Professional Documents
Culture Documents
USMLE Step 1 Equations PDF
Uploaded by
Angelica UgoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
USMLE Step 1 Equations PDF
Uploaded by
Angelica UgoCopyright:
Available Formats
USMLE Equations
Pharmacology
Question Answer
V<J Amount of drug In body / (Plasma drug concent rail on)
CL (Rate of elimination of drug) / (Plasma drug concentration)
Half Life (0.7 * Vd) / CL
Loading dose (Cp x Vd) IF — Plasma drug concentration * Vd / bioavailability
Maintenance dose Cp * CL / F
pH pKa + Log (HC03/[0 03 Pco2)
Km = [S] at ? [S] at SVmax
Non-competitive inhibitor Decreases efficacy (Vmax) -> inc 1/Vmax
Competitive inhibitor Decreases potency (increased Km)—> dec 1/Km
Respiratory
Question Answer
Dead space Tidat volume " ([PaC02 - Pexp air C02]/PaC02|
Alveolar ventilation (Tidal volume - Dead space)" Breaths/mln
PA 0 2 = PA02 = ( Fi02 ' (760 - 47)) - (PaC02 / 0.8) — at room air
(21% 02). PA02
= .21 ( 7 1 3 i - P a C 0 2 / 0 . 8
= 150 - PaC02 / 0.8 [1 instead of 0 8 if pt on
100% 02]
= 150 - 1 25 - P a C 0 2
A-a gradient Alveolar 02 - arterial 02 = (at room air) 150mmHg - Pa02
(given)
no mi a I A-a gradient 10mmHa or pt's age / 4
diffusion D - pressure x surface area x solubility / [membfane
thickness x sqrt molec wtj
Winter's formula (HC03- PaC02 = 1 5 x [HC03-] + 8 +/- 2
PaC02)
dec Pa02 with normal A-a gradient hypoventilation (inc PC02) . dec Fi02 (normal PC02)
dec Pa02 with inc A-a gradient shunt (does not improve •:;ith inc 02) ; — V'Q mismatch
or diffusion impairment (improve with inc 021
difference btwn V/Q mismatch and V/Q mismatch •• normal DLCO (diffusion): diffusion
diffusion Impairment impairment dec DLCO (diffusion)
causes of shunting (inc A-a Atelectasis, pulmonary edema. Intra cardiac shunt (Right-
gradient w/ no improvement on Left) due to VSD; ASD: Vascular shunt within the lungs
100% 02)
Cardiology
Question Answer
CO rate of 02 consumption/{Arterial 02-Venous 02)
CO SV ' M R
MAP CO * TPR = 2/3 diastolic + 1/3 systolic
sv EDV - ESV
EF SWEDV
R 8n 11 (pi) r ft 4
R in series R = R1 + R2
R in parallel 1/R = 1/R1 + 1/R2
factors that inc viscosity polycythemia, high protein (MM), spherocytosis
pulse pressure systolic - diastolic
Biostats
Question Answer
Sensitivity TP / (TP+FN) = 1 - FN = TP / all real Ps
Specificity TNI / (TN+FP) = 1 - FP = TN / all real Ns
IPPV TP / (TP+FP) = TP / all apparent Ps
INPV TN / (TN+FN) = TN / all apparent Ns
OR = (a/b)/ (c/d) = ad / be — where a (risk factor + ds); b (risk factor - ds)r
Odds ratio c (- risk factor + ds), d (- risk factor - ds)
|[a/(a+b)J / [c/(c+d)] — where a (risk factor + ds), lb (risk factor - ds), c (-
Relative risk risk factor + ds) d (- risk factor - ds) = Incidence of exposed / incidence of
unexposed
Attributable risk |[a/(a+b)] - [c/(c+d)] — where a (risk factor + ds). lb (risk factor - ds). c (-
risk factor + ds). d (- risk factor - ds) = Incidence of exposed - incidence of
unexposed
Positive
likelihood ratio Sens / [1 - Spec] = Sens / FP
Negative s
likelihood ratio [1 - Sens) / Spec FN / Spec
accuracy = ? accuracy = (TP+TN) / (TP+TN+FP+FN) = all accurates / total
IH a rdy-Weinberg p*2 + 2pq + q*2 = 1 p + q = 1
equil
confidence CI = mean +/- 2'slgma »> 95% CI
interval
type I error = ? b / (b+d)
type II error = ? c / (a+e)
Renal
GFR Uinulin / PinuJin * V= Cinulin
GFR Kf[Pgc-Pbs) - (ONCgc-ONCbs)]
RPF Upah / Ppah * V = Cpah
RBF RPF/(1-Hct)
FF GFFWRPF
You might also like
- Pathoma LectureDocument385 pagesPathoma LectureMustafa Thaier Al-Karaghouli91% (22)
- USMLE Step 1 EquationsDocument1 pageUSMLE Step 1 EquationsDina Nadeem100% (2)
- Goljan - Audio TranscriptsDocument296 pagesGoljan - Audio TranscriptsGurbir Singh Gill90% (30)
- USMLE Step I Boards BuzzwordsDocument11 pagesUSMLE Step I Boards BuzzwordsnisreenNo ratings yet
- USMLE Questions SummarizedDocument85 pagesUSMLE Questions SummarizedJamesIwu89% (19)
- Equations For Primary FRCADocument11 pagesEquations For Primary FRCAMustafa SharkawyNo ratings yet
- Step 1 Uworld PDFDocument25 pagesStep 1 Uworld PDFRegents Park Business Center100% (1)
- Pass ProgramDocument528 pagesPass ProgramEvelyn Lee Russell67% (3)
- Electronic Devices and Circuits Formula SheetDocument6 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits Formula Sheetmumsn83% (6)
- Buzzwords For The Boards: USMLE Step I: Study Online atDocument64 pagesBuzzwords For The Boards: USMLE Step I: Study Online atShyama SharmaNo ratings yet
- UW Allergy + Immuno - Educational Objectives PDFDocument25 pagesUW Allergy + Immuno - Educational Objectives PDFDrbee10No ratings yet
- Revised PPClues - 3-3-08Document16 pagesRevised PPClues - 3-3-08jeffjohnson909100% (2)
- Picmonic Glycogen Storage DiseasesDocument2 pagesPicmonic Glycogen Storage DiseasesLaylee Clare100% (3)
- High Yield Image Plates Gross - Patholog PDFDocument151 pagesHigh Yield Image Plates Gross - Patholog PDFld100% (2)
- El Husseinys Essentials of General PrinciplesDocument92 pagesEl Husseinys Essentials of General PrinciplesSara Alsubaie100% (1)
- Renal CastsDocument1 pageRenal Castsgregoryvo100% (4)
- Formulas For The MCAT: General ChemistryDocument1 pageFormulas For The MCAT: General Chemistrymissee728No ratings yet
- Formula Sheet Final 2013 Power ElectronicsDocument4 pagesFormula Sheet Final 2013 Power Electronicstlp56130% (1)
- S P99 41000099DisplayVendorListDocument31 pagesS P99 41000099DisplayVendorListMazen Sanad100% (1)
- Goljan High Yield 46 PG Notes.2004 EdnDocument47 pagesGoljan High Yield 46 PG Notes.2004 Edncipga100% (5)
- Revised Step2 MedDocument75 pagesRevised Step2 MedhippocamperNo ratings yet
- USMLE - VirusesDocument120 pagesUSMLE - Viruseszeal7777100% (1)
- USMLE Biochem Table ReviewDocument13 pagesUSMLE Biochem Table ReviewmkNo ratings yet
- FM Shelf Exam ReviewDocument5 pagesFM Shelf Exam ReviewMohammad Katato100% (1)
- Mnemonics Step 1Document4 pagesMnemonics Step 1Raji NaamaniNo ratings yet
- Goljan UsmleDocument2 pagesGoljan UsmleWidfdsafdsa0% (2)
- Hallmark FindingsDocument3 pagesHallmark Findingsphantomspb100% (3)
- PediatricsDocument8 pagesPediatricsMarek OferczakNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Step 1 Weird Exceptions and DetailDocument10 pagesMicrobiology Step 1 Weird Exceptions and DetailLucykesh100% (2)
- Penicillins Pen&G Pen&V: T.%pallidum% (Syphilis)Document1 pagePenicillins Pen&G Pen&V: T.%pallidum% (Syphilis)gregoryvo100% (5)
- Micro Not in SketchyDocument4 pagesMicro Not in Sketchyrpascua123No ratings yet
- USMLE Step 1 Material & Study PlanDocument3 pagesUSMLE Step 1 Material & Study PlanAditya Pavankumar Ganti100% (1)
- List of Forgettables - What You Need To Review Few Days Before The Exam - USMLE ForumsDocument1 pageList of Forgettables - What You Need To Review Few Days Before The Exam - USMLE ForumsJahanzeb AhmedNo ratings yet
- USMLE Step 1 Radiology Buzzwords - USMLE ForumsDocument5 pagesUSMLE Step 1 Radiology Buzzwords - USMLE Forumsfrabzi100% (2)
- Step 1 Study GuideDocument41 pagesStep 1 Study GuideJames Stafford100% (4)
- HY Mixed USMLE Review Part III 1Document18 pagesHY Mixed USMLE Review Part III 1Jennifer Ross-ComptisNo ratings yet
- USMLE Flashcards: Pharmacology - Side by SideDocument178 pagesUSMLE Flashcards: Pharmacology - Side by SideMedSchoolStuff67% (3)
- USMLE Vignette Flashcards: Anatomy, Behavioral and Biochem - Side by SideDocument12 pagesUSMLE Vignette Flashcards: Anatomy, Behavioral and Biochem - Side by SideMedSchoolStuff100% (1)
- Flashcards FinalDocument272 pagesFlashcards FinalMarie SantoroNo ratings yet
- MBBS Differential ListDocument58 pagesMBBS Differential Listsmoore1234No ratings yet
- Lippin NotesDocument8 pagesLippin Noteswalt65100% (1)
- RT EquationsDocument2 pagesRT EquationsClaudia BradleyNo ratings yet
- V V RR: (N 20-40%/critical 60%)Document1 pageV V RR: (N 20-40%/critical 60%)Robert BrowningNo ratings yet
- Extra Information For Chem 340 Exams:: Transport Temperature (T), Activity/concentration (A) W RT JDocument4 pagesExtra Information For Chem 340 Exams:: Transport Temperature (T), Activity/concentration (A) W RT JZevano C. SibaraniNo ratings yet
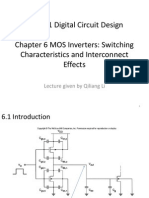
- ECE 431 Digital Circuit Design Chapter 6 MOS Inverters: Switching Characteristics and Interconnect EffectsDocument44 pagesECE 431 Digital Circuit Design Chapter 6 MOS Inverters: Switching Characteristics and Interconnect EffectsSneha S RevankarNo ratings yet
- Show Image Transcript: Expert-Veri EdDocument1 pageShow Image Transcript: Expert-Veri Edpicul 08No ratings yet
- Appendix and AcknowledgementsDocument58 pagesAppendix and AcknowledgementsNaveen GuptaNo ratings yet
- TD MODULE 4Document12 pagesTD MODULE 4mujeebNo ratings yet
- Fundamentos de Aeron Autica Formulario: Instructor: Arturo Galv An Rdz. 12 de Noviembre de 2009Document3 pagesFundamentos de Aeron Autica Formulario: Instructor: Arturo Galv An Rdz. 12 de Noviembre de 2009agalvan1311No ratings yet
- n-MOSFET (D) :: (I-V) Equations: Cut Off ModeDocument6 pagesn-MOSFET (D) :: (I-V) Equations: Cut Off ModeJo KontNo ratings yet
- Analog & Digital (Microp)Document3 pagesAnalog & Digital (Microp)Bharath ChNo ratings yet
- Cheat SheetDocument1 pageCheat Sheetkeng3915100% (4)
- Formula Sheet HET182Document1 pageFormula Sheet HET182Stanley RegaliaNo ratings yet
- MCAT Physics Equations SheetDocument4 pagesMCAT Physics Equations SheetAshley ShanaéNo ratings yet
- CHEE 3363 Spring 2014 Handout 24 Reading: Fox, Chapter 11Document19 pagesCHEE 3363 Spring 2014 Handout 24 Reading: Fox, Chapter 11kietniNo ratings yet
- TDM EquationsDocument4 pagesTDM EquationsMohammed AbdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet: Systolic DiastolicDocument3 pagesFormula Sheet: Systolic DiastolicJames LaiNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet SolarDocument1 pageCheat Sheet SolarshahabNo ratings yet
- 13 Problem Solving With MATLAB PDFDocument64 pages13 Problem Solving With MATLAB PDFAugusto De La Cruz CamayoNo ratings yet
- DAM Formulas KDocument6 pagesDAM Formulas KgabrielNo ratings yet
- TutUM UM MarcH-2017Document6 pagesTutUM UM MarcH-2017Dennis LingNo ratings yet
- Small Business and Entrepreneurship ProjectDocument38 pagesSmall Business and Entrepreneurship ProjectMădălina Elena FotacheNo ratings yet
- Sinamics g120p Cabinet Catalog d35 en 2018Document246 pagesSinamics g120p Cabinet Catalog d35 en 2018Edgar Lecona MNo ratings yet
- Ibragimova Lesson 4Document3 pagesIbragimova Lesson 4Dilnaz IbragimovaNo ratings yet
- Upadhyayaetal TrueliqtrigcurveDocument14 pagesUpadhyayaetal TrueliqtrigcurveVetriselvan ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Die Openbare BeskermerDocument3 pagesDie Openbare BeskermerJaco BesterNo ratings yet
- Mongodb TutorialDocument106 pagesMongodb TutorialRahul VashishthaNo ratings yet
- Bobcat E34 - E35Z Brochure - Adare MachineryDocument8 pagesBobcat E34 - E35Z Brochure - Adare MachineryNERDZONE TVNo ratings yet
- Chandigarh Distilers N BotlersDocument3 pagesChandigarh Distilers N BotlersNipun GargNo ratings yet
- Subject: PSCP (15-10-19) : Syllabus ContentDocument4 pagesSubject: PSCP (15-10-19) : Syllabus ContentNikunjBhattNo ratings yet
- 3 AcmeCorporation Fullstrategicplan 06052015 PDFDocument11 pages3 AcmeCorporation Fullstrategicplan 06052015 PDFDina DawoodNo ratings yet
- Operator'S Manual PM20X-X-X-BXX: 2" Diaphragm PumpDocument12 pagesOperator'S Manual PM20X-X-X-BXX: 2" Diaphragm PumpOmar TadeoNo ratings yet
- L5T-112 Manual - 2007 - Issue 1.1 PDFDocument16 pagesL5T-112 Manual - 2007 - Issue 1.1 PDFfluidaimaginacionNo ratings yet
- EPA Section 608 Type I Open Book ManualDocument148 pagesEPA Section 608 Type I Open Book ManualMehdi AbbasNo ratings yet
- Genie PDFDocument277 pagesGenie PDFOscar ItzolNo ratings yet
- Phenomenology of The SelfDocument5 pagesPhenomenology of The SelfGuilherme CastelucciNo ratings yet
- Mahindra First Choice Wheels LTD: 4-Wheeler Inspection ReportDocument5 pagesMahindra First Choice Wheels LTD: 4-Wheeler Inspection ReportRavi LoveNo ratings yet
- Ceo DualityDocument3 pagesCeo Dualitydimpi singhNo ratings yet
- 2021-01-01 - Project (Construction) - One TemplateDocument1,699 pages2021-01-01 - Project (Construction) - One TemplatemayalogamNo ratings yet
- 8D & 7QC ToolsDocument117 pages8D & 7QC ToolsAshok Kumar100% (1)
- Leibniz, Gottfried Wilhelm - Strickland, Lloyd - Leibniz's Monadology - A New Translation and Guide-Edinburgh University Press (2014)Document327 pagesLeibniz, Gottfried Wilhelm - Strickland, Lloyd - Leibniz's Monadology - A New Translation and Guide-Edinburgh University Press (2014)Gigla Gonashvili100% (1)
- Measures For FloodsDocument4 pagesMeasures For FloodsMutsitsikoNo ratings yet
- Internship Report PDFDocument71 pagesInternship Report PDFNafiz FahimNo ratings yet
- ISSA2013Ed CabinStores v100 Часть10Document2 pagesISSA2013Ed CabinStores v100 Часть10AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Project On Mahindra BoleroDocument35 pagesProject On Mahindra BoleroViPul75% (8)
- Evolution of Campus Switching: Marketing Presentation Marketing PresentationDocument35 pagesEvolution of Campus Switching: Marketing Presentation Marketing PresentationRosal Mark JovenNo ratings yet
- You're reading a free preview. Pages 4 to 68 are not shown in this preview. Leer la versión completa You're Reading a Free Preview Page 4 is not shown in this preview. DESCARGA You're Reading a Free Preview Page 5 is not shown in this preview. DESCARGA You're Reading a Free Preview Page 6 is not shown in this preview. DESCARGA You're Reading a Free Preview Page 7 is not shown in this preview. DESCARGA You're Reading a Free Preview Page 8 is not shown in this preview. DESCARGA You're Reading a Free Preview Page 9 is not shown in this preview. DESCARGA You're Reading a Free Preview Page 10 is not shown in this preview. DESCARGA You're Reading a Free Preview Page 11 is not shown in this preview. DESCARGA You're Reading a Free Preview Page 12 is not shown in this preview. DESCARGA You're Reading a Free Preview Page 13 is not shown in this preview. DESCARGA You're Reading a Free Preview Page 14 is not shown in this preview. DESCARGA You're Reading a Free Preview Page 15 is notDocument9 pagesYou're reading a free preview. Pages 4 to 68 are not shown in this preview. Leer la versión completa You're Reading a Free Preview Page 4 is not shown in this preview. DESCARGA You're Reading a Free Preview Page 5 is not shown in this preview. DESCARGA You're Reading a Free Preview Page 6 is not shown in this preview. DESCARGA You're Reading a Free Preview Page 7 is not shown in this preview. DESCARGA You're Reading a Free Preview Page 8 is not shown in this preview. DESCARGA You're Reading a Free Preview Page 9 is not shown in this preview. DESCARGA You're Reading a Free Preview Page 10 is not shown in this preview. DESCARGA You're Reading a Free Preview Page 11 is not shown in this preview. DESCARGA You're Reading a Free Preview Page 12 is not shown in this preview. DESCARGA You're Reading a Free Preview Page 13 is not shown in this preview. DESCARGA You're Reading a Free Preview Page 14 is not shown in this preview. DESCARGA You're Reading a Free Preview Page 15 is notFernando ToretoNo ratings yet
- Activity Based Costing TestbanksDocument18 pagesActivity Based Costing TestbanksCharlene MinaNo ratings yet
- How Muslim Inventors Changed The WorldDocument4 pagesHow Muslim Inventors Changed The WorldShadab AnjumNo ratings yet
- 6 RVFS - SWBL Ojt Evaluation FormDocument3 pages6 RVFS - SWBL Ojt Evaluation FormRoy SumugatNo ratings yet