon, and small intestine
➔ Left Iliac (Inguinal) Region
- Contains sigmoid colon
descending colon, small
intestine
● Hypogastric (Pubic) Region
- Inferior to the umbilical region
- Contains the bladder sigmoid colon,
small intestine, reproductive organs
these body cavities provide varying degrees
of protection to the organs within them
Other body cavities
● Smaller cavities, most in the head open to
the body exterior
● Oral and digestive cavities
- Oral cavity is connected with the
digestive cavity which open to the
anus
● Nasal cavity
- posterior to the nose
- respiratory
● Orbital cavities
- house eyes
- anterior position
● Middle ear cavities
- carve into the skull and lie medial to
the ear drums
- contains tiny bones that transmits
sound vibration to the hearing
receptors in the inner ear
You might also like
- Anatomy and Physiology NotesDocument9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology NotesBeatriz Nidea83% (6)
- Anatomical Terminology PDFDocument22 pagesAnatomical Terminology PDFProdosh Chatterjee100% (1)
- Chapter 2 General Orientation To Human Body and Basic Anatomical TerminologyDocument41 pagesChapter 2 General Orientation To Human Body and Basic Anatomical TerminologymintsaoraNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy 1 - Unit 1 - Language of AnatomyDocument5 pagesAnaPhy 1 - Unit 1 - Language of AnatomyAndrea JiongcoNo ratings yet
- OB Chap 22 - Normal LaborDocument4 pagesOB Chap 22 - Normal LaborChino Paolo SamsonNo ratings yet
- Origin and History of ETHOLOGY - Founders of EthologyDocument16 pagesOrigin and History of ETHOLOGY - Founders of Ethology7037Anant kumar prajapati100% (3)
- NCM 107 Rle 2Document2 pagesNCM 107 Rle 2Patricia RamosNo ratings yet
- Biology of CitrusDocument240 pagesBiology of CitrusEvaldoNo ratings yet
- PCR Troubleshooting and OptimizationDocument608 pagesPCR Troubleshooting and Optimizationlaytailieu20220% (1)
- Laboratory 1. Anatomical Position and TerminologiesDocument2 pagesLaboratory 1. Anatomical Position and TerminologiesAANo ratings yet
- Introduction To Anatomy and Physiology Part 2Document6 pagesIntroduction To Anatomy and Physiology Part 2Abby Claire SomeraNo ratings yet
- AnaphyDocument8 pagesAnaphyRachell Joy FloresNo ratings yet
- Happ Lab 1Document5 pagesHapp Lab 1Jerwin TullaoNo ratings yet
- Anakines Midterm X Finals GL PTRPDocument156 pagesAnakines Midterm X Finals GL PTRPGABRIEL MIGUEL ALEJANDRO YUMULNo ratings yet
- Anatomical PositionDocument36 pagesAnatomical PositionMoza AlaliliNo ratings yet
- General Orientation of The Body Part 1Document11 pagesGeneral Orientation of The Body Part 1Maria Faith Jeneen Bisnar100% (1)
- Week 1 - Terms, Tissues and Medical ImagingDocument17 pagesWeek 1 - Terms, Tissues and Medical Imagingatgriffo100% (1)
- Introduction To AnaPhy Pt. 2Document3 pagesIntroduction To AnaPhy Pt. 2Sofia LozanoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 - Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument9 pagesCHAPTER 6 - Anatomy and PhysiologyLaraib HabibNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - ANATOMICAL AND DIRECTIONAL TERMS, AND ANATOMICAL PLANESDocument6 pagesLesson 2 - ANATOMICAL AND DIRECTIONAL TERMS, AND ANATOMICAL PLANESlalaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy AND Physiology: Anatomical PositionDocument9 pagesAnatomy AND Physiology: Anatomical PositionRiyalynkate DellomesNo ratings yet
- Directional Terms Alvarez NikkaDocument14 pagesDirectional Terms Alvarez NikkaJewel BerbanoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Anatomy TransDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Anatomy Transchynne ongNo ratings yet
- Part 2 Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pagesPart 2 Anatomy and Physiologyzy- SBGNo ratings yet
- 01 The Human BodyDocument5 pages01 The Human BodyJinnwen MandocdocNo ratings yet
- Body CavitiesDocument7 pagesBody Cavitiesapi-421703226No ratings yet
- Activity 1: General Consideration On Animal Form: Other Anatomical TermsDocument3 pagesActivity 1: General Consideration On Animal Form: Other Anatomical TermsKamille PobleteNo ratings yet
- Directional TermsDocument7 pagesDirectional TermsMarjorie Balangue MacadaegNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Anatomical Position and TerminologiesDocument3 pagesLesson 2 Anatomical Position and TerminologiesniaNo ratings yet
- Axia College Material: Building A Medical Vocabulary Ch. 2Document3 pagesAxia College Material: Building A Medical Vocabulary Ch. 2lupitacuevasNo ratings yet
- Sas 4 AnaphyDocument6 pagesSas 4 AnaphyClarrinne Geralence Galo RomoNo ratings yet
- Anatomical PlanesDocument35 pagesAnatomical Planestaimas sallauNo ratings yet
- Anph111 Prelims (Lab)Document20 pagesAnph111 Prelims (Lab)Maria Clarisse ReyesNo ratings yet
- ANATOMYDocument6 pagesANATOMYMnemo SyneNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument14 pagesAnaphy ReviewerHyacinth AlbertoNo ratings yet
- The Language of AnatomyDocument4 pagesThe Language of Anatomyjava_biscocho122950% (2)
- MusclesDocument16 pagesMusclesEmma CannettiNo ratings yet
- Anaphy LabDocument70 pagesAnaphy LabOscar Angelo Jr.No ratings yet
- Wala LangDocument7 pagesWala Langmorla holaNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1670116886104 7004977935856889787Document5 pagesOrca Share Media1670116886104 7004977935856889787Jemelyn Tillano LoterteNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: An OverviewDocument59 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: An OverviewAera JulkanainNo ratings yet
- Human AnatomyDocument46 pagesHuman AnatomyVoteone EnhypenNo ratings yet
- OT 211 - Notes - IntroductionDocument21 pagesOT 211 - Notes - Introductionno nameNo ratings yet
- Axia College Material: Building A Medical Vocabulary Ch. 2Document3 pagesAxia College Material: Building A Medical Vocabulary Ch. 2Brandon ForeNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Planes and Frogs External PartsDocument4 pagesAnatomical Planes and Frogs External PartsKEANNA RUBIANo ratings yet
- Final Ob1Document14 pagesFinal Ob1crix crixNo ratings yet
- Leopolds Manuever - ReviewerDocument3 pagesLeopolds Manuever - ReviewerMika SaldañaNo ratings yet
- Typical Development Global PatternsDocument4 pagesTypical Development Global PatternsRiani DwiastutiNo ratings yet
- FOHA Reviewer Week 4 and 5Document32 pagesFOHA Reviewer Week 4 and 5Krisha Mabel TabijeNo ratings yet
- Pe1-Anatomical Reference Postion & Directional TermsDocument11 pagesPe1-Anatomical Reference Postion & Directional TermsJinky JunioNo ratings yet
- The Components of LaborDocument4 pagesThe Components of LaborMARIANNE JOY ELEAZARNo ratings yet
- Language of Anatomy (Word)Document4 pagesLanguage of Anatomy (Word)Macchi MagsNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lesson 1Document5 pagesAnaphy Lesson 1Agatha joy MadrazoNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Position Gives Us A ConsistentDocument6 pagesAnatomical Position Gives Us A ConsistentOlivaa WilderNo ratings yet
- Basic Anatomical TermsDocument12 pagesBasic Anatomical Termsoluebuben02No ratings yet
- Ana - Intro (Snell + Lecture)Document17 pagesAna - Intro (Snell + Lecture)Ma Rhodalyn Mae AtienzaNo ratings yet
- ANA 101 Lab: University of Northern PhilippinesDocument6 pagesANA 101 Lab: University of Northern PhilippinesAlphine DalgoNo ratings yet
- PRI-Daily Living GuideDocument16 pagesPRI-Daily Living GuidegastonuzzoNo ratings yet
- Kin2222 - Anatomical Terms, Planes - Movements 2 2Document2,607 pagesKin2222 - Anatomical Terms, Planes - Movements 2 2AmreenNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of A Family With An InfantDocument41 pagesNursing Care of A Family With An InfantDaniela Claire FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Ana - Intro (Snell + LectureDocument11 pagesAna - Intro (Snell + LectureMa Rhodalyn Mae AtienzaNo ratings yet
- THY - Unit 4Document2 pagesTHY - Unit 4Gwen KimNo ratings yet
- THY 1 - Unit 2Document7 pagesTHY 1 - Unit 2Gwen KimNo ratings yet
- THY 1 - Unit 1Document8 pagesTHY 1 - Unit 1Gwen KimNo ratings yet
- Thy 1 - Unit 3Document8 pagesThy 1 - Unit 3Gwen KimNo ratings yet
- Richa Shrivastava Assistant Professor Department of Pharmacy BITS PilaniDocument18 pagesRicha Shrivastava Assistant Professor Department of Pharmacy BITS PilaniCHOUGULE KISHOR SURYAKANTNo ratings yet
- Embryonic Stem CellsDocument3 pagesEmbryonic Stem CellsRajNo ratings yet
- Stafford & Golightly - LSDDocument102 pagesStafford & Golightly - LSDPicior de LemnNo ratings yet
- Recent Technological Innovations in Aquaculture: January 2003Document17 pagesRecent Technological Innovations in Aquaculture: January 2003Jinnie R. MamhotNo ratings yet
- Morph Overfiew - Docx Versi 1Document27 pagesMorph Overfiew - Docx Versi 1Bimo PamungkasNo ratings yet
- Flex Printing TenderDocument13 pagesFlex Printing TenderThe WireNo ratings yet
- Modernage Public School & College, Abbottabad Revised Daily Grand Test Schedule & Pre-Board Date Sheet For Class 10Document1 pageModernage Public School & College, Abbottabad Revised Daily Grand Test Schedule & Pre-Board Date Sheet For Class 10Jaadi 786No ratings yet
- Clinics in Chest MedicineDocument161 pagesClinics in Chest MedicineVeronica SimamoraNo ratings yet
- Ataxic Neurodegenerative Satiety Deficiency Syndrome: According To Dr. Steven C. SchlozmanDocument4 pagesAtaxic Neurodegenerative Satiety Deficiency Syndrome: According To Dr. Steven C. SchlozmanGabriel Martin100% (1)
- Manonmaniam Sundaranar University Tirunelveli: Scheme of ExaminationsDocument22 pagesManonmaniam Sundaranar University Tirunelveli: Scheme of ExaminationsSri NavinNo ratings yet
- S4 - Ojo FisiologiaDocument6 pagesS4 - Ojo FisiologiaLUIS FERNANDO MEZA GONZALESNo ratings yet
- Specimen QP - Paper 1 OCR (A) Biology As-LevelDocument23 pagesSpecimen QP - Paper 1 OCR (A) Biology As-LevelNatsaisheNo ratings yet
- Bakir 2017Document12 pagesBakir 2017fragariavescaNo ratings yet
- Metamorphosis Rock, Paper, Scissors: Teacher Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesMetamorphosis Rock, Paper, Scissors: Teacher Lesson Planriefta89No ratings yet
- Escherichia Coli DH10BDocument2 pagesEscherichia Coli DH10BSecc. 2 Marco Antonio Aviles RomeroNo ratings yet
- Hand Activities During RobberiesDocument3 pagesHand Activities During RobberiesRuben_Monroy_ClaudioNo ratings yet
- Tissue Reactions Report Draft For ConsultationDocument315 pagesTissue Reactions Report Draft For ConsultationMichaelAndreasNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology - Volume 5 - NanomedicineDocument407 pagesNanotechnology - Volume 5 - NanomedicineArrianna WillisNo ratings yet
- June 2018 (IAL) QP - Unit 1 Edexcel Biology A-Level PDFDocument24 pagesJune 2018 (IAL) QP - Unit 1 Edexcel Biology A-Level PDFMoataz NassefNo ratings yet
- Textile TestingDocument12 pagesTextile TestingFaiz-e Madina0% (1)
- (English (Auto-Generated) ) Debunking Myths About Adolescence (DownSub - Com)Document4 pages(English (Auto-Generated) ) Debunking Myths About Adolescence (DownSub - Com)Janine BaringNo ratings yet
- Mercury, Cadmium and Lead Levels in Three CommerciallyDocument7 pagesMercury, Cadmium and Lead Levels in Three Commerciallypasindu bambarandaNo ratings yet
- Weekly Science P4 February 2021 PDFDocument4 pagesWeekly Science P4 February 2021 PDFMs SinarNo ratings yet
- Te Cgpa Nov 14 Jalgaon DisDocument2,014 pagesTe Cgpa Nov 14 Jalgaon Disapi-276920450No ratings yet
- Bio ElectrodesDocument26 pagesBio ElectrodesSharok Nancy JoshuvaNo ratings yet
- Biology - Lab 5 - Collection and Preservation of AnimalsDocument6 pagesBiology - Lab 5 - Collection and Preservation of AnimalsBeyonce SkekelNo ratings yet