Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Human Anatomy
Uploaded by
KEANNA RUBIAOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Human Anatomy
Uploaded by
KEANNA RUBIACopyright:
Available Formats
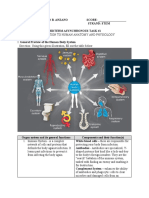
HUMAN ANATOMY blood and other substances throughout
the body, among other functions.
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM- is the set of
Muscles work in pairs
organs that forms the external covering
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM- group of organs
of the body and protects it from many
consisting of the central gastrointestinal
threats such as infection, desiccation,
(GI) tract and its associated accessory
abrasion, chemical assault and radiation
organs that break down food into
damage.
smaller components so that nutrients
can be absorbed and assimilated.
SKELETAL SYSTEM - provides support
and protection for the body’s internal
organs and gives the muscles a point of
attachment. RESPIRATORY SYSTEM- consists of
Humans have an the set of organs and tissues
endoskeleton, where our bones lie involved in the uptake of oxygen
underneath our skin and muscles. from the atmosphere and the
In other animals, such as insects, there release of carbon dioxide generated
is an exoskeleton on the outside of the during aerobic respiration.
body. There’s no digestion in large intestine.
An adult human has 206 bones in their This gas exchange is also called
body and variety of different joints. breathing or external respiration.
350 at birth
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
5 bones in hands, 3 bones for fingers
and 2 bones in tongue.
MUSCULAR SYSTEM- 650 muscles in
the body not only
support movement — controlling
walking, talking, sitting, standing,
eating and other daily functions that
people consciously perform — but also
help to maintain posture and circulate
Blood plasma- liquid, carries nutrients
Blood cells- carries oxygen and carbon
dioxide
Blood vessels- passageway
Arteries- carries oxygenated blood
4 CHAMBERS OF HEART
Eosinophil- bi-lobed nucleus, dark pink
1. Right atrium- Receives deoxygenated stained cytoplasmic granules.
blood from the body via the superior combat parasitic infections and play a role
and inferior vena cavae. It then pumps in allergic reactions. protect your body
this blood into the right ventricle. from parasites, allergens, foreign bacteria
2. Right ventricle- Receives deoxygenated and outside organisms.
blood from the right atrium and pumps
it to the lungs through the pulmonary
artery for oxygenation.
3. Left Atrium: Receives oxygenated blood
from the lungs through the pulmonary
veins. It then pumps this oxygen-rich Basophil- bi- lobed nucleus (usually cant
blood into the left ventricle. be seen). Lots of dark purple stained
4. Left Ventricle: Receives oxygenated cytoplasmic granules that take up entire
blood from the left atrium and pumps it cell.
out to the rest of the body through the play a role in a healthy immune
aorta, supplying oxygen and nutrients to system. releases histamine and other
tissues and organs. chemicals involved in inflammation and
allergic responses. They play a role in
WHITE BLOOD CELLS:
triggering the body's inflammatory
response to allergens and in defending
against parasites.
Neutrophil- multi-lobed nucleus, pale
red and blue cytoplasmic granules.
main function is to engulf and destroy
bacteria and other foreign particles
Monocyte- kidney shaped nucleus that
through a process called phagocytosis,
may appear lobed. No granules.
helping to fight off infections. Cytoplasm is very faintly stained blue.
find and destroy germs (viruses,
bacteria, fungi and protozoa) and
eliminate infected cells.
target organs. Instead, hormones can
act as chemical messengers for a large
number of cells and tissues
simultaneously.
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM- collection of
internal and external organs in both
Lymphocyte- large spherical nucleus. males and females — that work
No granules. Thin outer rim of faintly together for the purpose
blue stained cytoplasm. of procreating.
responsible for antibody NERVOUS SYTEM- the major control
production, direct cell-mediated system of homeostasis. It provides
killing of virus-infected and tumor monitoring, response, and regulation
cells, and regulation of the immune of all systems in the human body and
response. other organisms. It functions from the
LYMPHATIC SYSTEM- is a tiny level of individual cells to affecting
network of tissues and the whole body at once.
organs that help rid the BRAIN- is primarily made up of neurons,
body of toxins, waste and which send nerve impulses and store
other unwanted materials. information, and various support cells
3 MAIN FUNCTIONS which nurture, insulate, and protect
1. MAINTAINS THE BALANCE OF FLUID neurons so they can do their jobs
BETWEEN THE BLOOD AND TISSUES, reliably.
KNOWN AS FLUID HOMEOSTASIS. Cerebrum- controls thinking and
2. FORMS PART OF THE BODY’S IMMUNE awareness.
SYSTEM AND HELPS DEFEND AGAINST Right hemisphere- controls left side of
BACTERIA AND OTHER INTRUDERS. the body. Creativity and talents.
3. FACILITATES ABSORPTION OF FATS AND Left hemisphere- Controls right side.
FAT-SOLUBLE NUTRIENTS IN THE Numbers, science.
DIGESTIVE in humans, the brain weighs
SYSTEM. about three pounds and
EXCRETORY SYSTEM- consists consumes a stunning 20-25%
of organs which remove of all the body’s energy!
metabolic wastes and toxins
from the body. In humans, this
includes the removal of urea
from the bloodstream and other
wastes produced by the body.
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM- collection of
ductless glands that produce hormones
and secrete them into the circulatory
system.
ENDOCRINE GLANDS- work without
ducts for carrying secretions towards
SKELETAL SYSTEM
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
LYMPHATHIC SYSTEM
EXCRETORY SYSTEM (URINARY SYSTEM)
REPRODUCTIVE ORGANS
NERVOUS SYSTEM
You might also like
- Deciphering nCoV19, Quest for Cure, Prophylaxis, and VaccineFrom EverandDeciphering nCoV19, Quest for Cure, Prophylaxis, and VaccineNo ratings yet
- The Slim Book of Health Pearls: Man the Barricades - The Story of the Immune SystemFrom EverandThe Slim Book of Health Pearls: Man the Barricades - The Story of the Immune SystemNo ratings yet
- Lesson Proper For Week 7Document5 pagesLesson Proper For Week 7Merlyn NavarroNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument19 pagesAnaphy ReviewerGian Paolo P. CHAVEZNo ratings yet
- NST1501 Exam Ndou LDocument7 pagesNST1501 Exam Ndou Llufunondou12No ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Organs Systems P1Document8 pagesPlant and Animal Organs Systems P1ian laurence pedranoNo ratings yet
- Systems Generalities Functions Cardiovascular System: Luis Daniel Mendez García C.I. 26.051.086 Sección 5Document3 pagesSystems Generalities Functions Cardiovascular System: Luis Daniel Mendez García C.I. 26.051.086 Sección 5Luis Daniel Méndez GarcíaNo ratings yet
- General Principles OF Pathophysiology: "Cellular Physiology"Document111 pagesGeneral Principles OF Pathophysiology: "Cellular Physiology"yudhistira_29No ratings yet
- HAPP Human-Body-Orienation-Reviewer-lecDocument5 pagesHAPP Human-Body-Orienation-Reviewer-lecDenize Dela PenaNo ratings yet
- 04 Worksheet 1 (6) AyumaKristinejoyBDocument7 pages04 Worksheet 1 (6) AyumaKristinejoyBKristine Joy AyumaNo ratings yet
- Modules in Earth ScienceDocument22 pagesModules in Earth ScienceAlpha100% (1)
- Earth and Life ChuchuDocument2 pagesEarth and Life ChuchuAndrew TanecaNo ratings yet
- Cell To Organism WorksheetDocument7 pagesCell To Organism WorksheetSehasa PathiranaNo ratings yet
- AnaphyDocument2 pagesAnaphynaomimarielleNo ratings yet
- Discuss The Importance of Studying Anatomy and Physiology. Relate It With Your Daily ActivitiesDocument6 pagesDiscuss The Importance of Studying Anatomy and Physiology. Relate It With Your Daily ActivitiesJamaica SimanganNo ratings yet
- Immune System3Document10 pagesImmune System3Lizeth Tatiana Parra RodriguezNo ratings yet
- M3 Science (Summer Notes) : Unit 1: Biology (Tissues, Organs, and Systems)Document27 pagesM3 Science (Summer Notes) : Unit 1: Biology (Tissues, Organs, and Systems)Muskan HomeNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument2 pagesAnaphy ReviewerNarena BoniteNo ratings yet
- Activity1 - Introduction To Human AnatomyDocument7 pagesActivity1 - Introduction To Human AnatomyAdrian AnzanoNo ratings yet
- Four Systems For Happy YogaDocument109 pagesFour Systems For Happy YogaAwanish PandeyNo ratings yet
- 10 Major System of Responsible For Body FunctionDocument27 pages10 Major System of Responsible For Body Functionقى قىNo ratings yet
- KnowledgeDocument2 pagesKnowledgeSet FireNo ratings yet
- Functions of Immune SystemDocument6 pagesFunctions of Immune Systemanna jean oliquianoNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity 1: Definition of TermsDocument6 pagesLaboratory Activity 1: Definition of TermsCrystal Jade RetuyaNo ratings yet
- Human Body DR MellaliDocument20 pagesHuman Body DR MellaliSarah MellaliNo ratings yet
- Theory of Special CreationDocument9 pagesTheory of Special Creationnico peregrinoNo ratings yet
- Answer Sheet For ActivitiesDocument7 pagesAnswer Sheet For ActivitiesAlanah JaneNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument6 pagesAnatomygreatkill07No ratings yet
- Eals ACT2 ValdezDocument4 pagesEals ACT2 ValdezMicaella ValdezNo ratings yet
- Human Being Are Complex Multicellular OrganismsDocument9 pagesHuman Being Are Complex Multicellular OrganismsWilliam WongNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of DengueDocument8 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of DengueYim Yim25% (4)
- The Human Body: Gross /macroscopic AnatomyDocument8 pagesThe Human Body: Gross /macroscopic AnatomyMuhamad Hafiz Bin Mohd BakriNo ratings yet
- The Human Body OrientationDocument6 pagesThe Human Body OrientationHenry BuñagNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Physiology and Biochemistry-Notes For BBA (HA)Document12 pagesIntroduction of Physiology and Biochemistry-Notes For BBA (HA)devNo ratings yet
- Immunology Worksheet2Document4 pagesImmunology Worksheet2Caviles, Jasmin S.No ratings yet
- Biology ReviewerDocument3 pagesBiology ReviewerflowenceNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Anatomy and Physiology (Transes)Document9 pagesIntroduction To Human Anatomy and Physiology (Transes)Kathleen BalauagNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology ReviewerDocument12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology ReviewerAnn Fenelope AniscoNo ratings yet
- Organ SystemDocument9 pagesOrgan SystemMaycee ʚĭɞNo ratings yet
- Module 8-9Document5 pagesModule 8-9mirriam mag-asoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Physiology Study Guide Test 1Document15 pagesAnatomy Physiology Study Guide Test 1Jennifer BrownNo ratings yet
- Els Handouts (2ND)Document6 pagesEls Handouts (2ND)Xiena Reyes AlforqueNo ratings yet
- Body Systems Chart System Illustration Structures Function: DigestiveDocument3 pagesBody Systems Chart System Illustration Structures Function: DigestiveMicaela DNo ratings yet
- Anatomy-An-Overview (JTO)Document79 pagesAnatomy-An-Overview (JTO)Zild DarkNo ratings yet
- CelllllDocument9 pagesCelllllbasman1212No ratings yet
- Bio Anatomy ProjectDocument16 pagesBio Anatomy ProjectmillboarNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Pre LimDocument13 pagesAnaphy Pre LimKyle M. BayangosNo ratings yet
- Zikri Aiman-Cell Organization in AnimalsDocument37 pagesZikri Aiman-Cell Organization in AnimalsZikriAimanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy ReviewDocument13 pagesAnatomy ReviewGian Paolo P. CHAVEZNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 3 - Body Cells and TissuesDocument11 pagesLECTURE 3 - Body Cells and TissuesGGonzales KarlaNo ratings yet
- Physiology 1 IntroductionDocument101 pagesPhysiology 1 IntroductionBrian KipchumbaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology DengueDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology DengueKathleen DimacaliNo ratings yet
- Human Cells Journey: Organ Syste MDocument7 pagesHuman Cells Journey: Organ Syste MArina CucuruzaNo ratings yet
- Reference: Marieb, Elaine. Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. Tenth Ed. 2014Document16 pagesReference: Marieb, Elaine. Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. Tenth Ed. 2014ampalNo ratings yet
- Project Yani ScienceDocument18 pagesProject Yani ScienceCharline RadislaoNo ratings yet
- Anat Physio Basics 2008Document108 pagesAnat Physio Basics 2008Chandan AhireNo ratings yet
- Stem 11 Genbio 1 NotesDocument1 pageStem 11 Genbio 1 NotesKalila MckenzieNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiologybobadillamarie156No ratings yet
- Anph111 Prelims (Intro To Anaphy)Document9 pagesAnph111 Prelims (Intro To Anaphy)Maria Clarisse ReyesNo ratings yet
- What A Middle School 7 Grade Science Student Should Know: About ProtistsDocument3 pagesWhat A Middle School 7 Grade Science Student Should Know: About Protistsapi-300685908No ratings yet
- Ancient Invention Stone ToolsDocument1 pageAncient Invention Stone ToolsKEANNA RUBIANo ratings yet
- Miller and Harley Zoology 11ed Ch02Document50 pagesMiller and Harley Zoology 11ed Ch02KEANNA RUBIANo ratings yet
- STATISTICS ReviewerDocument4 pagesSTATISTICS ReviewerKEANNA RUBIANo ratings yet
- Developmental Psychology ReviewerDocument2 pagesDevelopmental Psychology ReviewerKEANNA RUBIANo ratings yet
- Early Adulthood Development TasksDocument2 pagesEarly Adulthood Development TasksKEANNA RUBIANo ratings yet
- 8 - Practice Problem Solutions - Light As An Electromagnetic WaveDocument5 pages8 - Practice Problem Solutions - Light As An Electromagnetic WaveKEANNA RUBIANo ratings yet
- 2ND Quarter ReviewerDocument46 pages2ND Quarter ReviewerKEANNA RUBIANo ratings yet
- BronchiectasisDocument40 pagesBronchiectasisyana jaeNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Function TestsDocument29 pagesPulmonary Function TestsOrion JohnNo ratings yet
- MCQ On PhototherapyDocument12 pagesMCQ On Phototherapylumina.s100% (1)
- PALS Systematic Approach Summary: Initial ImpressionDocument2 pagesPALS Systematic Approach Summary: Initial ImpressionMark Vergel II100% (3)
- First Aid Trainers ManualDocument70 pagesFirst Aid Trainers ManualGeoffrey AlleyneNo ratings yet
- DLL First Grading Period For Grade 9Document7 pagesDLL First Grading Period For Grade 9Jowell Obra Oaña90% (10)
- Eye, E.N.T. & Dental AnaesthesiaDocument22 pagesEye, E.N.T. & Dental AnaesthesiawellawalalasithNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For Management of Common IllnessDocument27 pagesReviewer For Management of Common Illnessmarie vennis hamchawanNo ratings yet
- Asthma & PneumoniaDocument5 pagesAsthma & PneumoniaRenjie ElizardeNo ratings yet
- NCP - Pott's DiseaseDocument23 pagesNCP - Pott's Diseasemhean azneitaNo ratings yet
- CSCS Cheat Sheet NEWDocument2 pagesCSCS Cheat Sheet NEWSanket Sawant100% (3)
- Guidelines For Surfactant Replacement Therapy in Neonates Canadian Paediatric SocietyDocument8 pagesGuidelines For Surfactant Replacement Therapy in Neonates Canadian Paediatric SocietyTiwi QiraNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Ventilation 2015Document18 pagesMechanical Ventilation 2015Nauman GilaniNo ratings yet
- Non-Invasive Ventilation 2Document25 pagesNon-Invasive Ventilation 2Ramanesh DNo ratings yet
- BspedDocument12 pagesBspedDisaster GamingNo ratings yet
- Questions Metabolic AcidosisDocument6 pagesQuestions Metabolic Acidosisyayooo2004No ratings yet
- Fundamentos de Auscultacion Pulmonar NEJM PDFDocument8 pagesFundamentos de Auscultacion Pulmonar NEJM PDFMaría Fernanda RíosNo ratings yet
- Esophageal and Transpulmonary Pressure in The Clinical Setting - Meaning, Usefulness and PerspectivesDocument14 pagesEsophageal and Transpulmonary Pressure in The Clinical Setting - Meaning, Usefulness and PerspectivesSüleyman YıldırımNo ratings yet
- Jurnal PPOKDocument11 pagesJurnal PPOKRhirin AkaseNo ratings yet
- BMR (Including Shivering) Thyroxine Output Rate of Cellular Metabolism Effect IsDocument13 pagesBMR (Including Shivering) Thyroxine Output Rate of Cellular Metabolism Effect IsMabesNo ratings yet
- 8Cc Getting Oxygen EPSDocument44 pages8Cc Getting Oxygen EPSZak Remtulla100% (1)
- Smoke Inhalation Injury SyndromeDocument5 pagesSmoke Inhalation Injury SyndromePedro VicinoNo ratings yet
- Intensive Care Ventilator MV200: Safety - Reliability - ComfortDocument7 pagesIntensive Care Ventilator MV200: Safety - Reliability - ComfortFathur ArRahmanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Impedance Tomography: Eduardo L.V. Costa, Raul Gonzalez Lima and Marcelo B.P. AmatoDocument7 pagesElectrical Impedance Tomography: Eduardo L.V. Costa, Raul Gonzalez Lima and Marcelo B.P. Amatojorgeluis.unknownman667No ratings yet
- Ch15 Lecture PPT ADocument67 pagesCh15 Lecture PPT AMiky rose De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Raus Respiratory Care Pharmacology 8th Edition Gardenhire Test BankDocument8 pagesRaus Respiratory Care Pharmacology 8th Edition Gardenhire Test Bankxuyenkeva3fon8100% (32)
- Pamphlet - 63 - Edition 8 - June 2011Document22 pagesPamphlet - 63 - Edition 8 - June 2011Krishnan RajappanNo ratings yet
- LaryngitisDocument5 pagesLaryngitisAngeliqueNo ratings yet
- Interventions For Clients Requiring Oxygen Therapy or TracheostomyDocument25 pagesInterventions For Clients Requiring Oxygen Therapy or TracheostomyFabricio Serna MarinNo ratings yet
- FA Pulmo PDFDocument32 pagesFA Pulmo PDFNARENDIRAN P MNo ratings yet