Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Module IV: Central Nervous System Medications
Uploaded by
Vincent Paul Santos0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views4 pagesOriginal Title
Module-IV-PHARMA (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views4 pagesModule IV: Central Nervous System Medications
Uploaded by
Vincent Paul SantosCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Module IV: Central Nervous - Dextroamphetamine Indication: obesity
System Medications (Dexedrine)
Ex. Dextroamphetamine (Dexadrine)
- Methylphenidate (concerta,
Ritalin)
A. CNS Stimulants
Narcolepsy Side Effects/adverse effects:
- Drugs that enhances the activities of
- Modafinil (Provigil) - Tachycardia, palpitatios,
neurotransmitters: dopamine,
- Pemoline (Cylert) dizziness, hypertension
norepinephrine, serotonin
- Sleeplessness, restlessness,
II. Analeptics
1. Amphetamines nervousness, tremors,
Action: stimulates CNS by either irritability
2. Analeptics
increasing neuronal discharge or - Increases hyperactivity
3. Anorexiants inhibiting neurotransmitters (INCOMPLETE)
Indication:
Contraindications/Precautions
I. Amphetamines - Reversal of anesthesia-induced - C:Glaucoma, severe CV
Action: acts on cerebral cortex, respiratory depression disease
reticular activity system - Stimulate respiration in (INCOMPLETE)
newborns
Indication :
Methylxanthines B. CNS Depressants
- Increases in narcolepsy
- Increases attention span, - Aminophylline Action: Drugs that have an CNS
cognition - Theophylline inhibitory effect
- Decreases hyperactivity, - Caffeine
Sedatives
impulsiveness, restlessness of NoDoz
ADHD - Reduces nervousness,
Doxapram (Dopram) excitability, and irritability
ADHD without causing sleep
III. Anorexiants
- Methamphetamine (Desoxyn) Sedativ-hypnotics
Action: suppress the appetite control
- Amphetamine (Adderall)
center in the brain
- Low doses: calm the CNS Ex. Pentobarbital NOTE! Benzodiazepines are the most
without inducing sleep (INCOMPLETE) frequently prescribes sedative-
- High doses: calm the CNS and hypnotics because of its favourable
causes sleep; also causes drug effects
respiratory depression Intermediate-acting
III. Non-benzodiazepines
I. Barbiturates - Induce and sustain sleep, for
Action: neurotransmitter inhibition
convulsion, but causes residual
II. benzodiazepines
drowsiness (hangover effect) Indication: treat short-term (<10 days)
III. Non-benzodiazepines Ex. (INCOMPLETE) insomnia
NOTE! Barbiturates are notorious Ex. Zolpidem (ambien), eszopiclone
enzyme inducers; it stimulates liver (Lunesta)
I. Baribiturates
enzymes, which speeds up drug
Drug Interactions;l
- Action: inhibits GABA, which metabolism resulting to shortened
inhibits nerve impulses in the cerebral duration of drug action - Alcohol, ethanol,
cortex; suppresses REM sleep antihistamines,
II. Benzodiazepines
benzodiazepines, MAOIs=
Indication: Hypnotics, sedatives,
Action: Interacts with GABA to increases effect, decreases
anticonvulsants, anesthesia
reduce neuron excitability; do not respirations with
Habit forming; low therapeutic suppresses REM sleep - MAOIs will prolong effects of
index barbiturates
Indication: agitation, anxiety, alcohol
- Decreases anticoagulant
Ultrashort-acting withdrawal, pre-operative sedation,
response, leading to possible
insomnia, seizure, skeletal muscle
- Used as a general anethetic clot formation
relaxation
Ex. Thipental sodium (pentothal) Side Effects/adverse effects
Long-acting
Short-acting - Residual drowsiness (Hangover
- Estazolam (Prosom),
- Induce sleep, controls Effect)
- Flurazepam (Dalmane)
convulsion, and no residual - Headache, vertigo
-
drowsiness - Fall hazard for frail elderly
INCOMPLETE
persons
- Drug dependence and tolerance Suppress Na influx - Primary treatment for acute
- Respiratory depression seizures: diazepam
- Phenytoin (Dilantin)
- Withdrawal symptoms - Short term effect; not for
Suppress Ca influx maintenance
Contraindication:
- Valproic acid - For petit mal seizures:
- Pregnancy, uncontrolled pain, clonazepam
INCOMPLETE
acute intermittent porphyria - High degree of tolerance
Types of Antinconvulsants - Adjunctive therapy for
C. Anticonvulsants
1. Hydantoin treatment of partial seizures:
Seizure Disorders clorazepate
2. Barbiturates
Seizure- abnormal electric discharges Succinimides
from neurons characterized by loss of 3. Benzodiazepines
consciousness. - Used to treat absence or petit
4. Succinimides mal seizures
Convulsion- sudden, violent, irregular INCOMPLETE
movement of a lim or of the body,
caused by involuntary contraction of Hydantoin D. Neuromuscular Medications
muscles and associated especially - Most commonly-used drug for Myasthenia Gravis
with brain disorders seizure control - Autoimmune disease caused by
Epilepsy- chronic, recurrent INCOMPLETE lack of nerve impulses and
occurrence of 2 or more unprovoked Barbiturates muscle responses at myoneural
seizure episodes junction due to lack of
- For grand mal acute episodes of acetylcholine reaching
Tonic- body’s defense status epilepticus cholinergic receptors
Action: Suppress abnormal neuron - Use long-acting barbiturate:
firing, inhibiting seizure activites phenobarbital Cholinesterase Inhibitors
- Lesser teratogenic effects than Action: transmission of
Indications: tonic-clonic seizure, phenytoin
status epilepticus, complete partial neuromuscular impulses by
seizures, arrhythmias, trigeminal Benzodiazepines preventing destruction of Ach- allows
neuralgia cholinergic response
INCOMPLETE - Headache, dizziness, seizures - Chronic, progressive,
- Hypotension, bradycardia, degenerative disorder due to
3 Medications
dysarrthmias neurotransmitter imbalance:
Neostigmine (Prostigmin) - INCOMPLETE dopamine<acetylcholine (ACh)
- Short-acting Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Anti-Parkinsonism Drugs
Edrophonium (Tensilon) - Autoimmune disorder that 1. Anticholinergic
- Ultrashort-acting for attacks myelin sheath of nerve
- benztropine, biperiden
diagnosing MG fibers
- Characteristics: INCOMPLETE - Block the effects of Ach by blocking
Pyridostigmine (Mestinon) cholinergic receptors
Muscle relaxants
INCOMPLETE Indication: muscle tremors and
- Provides relief of painful
muscle rigidity associated
musculoskeletal condition:
Myasthenia Crisis Muscle spasms INCOMPLETE
Management of spasticity of
- Underdosed severe chornic disorders
- Severe muscle weakness INCOMPLETE Alzheimers’s Disease
- Improves after edrophonium
Central Acting: CNS - Progressive, degenerative
Cholinergic crisis disease due to neuritic plaques
- Baclofen (Lioresal) formation and neurofibrillary
- Overdosed - Diazepam
- Severe muscle cramping tangels in neurons
- Clarisoprodol (Soma) INCOMPLETE
- Cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril)
INCOMPLETE Anomia- inability to remember names
Cholinesterase Inhibitors of things
E. Parkinson’s Diseases (PD) and
Side Effects Apraxia- misuse of object o
Alzheimer’s Diseases (AD)
- Pupil constriction INCOMPLETE
Parkinson’s Disease
- GI distress, abdominal cramps
- Excess saliva, sweating
You might also like
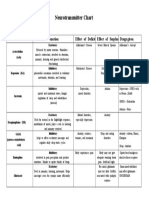
- Neurotransmitter ChartDocument1 pageNeurotransmitter Chartmonster40lbs100% (2)
- WB TBA19 020vadvance PDFDocument266 pagesWB TBA19 020vadvance PDFTran Khang92% (12)
- ChartDocument1 pageChartAnggi Dwi PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Design Scenario Chapter 5Document6 pagesDesign Scenario Chapter 5jtrillossNo ratings yet
- Neurotransmitters AnxietyDocument7 pagesNeurotransmitters AnxietyMatthew SyNo ratings yet
- Cns StimulantsDocument4 pagesCns StimulantsKienna GarciaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology: Reviewer For Final Exam: Nervous SystemDocument18 pagesPharmacology: Reviewer For Final Exam: Nervous Systempatty janeNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On CNSDocument19 pagesDrugs Acting On CNSAditya sagarNo ratings yet
- Anxiolytic, Sedative-Hypnotic DrugsDocument39 pagesAnxiolytic, Sedative-Hypnotic DrugsNina100% (1)
- Obat2 Yang Bekerja Pada Ganguan Kesadaran: Elly Usman Bagian Farmakologi Dan Terapi, Fakultas Kedokteran, UnandDocument29 pagesObat2 Yang Bekerja Pada Ganguan Kesadaran: Elly Usman Bagian Farmakologi Dan Terapi, Fakultas Kedokteran, UnandKhairani HakimNo ratings yet
- Cns AgentsDocument10 pagesCns Agentsroldanmarygrace023No ratings yet
- Drug AnalysisDocument49 pagesDrug Analysisjomalaw6714No ratings yet
- Central Nervous System StimulantsDocument6 pagesCentral Nervous System StimulantsNathalia CabalseNo ratings yet
- PHARM250 Nervous System Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument15 pagesPHARM250 Nervous System Cheat Sheet: by ViaThư PhạmNo ratings yet
- Pharma Topic 3 NotesDocument3 pagesPharma Topic 3 NotesAshley Franceska CansanayNo ratings yet
- 2018-2019 Cns DepressantsDocument5 pages2018-2019 Cns DepressantsMary AgorillaNo ratings yet
- Stereotypical Behavior: Rate Dependence EffectsDocument2 pagesStereotypical Behavior: Rate Dependence EffectsJustin HulinNo ratings yet
- Anestesi UmumDocument42 pagesAnestesi UmumBryan HoriandoNo ratings yet
- Modern Dravya GunaDocument21 pagesModern Dravya GunaAvinash Perfectt0% (2)
- CNS Depressants - Anxiolytics & Sedative HypnoticsDocument4 pagesCNS Depressants - Anxiolytics & Sedative HypnoticsJustin HulinNo ratings yet
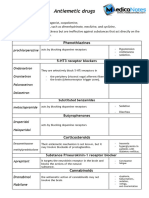
- Antiemetic DrugsDocument2 pagesAntiemetic DrugsAch Ri Fa INo ratings yet
- Drugs of AbuseDocument3 pagesDrugs of AbuseNovutry SiregarNo ratings yet
- Nursing Pharma (Chapter 4 - )Document1 pageNursing Pharma (Chapter 4 - )Jemima GasconNo ratings yet
- 7779087Document65 pages7779087MohamedNo ratings yet
- Neurotransmitters Cuadro PDFDocument2 pagesNeurotransmitters Cuadro PDFCarina Castillo ValdiviezoNo ratings yet
- Ch2neurotrans PDFDocument2 pagesCh2neurotrans PDFKentNo ratings yet
- Neurotransmitter Cheat Sheet AP ReviewDocument2 pagesNeurotransmitter Cheat Sheet AP ReviewNathania DawitNo ratings yet
- DiazepamDocument1 pageDiazepamGracia Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- CT Week 7 PharmaDocument15 pagesCT Week 7 PharmaJoelynMacalintalNo ratings yet
- Psychotropic Drugs: Bryan Mae H. DegorioDocument65 pagesPsychotropic Drugs: Bryan Mae H. DegorioBryan Mae H. Degorio100% (2)
- Drugs FOR Psychiatric & Neurologic Disorders: Clonazepam (Klonopin, Rivotril) Midazolam (Versed, Dormicum)Document5 pagesDrugs FOR Psychiatric & Neurologic Disorders: Clonazepam (Klonopin, Rivotril) Midazolam (Versed, Dormicum)Noriko MatsumotoNo ratings yet
- Sedative HypnoticsDocument39 pagesSedative HypnoticsFatima ShaukatNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting CNSDocument30 pagesDrugs Affecting CNSGwen De CastroNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology (1) - 104-122Document19 pagesPharmacology (1) - 104-122Dental LecturesMMQNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System: A Sedative Can Become A Hypnotic If It Is Given in Large Enough DosesDocument6 pagesCentral Nervous System: A Sedative Can Become A Hypnotic If It Is Given in Large Enough Doseschubbygunny_29776413No ratings yet
- Pharmacology of The Central Nervous System-1Document163 pagesPharmacology of The Central Nervous System-1Gølà Sèèñàà–baale irraaNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System 1 2 DEFINTIONS OF TERMSDocument3 pagesCentral Nervous System 1 2 DEFINTIONS OF TERMSKristina Mae BayanoNo ratings yet
- Print Pharma Cns DrugsDocument44 pagesPrint Pharma Cns DrugsRaphael FranciscoNo ratings yet
- AnxiolyticsDocument5 pagesAnxiolyticsRawan AlshammaNo ratings yet
- Anti ParkinsonsDocument4 pagesAnti ParkinsonsMichaela BernadasNo ratings yet
- Anxiolytics Sedatives Hypnotics Pharm 3Document38 pagesAnxiolytics Sedatives Hypnotics Pharm 3Peter Harris100% (1)
- HALOPERIDOLDocument1 pageHALOPERIDOLAlyxen Pelingen75% (4)
- Er-Drug StudyDocument41 pagesEr-Drug Studyrc_lacampuinganyahooNo ratings yet
- Neurological Disorder: NeuronDocument8 pagesNeurological Disorder: NeuronMaica Lectana100% (2)
- Pharmacology - Drugs For CNS DisordersDocument4 pagesPharmacology - Drugs For CNS DisordersJireh MejinoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 28 - 3rd Asessment - Sedatives, HypnoticsDocument32 pagesLecture 28 - 3rd Asessment - Sedatives, Hypnoticsapi-3703352100% (1)
- Ativan (Lorazepam) Drug StudyDocument3 pagesAtivan (Lorazepam) Drug StudyCHERISE CORDOVA100% (2)
- Pharma Midterms Review UwuDocument11 pagesPharma Midterms Review UwuAJ BayNo ratings yet
- Anti ParkinsonsDocument4 pagesAnti ParkinsonsMichaela BernadasNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledDE VERA, Jastisse MNo ratings yet
- Nm-Lec15 - (Anxiolytics, Sedatives & Hypnotics)Document39 pagesNm-Lec15 - (Anxiolytics, Sedatives & Hypnotics)geng gengNo ratings yet
- DS GadDocument2 pagesDS Gadbianca musicNo ratings yet
- Sedative and Hypnotics: MorphineDocument7 pagesSedative and Hypnotics: MorphineFathimath100% (1)
- PHARMACOLOGY Assisgnment 01Document5 pagesPHARMACOLOGY Assisgnment 01muhammadhamza muhammadiqbalNo ratings yet
- CNS Depressants and BZDocument64 pagesCNS Depressants and BZfayrouz fathiNo ratings yet
- Pharma NotesDocument4 pagesPharma NotesMayya FirdousNo ratings yet
- Depression PDFDocument10 pagesDepression PDFLyadelou FortuNo ratings yet
- Table of Sedative, Hypnotic, AntianxietyDocument4 pagesTable of Sedative, Hypnotic, AntianxietyirfanzukriNo ratings yet
- Sedative-Hypnotic Drugs - AMBOSSDocument8 pagesSedative-Hypnotic Drugs - AMBOSSRuva Oscass JimmyNo ratings yet
- NCM 106 Week 5 and 6 ReviewerDocument15 pagesNCM 106 Week 5 and 6 ReviewerCrecia Bullecer2No ratings yet
- Format of The Report On Art History/Art MovementDocument5 pagesFormat of The Report On Art History/Art MovementVincent Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- CONCLUSIONDocument1 pageCONCLUSIONVincent Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- Letter: Definition of Letter (Entry 1 of 3)Document2 pagesLetter: Definition of Letter (Entry 1 of 3)Vincent Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- DoktoratezDocument10 pagesDoktoratezVincent Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- Symptom Management Guidelines: ORAL MUCOSITIS: Focused Health AssessmentDocument11 pagesSymptom Management Guidelines: ORAL MUCOSITIS: Focused Health AssessmentVincent Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- Cityscape: ArchitectureDocument3 pagesCityscape: ArchitectureVincent Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- Maynila,: Manila (Document10 pagesMaynila,: Manila (Vincent Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- DDDDDocument2 pagesDDDDVincent Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- CCCCDocument1 pageCCCCVincent Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- Connecting With Space and Place: Physical GeographyDocument7 pagesConnecting With Space and Place: Physical GeographyVincent Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- Media Materials and Webcasts: Information DateDocument4 pagesMedia Materials and Webcasts: Information DateVincent Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- Disturbed Body Image DefinitionDocument1 pageDisturbed Body Image DefinitionVincent Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- BBBBDocument1 pageBBBBVincent Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- Authorized Use: Learn MoreDocument1 pageAuthorized Use: Learn MoreVincent Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- General Information: Viral VectorDocument3 pagesGeneral Information: Viral VectorVincent Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- Physical and Emotional Assessment: Checklist 87: Changing A Pouching System/Ostomy Appliance (Ileostomy or Colostomy)Document4 pagesPhysical and Emotional Assessment: Checklist 87: Changing A Pouching System/Ostomy Appliance (Ileostomy or Colostomy)Vincent Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- Disturbed Body Image DefinitionDocument1 pageDisturbed Body Image DefinitionVincent Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- Media Materials and Webcasts: Information DateDocument4 pagesMedia Materials and Webcasts: Information DateVincent Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- General Information: Viral VectorDocument3 pagesGeneral Information: Viral VectorVincent Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- Authorized Use: Learn MoreDocument1 pageAuthorized Use: Learn MoreVincent Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- DDDDDocument2 pagesDDDDVincent Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- CCCCDocument3 pagesCCCCVincent Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- 10.7 Ostomy Care: Clinical Procedures For Safer Patient CareDocument3 pages10.7 Ostomy Care: Clinical Procedures For Safer Patient CareVincent Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- Special ConsiderationsDocument3 pagesSpecial ConsiderationsVincent Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- DDDDDocument3 pagesDDDDVincent Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- EEEEDocument2 pagesEEEEVincent Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- Supine Brain: Nursing DiagnosisDocument4 pagesSupine Brain: Nursing DiagnosisVincent Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- Infection Anemia: Nursing Interventions RationaleDocument2 pagesInfection Anemia: Nursing Interventions RationaleVincent Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- Prepare Your StomaDocument2 pagesPrepare Your StomaVincent Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans: Ineffective (Uteroplacental) Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plans: Ineffective (Uteroplacental) Tissue PerfusionVincent Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- How To Write SpecificationsDocument9 pagesHow To Write SpecificationsLeilani ManalaysayNo ratings yet
- Shahid Change ManagementDocument1 pageShahid Change Managementtanveer azamNo ratings yet
- Renewal of ForgivenessDocument3 pagesRenewal of ForgivenessShoshannahNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Mathematical Literacy: Question Paper 1 MARKS: 150 TIME: 3 HoursDocument53 pagesGrade 12 Mathematical Literacy: Question Paper 1 MARKS: 150 TIME: 3 HoursOfentse MothapoNo ratings yet
- Resolution No. 1433Document2 pagesResolution No. 1433MA. DIVINA LAPURANo ratings yet
- Growrich PinoyDocument59 pagesGrowrich PinoyMarites FerolinoNo ratings yet
- Professional Practice - X Sem - 2017-18 As On 16032018Document89 pagesProfessional Practice - X Sem - 2017-18 As On 16032018harshinireddy mandadiNo ratings yet
- Ismu in EnglishDocument2 pagesIsmu in EnglishIsmilaYulianaNo ratings yet
- Management Final Paper 27062020 044941pm PDFDocument8 pagesManagement Final Paper 27062020 044941pm PDFHuzaifa KhanNo ratings yet
- Based On The 1979 Standards of Professional Practice/ SPPDocument10 pagesBased On The 1979 Standards of Professional Practice/ SPPOwns DialaNo ratings yet
- Social Class 10 2019Document14 pagesSocial Class 10 2019krishnareddy_chintalaNo ratings yet
- This Points Are Very Main Part of Self: How To Give Self Introduction in IterviewDocument22 pagesThis Points Are Very Main Part of Self: How To Give Self Introduction in Iterviewvijay kumarNo ratings yet
- Ruel Kennard O. Mallari: Objective Work ExperienceDocument3 pagesRuel Kennard O. Mallari: Objective Work ExperienceAntonette TagadiadNo ratings yet
- Gender Inequality in Bangladesh PDFDocument20 pagesGender Inequality in Bangladesh PDFshakilnaimaNo ratings yet
- Plot Journey - Brett MacDonell PDFDocument4 pagesPlot Journey - Brett MacDonell PDFBrett MacDonellNo ratings yet
- Periyava Times Apr 2017 2 PDFDocument4 pagesPeriyava Times Apr 2017 2 PDFAnand SNo ratings yet
- LRD Waiting ListDocument209 pagesLRD Waiting ListPrince PatelNo ratings yet
- The Barney Bag - Barney Wiki - FandomDocument6 pagesThe Barney Bag - Barney Wiki - FandomchefchadsmithNo ratings yet
- The Double Conjunctions Worksheet (Both ... And, Neither ... Nor, Either ... Or)Document2 pagesThe Double Conjunctions Worksheet (Both ... And, Neither ... Nor, Either ... Or)Ibrahim BenamiraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - 8ae AbsorptionDocument12 pagesLesson 5 - 8ae AbsorptionarnavprajeetNo ratings yet
- Sharp Lc-26sb25e S Ru Lc-32sb25e Lc-42sb55s e RuDocument172 pagesSharp Lc-26sb25e S Ru Lc-32sb25e Lc-42sb55s e RuПетя СтойчеваNo ratings yet
- Calibration Form: This Form Should Be Filled Out and Sent With Your ShipmentDocument1 pageCalibration Form: This Form Should Be Filled Out and Sent With Your ShipmentLanco SANo ratings yet
- Acordes para GuitarraDocument12 pagesAcordes para GuitarraLucas Sebastian MuñozNo ratings yet
- Content-Area Instruction For Ells: Connecti Es ArchDocument15 pagesContent-Area Instruction For Ells: Connecti Es Archnickelt23No ratings yet
- Test 5 - C Reading SectionDocument13 pagesTest 5 - C Reading SectionFaby SanchezNo ratings yet
- First Conditional Advice Interactive WorksheetDocument2 pagesFirst Conditional Advice Interactive WorksheetMurilo BaldanNo ratings yet
- PAL v. CIR (GR 198759)Document2 pagesPAL v. CIR (GR 198759)Erica Gana100% (1)
- Roman Empire Revived TheoryDocument173 pagesRoman Empire Revived TheoryBrenoliNo ratings yet