Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mancon Introduction Notes PDF
Mancon Introduction Notes PDF
Uploaded by
Makiri Sajili IIOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mancon Introduction Notes PDF
Mancon Introduction Notes PDF
Uploaded by
Makiri Sajili IICopyright:
Available Formats
MS 01_MANAGEMENT CONSULTANCY OCTOBER 2019
Calamba Review Center - Laguna (LCRC)
2F MMCO Building, 8000 Lakeview Ph3 Angela Street, Halang Calamba City Laguna, Philippines
Tel No. (02) 330-8617, (049) 523-6031; (02) 330-6057
CPA REVIEW (October 2019 Batch)
MAS Karim G. Abitago, CPA
MS01 – MANAGEMENT CONSULTANCY
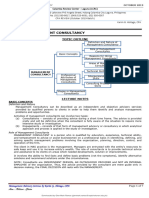
TOPIC OUTLINE
Definition and Nature of
Management Consultancy
Role of Management
Consultants
Basic Concepts
Reasons for Hiring
Management Consultants
Areas of Management
Consultancy
MANAGEMENT Technical Skills
CONSULTANCY Professional
Interpersonal
Attributes of
Skills
Management
Consultants
Consulting Process
Skills
Stages in Management
Consultancy
LECTURE NOTES
BASIC CONCEPTS
Definition and Nature
Management Consultancy can be described as an independent and objective advisory services
provided by qualified persons to clients in order to help them identify and analyze management
problems and opportunities.
Activities of management consultants can involve two types:
(a) Consultations – consists of providing advice during a short time frame. The advice is provided
orally and will be definitive when the consultant is fully aware of the situation to require more
intensive study or investigation.
(b) Engagements – consists of that form of management advisory or consultancy in which analytical
approach and process is applied in the study or investigation.
Role of Management Consultants
MANAGEMENT CONSULTANT is a person who is qualified by education, experience, technical ability,
and temperament to advise or assist businessmen on a professional basis in identifying, defining, and
solving specific management problems involving the organization, planning, direction, control, and
operation of the firm.
The client in MAS practice is the management. Managers are entrusted with the entity’s resources to
safe keep and use it to increase entity’s wealth. The role of consultants is to provide technical advice
and assistance to its clients on areas which needed development, solution or improvements.
It involves the ability to find facts and define basic problems (not the symptoms), identify alternative
solutions and recommend solutions under the circumstances.
NOTE: Consultants are INDEPENDENT PERSON, AN OUTSOURCED PROVIDER and NOT AN INTERNAL
EMPLOYEE of the organization. Thus, the advice provided by the consultant are mere guide only in
decision making, the FINAL DECISION still rests with the MANAGEMENT.
Management Advisory Services by Karim G. Abitago, CPA Page 1 of 7
Aim…Believe..Claim
MS 01_MANAGEMENT CONSULTANCY OCTOBER 2019
Reasons for hiring Management Consultants
(1) Independent point of view
A consultant is considered to be independent and objective to the dilemma faced by the organization.
Since the consultant is not part in the establishment of internal policies of the organization, his or her
suggestion is considered to be unbiased.
(2) Professional advisor and counselor
An experienced management consultant possesses special knowledge, skills and a variety of personal
attributes that make him the most desirable candidate to undertake the engagement involving his
area of expertise.
NOTE: Although law DOES NOT RESTRICTS the practice of management consultancy to CPAs,
business firms generally prefer CPAs as their consultants.
(3) Temporary professional service
The use of consultants is less expensive to the company than hiring new managers and employees to
provide professional advisory services
(4) Agent of change
A management consultant is a catalyst of change specifically in providing solutions to clients’
problems. These solutions tend to help management in the administration and improvement of the
organization.
Areas of MAS Work
BROAD AREAS OF MAS
A. Areas Normally Related to the Accounting and Finance Functions:
1. Financial Accounting Systems Design and Development
2. Management Accounting Systems Design and Development
3. Development and Establishment of Budgetary Controls
The field covers the following:
1. Cost Accounting
a. Development of standard cost system
b. Cost analysis and control
c. Variance analysis
2. Financial Management
a. Establishment of capital budgeting procedures
b. Study of the cost of capital and cost of debt
c. Financial analysis for project studies
d. Establishment of operating and cash budgets
e. Valuation of common stocks for purposes of mergers and sale.
B. Areas Not Normally Related to the Accounting and Finance Functions:
1. General Management Consultation
a. Management or Operations Audit
b. Measurement of Operating Performance
c. Mergers and Acquisitions Studies
d. Development of Compensation Programs
e. Pension Plan Review
f. Special Studies on Industry Potential
g. Long-Range Planning
2. Project Feasibility Studies
- involves financial, technical, and marketing evaluation of proposed projects.
3. Organization and Personnel
a. Review of Existing Organization Structure
b. Organization and Administrative Manual Preparation
c. Job Evaluation and Salary Administration
d. Development of Personnel Rating Programs
e. Retirement Plan Studies
f. Studies of Office Cost Reduction Systems
g. Determining Cost of Alternatives in Collective Bargaining Agreements
4. Industrial Engineering
a. Production, Planning, Scheduling, and Control
b. Plant Layout Studies
c. Inventory Management Studies
d. Materials Control System Design and Development
e. Preventive Maintenance System Design and Development
f. Development of Work Standards
g. Purchasing Management, including Value Analysis
Management Advisory Services by Karim G. Abitago, CPA Page 2 of 7
Aim…Believe..Claim
MS 01_MANAGEMENT CONSULTANCY OCTOBER 2019
5. Marketing
a. Product Profitability Analysis
b. Pricing Policy Determination
c. Market Forecasting
d. Distribution Cost Analysise. Salesmen's Incentive Compensation Evaluation
e. Salesmen’s Inventive Compensation Evaluation
6. Operations Research
- involves the use of mathematical techniques, such as linear programming, PERT/CPM,
queuing theory, simulation, etc. to solve operational problems.
The services listed above are not necessarily exhaustive nor complete. The practitioner may offer
other services not mentioned above depending on the practitioner's competence, experience,
technical ability, and professional integrity to meet or deliver such other services he offers.
MAS CLASSIFICATIONS BASED ON REQUIRED EXPERTISE
1. Usual Services:
a. Evaluation of form of business organization
b. Analysis of financial and operating statements
c. Design and installation of accounting systems
d. Design of filing systems for storing accounting records
e. Suggestions for improvements in internal control
f. Establishment of control to assist management and expedite the audit process
g. Preparation of insurance claims in case of business interruption
h. Research and evaluation of alternative methods of handling a transaction for its effect on
finance and tax consequences
i. Assistance in the preparation of forecasts and budgets
j. Presentation and explanation of statements
k. Assisting clients in purchase or sale of business
l. Testifying on client's behalf
m. Determination of the effect of various employee compensation plans on net income
n. Aid in labor union negotiations
2. Somewhat Specialized Services:
a. Assisting in the installation of a mechanized accounting system
b. Making a cost analysis of operations
c. Finding sources of capital and figuring the approximate cost of small business loans, bond issue,
and stock issuance
d. Giving advice on dividend policy and plans for expansion
e. Calculations on government contracts and allocating costs incompliance with reporting
requirements
f. Advising on accounting and tax matters relative to estate planning
g. Surveying credit losses
h. Assisting in bankruptcy and receivership proceedings
i. Recruiting accounting and bookkeeping personnel for the client
j. Preparing an analysis of paper flow
k. Presenting and analyzing the pros and cons of various retirement and profit-sharing plans
l. Advising on various wage incentive plans
3. Highly Specialized Services:
a. Reviewing the organization structure
b. Auditing management policies
c. Conducting motion studies
d. Surveying an industry of trade for current trends
e. Evaluating the desirability of a particular area for plant location
f. Preparing market analysis
g. Reviewing an insurance program
h. Advising on data processing allocation
PROFESSIONAL ATTRIBUTES OF MANAGEMENT CONSULTANTS
Management consultants must possess the following professional attributes or skills:
(1) Technical Skills
- include understanding and experience in technical discipline such as information technology,
marketing, engineering, accounting and organizational behavior.
(2) Interpersonal Skills
- include personal attributes that make an individual amiable among people and effective in
accomplishing desirable objectives through people.
(3) Consulting Process Skills
- include ability to define problems, identify alternative solutions and recommend solutions under the
circumstances.
Management Advisory Services by Karim G. Abitago, CPA Page 3 of 7
Aim…Believe..Claim
MS 01_MANAGEMENT CONSULTANCY OCTOBER 2019
STAGES OF MANAGEMENT CONSULTANCY
STAGE 1: NEGOTIATING THE ENGAGEMENT
This stage involves preliminary discussion with the client, client background investigation, preparation
of proposal letter and engagement contract and establishing fees and billing arrangement.
PROPOSAL LETTER: is a written communication between the CPA and the client setting forth the
terms and conditions of a proposed consultancy work.
ENGAGEMENT CONTRACT: is the legal contract binding both parties to the engagement.
CONSULTANCY FEES:
The cost of consultancy shall consist the following and shall be presented in the agreement in the like
manner:
(1) Salaries or billing rates
(2) Reimbursable costs or out-of-pocket costs
(3) Contingency costs
METHODS OF BILLING CLIENTS:
(1) Actual time basis / per diem basis – billing is done on the basis of actual time spent multiplied by the
hourly rates agreed upon.
(2) Flat or fixed basis – client is billed flat but all inclusive pre-arranged amount for the entire
engagement.
(3) Maximum fee basis – client is charged on a per diem basis with the arrangement that the total
charges will not exceed a certain agreed amount.
(4) Retainer basis – consultant is paid a fixed predetermined fee for all services rendered during a
designated period of time, say on a monthly or semi-annual basis.
STAGE 2: PREPARING FOR AND STARTING THE ENGAGEMENT
This stage is all about engagement planning.
Engagement Planning involves preparing a work plan (A.K.A. Engagement Program), selection of
personnel, scheduling of tasks, determining project cost and professional fees.
STAGE 3: CONDUTING THE ENGAGEMENT
Under this stage, four (4) necessary activities are done:
(1) Problem Identification – It is the first phase of the problem-solving process and its position in the
process is well established.
NOTE: A problem is said to exist when the observed behavior of a system or process violates the
bounds of reasonable expectations.
(2) Data Gathering – It deals with fact sources and identifies places where the consultant can look to find
facts associated with the operation of the client. Sources of the consultant could be internal or
external.
DATA GATHERING TECHNIQUES: (a) Interviews; (b) Questionnaire; (c) Observation; (d) Document
Gathering; (e) Charting
(3) Data Analysis and Diagnosis
(a) Decision-level Analysis – has the purpose of depicting the varied interrelationships among the
decisions made throughout the segments and levels of organization.
(b) Input / Output Analysis – analysis of the problem in terms of input or output.
(c) Structured Analysis – the key assumption underlying this approach is that any organization is
comprised of a number of well-defined functions, which in turn are made up of group of
activities.
(4) Solution Development – It involves generation and evaluation of solution alternatives, making a
choice of solution alternative and detailed development of selected solution.
STAGE 4: PREPARING AND PRESENTING THE REPORT AND RECOMMENDATION
Presentation of the report and recommendation could be in the following form: (a) oral; (b) written;
(c) visual NOTE: The recommended solution should be presented in a persuasive manner of the
consultant expects to obtain client’s acceptance of the recommendation.
STAGE 5: IMPLEMENTING THE RECOMMENDATION
This stage is considered to be the important lengthy phase that follows solution development phase.
NOTE: It must be understood that the CPA or the CONSULTANT SHOULD NOT TAKE RESPONSIBILITY
for making management and policy decisions.
STAGE 6: EVALUATING THE ENGAGEMENT
Evaluation is necessary for CONSTANT IMPROVEMENT AND REFINEMENT in the QUALITY of future
advisory services of the consultant.
STAGE 7: POST-ENGAGEMENT FOLLOW-UP
Management Advisory Services by Karim G. Abitago, CPA Page 4 of 7
Aim…Believe..Claim
MS 01_MANAGEMENT CONSULTANCY OCTOBER 2019
DISCUSSION EXERCISES
MULTIPLE CHOICE:
BASIC CONCEPTS
1. Which of the following characterizes MAS?
I. Broad and diversity in scope. III. Management is the main beneficiary of the service
II. Limited to CPAs.
A. I and II D. I, II and III
B. II and III E. Answer not given
C. I and III
2. In Advisory Services, the practitioner's function is to
A. provide counsel in a short time frame, based mostly, if not entirely, on existing personal knowledge
about the client, the circumstances, the technical matters involved, client representations, and
mutual intent of the parties.
B. develop findings, conclusions, and recommendations for the practitioner's consideration and decision
making.
C. put an action plan into effect.
D. provide services related to specific client transaction generally with a third party.
3. Which of the following statements is false?
A. CPAs have historically been business consultants to their clients.
B. Management consultants are licensed and regulated by laws.
C. The primary purpose of management consultancy is to improve the firm's use of its capabilities and
resources to achieve its objectives.
D. Management consultancy services are provided not only to big business enterprises but also to
medium-size and small companies.
4. Which of the following is not an analytical approach in MAS engagement?
A. Ascertaining the pertinent facts and circumstances
B. Defining the problem or opportunity for improvement
C. Presenting findings and recommendations
D. Counseling management in planning, operating and controlling functions.
5. Reasons for hiring management consultant:
I. A consultant is considered as an additional employee of the company in solving problems faced by it.
II. A management consultant is considered to be a catalyst change.
A. I only C. Both I and II
B. II only D. Neither I nor II
6. Following are possible end-products of an MAS engagement, except
A. an organization plan with statements of duties and responsibilities.
B. blue print of a construction project.
C. an electronic data processing system.
D. sales reporting system.
7. MAS areas which are not normally related to the accounting and finance functions may include
A. preparation of accounting systems and procedure manuals.
B. development of management oriented accounting and reporting systems.
C. cost reduction studies.
D. operations research.
8. Management advisory services classified as usual services include
A. giving advice on dividend policy and plans for expansion.
B. analysis of financial and operating statements for management, stockholders, banks, and others.
C. advising on accounting and tax matters relative to estate planning in cooperation with legal and
insurance counsel.
D. calculations on government contracts and allocating costs in compliance with reporting requirement.
PROFESSIONAL ATTRIBUTES OF MANAGEMENT CONSULTANTS
9. All of the following are manifestations of consultant’s interpersonal skills except
A. ability to work effectively as a team member
B. ability to grasp and represent facts unbiased by prejudice or objectivity
C. ability and reasoning power to arrive at a wise decision or judgment
D. ability to absorb and relate facts in a logical and orderly fashion and to reason inductively and
deductively or intelligence
10. Ability to define objectives and outcomes is an example of a consultants
A. Rapport-building skills C. Analysis skills
B. Project management skills D. Interpersonal skills
STAGES OF MANAGEMENT CONSULTANCY
11. A CPA should reject an MAS engagement if
A. It would require him to make management decisions for an audit client.
B. His recommendations are to be subject to review by the client.
C. He audits the financial statements of a subsidiary of the prospective client.
D. The proposed engagement is not accounting-related.
Management Advisory Services by Karim G. Abitago, CPA Page 5 of 7
Aim…Believe..Claim
You might also like
- CH 06 - Analyzing Operating ActivitiesDocument49 pagesCH 06 - Analyzing Operating Activitieshy_saingheng_760260985% (13)
- SAIF VC Fund Takes Shanda Inc. Public by Mikael ThakurDocument20 pagesSAIF VC Fund Takes Shanda Inc. Public by Mikael ThakurMikael ThakurNo ratings yet
- Investment in Equity Securities - SeatworkDocument2 pagesInvestment in Equity Securities - SeatworkLester ColladosNo ratings yet
- Tax RemediesDocument5 pagesTax RemediesCherrelyne AlmazanNo ratings yet
- Nfjpia Nmbe RFBT 2017 Ans1Document8 pagesNfjpia Nmbe RFBT 2017 Ans1Harvey CalabiaNo ratings yet
- Kalinga State University College of Business, Entrepreneurship & Accountancy Test Questions Mockbord Theory of Accounts Midterm ExaminationDocument10 pagesKalinga State University College of Business, Entrepreneurship & Accountancy Test Questions Mockbord Theory of Accounts Midterm ExaminationJaymee Andomang Os-agNo ratings yet
- tAX FINALSDocument8 pagestAX FINALSAmie Jane MirandaNo ratings yet
- Audit of Liabilities - Guidance Note PDFDocument22 pagesAudit of Liabilities - Guidance Note PDFRicalyn E. SumpayNo ratings yet
- Govt. Acctg. CHP 9Document11 pagesGovt. Acctg. CHP 9Shane KimNo ratings yet
- Accreditation Public PracticeDocument36 pagesAccreditation Public Practicejanpeters0n100% (1)
- Audit of ReceivablesDocument2 pagesAudit of ReceivablesCarmelaNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Audit IIDocument9 pagesCH 2 Audit IIsamuel debebeNo ratings yet
- 4 Revenue From Contracts With Customers (PFRS 15)Document11 pages4 Revenue From Contracts With Customers (PFRS 15)Mark TaysonNo ratings yet
- 7103 - Notes Receivable and Loan ImpairmentDocument2 pages7103 - Notes Receivable and Loan ImpairmentGerardo YadawonNo ratings yet
- Sample MC Questions CooperativesDocument5 pagesSample MC Questions CooperativesLeny Joy DupoNo ratings yet
- Fin Man Case Study On Fs AnalysisDocument6 pagesFin Man Case Study On Fs AnalysisRechelleNo ratings yet
- Notes From Sir Red Sirug Handouts On Auditing TheoryDocument104 pagesNotes From Sir Red Sirug Handouts On Auditing TheoryAmithy GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash Equivalents QuestionsDocument5 pagesCash and Cash Equivalents QuestionsMikaerika AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- AUDITING-Audit of LiabilitiesDocument9 pagesAUDITING-Audit of LiabilitiesJamhel MarquezNo ratings yet
- AFAR-06 (Revenue From Customer Contracts - Other Topics)Document26 pagesAFAR-06 (Revenue From Customer Contracts - Other Topics)mysweet surrenderNo ratings yet
- CFAS Reviewer - Module 4Document14 pagesCFAS Reviewer - Module 4Lizette Janiya SumantingNo ratings yet
- Resolution No.23 2010Document13 pagesResolution No.23 2010Ronald ParrenoNo ratings yet
- Optional Standard Deductions ExampleDocument7 pagesOptional Standard Deductions ExampleSandia EspejoNo ratings yet
- NegoDocument6 pagesNegoIvhy Cruz EstrellaNo ratings yet
- ACP311 Special Transaction LecturesDocument33 pagesACP311 Special Transaction LecturesJohn Stephen PendonNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Pfrs 15 Revenue From Contracts With CustomersDocument4 pagesReviewer Pfrs 15 Revenue From Contracts With CustomersMaria TheresaNo ratings yet
- Substantive Audit Testing: Expenditure Cycle: Multiple ChoiceDocument20 pagesSubstantive Audit Testing: Expenditure Cycle: Multiple ChoiceMark Dwayne MalonzoNo ratings yet
- AP Summary Lecture (16 May 2021)Document9 pagesAP Summary Lecture (16 May 2021)Joanna MalubayNo ratings yet
- My Resume For InternshipDocument3 pagesMy Resume For InternshipmythriyaNo ratings yet
- St. Vincent'S College Incorporated College of Accounting EducationDocument8 pagesSt. Vincent'S College Incorporated College of Accounting Educationrey mark hamacNo ratings yet
- ICARE Preweek AT Preweek LectureDocument15 pagesICARE Preweek AT Preweek Lecturejohn paulNo ratings yet
- MidtermExam CostingDocument9 pagesMidtermExam CostingUnknownNo ratings yet
- Accounting PresentationDocument12 pagesAccounting Presentationgelly studiesNo ratings yet
- Auditing - Final ExaminationDocument7 pagesAuditing - Final ExaminationFrancis MateosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19Document9 pagesChapter 19Marc Siblag IIINo ratings yet
- At - Prelim Rev (875 MCQS) Red Sirug Page 1 of 85Document85 pagesAt - Prelim Rev (875 MCQS) Red Sirug Page 1 of 85Waleed MustafaNo ratings yet
- Statement of Cash Flows Quiz Set ADocument5 pagesStatement of Cash Flows Quiz Set AImelda lee0% (1)
- Standard Costing Multiple ChoiceDocument11 pagesStandard Costing Multiple ChoiceRuiz, CherryjaneNo ratings yet
- At 1 Theory Palang With Questions 1Document12 pagesAt 1 Theory Palang With Questions 1Sharmaine JoyceNo ratings yet
- Naqdown Clincher QuestionDocument13 pagesNaqdown Clincher QuestionsarahbeeNo ratings yet
- Aaca Receivables and Sales ReviewerDocument13 pagesAaca Receivables and Sales ReviewerLiberty NovaNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument43 pagesReviewergnim1520No ratings yet
- Accounting For Business CombinationsDocument32 pagesAccounting For Business CombinationsAmie Jane MirandaNo ratings yet
- ACCTG 2A and B Accounting For PartnershiDocument16 pagesACCTG 2A and B Accounting For PartnershiMarvin RabinoNo ratings yet
- 40 - Financial Statements - TheoryDocument9 pages40 - Financial Statements - TheoryクロードNo ratings yet
- Mas Study Plan: May 2019 Exam RecapDocument5 pagesMas Study Plan: May 2019 Exam RecapoxennnnNo ratings yet
- Specialized Prelim Exam UCPDocument6 pagesSpecialized Prelim Exam UCPlois martinNo ratings yet
- Finals Reviewer AudtheoDocument36 pagesFinals Reviewer AudtheoMae VillarNo ratings yet
- Quizzer Variable CostingAdditionalDocument6 pagesQuizzer Variable CostingAdditionalNaddieNo ratings yet
- PCPAr Special Materials 2Document83 pagesPCPAr Special Materials 2Sherri BonquinNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Audit of Ppe1Document4 pagesAssignment - Audit of Ppe1Wam OwnNo ratings yet
- Fraud Error Non-Compliance and Legal Liability Final1 PDFDocument7 pagesFraud Error Non-Compliance and Legal Liability Final1 PDFJa NilNo ratings yet
- JPIA Soli LetterDocument1 pageJPIA Soli LetterNatasha MilitarNo ratings yet
- Receivables ProblemsDocument4 pagesReceivables ProblemsLarpii MonameNo ratings yet
- Quantitative MethodsDocument19 pagesQuantitative MethodsSerena Van der WoodsenNo ratings yet
- Auditing Theory ReviewerDocument6 pagesAuditing Theory ReviewerHans Even Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- AnswerDocument21 pagesAnswerStephanie EspalabraNo ratings yet
- MS01Document4 pagesMS01Leodeza MactalNo ratings yet
- C'o, 4i1) k873387 @Document3 pagesC'o, 4i1) k873387 @Jen JenNo ratings yet
- Overview of Management Advisory ServicesDocument52 pagesOverview of Management Advisory ServicesGennelyn Grace PenaredondoNo ratings yet
- Strategic Cost Management - Management ConsultancyDocument7 pagesStrategic Cost Management - Management ConsultancyVanna AsensiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1. Basic Concepts of Managerial AccountingDocument32 pagesUnit 1. Basic Concepts of Managerial AccountingWoodsville HouseNo ratings yet
- Europe and China Play A Role-Reversal: European Investment StrategyDocument23 pagesEurope and China Play A Role-Reversal: European Investment StrategySiphoKhosaNo ratings yet
- Holigrail Afl For AmibrokerDocument27 pagesHoligrail Afl For AmibrokerVirat InstituteNo ratings yet
- Yield To Maturity Yield To CallDocument14 pagesYield To Maturity Yield To CallAdamNo ratings yet
- Audit Chapter 6Document6 pagesAudit Chapter 6elysabet christyNo ratings yet
- Sector Watch Barbell PortfolioDocument4 pagesSector Watch Barbell Portfoliotmoney5151No ratings yet
- Gitman - PPT - ch06 Bond ValuationDocument56 pagesGitman - PPT - ch06 Bond ValuationFerry GumilarNo ratings yet
- Corporate StrategyDocument15 pagesCorporate StrategyAbhilasha BagariyaNo ratings yet
- Audit of Investment StudentsDocument11 pagesAudit of Investment StudentsJames R JunioNo ratings yet
- HSBC Investment AnalystDocument5 pagesHSBC Investment AnalystSanjana SinghNo ratings yet
- Fixed Asset Policy & Procedures: June 2012Document35 pagesFixed Asset Policy & Procedures: June 2012Sohrab KhaskheliNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 Cost ControlDocument18 pagesChap 2 Cost ControlKah KeattNo ratings yet
- 2020 Level I OnDemandVideo SS13 R41 Module 2Document6 pages2020 Level I OnDemandVideo SS13 R41 Module 2Arturos lanNo ratings yet
- RegularisationDocument11 pagesRegularisationAnand DubeyNo ratings yet
- Valuation of SharesDocument24 pagesValuation of Sharesshalini0703No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Advanced Valuation Issues ModuleDocument12 pagesChapter 5 Advanced Valuation Issues ModuleJoannah maeNo ratings yet
- Apm Final Project FinalDocument29 pagesApm Final Project FinalMano RajpootNo ratings yet
- Default Pay Scale/Grade Structure From Table V - 001P - CDocument7 pagesDefault Pay Scale/Grade Structure From Table V - 001P - CDeepa ShiligireddyNo ratings yet
- West Visayas State University-Pototan CampusDocument11 pagesWest Visayas State University-Pototan CampusChu ChuNo ratings yet
- Solution To Biological Assets ProblemsDocument9 pagesSolution To Biological Assets ProblemsBella De LiañoNo ratings yet
- A Study On Financial Statement Analysis With Reference To CIMS Medica India Private Limited.Document66 pagesA Study On Financial Statement Analysis With Reference To CIMS Medica India Private Limited.shubhangi sawaleNo ratings yet
- HONY, CIFA, AND ZOOMLION: Creating Value and Strategic Choices in A Dynamic MarketDocument5 pagesHONY, CIFA, AND ZOOMLION: Creating Value and Strategic Choices in A Dynamic MarketJitesh ThakurNo ratings yet
- IIM Ranchi - Naman AroraDocument1 pageIIM Ranchi - Naman AroraDishant KhanejaNo ratings yet
- Material Ledger StartupDocument21 pagesMaterial Ledger StartupSandro Domeneghetti100% (1)
- Financial Accounting and Reporting: IFRS - 2017 June QPDocument8 pagesFinancial Accounting and Reporting: IFRS - 2017 June QPMarchella LukitoNo ratings yet
- CFA Level II - Equity - RIDocument10 pagesCFA Level II - Equity - RIQuy Cuong BuiNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Enterprenership ChallengesDocument32 pagesTopic 1 Enterprenership ChallengesMasumHasanNo ratings yet
- Bond Valuation (IBF)Document52 pagesBond Valuation (IBF)Zain AbbasNo ratings yet
- LBP vs. Heirs of TrinidadDocument12 pagesLBP vs. Heirs of Trinidadkimgoopio100% (1)