Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Laboratory 1. Anatomical Position and Terminologies
Uploaded by
AAOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Laboratory 1. Anatomical Position and Terminologies
Uploaded by
AACopyright:
Available Formats
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY WITH PATHOPHYSIOLOGY (LABORATORY)
o Sagittal Plane – vertical plane passing
longitudinally dividing body into two
unequal equal halves, the left and the
right
o Coronal (frontal) plane – Perpendicular
to the sagittal plane and divides the body
into two unequal halves:
▪ Anterior (front)
▪ Posterior (back)
o Transverse (longitudinal, axial,
horizontal) plane – Divides the body to
produce unequal superior (upper) and
inferior (lower)
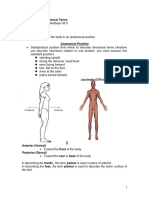
- Planes are used to describe sections:
• Stand erect
• Feet flat on the floor
• Palms and face facing forward
• Arms at the side
BODY REGIONS
➢ Head – brain, face with eyes, nose, mouth and
ears
o Longitudinal – lengthwise
➢ Neck – connects head and trunk
o Transverse – cross section
➢ Trunk
o Oblique – diagonal
o Thorax – heart and lungs
o Abdomen – most parts of digestive
system and urinary system
o Pelvic Cavity – with reproductive organs
and distal parts of digestive and urinary
system
➢ Upper Extremities
➢ Lower Extremities
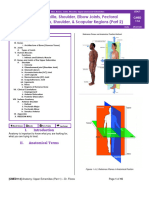
ATOMICAL PLANES
- Four Imaginary Planes that pass through the
body in the anatomical position
1. Superior (cranial) – nearer/towards to the head
➢ Ex: The neck is superior to the chest
2. Inferior (caudal) – nearer/towards the foot
➢ Ex: The abdomen is inferior to the chest
3. Anterior (ventral) – nearer/towards to the front
➢ Ex: The chest bone is anterior to the
heart
4. Posterior (dorsal) – nearer/towards the back
➢ Ex: The heart is posterior to the sternum
o Median Plane – vertical plane passing
5. Medial – nearer/towards to the medial plane
longitudinally dividing body into two
➢ Ex: The index finger is medial to the
equal halves, the left and the right
thumb
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY WITH PATHOPHYSIOLOGY (LABORATORY)
6. Lateral – farther/away from the median plane 7. Supination – rotating the forearm laterally such
➢ Ex: The thumb is medial to the index that the palm faces superiority
finger 8. Pronation – rotating the forearm medially such
7. Proximal – nearer/towards to the trunk or point that the palm faces inferiorly
of origin
➢ Ex: The arm is proximal to the elbow and
the proximal part of stomach is near the
esophagus
8. Distal – farther/away from the trunk or point of 9. Inversion – sole of foot faces or turns medially
origin 10. Eversion – sole of foot faces or turns laterally
➢ Ex: The elbow is distal to the arm and the
distal part of the stomach is near the
duodenum
9. Superficial – nearer/towards to the surface
10. Deep – farther/away from the surface
➢ Ex: Epidermis, Dermis
11. Central – nearer/towards to the center
12. Peripheral – farther/away from the center
13. Parietal – pertaining to the external wall of a 11. Protraction – antero-lateral movement of the
body cavity scapula
14. Visceral – pertaining to the covering of an organ
1. Gliding – bony surfaces of bone slide or glide
over each other
12. Protrusion – jutting out of jaw
2. Flexion – bending movement that decreases the
angle of the joint
3. Extension – movement that increases angle of
the joint
13. Elevation – raise or move a part superiorly
14. Depression – lowering of limb or body inferiorly
4. Abduction – moving away from the longitudinal
axis 15. Opposition – to bring the thumb and index
5. Adduction – moving toward from the fingertips together
longitudinal axis
6. Rotation – turning the bone or limb around its
long axis
16. Circumduction – combination of all movement
You might also like
- Anatomical PositionDocument36 pagesAnatomical PositionMoza AlaliliNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Anatomical Position and TerminologiesDocument3 pagesLesson 2 Anatomical Position and TerminologiesniaNo ratings yet
- General Orientation of The Body Part 1Document11 pagesGeneral Orientation of The Body Part 1Maria Faith Jeneen Bisnar100% (1)
- Happ Lab 1Document5 pagesHapp Lab 1Jerwin TullaoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - ANATOMICAL AND DIRECTIONAL TERMS, AND ANATOMICAL PLANESDocument6 pagesLesson 2 - ANATOMICAL AND DIRECTIONAL TERMS, AND ANATOMICAL PLANESlalaNo ratings yet
- Anatomical TermsDocument7 pagesAnatomical TermsKathleenJoyGalAlmasinNo ratings yet
- AnaphyDocument8 pagesAnaphyRachell Joy FloresNo ratings yet
- ANPH111 PRELIMS [LAB]Document20 pagesANPH111 PRELIMS [LAB]Maria Clarisse ReyesNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Terminology PDFDocument22 pagesAnatomical Terminology PDFProdosh Chatterjee100% (1)
- Anatomical PositionDocument7 pagesAnatomical PositionJeffrey SyliongcoNo ratings yet
- Anatomical TerminologyDocument11 pagesAnatomical TerminologyAhmed SalahNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy 1 - Unit 1 - Language of AnatomyDocument5 pagesAnaPhy 1 - Unit 1 - Language of AnatomyAndrea JiongcoNo ratings yet
- PT1011 Introduction to Anatomy Key TermsDocument19 pagesPT1011 Introduction to Anatomy Key Termschynne ongNo ratings yet
- Introduction in Human AnatomyDocument60 pagesIntroduction in Human AnatomyAngela Bautista85% (13)
- Chapter I IntroductionDocument58 pagesChapter I Introductionnot meNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature and Descriptive TerminologiesDocument28 pagesNomenclature and Descriptive TerminologiesEzri ChilengweNo ratings yet
- Basic Anatomical TermsDocument12 pagesBasic Anatomical Termsoluebuben02No ratings yet
- ANATOMICAL POSITION Amen AmenDocument12 pagesANATOMICAL POSITION Amen AmenJyross MacapogasNo ratings yet
- Wala LangDocument7 pagesWala Langmorla holaNo ratings yet
- Language of AnatomyDocument6 pagesLanguage of AnatomyGwen KimNo ratings yet
- Anaphy 1BDocument7 pagesAnaphy 1BFheonna De La PeñaNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and Physiology LaboratoryDocument26 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology LaboratoryRuth Marrionne Calderon100% (1)
- Activity 1: General Consideration On Animal Form: Other Anatomical TermsDocument3 pagesActivity 1: General Consideration On Animal Form: Other Anatomical TermsKamille PobleteNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 1.1 Anatomy in Motion 1 Semester SY 2013-2014: I. Anatomical PositionDocument5 pagesAnatomy 1.1 Anatomy in Motion 1 Semester SY 2013-2014: I. Anatomical PositionCarmen ClosetNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 - Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument9 pagesCHAPTER 6 - Anatomy and PhysiologyLaraib HabibNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AnaPhy Pt. 2Document3 pagesIntroduction To AnaPhy Pt. 2Sofia LozanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 General Orientation To Human Body and Basic Anatomical TerminologyDocument41 pagesChapter 2 General Orientation To Human Body and Basic Anatomical TerminologymintsaoraNo ratings yet
- Directional Terms, PlanesDocument6 pagesDirectional Terms, PlanesRuby Jane LaquihonNo ratings yet
- Sas 4 AnaphyDocument6 pagesSas 4 AnaphyClarrinne Geralence Galo RomoNo ratings yet
- Lower Limb Anatomy Class NotesDocument87 pagesLower Limb Anatomy Class NotesSalina Amir88% (16)
- Anatomical TermsDocument8 pagesAnatomical TermsDAGUMAN, FIONA DEI L.No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology OrientationDocument9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology OrientationBeatriz Nidea83% (6)
- Anatomical TerminologiesDocument5 pagesAnatomical TerminologiesAngela RaeNo ratings yet
- MusclesDocument16 pagesMusclesEmma CannettiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Anatomy and Physiology Part 2Document6 pagesIntroduction To Anatomy and Physiology Part 2Abby Claire SomeraNo ratings yet
- REHA2171 - Osteopathy Theory and Practice 1: Anatomical PlanesDocument3 pagesREHA2171 - Osteopathy Theory and Practice 1: Anatomical PlanesHammad -ullahNo ratings yet
- Anakines Midterm X Finals GL PTRPDocument156 pagesAnakines Midterm X Finals GL PTRPGABRIEL MIGUEL ALEJANDRO YUMULNo ratings yet
- Introduction in Human AnatomyDocument60 pagesIntroduction in Human Anatomyroooshi612100% (1)
- Week 1 - Terms, Tissues and Medical ImagingDocument17 pagesWeek 1 - Terms, Tissues and Medical Imagingatgriffo100% (1)
- Anatomy of the Human BodyDocument6 pagesAnatomy of the Human BodyMnemo SyneNo ratings yet
- Part 2 Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pagesPart 2 Anatomy and Physiologyzy- SBGNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY I Lecture 01, GENERAL ANATOMY 1, Introduction To AnatomyDocument40 pagesANATOMY I Lecture 01, GENERAL ANATOMY 1, Introduction To AnatomyHalima NazarNo ratings yet
- PE1 Introduction To MovementsDocument4 pagesPE1 Introduction To MovementsDaniela AnsayNo ratings yet
- CMED 114 002.1 AnatomyPart 1Document16 pagesCMED 114 002.1 AnatomyPart 1cesjopsNo ratings yet
- LAB EXERCISE 1 Organization of The Human Body - BS PSYCH 1 B 1Document10 pagesLAB EXERCISE 1 Organization of The Human Body - BS PSYCH 1 B 1Louise BarrientosNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Movements and Directional Terms NotesDocument2 pagesAnatomical Movements and Directional Terms NotesGerardo RitchelNo ratings yet
- Introduction of AnatomyDocument37 pagesIntroduction of Anatomylawnce 1No ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION OF ANATOMYDocument37 pagesINTRODUCTION OF ANATOMYRashini FernandoNo ratings yet
- 1.0 AnatomyDocument16 pages1.0 AnatomychaaarrNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument14 pagesAnaphy ReviewerHyacinth AlbertoNo ratings yet
- 1 KinesiologyTerminologyDocument26 pages1 KinesiologyTerminologyenzoaguba28No ratings yet
- Ana - Intro (Snell + LectureDocument11 pagesAna - Intro (Snell + LectureMa Rhodalyn Mae AtienzaNo ratings yet
- 'Aliah's Anatomy NotesDocument31 pages'Aliah's Anatomy NotesLuqman Al-Bashir Fauzi100% (2)
- 1 Week - Laboratory ExercisesDocument83 pages1 Week - Laboratory ExercisesGeevee Naganag VentulaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Best Short Notes and Flow ChartDocument5 pagesAnatomy Best Short Notes and Flow ChartNikhilNo ratings yet
- anatomical-planes-and-frogs-external-partsDocument4 pagesanatomical-planes-and-frogs-external-partsKEANNA RUBIANo ratings yet
- Introduction in Human AnatomyDocument60 pagesIntroduction in Human AnatomyRPh Krishna Chandra JagritNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Bones and Muscles on FormFrom EverandThe Influence of Bones and Muscles on FormRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Human anatomy and physiology lectureDocument5 pagesHuman anatomy and physiology lectureAANo ratings yet
- Lecture 2. Cells and TissuesDocument15 pagesLecture 2. Cells and TissuesAANo ratings yet
- Lecture 1. Overview and Orientation of The Human BodyDocument4 pagesLecture 1. Overview and Orientation of The Human BodyAANo ratings yet
- Laboratory 2. MicroscopeDocument3 pagesLaboratory 2. MicroscopeAANo ratings yet
- Identificación AlternariaDocument42 pagesIdentificación AlternariaDiana BecerraNo ratings yet
- Ribosomes - Protein Construction Teams: RibosomeDocument2 pagesRibosomes - Protein Construction Teams: RibosomeIs SianNo ratings yet
- Placenta Previa NCP 1Document6 pagesPlacenta Previa NCP 1Nicole ArandingNo ratings yet
- Chlorhexidine & Its UsesDocument40 pagesChlorhexidine & Its UsesSriya Saatwika ReddyNo ratings yet
- Collecting Objective DataDocument3 pagesCollecting Objective DataJasmine MayeNo ratings yet
- Specimen QP - Paper 3 OCR Biology (A) A-LevelDocument20 pagesSpecimen QP - Paper 3 OCR Biology (A) A-LevelAbir OmarNo ratings yet
- The Smoking Scare De-Bunked William T WithbyDocument61 pagesThe Smoking Scare De-Bunked William T WithbyPietje PukNo ratings yet
- Correlational Study On Hypertension and Dietary Regimen Among Young Adults in Bontoc, Mountain Province PhilippinesDocument6 pagesCorrelational Study On Hypertension and Dietary Regimen Among Young Adults in Bontoc, Mountain Province PhilippinesMel MacatangayNo ratings yet
- To Study The Transverse Section of Clove BudsDocument3 pagesTo Study The Transverse Section of Clove Budspooja arya100% (1)
- Firs Quarter-First Summative TestDocument9 pagesFirs Quarter-First Summative TestDjsana HiterozaNo ratings yet
- 2018-05 WisnewsletterDocument7 pages2018-05 Wisnewsletterapi-353949457No ratings yet
- 2023 Wisent Pricing AlbertaDocument7 pages2023 Wisent Pricing Albertavetman8842No ratings yet
- Activity Book 2Document14 pagesActivity Book 2Josune Arévalo75% (4)
- Impact of Yeast-Handling Procedures On Beer Flavour Development During FermentationDocument7 pagesImpact of Yeast-Handling Procedures On Beer Flavour Development During FermentationMayra Schmidt RechsteinerNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 Fetal DevelopmentDocument1 pageQuiz 2 Fetal DevelopmentDENNIS N. MUÑOZNo ratings yet
- Grade-10-IM-Inventory - RODGEDocument10 pagesGrade-10-IM-Inventory - RODGEPaul AniceteNo ratings yet
- Temporalis Masseter Medial Pterygoid Lateral Pterygoid Muscles Temporal Fossa Infratemporal Fossa Mandible Temporomandibular JointDocument5 pagesTemporalis Masseter Medial Pterygoid Lateral Pterygoid Muscles Temporal Fossa Infratemporal Fossa Mandible Temporomandibular JointpmNo ratings yet
- Malina 2020Document10 pagesMalina 2020Jaime VZNo ratings yet
- Brain CHipsDocument17 pagesBrain CHipsmagicalrockerNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter on Cells and TissuesDocument33 pagesBiology Chapter on Cells and TissuesKaka KNo ratings yet
- PVA Nanoparticles for Protein DeliveryDocument10 pagesPVA Nanoparticles for Protein DeliverySandeep GargNo ratings yet
- Questões de Inglês Com ResoluçãoDocument13 pagesQuestões de Inglês Com ResoluçãoHanns MüllerNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Class 10Document35 pagesNervous System Class 10Just JaenNo ratings yet
- AQA Biology GCSE - Homeostasis MechanismsDocument4 pagesAQA Biology GCSE - Homeostasis MechanismsMareeb ShahNo ratings yet
- Glycosylation Methods and Analysis SigmaDocument87 pagesGlycosylation Methods and Analysis SigmabogobonNo ratings yet
- Blastocystis Sp. To Treat or Not To Treat. 2012Document6 pagesBlastocystis Sp. To Treat or Not To Treat. 2012Nico RochaNo ratings yet
- Eugenics Issue PaperDocument4 pagesEugenics Issue Paperapi-300850424No ratings yet
- Chapter 25 Review QuestionsDocument2 pagesChapter 25 Review QuestionsGabriela QuiñonesNo ratings yet
- Protein Data BankDocument5 pagesProtein Data Bankwilliam919No ratings yet
- Animal Diversity PearsonDocument55 pagesAnimal Diversity PearsonaidanajihahNo ratings yet






![ANPH111 PRELIMS [LAB]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/719863137/149x198/c165ee1737/1712198106?v=1)