Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anatomical Planes and Frogs External Parts
Uploaded by
KEANNA RUBIAOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anatomical Planes and Frogs External Parts
Uploaded by
KEANNA RUBIACopyright:
Available Formats
lOMoARcPSD|13985848
Anatomical Planes and Frog's External Parts
Foundation of Zoology (Centro Escolar University)
Scan to open on Studocu
Studocu is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university
Downloaded by KEANNA RUBIA (rubia.keanna@ue.edu.ph)
lOMoARcPSD|13985848
PCZO101 : GENERAL ZOOLOGY (LAB)
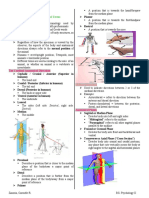
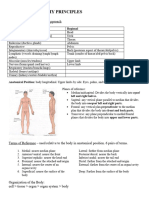
ANATOMICAL TERMS, PLANES, AND AXES
FROG’S EXTERNAL PARTS
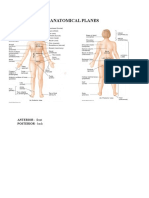
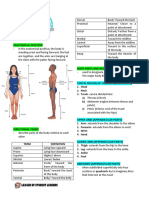
ANATOMICAL TERMS/DIRECTIONAL TERMS Distal - away from the main mass of the body
→ Terms used in locating and identifying parts.
Anterior - head region
Posterior - tail region
Dorsal - upper side or back
Ventral - under side or front
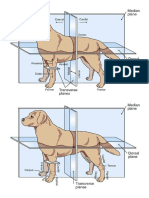
PLANES AND AXES
→ PLANES: flat surfaces; AXES: imaginary lines
Frontal plane - runs from anterior to posterior
and separates the dorsal and ventral
Transverse plane - runs from dorsal to ventral
and separates the anterior and posterior
Mid-sagittal - runs from anterior to posterior
and separates right and left equally
Parasagittal - runs from anterior to posterior
2 legged human and 4 legged animal and separates right and left unequally
MODULES
Medial - toward the center
Lateral - toward the sides
Central - at the middle
Peripheral - away from the center
- outer edges
Anatomical Terms
Anterior, Cephalic or Cranial -the
front or head end
Posterior or Caudal -the hind or tail
end
Medial -at or near the middle or
Superficial - on the surface
midline of a body or organ
Deep - beneath the surface
Lateral -the side of a body (right and
left sides)
Dorsal -the back, upper side, or upper
part
Ventral -the belly, lower side, or lower
part
Central -the part nearest the middle
Peripheral -the part nearest the
surface
Proximal -near the main mass of the
body/point of attachment
Distal -away from the main mass of
Proximal - near the main mass of the body the body/point of attachment
Downloaded by KEANNA RUBIA (rubia.keanna@ue.edu.ph)
lOMoARcPSD|13985848
PCZO101 : GENERAL ZOOLOGY (LAB)
ANATOMICAL TERMS, PLANES, AND AXES
FROG’S EXTERNAL PARTS
Superior -above *maxillary teeth(row of teeth) and vomerine
Inferior -below teeth(pair of teeth)- for gripping the prey
*Eustachian tubes- equalize pressure when frog
Anatomic Axes is swimming
*esophagus->glottis->(epiglottis)->trachea->lungs
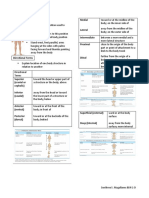
Longitudinal Axis -anterior-posterior
External nares: openings posterior to the snout
axis
Browspot: vestigial eye; white dot between the
Dorso-ventral Axis -up/down axis
eyes
Left-Right Axis
Eyeballs: bulging structures posterior to the
Anatomic Planes nostrils
3 Eyelids: protect the eyeballs; composed of the
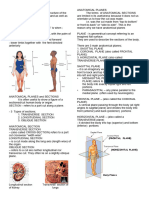
Sagittal plane / Sagittal section -a *upper eyelid, *lower eyelid (*protects eyes when
cut in this plane; longitudinal section frog is on land), and nictating membrane (protects
through the median vertical plane that eyes when frog is underwater)
divides the body into right and left Tympanic membranes: for hearing; flat, rounded
halves structures; posterior to the eyeballs (male’s
Parasagittal section -section to one size>eyes, female’s size<or=eyes)
side of the midline, separates right
and left portions of unequal size LIMBS
Frontal plane / Frontal section -a cut Forelimb
in this plane; longitudinal section - upper/anterior
made at right angles to a sagittal - upper arm
section - lower arm/forearm
Transverse plane / Transverse - carpus (wrist)
section or Cross section -a cut in - manus (digits)
this plane; any section made through Hindlimb
and at right angles to the longitudinal - lower / posterior
axis - thigh
- shank
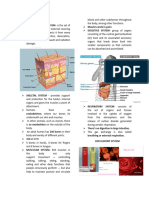
FROG’S EXTERNAL PARTS AND FUNCTIONS - tarsus
FROG’S TAXONOMY - pes
KEEP PONDS CLEAN OR FROGS GET SICK Digits
ACAARRV - toes/fingers
(mnemonics) - prehallux/calcar
KINGDOM: Animalia Web (only found on the hindlimb)
PHYLUM: Chordata - in between the toes
CLASS: Amphibia
ORDER: Anura COMPARISON BETWEEN M AND F (FROGS)
FAMILY: Ranidae
GENUS: Rana
SPECIES: Vittigera
SCIENTIFIC NAME: Rana vittigera
Rana vittigera – when written
BODY DIVISIONS
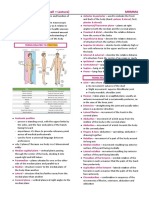
Head: most anterior (outer) region
Trunk: main mass of the body
Limbs: extremities
*male frog has a dark colored spots in the
EXTERNAL PARTS neck
Snout: most anterior tip of the head *male frog head or snout is more narrow than
Mouth: anterior opening a female frog
*internal nares
*ONLY male frogs produce calls & sounds
*frog’s tongue is split in the middle(attached
towards the front of the mouth)
Downloaded by KEANNA RUBIA (rubia.keanna@ue.edu.ph)
lOMoARcPSD|13985848
PCZO101 : GENERAL ZOOLOGY (LAB)
ANATOMICAL TERMS, PLANES, AND AXES
FROG’S EXTERNAL PARTS
MODULES
Frog’s body- possesses a distinct shape and
proportions that give them an advantage in
inhabiting both land and water
-divided into head and trunk; no neck and tail
Head- where brain and sense organs are
contained
Trunk- most of the internal organs or viscera
occupying one cavity, that is the coelom or
abdominal cavity
Body Regions
1. Head - situated “ahead”; contains the brain and
the sense organs
2. Trunk - where the body cavity or coelom is
found, this encloses the internal organs or viscera
Neck - extension of the head; no associated
coelom
*usually absent in fishes and amphibians
3. Tail - extends beyond the anus/vent; comprise
of body-wall muscles, axial skeleton, nerves and
blood vessels
*present in the vertebrate embryo but may be
absent in some adult vertebrates
4. Appendages - two pairs (Forelimbs and
Hindlimbs) are connected to the trunk
*may be lost or vestigial (small remnant) in some
vertebrates such as snakes and lizards
Downloaded by KEANNA RUBIA (rubia.keanna@ue.edu.ph)
You might also like
- A Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)From EverandA Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)No ratings yet
- Happ Lab 1Document5 pagesHapp Lab 1Jerwin TullaoNo ratings yet
- Kin2222 - Anatomical Terms, Planes - Movements 2 2Document2,607 pagesKin2222 - Anatomical Terms, Planes - Movements 2 2AmreenNo ratings yet
- Anatomical TerminologiesDocument5 pagesAnatomical TerminologiesAngela RaeNo ratings yet
- Foz Lab m4 Planes AxesDocument2 pagesFoz Lab m4 Planes AxesjsbitsoflyfNo ratings yet
- Radposi Lesson 1 and 2Document17 pagesRadposi Lesson 1 and 2Cesarina BlancaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 1. Anatomical Position and TerminologiesDocument2 pagesLaboratory 1. Anatomical Position and TerminologiesAANo ratings yet
- General ZoologyDocument64 pagesGeneral ZoologyCarmelle ZanoriaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 ImagesDocument4 pagesChapter 1 ImagesKiara VisserNo ratings yet
- Directional Terms Alvarez NikkaDocument14 pagesDirectional Terms Alvarez NikkaJewel BerbanoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology NotesDocument9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology NotesBeatriz Nidea83% (6)
- Anatomical PlanesDocument3 pagesAnatomical PlanesCorine RepatoNo ratings yet
- WEEK 2 TRANS AnaphyDocument4 pagesWEEK 2 TRANS AnaphygazzyngsalvadorNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Anatomical Position and TerminologiesDocument3 pagesLesson 2 Anatomical Position and TerminologiesniaNo ratings yet
- Directional Terms, PlanesDocument6 pagesDirectional Terms, PlanesRuby Jane LaquihonNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument3 pagesAnaphy Reviewerchicken nuggetsNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy 1 - Unit 1 - Language of AnatomyDocument5 pagesAnaPhy 1 - Unit 1 - Language of AnatomyAndrea JiongcoNo ratings yet
- Language of Anatomy (Word)Document4 pagesLanguage of Anatomy (Word)Macchi MagsNo ratings yet
- IntrodutionDocument13 pagesIntrodutionmay498550No ratings yet
- Anatomy1 2Document9 pagesAnatomy1 2Gladys Mae S. BañesNo ratings yet
- 1.an Overview of AnatomyDocument23 pages1.an Overview of AnatomyAmrith LordNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - ANATOMICAL AND DIRECTIONAL TERMS, AND ANATOMICAL PLANESDocument6 pagesLesson 2 - ANATOMICAL AND DIRECTIONAL TERMS, AND ANATOMICAL PLANESlalaNo ratings yet
- Anatomical PositionDocument7 pagesAnatomical PositionJeffrey SyliongcoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AnaPhy Pt. 2Document3 pagesIntroduction To AnaPhy Pt. 2Sofia LozanoNo ratings yet
- Gen Ana Lec EthanbatumbakalDocument14 pagesGen Ana Lec EthanbatumbakalYuki MendezNo ratings yet
- Introduction in Human AnatomyDocument60 pagesIntroduction in Human AnatomyAngela Bautista85% (13)
- Physiobio Brain Anatomy ReviewerDocument4 pagesPhysiobio Brain Anatomy ReviewerEricka NonatoNo ratings yet
- Anaphy 1BDocument7 pagesAnaphy 1BFheonna De La PeñaNo ratings yet
- Ana - Intro (Snell + LectureDocument11 pagesAna - Intro (Snell + LectureMa Rhodalyn Mae AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1: General Consideration On Animal Form: Other Anatomical TermsDocument3 pagesActivity 1: General Consideration On Animal Form: Other Anatomical TermsKamille PobleteNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Intro Part 1Document2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Intro Part 1SvvvaNo ratings yet
- External Parts of The FrogDocument12 pagesExternal Parts of The FrogMary Grace Gonzales100% (3)
- Many Similarities To Higher Vertebrates and in Man. 2. Ease of Manipulation 3. Inexpensive 4. AvailabilityDocument28 pagesMany Similarities To Higher Vertebrates and in Man. 2. Ease of Manipulation 3. Inexpensive 4. AvailabilityClaire Anne CaringalNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Anatomical TermsDocument3 pagesActivity 1 Anatomical TermsJerico YoNo ratings yet
- Structures and Functions of Vertebrates (The Frog) : A. Anatomical RegionsDocument3 pagesStructures and Functions of Vertebrates (The Frog) : A. Anatomical RegionsJanee JaneNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 1.1 Anatomy in Motion 1 Semester SY 2013-2014: I. Anatomical PositionDocument5 pagesAnatomy 1.1 Anatomy in Motion 1 Semester SY 2013-2014: I. Anatomical PositionCarmen ClosetNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Terms and PlanesDocument3 pagesAnatomical Terms and PlanesAshera Queenielet Magboo100% (1)
- Anatomical Terms and Planes PDFDocument3 pagesAnatomical Terms and Planes PDFAshera Queenielet MagbooNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Handbook-CodeworksDocument171 pagesAnatomy Handbook-CodeworksBe GameNo ratings yet
- Introduction in Human AnatomyDocument60 pagesIntroduction in Human Anatomyroooshi612100% (1)
- Introduction of AnatomyDocument37 pagesIntroduction of AnatomyRashini FernandoNo ratings yet
- Maintaining Life: Necessary Life FunctionsDocument4 pagesMaintaining Life: Necessary Life FunctionsEdralyn EgaelNo ratings yet
- Introduction of AnatomyDocument37 pagesIntroduction of Anatomylawnce 1No ratings yet
- Introduction of AnatomyDocument37 pagesIntroduction of Anatomysaadahmad323044No ratings yet
- ANATOMYDocument6 pagesANATOMYMnemo SyneNo ratings yet
- Language of AnatomyDocument31 pagesLanguage of AnatomyAlexa UyNo ratings yet
- Chapter I IntroductionDocument58 pagesChapter I Introductionnot meNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and Physiology LaboratoryDocument26 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology LaboratoryRuth Marrionne Calderon100% (1)
- Anatomical Position of The BodyDocument5 pagesAnatomical Position of The BodyPrecious MapehNo ratings yet
- CMED 114 002.1 AnatomyPart 1Document16 pagesCMED 114 002.1 AnatomyPart 1cesjopsNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Anatomy and Physiology Part 2Document6 pagesIntroduction To Anatomy and Physiology Part 2Abby Claire SomeraNo ratings yet
- Introduction - of - Anatomy 1Document26 pagesIntroduction - of - Anatomy 1adil fahadNo ratings yet
- CH 1-GENERAL ANATOMY PRINCIPLESDocument1 pageCH 1-GENERAL ANATOMY PRINCIPLESStephanieNo ratings yet
- Anaphy (Intro - Skeletal System) ReviewerDocument34 pagesAnaphy (Intro - Skeletal System) ReviewerYanna G.No ratings yet
- Basic Rad PosDocument14 pagesBasic Rad PosJayson EsplanaNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument15 pagesAnatomyFRANCINE JANE PATI�ONo ratings yet
- Anatomical Terminology PDFDocument22 pagesAnatomical Terminology PDFProdosh Chatterjee100% (1)
- Introductcion de La Antomia 2Document37 pagesIntroductcion de La Antomia 2VERONICA HERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Terms and Intro. To FrogDocument34 pagesAnatomical Terms and Intro. To FrogPaolo Naguit100% (7)
- Ancient Invention Stone ToolsDocument1 pageAncient Invention Stone ToolsKEANNA RUBIANo ratings yet
- Miller and Harley Zoology 11ed Ch02Document50 pagesMiller and Harley Zoology 11ed Ch02KEANNA RUBIANo ratings yet
- STATISTICS ReviewerDocument4 pagesSTATISTICS ReviewerKEANNA RUBIANo ratings yet
- Early Adulthood Development TasksDocument2 pagesEarly Adulthood Development TasksKEANNA RUBIANo ratings yet
- Developmental Psychology ReviewerDocument2 pagesDevelopmental Psychology ReviewerKEANNA RUBIANo ratings yet
- Human AnatomyDocument10 pagesHuman AnatomyKEANNA RUBIANo ratings yet
- 8 - Practice Problem Solutions - Light As An Electromagnetic WaveDocument5 pages8 - Practice Problem Solutions - Light As An Electromagnetic WaveKEANNA RUBIANo ratings yet
- 2ND Quarter ReviewerDocument46 pages2ND Quarter ReviewerKEANNA RUBIANo ratings yet
- Guia 4 de 4to GradoDocument31 pagesGuia 4 de 4to GradoYaritza RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Hominin Evolution: by Gary Bradley Biology Capstone, 2009Document69 pagesHominin Evolution: by Gary Bradley Biology Capstone, 2009ShaneNo ratings yet
- Oxford Discover 2 Unit 1 Lesson 3Document11 pagesOxford Discover 2 Unit 1 Lesson 3Dương HạNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 (Animal Diversity)Document5 pagesChapter-1 (Animal Diversity)TahsinNo ratings yet
- C10LFFCh3a His First FlightDocument12 pagesC10LFFCh3a His First FlightPieNo ratings yet
- American FlamingoDocument13 pagesAmerican FlamingoszitupppNo ratings yet
- Top CardsDocument4 pagesTop CardsYolandaOrduñaNo ratings yet
- Characteristic Features of Phylum ArthropodaDocument3 pagesCharacteristic Features of Phylum ArthropodaLiezel CarandangNo ratings yet
- St. Thomas Higher Secondary School, Badnagar: Semester - I Examination, 2022-23 General Knowledge, Class - IVDocument3 pagesSt. Thomas Higher Secondary School, Badnagar: Semester - I Examination, 2022-23 General Knowledge, Class - IVAbhishek ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Taxonomia y Variacion Geográfica de Especies Del Genero Alouatta en BrasilDocument81 pagesTaxonomia y Variacion Geográfica de Especies Del Genero Alouatta en BrasilGerardo RiveroNo ratings yet
- Formicidae PDFDocument3,127 pagesFormicidae PDFCindy GarciaNo ratings yet
- Elementary: Pack #3Document6 pagesElementary: Pack #3lin xuNo ratings yet
- Winnie, The WitchDocument6 pagesWinnie, The WitchBárbara UrsagastiNo ratings yet
- FAO Species Identification Guide For Fishery Purposes (Penaeid) PDFDocument7 pagesFAO Species Identification Guide For Fishery Purposes (Penaeid) PDFGhina TazkiaNo ratings yet
- Bones Forming The JointDocument29 pagesBones Forming The JointvrajNo ratings yet
- 5 ĐỀ THI HK1-FAMILY AND FRIENDS LỚP 3 - ĐANG CHỈNH SỬADocument11 pages5 ĐỀ THI HK1-FAMILY AND FRIENDS LỚP 3 - ĐANG CHỈNH SỬABao ChauNo ratings yet
- LEC - Bob Iger v1Document22 pagesLEC - Bob Iger v1Warda AhsanNo ratings yet
- Etextbook 978 0849319259 American Beetles Volume I Archostemata Myxophaga Adephaga Polyphaga Staphyliniformia 1Document62 pagesEtextbook 978 0849319259 American Beetles Volume I Archostemata Myxophaga Adephaga Polyphaga Staphyliniformia 1frank.robins662100% (45)
- Evolution of MetamerismDocument3 pagesEvolution of MetamerismBs JanNo ratings yet
- Full Download Test Bank For Communication in Nursing 8Th Edition Julia Balzer Riley PDFDocument26 pagesFull Download Test Bank For Communication in Nursing 8Th Edition Julia Balzer Riley PDFsamantha.streeter657100% (13)
- Siput PDFDocument126 pagesSiput PDFFajar FirdausNo ratings yet
- LABORATORY MANUAL in GENERAL ANATOMY 1 PART 1Document29 pagesLABORATORY MANUAL in GENERAL ANATOMY 1 PART 1Ian Mar ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Animal Adaptations Activity BookDocument8 pagesAnimal Adaptations Activity Bookapi-450175685No ratings yet
- Latihan Soal Simple Present Tense 30Document8 pagesLatihan Soal Simple Present Tense 30Naufal DzakyNo ratings yet
- Triptico Serpientes Comunes de YucatánDocument3 pagesTriptico Serpientes Comunes de YucatánAlexander Miguel LoezaNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Theory EasyDocument17 pages1.1 Theory EasyJunAnn LimNo ratings yet
- Reading Short Answer QuestionDocument3 pagesReading Short Answer QuestionArpita Bala ChaityNo ratings yet
- Coddington Et Al Arachnida04Document23 pagesCoddington Et Al Arachnida04Putri AritonangNo ratings yet
- 1st Head & Neck Anatomical Lab DR - Nassr Al-Hutbany Norma Frontalis 2024Document21 pages1st Head & Neck Anatomical Lab DR - Nassr Al-Hutbany Norma Frontalis 2024Dr.NASSR AL-HUTBANYNo ratings yet
- Engleza Cls A 10 A A VarDocument4 pagesEngleza Cls A 10 A A VarradulsbNo ratings yet
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (517)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (393)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (397)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Return of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseFrom EverandReturn of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (52)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (812)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)From EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (411)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainFrom EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (65)
- Seven and a Half Lessons About the BrainFrom EverandSeven and a Half Lessons About the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (110)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomFrom EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (216)
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperFrom EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (16)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveFrom EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (66)
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueFrom EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (38)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldFrom EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (596)
- Moral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemFrom EverandMoral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (115)
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouFrom EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (62)
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindFrom EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (93)