Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Capital Markets
Uploaded by
Shane Tabunggao0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views1 pageA capital market is a financial market where longer-term debt and equity instruments are traded. It allows people and entities needing capital to issue securities like bonds and stocks, and investors to purchase these securities. The primary issuers of capital market securities are governments and corporations seeking to fund activities or investments. Bonds are traded on this market, and represent loans made to the issuer. Bond ratings by agencies indicate the risk of default, with poorer ratings demanding higher expected returns. Common stock represents ownership in a company, while preferred stock has preference in dividends and liquidation but lacks voting rights.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA capital market is a financial market where longer-term debt and equity instruments are traded. It allows people and entities needing capital to issue securities like bonds and stocks, and investors to purchase these securities. The primary issuers of capital market securities are governments and corporations seeking to fund activities or investments. Bonds are traded on this market, and represent loans made to the issuer. Bond ratings by agencies indicate the risk of default, with poorer ratings demanding higher expected returns. Common stock represents ownership in a company, while preferred stock has preference in dividends and liquidation but lacks voting rights.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views1 pageCapital Markets
Uploaded by
Shane TabunggaoA capital market is a financial market where longer-term debt and equity instruments are traded. It allows people and entities needing capital to issue securities like bonds and stocks, and investors to purchase these securities. The primary issuers of capital market securities are governments and corporations seeking to fund activities or investments. Bonds are traded on this market, and represent loans made to the issuer. Bond ratings by agencies indicate the risk of default, with poorer ratings demanding higher expected returns. Common stock represents ownership in a company, while preferred stock has preference in dividends and liquidation but lacks voting rights.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
CAPITAL MARKETS
1. Explain what capital market is.
A capital market is a financial market in which longer-term debt and equity instruments are being
traded. It is the venue for people who have and in need of capital wherein savings and investment
are being carried on. It is also composed of primary and secondary market.
2. Who are the primary issuers of capital market securities?
The primary issuers of capital market securities are National and local government and
corporations.
National government - issues long-term notes and bonds to fund the national debt
Local governments – issue notes and bonds to finance capital projects
Corporations – issue both bonds and stock to finance capital investment expenditures and fund
other investment opportunities.
3. What are the bonds? How are they traded?
A bond is any long-term promissory note issued by the firm. A bond certificate is the tangible
evidence of debt issued by a corporation or a government body and represents a loan made by
investors to the issuer.
Bonds are traded occurs in either a public offering, using an investment bank serving as a security
underwriter or through a private placement to a small group of investors.
4. What is the relationship between bond rating and expected rate of return?
Bond ratings involve judgment about the future risk potential of the bond provided by rating
agencies. It is affected by low utilization of financial leverage, profitable operations, low
variability of past earnings, large firm size, and little use of subordinated debt. The poorer the
bond rating, the higher the expected rate of return demanded in the capital markets.
5. Distinguish between ordinary or common stock and preferred stock.
Ordinary or common stock is a form of long-term equity that represents ownership interest of the
firm. Ordinary equity shareholders are the true owners of the corporation and consequently bear
the ultimate risks and rewards of ownership.
Preferred share is a class of equity shares which has preference over ordinary equity shares in the
payment of dividends and in the distribution of corporation assets in the event of liquidation.
In ordinary stock, there are voting rights bestowed in the ordinary equity shareholders while
preferred stock has none. Preferred stock shareholders have priority over the company’s income
and therefore they are paid dividends. Whereas in ordinary equity shareholders, they are the last
to acquire company assets, meaning, they will be paid out after creditors, bondholders, and
preferred shareholders.
You might also like
- CA Corporations CodeDocument1,000 pagesCA Corporations CodeMaxx Garrison KurzunskiNo ratings yet
- Korea - Securities Lending and BorrowingDocument41 pagesKorea - Securities Lending and BorrowingtrucnhtNo ratings yet
- Microsoft IPO ProspectusDocument52 pagesMicrosoft IPO Prospectusjohnnyg31100% (1)
- Assignment - Financial MarketsDocument9 pagesAssignment - Financial MarketsTaruntej Singh100% (3)
- MODULE 1 Lecture Notes (Jeff Madura)Document4 pagesMODULE 1 Lecture Notes (Jeff Madura)Romen CenizaNo ratings yet
- Tabunggao, Shane Josa Marie M. AC23 Exercises On Cash Flow Statement Analysis Theories: Investing FinancingDocument3 pagesTabunggao, Shane Josa Marie M. AC23 Exercises On Cash Flow Statement Analysis Theories: Investing FinancingShane TabunggaoNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument5 pagesFinancial Statement AnalysisShane Tabunggao100% (1)
- Chapter 13: Basics of Commercial BankingDocument2 pagesChapter 13: Basics of Commercial BankingShane Tabunggao100% (1)
- Memorial For The PetitionerDocument27 pagesMemorial For The PetitionerShreyaTewari100% (1)
- Interview QuestionsDocument7 pagesInterview QuestionsGaurav TripathiNo ratings yet
- Intro CMDocument6 pagesIntro CMFreddierick JuntillaNo ratings yet
- Ch01 Solutions Manual An Overview of FM and The Financial Management and The FinancialDocument4 pagesCh01 Solutions Manual An Overview of FM and The Financial Management and The FinancialAM FMNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document13 pagesChapter 1mark sanadNo ratings yet
- Capital Market:: What Does Capital Markets Mean?Document5 pagesCapital Market:: What Does Capital Markets Mean?Nadeem AhmadNo ratings yet
- Common Stocks-Common Stock, by Means of Capital Growth, Yields Higher Returns Than Almost EveryDocument4 pagesCommon Stocks-Common Stock, by Means of Capital Growth, Yields Higher Returns Than Almost EveryJuliet ToriagaNo ratings yet
- W I AS ?: HAT S EcurityDocument6 pagesW I AS ?: HAT S EcurityMuhammad SaadullahNo ratings yet
- Compilation of All Activities: Opol Community College Poblacion, Opol Misamis OrientalDocument24 pagesCompilation of All Activities: Opol Community College Poblacion, Opol Misamis OrientalAngie CondezaNo ratings yet
- The Role of The Financial MarketsDocument6 pagesThe Role of The Financial Marketsrosalyn mauricioNo ratings yet
- Functions:: Financial InstitutionsDocument3 pagesFunctions:: Financial InstitutionskimNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document2 pagesLesson 3Safh SalazarNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Abdullah (6772) Capital & Money MarketDocument5 pagesMuhammad Abdullah (6772) Capital & Money MarketMuhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- The Basic Structure of Financial MarketsDocument10 pagesThe Basic Structure of Financial Markets202220012No ratings yet
- Financial SecurityDocument3 pagesFinancial SecurityJackie BallaranNo ratings yet
- Specialty CorporationDocument171 pagesSpecialty CorporationAdrian Steven Claude CosicoNo ratings yet
- CM Assignment BBA 5th SemDocument7 pagesCM Assignment BBA 5th Semnamyruleforever9No ratings yet
- Fmi CH 1 130730050202 Phpapp01Document36 pagesFmi CH 1 130730050202 Phpapp01Jubayet HossainNo ratings yet
- CM Chapter 3 - CarlomanDocument21 pagesCM Chapter 3 - CarlomanJonavel Torres MacionNo ratings yet
- Money Markets and Capital MarketsDocument4 pagesMoney Markets and Capital MarketsEmmanuelle RojasNo ratings yet
- 2 Types of SecuritiesDocument2 pages2 Types of SecuritiesMark MatyasNo ratings yet
- Securities and MarketsDocument51 pagesSecurities and MarketsBilal JavedNo ratings yet
- Capital Market - A BriefDocument7 pagesCapital Market - A BriefasfaarsafiNo ratings yet
- Case 4Document3 pagesCase 4Melana MuliNo ratings yet
- Debt Securities MarketDocument3 pagesDebt Securities MarketSean ThyrdeeNo ratings yet
- Capital MarketDocument38 pagesCapital Marketapi-3798892No ratings yet
- Capital Market and Portfolio ManagementDocument3 pagesCapital Market and Portfolio ManagementAshutosh SinghNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets (Chapter 8)Document4 pagesFinancial Markets (Chapter 8)Kyla DayawonNo ratings yet
- FMP TheoryDocument6 pagesFMP TheoryMuhammad Awall RazaNo ratings yet
- Financial Instruments PresentationDocument13 pagesFinancial Instruments Presentationh.rshaikh747No ratings yet
- Instruments of The Capital MarketDocument3 pagesInstruments of The Capital MarketHarsh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Business Finance Hand Outs 02Document4 pagesBusiness Finance Hand Outs 02Shane VeiraNo ratings yet
- MNGT M2Document3 pagesMNGT M2Melody MadarraNo ratings yet
- Assets (Meaning) .: 1 8 BCF 412 (Asset Management) - NotesDocument8 pagesAssets (Meaning) .: 1 8 BCF 412 (Asset Management) - NotessamNo ratings yet
- Capital Markets Securities Funding Stock Bond Underwriting Initial Public Offering ProspectusDocument9 pagesCapital Markets Securities Funding Stock Bond Underwriting Initial Public Offering ProspectusGracy KadrikotaNo ratings yet
- W ElcomeDocument18 pagesW ElcomeRamesha SNo ratings yet
- Content PDFDocument18 pagesContent PDFSecurity Bank Personal LoansNo ratings yet
- FE - Financial Assets and SecuritiesDocument7 pagesFE - Financial Assets and SecuritiesJUAN BERMUDEZNo ratings yet
- ForwardDocument2 pagesForwardKhristialynne De LeonNo ratings yet
- Financing and Asset Management DecisionsDocument7 pagesFinancing and Asset Management DecisionsMelissa Abdul KarimNo ratings yet
- Chapter IV Suplimentary 2Document25 pagesChapter IV Suplimentary 2henokal99No ratings yet
- Financial MarketsDocument3 pagesFinancial MarketsAguit, Queene JoyNo ratings yet
- FM MidDocument4 pagesFM MidImtiaz SultanNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Introduction To InvestmentDocument10 pagesChapter One Introduction To InvestmentMIKIYAS BERHENo ratings yet
- Chapter Two-The Financial Environment: Markets, Institutions and Investment BanksDocument4 pagesChapter Two-The Financial Environment: Markets, Institutions and Investment Banksmaquesurat ferdousNo ratings yet
- BondMarket FinancialMarketsDocument38 pagesBondMarket FinancialMarketsDummy GoogleNo ratings yet
- Composition of Financial SystemDocument10 pagesComposition of Financial SystemKareen Tapia PublicoNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document5 pagesModule 2Marivica DagunaNo ratings yet
- Megha Malani Roll No.07 FybbiDocument18 pagesMegha Malani Roll No.07 Fybbiakotian91No ratings yet
- Stock Market Group 4Document11 pagesStock Market Group 4Kristine MartinezNo ratings yet
- Tamrat Mersha Individual AssignmentDocument6 pagesTamrat Mersha Individual AssignmentTamrat MershaNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Palawan State University College of Business and Accountancy Puerto Princesa CityDocument3 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Palawan State University College of Business and Accountancy Puerto Princesa CitybaneNo ratings yet
- Name: Chenee Yvette Torbeles Chapter 4. Key Players in The Financial SystemDocument2 pagesName: Chenee Yvette Torbeles Chapter 4. Key Players in The Financial SystemTorbeles ChenNo ratings yet
- Financial Environment - Lecture2Document20 pagesFinancial Environment - Lecture2mehnaz kNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics (Stocks and Bonds)Document22 pagesGeneral Mathematics (Stocks and Bonds)Synta FluxNo ratings yet
- NAME: Jimenez, Ross John C. Year-Course-Section: 3-BSMA-A: InstrumentsDocument2 pagesNAME: Jimenez, Ross John C. Year-Course-Section: 3-BSMA-A: InstrumentsRoss John JimenezNo ratings yet
- Unit 1. Nature and Scope of Investment and Portfolio ManagementDocument7 pagesUnit 1. Nature and Scope of Investment and Portfolio ManagementCLIVE100% (1)
- Equity Investment for CFA level 1: CFA level 1, #2From EverandEquity Investment for CFA level 1: CFA level 1, #2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- On Clifford's Argument: Intro Philosophy, Paper 1Document4 pagesOn Clifford's Argument: Intro Philosophy, Paper 1Shane TabunggaoNo ratings yet
- Audit ProblemsDocument32 pagesAudit ProblemsShane TabunggaoNo ratings yet
- Audit ProblemsDocument47 pagesAudit ProblemsShane TabunggaoNo ratings yet
- Carpolaw Com Everything You Need To Know About Create Act in The PhilippinesDocument8 pagesCarpolaw Com Everything You Need To Know About Create Act in The PhilippinesShane TabunggaoNo ratings yet
- Audit Problems FinalDocument48 pagesAudit Problems FinalShane TabunggaoNo ratings yet
- Art Journal ExampleDocument8 pagesArt Journal ExampleShane TabunggaoNo ratings yet
- Database Management SystemDocument1 pageDatabase Management SystemShane TabunggaoNo ratings yet
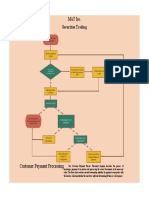
- Customer Payment Processing: MAT Inc. Securities TradingDocument1 pageCustomer Payment Processing: MAT Inc. Securities TradingShane TabunggaoNo ratings yet
- Debit Balances Increase (Decrease) Credit Balances Increase (Decrease)Document7 pagesDebit Balances Increase (Decrease) Credit Balances Increase (Decrease)Shane TabunggaoNo ratings yet
- Shane Josa Marie M. Tabunggao AC22Document15 pagesShane Josa Marie M. Tabunggao AC22Shane TabunggaoNo ratings yet
- Negotiable Instruments OutlineDocument34 pagesNegotiable Instruments OutlineShane TabunggaoNo ratings yet
- Answer: Accounting Information System: PresentDocument2 pagesAnswer: Accounting Information System: PresentShane TabunggaoNo ratings yet
- ACCA105Document2 pagesACCA105Shane TabunggaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Nature, Form, and Kinds of AgencyDocument21 pagesChapter 1: Nature, Form, and Kinds of AgencyShane TabunggaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Corporate Governance Review QuestionsDocument2 pagesChapter 1: Corporate Governance Review QuestionsShane Tabunggao100% (1)
- Phis102 Digest 1Document6 pagesPhis102 Digest 1Shane TabunggaoNo ratings yet
- Statement of Financial Position/Retained EarningsDocument5 pagesStatement of Financial Position/Retained EarningsShane TabunggaoNo ratings yet
- INTACC2 - Chapter 30Document2 pagesINTACC2 - Chapter 30Shane TabunggaoNo ratings yet
- K-12 Program Should Continue To Be Implemented in The Philippines I. Features of K-12 ProgramDocument1 pageK-12 Program Should Continue To Be Implemented in The Philippines I. Features of K-12 ProgramShane TabunggaoNo ratings yet
- Application Letter ExampleDocument2 pagesApplication Letter ExampleShane TabunggaoNo ratings yet
- INTACC2 - Chapter 29Document4 pagesINTACC2 - Chapter 29Shane TabunggaoNo ratings yet
- Practice Exercises - Note PayableDocument2 pagesPractice Exercises - Note PayableShane TabunggaoNo ratings yet
- Art Journal SampleDocument8 pagesArt Journal SampleShane TabunggaoNo ratings yet
- Hosking Post Collection Aug22Document50 pagesHosking Post Collection Aug22TimothyNgNo ratings yet
- Iap PresentationDocument49 pagesIap PresentationPruthvi Shetty ShettyNo ratings yet
- Fundamental and Technical Analysis For Idiots Part 2Document33 pagesFundamental and Technical Analysis For Idiots Part 2Nataraja UpadhyaNo ratings yet
- Kajal BS Presentation 12Document15 pagesKajal BS Presentation 12Kajal JasejaNo ratings yet
- Abhijeet Power - DRHPDocument538 pagesAbhijeet Power - DRHPsheetal_incNo ratings yet
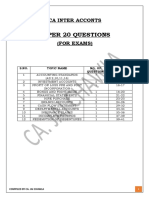
- Inter Accounts Super 20 QuestionsDocument41 pagesInter Accounts Super 20 QuestionsOm AgarwalNo ratings yet
- FAQs On Sovereign Gold Bond SCHEME Annx1Document6 pagesFAQs On Sovereign Gold Bond SCHEME Annx1Alok Kr MishraNo ratings yet
- Prime BrokerageDocument28 pagesPrime BrokeragePrat Don100% (1)
- Introduction - Lending Operations & Risk Management-Lecture-1Document111 pagesIntroduction - Lending Operations & Risk Management-Lecture-1nawazjiskani100% (2)
- Palting Vs San Jose PetroleumDocument10 pagesPalting Vs San Jose Petroleumyelina_kuranNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Solution Week 2Document4 pagesTutorial Solution Week 2Arlene Lan100% (1)
- Financial Notes by JMR SirDocument70 pagesFinancial Notes by JMR SirAlekhya ThirumaniNo ratings yet
- Washington Mutual (WMI) - Attachments/Exhibits To The Final Report of The Examiner (Part 8/10)Document427 pagesWashington Mutual (WMI) - Attachments/Exhibits To The Final Report of The Examiner (Part 8/10)meischerNo ratings yet
- Islamic Private Debt SecuritiesDocument6 pagesIslamic Private Debt SecuritiesMuhammad Shahrul NazwinNo ratings yet
- United States - Industry Reports (NAICS)Document13 pagesUnited States - Industry Reports (NAICS)Amir JungkookNo ratings yet
- NISM-Series-VI-Depository Operations-May 2021 VersionDocument224 pagesNISM-Series-VI-Depository Operations-May 2021 VersionLohit BharambeNo ratings yet
- Securitisation and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest Act, 2002 (Sarfaesi Act)Document18 pagesSecuritisation and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest Act, 2002 (Sarfaesi Act)varun100% (1)
- 09 Chapter 3Document35 pages09 Chapter 3Vienna Corrine Q. Abucejo100% (1)
- 22 Assets-2Document5 pages22 Assets-2Arturo VillarragaNo ratings yet
- Dig 041564Document2 pagesDig 041564OSCAR SPENCER RAMIREZNo ratings yet
- Financial Ratios 6Document171 pagesFinancial Ratios 6Mohammed UsmanNo ratings yet
- Moneylife 13 Oct 2016 PDFDocument68 pagesMoneylife 13 Oct 2016 PDFUpendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Banking Adbl EnglishDocument74 pagesBanking Adbl Englishdevi ghimireNo ratings yet
- Mba Black Book Project On HDFC MFDocument5 pagesMba Black Book Project On HDFC MFPooja SinghNo ratings yet
- Shubham MoreDocument60 pagesShubham MoreNagesh MoreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document22 pagesChapter 7trevorsum123No ratings yet