Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Primary and Secondary Sources
Primary and Secondary Sources
Uploaded by
Ruben Sosing LeybaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Primary and Secondary Sources
Primary and Secondary Sources
Uploaded by
Ruben Sosing LeybaCopyright:
Available Formats
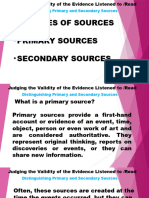
Primary Sources Secondary Sources
A primary source is anything that gives you direct evidence A secondary source is anything that describes, interprets,
about the people, events, or phenomena that you are evaluates, or analyzes information from primary sources.
researching. Primary sources will usually be the main objects Common examples include:
of your analysis. Books, articles and documentaries that synthesize information
on a topic
If you are researching the past, you cannot directly access it Synopses and descriptions of artistic works
yourself, so you need primary sources that were produced at Encyclopedias and textbooks that summarize information and
the time by participants or witnesses (e.g. letters, ideas
photographs, newspapers).
Reviews and essays that evaluate or interpret something
When you cite a secondary source, it’s usually not to analyze it
If you are researching something current, your primary directly. Instead, you’ll probably test its arguments against new
sources can either be qualitative or quantitative data that you evidence or use its ideas to help formulate your own.
collect yourself (e.g. through interviews, surveys,
experiments) or sources produced by people directly involved
in the topic (e.g. official documents or media texts).
You might also like
- Differences Between Primary and Secondary SourcesDocument9 pagesDifferences Between Primary and Secondary SourcesJamesBuensalidoDellava100% (2)
- Lesson 5 Media and Information SourcesDocument47 pagesLesson 5 Media and Information SourcesKristel EbradaNo ratings yet
- CESC Week 6 Part 2Document19 pagesCESC Week 6 Part 2Ruben Sosing Leyba67% (3)
- Las Learning Acitivity Sheet Week: Department of EducationDocument21 pagesLas Learning Acitivity Sheet Week: Department of EducationRuben Sosing Leyba100% (2)
- Sources of InformationDocument4 pagesSources of InformationRachelle GuevarraNo ratings yet
- PRIMARY AND SECONDARY SourcesDocument19 pagesPRIMARY AND SECONDARY SourcesJovy ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Primary and Secondary Sources 1Document34 pagesWeek 2 Primary and Secondary Sources 1Pamela AmitNo ratings yet
- Distinction Between Primary and Secondary SourcesDocument6 pagesDistinction Between Primary and Secondary SourcesJelly Ann EstonidoNo ratings yet
- English Reflection - LAGULAYDocument1 pageEnglish Reflection - LAGULAYlagurashannelleNo ratings yet
- Primary & Secondary SourcesDocument2 pagesPrimary & Secondary SourcesMarjorie DodanNo ratings yet
- Primary Vs Secondary Sources of Literature ReviewDocument5 pagesPrimary Vs Secondary Sources of Literature ReviewSabarishNo ratings yet
- Primary and SecondaryDocument3 pagesPrimary and SecondaryFchelle Ann Delgado PereaNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument4 pagesGlobal WarmingSophiaMarie BarrientosNo ratings yet
- Primary & Secondary SourcesDocument6 pagesPrimary & Secondary SourcesFJ Marzado Sta MariaNo ratings yet
- Information SourcesDocument1 pageInformation Sourceslatoya andersonNo ratings yet
- Alcover, Roxie Jan D. BSCE 2ADocument3 pagesAlcover, Roxie Jan D. BSCE 2ARoxie AlcoverNo ratings yet
- Infographic Project DavidDocument1 pageInfographic Project DavidJoice Racquelle MendozaNo ratings yet
- Sources of InformationDocument11 pagesSources of Information7735330.vuNo ratings yet
- Types of Information SourcesDocument3 pagesTypes of Information SourcesRhoana de guzmanNo ratings yet
- Primary Sources: Examples of Primary Source MaterialsDocument2 pagesPrimary Sources: Examples of Primary Source MaterialsNingning RomarateNo ratings yet
- BooksDocument3 pagesBooksAbigail SalazarNo ratings yet
- HistoryDocument2 pagesHistoryMark AngeloNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 RPHDocument10 pagesLesson 1 RPHBea BautistaNo ratings yet
- Judging The Validity of The Evidence Listened To Read AutosavedDocument28 pagesJudging The Validity of The Evidence Listened To Read Autosavedhannahleebuccat29No ratings yet
- Primary Sources Provide A First-Hand Account of An Event or Time Period and Are Considered To Be AuthoritativeDocument2 pagesPrimary Sources Provide A First-Hand Account of An Event or Time Period and Are Considered To Be AuthoritativeNoreen Licca CastilloNo ratings yet
- Discoursing The Content and Context of Some Primary Sources in Philippine HistoryDocument3 pagesDiscoursing The Content and Context of Some Primary Sources in Philippine Historyjohn marlo andradeNo ratings yet
- Script For EnglishDocument1 pageScript For EnglishIsaaNo ratings yet
- Primary and Secondary Sources of InformationDocument2 pagesPrimary and Secondary Sources of InformationS M NikkiNo ratings yet
- Sources of Information: Using Primary and Secondary SourcesDocument16 pagesSources of Information: Using Primary and Secondary SourcesSophia Denise AgbuyaNo ratings yet
- Historical Sources and Criticism: Lesson ProperDocument4 pagesHistorical Sources and Criticism: Lesson ProperKyla CelebreNo ratings yet
- Primary and Secondary SourcesDocument2 pagesPrimary and Secondary SourcesanneNo ratings yet
- Primary and Secondary SourceDocument3 pagesPrimary and Secondary SourceAjit YadavNo ratings yet
- Sources of History and Historical CriticismDocument4 pagesSources of History and Historical CriticismMarc Kristjan CamarilloNo ratings yet
- Primary and Secondary SourcesDocument2 pagesPrimary and Secondary SourcesTasaduq100% (1)
- Review of Related LiteratureDocument9 pagesReview of Related LiteratureKEAN CHRISTOPHER A NUNEZNo ratings yet
- Sources of InformationDocument4 pagesSources of InformationRachelle GuevarraNo ratings yet
- RPH - Primary and Secondary SourcesDocument2 pagesRPH - Primary and Secondary SourcesGwyneth MalagaNo ratings yet
- Resarch Paper's PaperDocument9 pagesResarch Paper's PaperMahmoodNo ratings yet
- Research Methods Chapter 2 SummaryDocument4 pagesResearch Methods Chapter 2 Summaryalex peprahNo ratings yet
- RPHDocument1 pageRPHMonteza Lyresh AnnNo ratings yet
- Game Researching A TopicDocument4 pagesGame Researching A TopicNoemie LongcayanaNo ratings yet
- Readings in Phil. History Research TopicDocument2 pagesReadings in Phil. History Research TopicMaylene CalicdanNo ratings yet
- Riph SS1CDocument3 pagesRiph SS1CTom Cyrus VallefasNo ratings yet
- English 10 Module L14Document9 pagesEnglish 10 Module L14Jordan CodaneNo ratings yet
- From Problems To SourcesDocument17 pagesFrom Problems To SourcesAmr khaledNo ratings yet
- CPH Primary and Secondary SourcesDocument2 pagesCPH Primary and Secondary SourcesnotjlsnzNo ratings yet
- Primary or Secondary SourcesDocument6 pagesPrimary or Secondary SourcesLiz BomesNo ratings yet
- There Are Generally Two Types of SourcesDocument4 pagesThere Are Generally Two Types of SourcesJasmey BermusaNo ratings yet
- Blis 222Document15 pagesBlis 222sandeepNo ratings yet
- Code 1a-421 CRPHDocument2 pagesCode 1a-421 CRPHAshlyn Grace RetiroNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Types of Historical SourcesDocument3 pages2.2 Types of Historical Sourceskim taehyungNo ratings yet
- 1 Primary and Secondary SourcesDocument2 pages1 Primary and Secondary SourcesApple Mae TonacaoNo ratings yet
- Primary and Secondary SourcesDocument2 pagesPrimary and Secondary SourcesAristotle ManievoNo ratings yet
- English 10 Quarter 1 Lesson 1 Sources of InformationDocument11 pagesEnglish 10 Quarter 1 Lesson 1 Sources of InformationIvan PalganNo ratings yet
- Primary Source Analysis WorksheetDocument1 pagePrimary Source Analysis Worksheetapi-407738940No ratings yet
- Primary Sources Defined: Michelangelo's Sculpture, DavidDocument4 pagesPrimary Sources Defined: Michelangelo's Sculpture, DavidDonita BinayNo ratings yet
- Hist 1013 (Week 2)Document4 pagesHist 1013 (Week 2)Tito Lebelo IllNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - The Importance of Primary Source in HistoryDocument2 pagesModule 1 - The Importance of Primary Source in HistoryAngelica EndrenalNo ratings yet
- Clase Meet Met. Inv. Ii L-V 1Document16 pagesClase Meet Met. Inv. Ii L-V 1DANNY ARELY CARRASCO PINEDANo ratings yet
- Sources of Literature Review: Presented BY Kilda.S Associate Professor, MSN DeptDocument10 pagesSources of Literature Review: Presented BY Kilda.S Associate Professor, MSN DeptsanthiyasandyNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Reading in Philippine HistoryDocument10 pagesReviewer in Reading in Philippine HistoryJohn Harrish AsiloNo ratings yet
- PFA WHLP Grade 12 AbmDocument2 pagesPFA WHLP Grade 12 AbmRuben Sosing LeybaNo ratings yet
- Lac SessionDocument8 pagesLac SessionRuben Sosing LeybaNo ratings yet
- Think and RecallDocument6 pagesThink and RecallRuben Sosing Leyba0% (1)
- ABSDocument21 pagesABSRuben Sosing LeybaNo ratings yet
- Exact: Course Duration Time/Room Instructor Group No. MembersDocument2 pagesExact: Course Duration Time/Room Instructor Group No. MembersRuben Sosing LeybaNo ratings yet
- Plan For October 22Document6 pagesPlan For October 22Ruben Sosing LeybaNo ratings yet