Professional Documents
Culture Documents
6.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring VLANs (1) My Answers
Uploaded by
Armel Bacdayan Lacanaria0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
199 views6 pagesThis document describes configuring VLANs on three switches - S1, S2, and S3. It involves verifying the default VLAN configuration, creating and naming VLANs, and assigning ports on each switch to the appropriate VLAN. The objectives are to partition switch ports into logical VLANs for different groups of end users and devices.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document describes configuring VLANs on three switches - S1, S2, and S3. It involves verifying the default VLAN configuration, creating and naming VLANs, and assigning ports on each switch to the appropriate VLAN. The objectives are to partition switch ports into logical VLANs for different groups of end users and devices.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
199 views6 pages6.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring VLANs (1) My Answers
Uploaded by
Armel Bacdayan LacanariaThis document describes configuring VLANs on three switches - S1, S2, and S3. It involves verifying the default VLAN configuration, creating and naming VLANs, and assigning ports on each switch to the appropriate VLAN. The objectives are to partition switch ports into logical VLANs for different groups of end users and devices.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
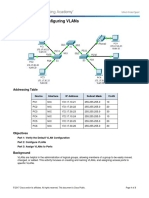
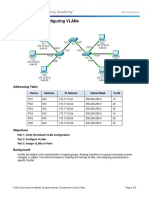
Packet Tracer – Configuring VLANs
Addressing Table
Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask VLAN
PC1 NIC 172.17.10.21 255.255.255.0 10
PC2 NIC 172.17.20.22 255.255.255.0 20
PC3 NIC 172.17.30.23 255.255.255.0 30
PC4 NIC 172.17.10.24 255.255.255.0 10
PC5 NIC 172.17.20.25 255.255.255.0 20
PC6 NIC 172.17.30.26 255.255.255.0 30
Objectives
Part 1: Verify the Default VLAN Configuration
Part 2: Configure VLANs
Part 3: Assign VLANs to Ports
Background
VLANs are helpful in the administration of logical groups, allowing members of a group to be easily
moved, changed, or added. This activity focuses on creating and naming VLANs, and assigning
access ports to specific VLANs.
Part 1: View the Default VLAN Configuration
Step 1: Display the current VLANs.
On S1, issue the command that displays all VLANs configured. By default, all interfaces are assigned
to VLAN 1.
Step 2: Verify connectivity between PCs on the same network.
Notice that each PC can ping the other PC that shares the same network.
· PC1 can ping PC4
· PC2 can ping PC5
· PC3 can ping PC6
Pings to PCs in other networks fail.
What benefit will configuring VLANs provide to the current configuration?
- Security, cost reduction, higher performance, broadcast storm mitigation, improved IT staff
efficiency, and simpler project and application management.
Part 2: Configure VLANs
Step 1: Create and name VLANs on S1.
Create the following VLANs. Names are case-sensitive:
· VLAN 10: Faculty/Staff
· VLAN 20: Students
· VLAN 30: Guest(Default)
· VLAN 99: Management&Native
· VLAN 150: VOICE
Step 2: Verify the VLAN configuration.
Which command will only display the VLAN name, status, and associated ports on a switch?
Step 3: Create the VLANs on S2 and S3.
Using the same commands from Step 1, create and name the same VLANs on S2 and S3.
Step 4: Verify the VLAN configuration.
Part 3: Assign VLANs to Ports
Step 1: Assign VLANs to the active ports on S2.
Configure the interfaces as access ports and assign the VLANs as follows:
· VLAN 10: FastEthernet 0/11
· VLAN 20: FastEthernet 0/18
· VLAN 30: FastEthernet 0/6
Step 2: Assign VLANs to the active ports on S3.
S3 uses the same VLAN access port assignments as S2. Configure the interfaces as access ports
and assign the VLANs as follows:
· VLAN 10: FastEthernet 0/11
· VLAN 20: FastEthernet 0/18
· VLAN 30: FastEthernet 0/6
Step 3: Assign the VOICE VLAN to FastEthernet 0/11 on S3.
As shown in the topology, the S3 FastEthernet 0/11 interface connects to a Cisco IP Phone and PC4.
The IP phone contains an integrated three-port 10/100 switch. One port on the phone is labeled
Switch and connects to F0/4. Another port on the phone is labeled PC and connects to PC4. The IP
phone also has an internal port that connects to the IP phone functions.
The S3 F0/11 interface must be configured to support user traffic to PC4 using VLAN 10 and voice
traffic to the IP phone using VLAN 150. The interface must also enable QoS and trust the Class of
Service (CoS) values assigned by the IP phone.
Step 4: Verify loss of connectivity.
Previously, PCs that shared the same network could ping each other successfully.
Try pinging between PC1 and PC4. Although the access ports are assigned to the appropriate
VLANs, were the pings successful? Why?
- No, the ping failed because the ports between the switches are in VLAN 1 and PC1 and PC4 are
in VLAN 10.
What could be done to resolve this issue?
- Configure ports between switches as trunk ports
Suggested Scoring Rubric
Question Possible Earned
Activity Section Location Points Points
Part 1: Verify the Default VLAN Configuration Step 2 2
Part 2: Configure VLANs Step 2 2
Part 3: Assign VLANs to Ports Step 3 2
Packet Tracer Score 94
Total Score 100
You might also like
- 3.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring VLANs Instructions PDFDocument3 pages3.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring VLANs Instructions PDFShaun75% (4)
- CCNA 3 v7 Modules 13 - 14: Emerging Network Technologies Exam AnswersDocument11 pagesCCNA 3 v7 Modules 13 - 14: Emerging Network Technologies Exam AnswersLeandro J. HinestrozaNo ratings yet
- IPCop With DansGuardian Installation and ConfigurationDocument6 pagesIPCop With DansGuardian Installation and ConfigurationnopeiccoNo ratings yet
- STP ConfigureDocument608 pagesSTP ConfiguregopihcNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 4 3Document3 pagesLab 6 4 3Peter Anti-AbhisitNo ratings yet
- BVI CiscoDocument6 pagesBVI CiscoJESUS REYESNo ratings yet
- CCNA Final Project TastDocument3 pagesCCNA Final Project Tastsathish77s100% (1)
- Lab - Activity CCNA 2 Exp: 3.5.2Document4 pagesLab - Activity CCNA 2 Exp: 3.5.2Rico Agung FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- How To Recover Password On A Cisco 2950, 2960 SwitchDocument5 pagesHow To Recover Password On A Cisco 2950, 2960 SwitchRicardo RomeroNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 - AAA Authentication On Cisco Routers - InstruccionesDocument6 pagesLab 3 - AAA Authentication On Cisco Routers - InstruccionesFelipe Andres Oyarzun QuirozNo ratings yet
- L2Tp/Ipsec Remote Access VPN Configuration ExampleDocument4 pagesL2Tp/Ipsec Remote Access VPN Configuration ExampleBruno PereiraNo ratings yet
- 10.8.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration Challenge - InstructorDocument11 pages10.8.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration Challenge - InstructorMichael oliverosNo ratings yet
- Ccna HCL Exam QuestionsDocument25 pagesCcna HCL Exam Questionsshyam80No ratings yet
- Lab 5.6.2 Challenge RIP ConfigurationDocument4 pagesLab 5.6.2 Challenge RIP ConfigurationJosue Isahu Sanchez MedinaNo ratings yet
- 9.2.1.5 Packet Tracer - Designing and Implementing A VLSM Addressing Scheme InstructDocument4 pages9.2.1.5 Packet Tracer - Designing and Implementing A VLSM Addressing Scheme InstructGanti nama100% (1)
- 3.2.4.8 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting A VLAN Implementation - Scenario 2 InstructionsDocument2 pages3.2.4.8 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting A VLAN Implementation - Scenario 2 Instructionsmvpdagawd0% (1)
- Configuring ASA Basic Settings and Firewall Using CLIDocument16 pagesConfiguring ASA Basic Settings and Firewall Using CLIGiovanny DíazNo ratings yet
- 8 4 1 3 Lab Configure Site To Site VPN Using CLI InstructorDocument15 pages8 4 1 3 Lab Configure Site To Site VPN Using CLI InstructorMujeeb Rahman DostNo ratings yet
- Cap. 5: Reto de Integración de Habilidades de Packet Tracer: Topology DiagramDocument6 pagesCap. 5: Reto de Integración de Habilidades de Packet Tracer: Topology DiagramJose rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Jarkom 2 (Vlan) Lan Design: Tasmi, S.Si,. M.Kom, MTCNA, MTCREDocument26 pagesJarkom 2 (Vlan) Lan Design: Tasmi, S.Si,. M.Kom, MTCNA, MTCREBagus wirawanNo ratings yet
- Configuring Cisco Switch and RouterDocument23 pagesConfiguring Cisco Switch and RouterAmourtaha UsiNo ratings yet
- PT Simulation 1 - Intro To Cisco Packet TracerDocument6 pagesPT Simulation 1 - Intro To Cisco Packet TracerRaymond NocheteNo ratings yet
- 7.2.4.3 Laboratorio Cisco Paket Tracer para CertificacionbDocument22 pages7.2.4.3 Laboratorio Cisco Paket Tracer para CertificacionbDavid0% (1)
- OS Lecture3 - Inter Process CommunicationDocument43 pagesOS Lecture3 - Inter Process CommunicationFurious FiveNo ratings yet
- ORACLE-BASE - Oracle Database 19c Installation On Oracle Linux 8 (OL8) - 2Document7 pagesORACLE-BASE - Oracle Database 19c Installation On Oracle Linux 8 (OL8) - 2Claude bernardNo ratings yet
- Skills-Based Assessment (Version A) : TopologyDocument5 pagesSkills-Based Assessment (Version A) : TopologyYagui100% (1)
- CCNA Basic Switch Configuration Commands SheetDocument3 pagesCCNA Basic Switch Configuration Commands Sheetwnelson7No ratings yet
- 7.2.4.3 Lab - Using Wireshark To Examine FTP and TFTP Captures - OQDocument14 pages7.2.4.3 Lab - Using Wireshark To Examine FTP and TFTP Captures - OQskarjosueNo ratings yet
- Cisco CommandDocument4 pagesCisco CommandGaLuh PurnamaNo ratings yet
- Cisco IOS Basic Skills: Configuring The Router From A PCDocument8 pagesCisco IOS Basic Skills: Configuring The Router From A PCjagan36No ratings yet
- ES CCNPv6 ROUTE Lab7-1 Branch Office Config InstructorDocument15 pagesES CCNPv6 ROUTE Lab7-1 Branch Office Config InstructorSebastian Molina FernandezNo ratings yet
- 3.2.3.8 Packet Tracer - Home IoE ImplementationDocument2 pages3.2.3.8 Packet Tracer - Home IoE ImplementationRom'sNo ratings yet
- DRSEnt Chapter 7 - CCNA Discovery Introducing Routing and Switching in The Enterprise - Version 4.0Document8 pagesDRSEnt Chapter 7 - CCNA Discovery Introducing Routing and Switching in The Enterprise - Version 4.0Jesusforgiveme100% (1)
- MikroTik Lesson-02Document29 pagesMikroTik Lesson-02Tanvir AhmedNo ratings yet
- 2.9.2 Lab - Basic Switch and End Device Configuration - ILMDocument12 pages2.9.2 Lab - Basic Switch and End Device Configuration - ILMMariano PereyraNo ratings yet
- CCNA1 - 3 V7 Final ExamDocument167 pagesCCNA1 - 3 V7 Final ExamTsehayou SieleyNo ratings yet
- Monitoring Netflow With NfSenDocument5 pagesMonitoring Netflow With NfSenThanhNN0312No ratings yet
- TDC-460 Cisco Packet Tracer Lab - ShrutiParikhDocument6 pagesTDC-460 Cisco Packet Tracer Lab - ShrutiParikhKushan Gajjar100% (1)
- Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP)Document2 pagesLightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP)Dayakar MeruguNo ratings yet
- 9.2.1.5 Packet Tracer Designing and Implementing A VLSM Addressing Scheme Instruct IGDocument8 pages9.2.1.5 Packet Tracer Designing and Implementing A VLSM Addressing Scheme Instruct IGKe Syukuran KuNo ratings yet
- Instalar Oracle 10g en Ubuntu La EfectivaDocument11 pagesInstalar Oracle 10g en Ubuntu La EfectivaSantiago GrandesNo ratings yet
- DHCP and NAT - Knowledge BaseDocument6 pagesDHCP and NAT - Knowledge BaseHasib Hamidul HaqueNo ratings yet
- 8.4.1.3 Lab - Configure Site-To-Site VPN Using CLIDocument16 pages8.4.1.3 Lab - Configure Site-To-Site VPN Using CLIngangaNo ratings yet
- 9.2.1.11 Packet Tracer - Configuring Named Standard ACLs Instructions IG - Alexis PedrozaDocument10 pages9.2.1.11 Packet Tracer - Configuring Named Standard ACLs Instructions IG - Alexis Pedrozaalexis pedrozaNo ratings yet
- Router Switch CommandscDocument128 pagesRouter Switch CommandscIonel GherasimNo ratings yet
- En ENetwork IPTM v4040Document38 pagesEn ENetwork IPTM v4040abdelhf1No ratings yet
- CCNA 3 Exploration ESwitching Final Exam Form3 V 4.0Document17 pagesCCNA 3 Exploration ESwitching Final Exam Form3 V 4.0sEcZxNo ratings yet
- Cisco Switch Layer2 Layer3 Design and Configuration PDFDocument8 pagesCisco Switch Layer2 Layer3 Design and Configuration PDFSimar NagraNo ratings yet
- 6.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring VLANs InstructionsDocument3 pages6.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring VLANs InstructionsMuhamad Rama Ardiansyah100% (1)
- 6.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring VLANs InstructionsDocument3 pages6.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring VLANs InstructionsKietumetse Tsimane100% (1)
- 3.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring VLANs Instructions IGDocument3 pages3.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring VLANs Instructions IGBERO2403100% (1)
- 3.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring VLANs Instructions IGDocument14 pages3.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring VLANs Instructions IGKaterine Fdz CNo ratings yet
- 3.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring VLANs Instructions IGDocument7 pages3.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring VLANs Instructions IGBrayam Martínez PerdomoNo ratings yet
- 3.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring VLANs InstructionsDocument3 pages3.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring VLANs InstructionsewmbtrakNo ratings yet
- Packet Tracer - Configuring Vlans: TopologyDocument3 pagesPacket Tracer - Configuring Vlans: TopologyEmerson Emerson AemersonNo ratings yet
- 6.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring VLANs InstructionsDocument4 pages6.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring VLANs InstructionsMubba AhmedNo ratings yet
- Packet Tracer - Configuring Vlans: TopologyDocument5 pagesPacket Tracer - Configuring Vlans: TopologyGodsendNo ratings yet
- 3.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring VLANs InstructionsDocument8 pages3.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring VLANs InstructionsViny Alexander MendietaNo ratings yet
- Packet Tracer - VLAN Configuration: Addressing TableDocument4 pagesPacket Tracer - VLAN Configuration: Addressing TableSebastian Victor Garcia LeonNo ratings yet
- Write Down 10 Different Learnings or Takeaways That You Were Able To Glean From The ContentDocument3 pagesWrite Down 10 Different Learnings or Takeaways That You Were Able To Glean From The ContentArmel Bacdayan LacanariaNo ratings yet
- Quiz-Truth Table 1Document3 pagesQuiz-Truth Table 1Armel Bacdayan Lacanaria50% (2)
- Subject Offering 1T2223 August20V.6 1Document15 pagesSubject Offering 1T2223 August20V.6 1Armel Bacdayan LacanariaNo ratings yet
- R Q R Q R Q R (Q Q (Q QV (Q R Q: Mabeninsig@uc-Bcf - Edu.phDocument1 pageR Q R Q R Q R (Q Q (Q QV (Q R Q: Mabeninsig@uc-Bcf - Edu.phArmel Bacdayan LacanariaNo ratings yet
- University of The Cordilleras College of Information Technology and Computer ScienceDocument1 pageUniversity of The Cordilleras College of Information Technology and Computer ScienceArmel Bacdayan LacanariaNo ratings yet
- University of Cordilleras: College of Information Technology / Computer ScienceDocument7 pagesUniversity of Cordilleras: College of Information Technology / Computer ScienceArmel Bacdayan LacanariaNo ratings yet
- Documentation: Armel B. LacanariaDocument2 pagesDocumentation: Armel B. LacanariaArmel Bacdayan LacanariaNo ratings yet
- CC8 Determining MLBB Causes Video Game Addiction To The CITCS-1DDocument7 pagesCC8 Determining MLBB Causes Video Game Addiction To The CITCS-1DArmel Bacdayan LacanariaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise in Data Structures 1Document2 pagesLaboratory Exercise in Data Structures 1Armel Bacdayan LacanariaNo ratings yet
- Javelin BoardDocument2 pagesJavelin BoardArmel Bacdayan LacanariaNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Globalization On Communication and EducationDocument2 pagesThe Impact of Globalization On Communication and EducationArmel Bacdayan LacanariaNo ratings yet
- Host Driver Logs 001Document7,867 pagesHost Driver Logs 001Did You Know ?No ratings yet
- Switch#erase Startup-Config Switch#delete Flash:vlan - Dat Switch#reload Switch Enable S1#show VlanDocument10 pagesSwitch#erase Startup-Config Switch#delete Flash:vlan - Dat Switch#reload Switch Enable S1#show Vlansc1ri2bd3No ratings yet
- Installation Guide: LED ExplanationDocument2 pagesInstallation Guide: LED Explanationpaul esparagozaNo ratings yet
- VLAN TaggingDocument7 pagesVLAN TaggingMohammad SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Radwin Idu-S: Layer 2 Indoor SwitchDocument4 pagesRadwin Idu-S: Layer 2 Indoor Switchcephas01No ratings yet
- Boq HMRP OSC 0058 AND 0059Document3 pagesBoq HMRP OSC 0058 AND 0059ritu gaurNo ratings yet
- 02 - Alcatel-Lucent Price CatalogDocument330 pages02 - Alcatel-Lucent Price CatalogThanh NguyenNo ratings yet
- 4.1.2.4 Lab - Identifying Network Devices and CablingDocument3 pages4.1.2.4 Lab - Identifying Network Devices and CablingAnonymous YetiFo5kMa0% (1)
- AFS Overview 1KHA-001 138-SEN-0110 InternalDocument2 pagesAFS Overview 1KHA-001 138-SEN-0110 Internalgonzalo_tenorio_2100% (1)
- Cotacao - Top UpDocument1 pageCotacao - Top UpOsvaldo AraujoNo ratings yet
- Ag© 'K©B: Bdwbu 3Document17 pagesAg© 'K©B: Bdwbu 3sports newsNo ratings yet
- Tecnologias LANDocument31 pagesTecnologias LANAlexAnguloAbadNo ratings yet
- SFP Quick Reference Guide (Switch)Document3 pagesSFP Quick Reference Guide (Switch)juanNo ratings yet
- Junos Enterprise Switching JexDocument2 pagesJunos Enterprise Switching Jexpankajagr83No ratings yet
- EtherCAT Introduction enDocument86 pagesEtherCAT Introduction enJarmo LatvalaNo ratings yet
- 24+4g-Port Layer 2/layer 3 Gigabit Modular Managed Ethernet SwitchesDocument6 pages24+4g-Port Layer 2/layer 3 Gigabit Modular Managed Ethernet SwitchesAmc Forklift ElektrikNo ratings yet
- S8000-E Ring NetworkDocument90 pagesS8000-E Ring NetworkNguyen Kim Thanh67% (3)
- MEF-CECP Carrier Ethernet Certified Professional Exam Blueprint D 2018Document2 pagesMEF-CECP Carrier Ethernet Certified Professional Exam Blueprint D 2018Angelo James BruanNo ratings yet
- Fisa Tehnica Switch Cu 16 Porturi Gigabit Hikvision DS-3E0520HP-EDocument5 pagesFisa Tehnica Switch Cu 16 Porturi Gigabit Hikvision DS-3E0520HP-Eremus31No ratings yet
- PDFDocument3 pagesPDFRohit Kumar DasNo ratings yet
- Wireless-Tek: Price ModelDocument7 pagesWireless-Tek: Price ModelNay LinNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 13 - Topic 180 To 190Document48 pagesChapter - 13 - Topic 180 To 190bc200403674No ratings yet
- H2 Ccie4career - Com v1.1 PDFDocument94 pagesH2 Ccie4career - Com v1.1 PDFhem777No ratings yet
- Experiment3 VLANDocument13 pagesExperiment3 VLANAbed El Rhman Hamed100% (2)
- CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Lab3-2 ETHERCHANNEL STUDENTDocument18 pagesCCNPv7.1 SWITCH Lab3-2 ETHERCHANNEL STUDENTcamila veraNo ratings yet
- Ieee 802Document3 pagesIeee 802M Zubair AslamNo ratings yet
- 3.Мрежна опрема - ценовник 10.2023Document12 pages3.Мрежна опрема - ценовник 10.2023Ana Odzaklieska Krste SmileskiNo ratings yet
- Ethernet Cable Wiring Diagram PDFDocument2 pagesEthernet Cable Wiring Diagram PDFTimNo ratings yet
- 1.iPASSO 200 - 1000 Introduction Nov2011 2 PDFDocument33 pages1.iPASSO 200 - 1000 Introduction Nov2011 2 PDFAllawane Adam BrahimNo ratings yet
- How To Connect Oracle Exadata To 10 G Networks Using Oracle's Ethernet SwitchesDocument22 pagesHow To Connect Oracle Exadata To 10 G Networks Using Oracle's Ethernet SwitchesfacelessboyzNo ratings yet