Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Top-200-Drug ETSY
Uploaded by
Betsy Brown Byersmith0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
216 views31 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
216 views31 pagesTop-200-Drug ETSY
Uploaded by
Betsy Brown ByersmithCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 31
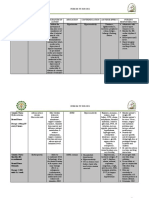
Drug Mechanism of Action 3 Highly Testable Pearls
Hydrocodone/acetaminophen Hydrocodone - Binds, • Addiction/dependence risk
(Vicodin, Lortab, Norco) activates mu-opioid • Respiratory depression
receptor, Acetaminophen • Constipation
– suspected to inhibit
prostaglandin synthesis
which reduces pain
Lisinopril (Prinivil) Inhibits angiotensin • Cough
converting enzyme which • Hyperkalemia
ultimately leads to • Used to help protect the kidneys in
reduction in angiotensin 2 diabetes
(a potent vasoconstrictor)
Simvastatin (Zocor) Inhibits HMG-CoA • Myopathy
reductase – this enzyme is • Reduces risk of heart attack/stroke
the rate limiting step in • Dosed at night
cholesterol formation
Levothyroxine (Synthroid) Synthetic form of thyroid • Binding interactions with calcium
hormone (T4) and iron can lower concentrations
• TSH is monitored to adjust dose
• Signs of hypothyroid –
fatigue, dry skin,
constipation
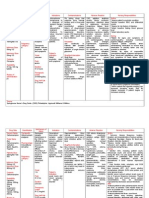
Amoxicillin (Amoxil) Inhibits penicillin binding • Diarrhea
protein which prevents • Nausea/Vomiting
cell wall synthesis • Rash
Azithromycin (Zithromax) Binds 50s ribosomal • Longer half-life than many
subunit and prevents antibiotics
protein synthesis • GI adverse effects
• Rare risk for QTc prolongation
Hydrochlorothiazide Blocks sodium • Frequent urination
(HCTZ);(Microzide) reabsorption in the distal • Elevate uric acid level (exacerbate
convoluted tubule of gout)
kidney • Can help with edema and
hypertension
Amlodipine (Norvasc) Blocks the entry of • Edema
calcium into smooth • No action on the heart (compared to
muscle, causing diltiazem, verapamil)
vasodilation
• Used to help prevent angina
Alprazolam (Xanax) Enhances GABA activity • Used for acute
which has sedative, management of anxiety
hypnotic, anticonvulsant, • Dizziness/sedation
and muscle relaxant • Generally avoid in elderly
properties
Metformin (Glucophage) Primarily decreases • Avoid in moderate to severe
hepatic glucose kidney disease, rare risk of
production lactic acidosis
• GI side effects like diarrhea
is most prominent
• First line agent in type 2
diabetes
Atorvastatin (Lipitor) Inhibits HMG-CoA • Myopathy
reductase – this enzyme is • Reduces risk of heart
the rate limiting step in attack/stroke
cholesterol formation • Higher intensity statin
Omeprazole (Prilosec) Inhibits H+/K+ ATPase • Short term only
pump in gastric parietal recommended for GERD
cells (reduces hydrogen • Associated with low
ion – stomach acid magnesium and B12
concentration in stomach) • Most potent acid blocking
medication
class
Amoxicillin/Clavulanate Amoxicillin – see agent; • Diarrhea
(Augmentin) clavulanate – inhibits • Nausea/vomiting
beta-lactamase which is • Rash
produced by bacteria to
break down beta lactam
antibiotics
Atenolol (Tenormin) Blocks beta-1 receptors • Pulse monitoring
(found primarily in the • Can blunt beta-agonist activity
heart); prevents activity of (potentially exacerbate asthma,
sympathetic nervous COPD)
system leading to • Can block signs of
reduction in heart rate hypoglycemia
and BP (exception sweating)
Furosemide (Lasix) Blocks reabsorption of • Hypokalemia
sodium, chloride and • Frequent urination
water from the ascending • Can lead to
limb of the loop of Henle dehydration (rising
– increases urine output creatinine)
Metoprolol (Lopressor) Blocks beta-1 receptors • Pulse monitoring
(found primarily in the • Can blunt beta-agonist
heart); prevents activity of activity (potentially
sympathetic nervous exacerbate asthma,
system leading to COPD)
reduction in heart rate • Block signs of
and BP hypoglycemia
(exception sweating)
Sertraline (Zoloft) Inhibits reuptake of • Takes a significant
serotonin which leads to amount of time to
higher concentrations in work (usually weeks)
the synapse • GI side effects
• Serotonin syndrome
risk (Elevated
temperature, BP,
Heart rate)
Zolpidem (Ambien) Enhances GABA activity • Used for insomnia
which has sedative, only
hypnotic effects • Dizziness/sedation
• Generally avoid in
elderly
Oxycodone/APAP (Percocet) Oxycodone - Binds, • Addiction/dependence
activates mu-opioid risk
receptor, Acetaminophen • Respiratory
– suspected to inhibit depression
prostaglandin synthesis • Constipation
which reduces pain
Esomeprazole (Nexium) Inhibits H+/K+ ATPase • Short term only
pump in gastric parietal recommended for
cells (reduces hydrogen GERD
ion – stomach acid • Associated with low
concentration in stomach) magnesium and B12
• Most potent acid
blocking medication
class
Clopidogrel (Plavix) Blocks binding of ADP to • Prodrug – converted
the P2Y12 receptor; by to its active
doing this, it prevents metabolite by
platelet aggregation CYP2C19
• Bleed risk
• Often used in
combination with
aspirin following
stenting
Montelukast (Singulair) Blocks leukotriene • Used in asthma and
receptors in the lungs allergies
which reduces • Not a rescue
bronchoconstriction and medication
inflammation • Rare reports of
psychiatric adverse
events
Prednisone (Sterapred) Multiple possible • Suppression of HPA
pathways of reducing axis
inflammation and • Increases blood
suppressing the immune sugars, causes
system (inhibition of insomnia and GI upset
cytokines, chemokines, • Increases risk of
arachidonic acid etc.) osteoporosis
Escitalopram (Lexapro) Inhibits reuptake of • Takes a significant
serotonin which leads to amount of time to
higher concentrations in work (usually weeks)
the synapse • GI side effects
• Serotonin syndrome
risk (Elevated
temperature, BP,
Heart rate)
Ibuprofen (Advil) Non-selective inhibitor of • Increase GI Bleed risk;
cyclooxygenase (COX) – take with food
which ultimately reduces • Exacerbates
the production of CHF/edema
prostaglandins which are • Inhibits platelet
involved in activity
pain/inflammation
Citalopram (Celexa) Inhibits reuptake of • Takes a significant
serotonin which leads to amount of time to
higher concentrations in work (usually weeks)
the synapse • QTc prolongation risk
(higher doses, elderly
more susceptible)
• Serotonin syndrome
risk (Elevated
temperature, BP,
Heart rate)
Albuterol (ProAir) Beta-2 adrenergic • Tremor
receptor agonist – relaxes • Tachycardia
bronchial smooth muscle • Usual drug of choice
and opens airways for acute relief of
respiratory symptoms
Fluoxetine (Prozac) Inhibits reuptake of • Takes a significant
serotonin which leads to amount of time to
higher concentrations in work (usually weeks)
the synapse • GI side effects
• Serotonin syndrome
risk (Elevated
temperature, BP,
Heart rate)
Gabapentin (Neurontin) Not well understood – • Dizziness
possible action on voltage • Sedation
sensitive calcium channels • Can accumulate in
renal disease
Warfarin (Coumadin) Inhibits vitamin K • Bleed risk
dependent production of • Routine INR
clotting factors 2, 7, 9, monitoring require
and 10 (most often goal is 2-3
with a few exceptions)
• Tons of drug
interactions
(metronidazole,
amiodarone, Bactrim
etc.)
Tramadol (Ultram) Binds, activates mu-opioid • Increases seizure risk
receptors leading to • Sedation
analgesic effects • Risk of dependence
and addiction
Clonazepam (Klonopin) Enhances GABA activity • Used for acute
which has sedative, management of
hypnotic, anticonvulsant, anxiety
and muscle relaxant • Dizziness/sedation
properties • Generally avoid in
elderly
Lorazepam (Ativan) Enhances GABA activity • Used for acute
which has sedative, management of
hypnotic, anticonvulsant, anxiety
and muscle relaxant • Dizziness/sedation
properties • Generally avoid in
elderly
Cephalexin (Keflex) Inhibits penicillin binding • Diarrhea
protein which prevents • Nausea/Vomiting
bacterial cell wall • Primarily gram +
synthesis bacteria coverage
Cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril) Not well understood – • Sedating
skeletal muscle relaxant • Anticholinergic
possibly gamma and alpha potential (i.e. dry
motor system effects mouth, confusion,
etc.)
• Not well tolerated in
the elderly
Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim Sulfamethoxazole – • Significant interaction
(Bactrim, Septra) interferes with bacterial with warfarin
folate synthesis; • Beware of patients
trimethoprim blocks with a sulfa allergy –
production of should not take this
tetrahydrofolic acid in medication
bacteria by binding • Take with full glass of
dihydrofolate reductase water
Ciprofloxacin (Cipro) Inhibits DNA gyrase in • Risk of spontaneous
bacteria which prevents tendonitis or tendon
DNA separation and cell rupture
division • Dose adjustments
with poor kidney
function
• Binding interaction
with iron and calcium
can reduce absorption
Fluticasone (Flonase) Stimulates glucocorticoid • May work a little
receptors which leads to better if taken
reduced inflammation routinely
• Nose bleeding,
irritation
• Used in allergic rhinitis
Triamterene/HCTZ (Dyazide) Triamterene – blocks • Elevated K+ possible
epithelial sodium with triamterene
channels, causing a • Lowers blood pressure
diuretic type effect in the • In combo with HCTZ
kidney can help even out
potassium levels as
HCTZ lowers levels
Pravastatin (Pravachol) Inhibits HMG-CoA • Myopathy
reductase – this enzyme is • Reduces risk of heart
the rate limiting step in attack/stroke
cholesterol formation • If patients can’t
tolerate simvastatin or
atorvastatin, this one
is often tried
Rosuvastatin (Crestor) Inhibits HMG-CoA • Myopathy
reductase – this enzyme is • Reduces risk of heart
the rate limiting step in attack/stroke
cholesterol formation • Higher intensity statin
Fluticasone + salmeterol Corticosteroid combined • Rinse mouth following
(Advair) with long acting beta use of steroid
agonist – steroid works on (Reduces thrush risk)
inflammation and • Controller medication,
salmeterol opens up the not for rescue
airway • Beta agonist effects –
increased heart rate,
tremor
Trazodone (Desyrel) Possible serotonin type • Dry mouth
activity, not well • Most often used for
understood; histamine sleep, rarely used for
blockade may be straight depression
responsible for sedative • Possibly a little safer in
effect elderly than Z-drugs
like Zolpidem
Alendronate (Fosamax) Inhibits resorption of • Extremely long half life
bone by osteoclasts • Administration
without other drugs,
food – with a plain
glass of water, patient
to remain upright
after
• Usually reassessed
after 5 years of use
Fexofenadine (Allegra) Selective H1 receptor • Sedation
antagonist which leads to • Dry mouth
relief of allergy symptoms • Once daily dosing
Lovastatin (Mevacor) Inhibits HMG-CoA • Myopathy
reductase – this enzyme is • Reduces risk of heart
the rate limiting step in attack/stroke
cholesterol formation • Risk of rhabdomyolysis
(Associated with all
statins)
Carvedilol (Coreg) Blocks beta-1 receptors • Pulse monitoring
(found primarily in the • Can blunt beta-agonist
heart); prevents activity of activity (potentially
sympathetic nervous exacerbate asthma,
system leading to COPD)
reduction in heart rate • Can block signs of
and BP; has some alpha hypoglycemia
blockade as well (exception sweating)
Paroxetine (Paxil) Inhibits reuptake of • Takes a significant
serotonin which leads to amount of time to
higher concentrations in work (usually weeks)
the synapse • GI side effects
• Serotonin syndrome
risk (Elevated
temperature, BP,
Heart rate)
Meloxicam (Mobic) Non-selective inhibitor of • Increase GI Bleed risk;
cyclooxygenase (COX) – take with food
which ultimately reduces • Exacerbates
the production of CHF/edema
prostaglandins which are • Inhibits platelet
involved in activity
pain/inflammation
Diazepam (Valium) Enhances GABA activity • Used for acute
which has sedative, management of
hypnotic, anticonvulsant, anxiety/seizure
and muscle relaxant • Dizziness/sedation
properties • Generally avoid in
elderly
Valsartan (Diovan) Angiotensin receptor • Hyperkalemia
blocker – prevents the • Alternate to ACE
activity of angiotensin Inhibitor
which is a vasoconstrictor • Less incidence of
cough compared to
ACE inhibitors
Duloxetine (Cymbalta) Serotonin and • More beneficial for
Norepinephrine reuptake pain than SSRI’s
inhibitor which increases (Neuropathy)
concentrations of both in • Possible increase in
the brain synapses hypertension at high
doses
• GI side effects,
serotonin syndrome
risk
Venlafaxine (Effexor) Serotonin and • More beneficial for
Norepinephrine reuptake pain than SSRI’s
inhibitor which increases (Neuropathy)
concentrations of both in • Possible increase in
the brain synapses hypertension at high
doses
• GI side effects,
serotonin syndrome
risk
Ranitidine (Zantac) Histamine 2 Receptor • Slightly less potent
Antagonist which reduces than the PPI’s
gastric acid secretion • Can accumulate in
leading to relief of kidney disease
heartburn and GI • Tend to work a little
symptoms quicker than the PPI’s
Fluconazole (Diflucan) Inhibits fungal • 3A4 drug interactions
cytochrome P450 enzyme (amiodarone,
14alpha-demthylase phenytoin, warfarin,
etc.)
• GI upset
• Liver concerns
Naproxen (Aleve) Non-selective inhibitor of • Increase GI Bleed risk;
cyclooxygenase (COX) – take with food
which ultimately reduces • Exacerbates
the production of CHF/edema
prostaglandins which are • Inhibits platelet
involved in activity
pain/inflammation
Doxycycline (Vibramycin) Inhibits bacterial protein • Increases sensitivity to
synthesis by binding to sunburn
the 30s ribosomal subunit • Binding interactions
with calcium and iron
• Avoid in pregnancy
Potassium (Klor-Con) Potassium replacement • Often used for
patients on diuretics
that deplete
potassium
• GI upset
• Often patient do have
trouble swallowing
larger doses (big pills)
– some forms can be
dissolved in water
Amitriptyline (Elavil) Inhibits norepinephrine • Highly anticholinergic
and serotonin reuptake, (sedation, confusion,
leading to increased dry eye, etc.)
concentrations in the • Can be used for pain
synapse syndromes (migraines,
fibromyalgia, etc.)
• Higher risk of cardiac
concerns in overdose
compared to SSRI’s so
less often used for
depression
Lansoprazole (Prevacid) Inhibits H+/K+ ATPase • Short term only
pump in gastric parietal recommended for
cells (reduces hydrogen GERD
ion – stomach acid • Associated with low
concentration in stomach) magnesium and B12
• Most potent acid
blocking medication
class
Pioglitazone (Actos) Decreases insulin • Weight gain
resistance in the • Edema
periphery; leading to • Generally avoid in CHF
greater uptake of glucose patients
into muscle tissue and
lower blood sugar
Methylprednisolone (Medrol) Multiple possible • Suppression of HPA
pathways of reducing axis
inflammation and • Increases blood
suppressing the immune sugars, causes
system (inhibition of insomnia and GI upset
cytokines, chemokines, • Increases risk of
arachidonic acid etc.) osteoporosis
Allopurinol (Zyloprim) Inhibition of xanthine • Not meant for acute
oxidase which results in gout flares
less production of uric • Rash
acid and lower levels • Can accumulate in
kidney disease
Codeine + APAP (Tylenol #3) codeine - Binds, activates • Addiction/dependence
mu-opioid receptor, risk
Acetaminophen – • Respiratory
suspected to inhibit depression
prostaglandin synthesis • Constipation
which reduces pain
Enalapril (Vasotec) Inhibits angiotensin • Cough
converting enzyme which • Hyperkalemia
ultimately leads to • Used to help protect
reduction in angiotensin 2 the kidneys in
(a potent vasoconstrictor) diabetes
Carisoprodol (Soma) Not well understood, • Sedation
potential effects at GABA • Controlled substance
receptors • Dizziness
Tamsulosin (Flomax) Blocks alpha-1a receptors • Dizziness, low blood
which causes smooth pressure
muscle relaxation of the • Work fairly quickly
bladder neck and prostate compared to 5 alpha
reductase inhibitors
• Rare risk of floppy iris
syndrome in patients
having eye surgery
Ezetimibe (Zetia) Inhibits intestinal • GI upset
absorption of cholesterol • Not great evidence
leading to lower levels that indicates it
reduces the risk of
heart attack and
stroke
• 2nd or third line agent
for lowering
cholesterol (statins are
drug of choice)
Quetiapine (Seroquel) Blockade of dopamine 2 • Sedation and
receptors is primary orthostasis risk
mechanism • Extrapyramidal
symptoms
• Metabolic syndrome
and QTc prolongation
risk
Levofloxacin (Levaquin) Inhibits DNA gyrase in • Risk of spontaneous
bacteria which prevents tendonitis or tendon
DNA separation and cell rupture
division • Dose adjustments
with poor kidney
function
• Binding interaction
with iron and calcium
can reduce absorption
Fenofibrate (Tricor) Activates lipoprotein • Target for elevated
lipase and reduces triglycerides, SE =
synthesis of apoprotein C- myopathy
3; both of these • Statins reserved for
mechanisms work to cardiovascular risk
lower cholesterol reduction and LDL
lowering
• Elevated triglycerides
increase risk of
pancreatitis
Clonidine (Catapres) Stimulates centrally acting • Dry mouth
alpha-2 receptors causing • Dizziness, CNS changes
reduced sympathetic • Generally avoided in
outflow which lowers BP the elderly
and pulse
Promethazine (Phenergan) Possible anticholinergic • Used for motion
(blocks acetylcholine) and sickness, nausea and
antihistamine effects, also vomiting
may mildly block • Sedating
dopamine receptors • Anticholinergic side
effects
Ethinyl estradiol + Drosperinone Oral contraceptive – • DVT/PE
(Yaz) estrogen prevents • Hypertension
ovulation and reduces risk • Headache/GI
of pregnancy symptoms
Sildenafil (Viagra) Inhibition of • Low blood pressure
phosphodiesterace-5 • Rare vision adverse
(PDE-5) causes smooth effect
muscle relaxation and • Avoid using with
increased blood flow to nitrates
the penis
Celecoxib (Celebrex) Selective inhibition of • GI side effects
COX-2 leads to reduced generally less than
formation of arachidonic traditional NSAIDs
acid and prostaglandins • Edema risk
• Kidney risk still the
same as traditional
NSAIDs
Loratadine (Claritin) Selective H1 receptor • Sedation
antagonist which leads to • Dry mouth
relief of allergy symptoms • Once daily dosing
Oxycodone (OxyContin) Oxycodone - Binds, • Addiction/dependence
activates mu-opioid risk
receptor • Respiratory
depression
• Constipation
Glargine (Lantus, Basaglar) Long acting insulin analog • Weight gain
• Hypoglycemia risk
• Dose once daily and
targets fasting blood
sugars
Mometasone (Nasonex) Stimulates glucocorticoid • May work a little
receptors which leads to better if taken
reduced inflammation routinely
• Nose bleeding,
irritation
• Used in allergic rhinitis
Pregabalin (Lyrica) Not well known; • Sedation
suspected that it might • Dizziness
bind the alpha2-delta • Weight gain
subunits leading to a
reduction in neuronal
excitability
Amaryl (Glimepiride) Stimulates pancreatic • Weight gain
beta cells to release • Hypoglycemia
insulin • Inexpensive
Temazepam (Restoril) Enhances GABA activity • Shorter half-life than
which has sedative, others, so may see this
hypnotic, anticonvulsant, one used for sleep
and muscle relaxant • Dizziness/sedation
properties • Generally avoid in
elderly
Conjugated Estrogen (Premarin) Replacement estrogen in • DVT/PE
postmenopausal women • Hypertension
who experience • Increased risk of
symptoms like hot flashes, breast cancer
vaginal dryness, etc.
Folic acid (Folvite) Supplement of folic acid • Tolerability is usually
fine
• Given with
methotrexate for
RA/psoriasis etc.
• Deficiency can lead to
anemia
Spironolactone (Aldactone) Aldosterone antagonist • Hyperkalemia
that blocks the effects of • Gynecomastia (Man-
aldosterone, leading to boobs)
lower blood pressure and • Monitor kidney
a diuretic effect function
Digoxin (Lanoxin) Inhibits sodium, • Used in atrial
potassium ATPase leading fibrillation or CHF
to an increase in the force • Toxicity signs include
of contraction of the heart GI, CNS changes, visual
changes, and weight
loss
• Can accumulate in
kidney disease and
cause more toxicity
with low potassium
levels
Isosorbide Mononitrate (Imdur) Increase in nitric oxide • Headache
leads to venous and • Dizziness
arterial dilation • Can become tolerate
to effects, usually
recommended to have
a nitrate free period
during the day
Cefdinir (Omnicef) Inhibits penicillin binding • Diarrhea
protein which prevents • Nausea/Vomiting
bacterial cell wall • broader spectrum
synthesis coverage than
cephalexin
Ramipril (Altace) Inhibits angiotensin • Cough
converting enzyme which • Hyperkalemia
ultimately leads to • Used to help protect
reduction in angiotensin 2 the kidneys in
(a potent vasoconstrictor) diabetes
Triamcinolone (Nasacort) Stimulates glucocorticoid • May work a little
receptors which leads to better if taken
reduced inflammation routinely
• Nose bleeding,
irritation
• Used in allergic rhinitis
Losartan (Cozaar) Angiotensin receptor • Hyperkalemia
blocker – prevents the • Alternate to ACE
activity of angiotensin Inhibitor
which is a vasoconstrictor • Less incidence of
cough compared to
ACE inhibitors
Methylphenidate (Concerta) Prevents catecholamine • Weight loss
reuptake in CNS synapses • Insomnia
leading to increased • Anxiety, tachycardia,
dopamine and and increased BP
norepinephrine
Glyburide (Diabeta) Stimulates pancreatic • Weight gain
beta cells to release • Hypoglycemia
insulin • Inexpensive
Valacyclovir (Valtrex) Inhibits DNA Polymerase • Treatment of herpes
which prevent viral and varicella viruses
replication • GI upset
• Prodrug; converted to
acyclovir
Oseltamivir (Tamiflu) Inhibits influenza virus • GI side effects
neuraminidase, which • Dose adjusted based
likely alters replication or on kidney function
release of budding viruses • Used in treatment and
prophylaxis of
influenza
Tiotropium (Spiriva) Long acting • One of the drugs of
antimuscarinic choice in COPD
(anticholinergic) that maintenance therapy
binds to M3 receptors • Not intended for acute
which relaxes smooth relief (rescue) of
muscle leading to symptoms
bronchodilation • Dry mouth
Benazepril (Lotensin) Inhibits angiotensin • Cough
converting enzyme which • Hyperkalemia
ultimately leads to • Used to help protect
reduction in angiotensin 2 the kidneys in
(a potent vasoconstrictor) diabetes
Lamotrigine (Lamictal) Inhibits voltage sensitive • Can be used for
sodium channels which seizures or mood
stabilizes neuronal disorders like bipolar
membranes • Drug interaction with
valproic acid
• Rash (possibly severe
Stephen Johnson’s
Syndrome)
Olmesartan (Benicar) Angiotensin receptor • Hyperkalemia
blocker – prevents the • Alternate to ACE
activity of angiotensin Inhibitor
which is a vasoconstrictor • Less incidence of
cough compared to
ACE inhibitors
Donepezil (Aricept) Acetylcholinesterase • Weight loss
Inhibitor which helps • Diarrhea
increase acetylcholine in • Does not reverse
the brain (Remember dementia
than anticholinergics can
cause confusion)
Risperidone (Risperdal) Blockade of dopamine 2 • Sedation and
receptors is primary orthostasis risk
mechanism • Extrapyramidal
symptoms
• Metabolic syndrome
and QTc prolongation
risk
Glipizide (Glucotrol) Stimulates pancreatic • Weight gain
beta cells to release • Hypoglycemia
insulin • Inexpensive
Amphetamine salts (Adderall) Prevents catecholamine • Weight loss
reuptake in CNS synapses • Insomnia
leading to increased • Anxiety, tachycardia,
dopamine and and increased BP
norepinephrine
Aripiprazole (Abilify) Blockade of dopamine 2 • Indicated for
receptors is primary augmentation of
mechanism
depression as well as
schizophrenia
• Extrapyramidal
symptoms
• Metabolic syndrome
and QTc prolongation
risk
Verapamil (Verelan) Non-dihydropyridine; • Used in Afib, HTN, or
Blocks the entry of chronic headaches
calcium into smooth • Monitor pulse
muscle and heart, causing • Edema
vasodilation and slowing
of heart rate
Clindamycin (Cleocin) Bind 50s subunit of • GI side effects
bacterial ribosome which • Higher risk of colitis
prevents protein synthesis and C.diff
• Good for anaerobic
bacteria
Metronidazole (Flagyl) Disrupts bacterial DNA • Interaction with
synthesis warfarin
• Avoid alcohol when
taking medication
• Used for Anaerobic
bacteria
Ethinyl Estradiol + Norgestimate Oral contraceptive – • DVT/PE
(Ortho Tri-Cyclen) estrogen prevents • Hypertension
ovulation and reduces risk • GI/Headache
of pregnancy
Tadalafil (Cialis) Inhibition of • Low blood pressure
phosphodiesterace-5 • Rare vision adverse
(PDE-5) causes smooth effect
muscle relaxation and • Avoid using with
increased blood flow to nitrates
the penis
Phentermine (Adipex) Sympathetic amine – • Used for weight loss
increases adrenaline, • Monitor for cardiac
dopamine, and possibly concerns; increase in
serotonin BP and pulse
• Can cause insomnia or
anxiety
Hydroxyzine (Vistaril) H1 receptor antagonist • Anticholinergic effects
which leads to relief of • Used for anxiety
allergy symptoms and • Considered a 1st
causes sedation generation
antihistamine
(sedating)
Diclofenac (Cataflam) Non-selective inhibitor of • Increase GI Bleed risk;
cyclooxygenase (COX) – take with food
which ultimately reduces • Exacerbates
the production of CHF/edema
prostaglandins which are • Inhibits platelet
involved in activity
pain/inflammation
Metoclopramide (Reglan) Inhibition of D2 receptors • Risk of movement
in chemoreceptor trigger disorders like EPS
zone • Often used in
gastroparesis
• Can exacerbate
Parkinson’s disorder
Gemfibrozil (Lopid) Not well known - targets • Risk of myopathy
triglycerides and can • Interaction with
possibly help raise HDL statins (increases risk
of myopathy and
rhabdomyolysis)
• Indicated for
significantly high
triglycerides
Diltiazem (Cardizem) Non-dihydropyridine; • Used in Afib, HTN, or
Blocks the entry of chronic headaches
calcium into smooth • Monitor pulse
muscle and heart, causing • Edema
vasodilation and slowing
of heart rate
Divalproex (Depakote) Not well known, possibly • Sedation
increasing GABA in the • Weight gain
brain • Ataxia, CNS changes
Nitrofurantoin (Macrobid) Altered by bacterial • GI upset
flavoproteins to reactive • Nitrofurantoin lung
intermediates which (rare)
breakdown bacterial • Avoid use if suspected
ribosomal proteins kidney/systemic
infection, good for UTI
only
Mirtazapine (Remeron) Multiple potential • Weight gain
mechanisms include • Sedating
blocking alpha-2 • Classified as
receptors, as well as antidepressant but
serotonin subtypes and often used for
histamine blockade sleep/sedative
properties
Latanoprost (Xalatan) Prostaglandin agonist • Used for glaucoma
which increases aqueous • Will help eye lashes
humor outflow and grow
reduces intraocular • Can alter color of the
pressure eye
Sitagliptin (Januvia) DPP-4 inhibitor – DPP-4 • Rare pancreatitis risk
breaks down incretins like • GI side effects
GLP-1 which are • Low risk of
hormones that can reduce hypoglycemia when
blood sugars by used alone
promoting fullness
Acyclovir (Zovirax) Inhibits DNA Polymerase • Treatment of herpes
which prevent viral and varicella viruses
replication • GI upset
• Can accumulate in
kidney disease
Doxazosin (Cardura) Blocks alpha receptors • Orthostasis risk
which causes smooth • Not selective for
muscle relaxation of the bladder so can be
bladder neck and prostate used for HTN and BPH
and vasodilation • Usually dosed at night
Eszopiclone (Lunesta) Enhances GABA activity • Used for insomnia
which has sedative, only
hypnotic effects • Dizziness/sedation
• Generally avoid in
elderly
Niacin (Niaspan) Inhibition of triglyceride • Can cause flushing
synthesis by stimulating • Increases uric acid
intracellular Apo-B • Option in reducing
degradation and reduces triglycerides
release of VLDL and LDL
Propranolol (Inderal) Non-selective beta • Pulse monitoring
blocker; reduced heart • Can blunt beta-agonist
rate, blood pressure; may activity (potentially
have higher risk for exacerbate asthma,
adverse effects due to COPD)
non-selectivity (also lot of • Can block signs of
unique uses – tremor, hypoglycemia
esophageal varices, (exception sweating)
migraines)
Buprenorphine/naloxone Partial opioid agonist that • Possible opioid like
(Suboxone) has a peak effect on effects to a certain
stimulating the mu extent
receptors combine with a • Prevents full opioid
full opioid antagonist agonists from binding
(naloxone), used to treat in management of
opioid use disorder addiction
• Need a special
prescribing certificate
to prescribe for opioid
use disorder
Bupropion (Wellbutrin) Inhibits reuptake of • Used in smoking
norepinephrine, cessation
dopamine and possibly • Avoid in patients with
serotonin to help treat seizures
depression • Can contribute to
insomnia
Guaifenesin (Robitussin) Increases volume and • Well tolerated
reduces thickness of • Questionable
mucous (expectorant) effectiveness
• Take with lots of water
Topiramate (Topamax) Blocks voltage dependent • Cognitive slowing,
sodium and calcium confusion
channels, may have some • Sedation
activity on GABA as well • Antiseizure
medication, but often
used for migraines
Buspirone (Buspar) Serotonin partial agonist • Takes a while to work
and 5HT1A receptors; • Used in anxiety
possible activity at • Pretty well tolerated
dopamine receptors as compared to
well benzodiazepines
especially in elderly
Meclizine (Antivert) Antihistamine effects at • Sedation
H1 receptors • Anticholinergic side
effects
• Primarily used for
nausea and motion
sickness
Tolterodine (Detrol) Antagonist at muscarinic • Dry mouth
(M2 and M3) receptors • Confusion
which helps in the • Can exacerbate
management of urinary retention
overactive bladder
Lisdexamfetamine (Vyvanse) Prevents catecholamine • Weight loss
reuptake in CNS synapses • Insomnia
leading to increased • Anxiety, tachycardia,
dopamine and and increased BP
norepinephrine
Quinapril (Accupril) Inhibits angiotensin • Cough
converting enzyme which • Hyperkalemia
ultimately leads to • Used to help protect
reduction in angiotensin 2 the kidneys in
(a potent vasoconstrictor) diabetes
Mupirocin (Bactroban) Inhibits bacterial protein • Topical antibiotic
and RNA synthesis • Skin irritation
• MRSA coverage (but
only as a topical
agent)
Methotrexate (Rheumatrex) Inhibition of dihydrofolate • Low doses used for RA
reductase (anticancer) • Need to supplement
also is classified as a with folic acid
disease modifying anti- • Dose once weekly and
rheumatic drug (DMARD) monitor liver function
Polyethylene Glycol (Miralax) Osmotic laxative that • Diarrhea
draws moisture into the • Mix with 8oz. of fluid
bowel to help relieve • Rare possibility for
constipation electrolyte
abnormalities
Fentanyl (Duragesic) Binds, activates mu-opioid • Patch formulation
receptor • NOT for acute pain
• Very slow onset/offset
Benzonatate (Tessalon Pearls) Anesthetic type effects • Sedation
which can numb the • GI upset
throat and suppress • Make sure you aren’t
cough masking ACE inhibitor
cough
Irbesartan (Avapro) Angiotensin receptor • Hyperkalemia
blocker – prevents the • Alternate to ACE
activity of angiotensin Inhibitor
which is a vasoconstrictor
• Less incidence of
cough compared to
ACE inhibitors
Albuterol + Ipratropium Combination beta-agonist • Dry mouth
(Duonebs, Combivent) and short acting • Tachycardia
anticholinergic • Tremor
Ibandronate (Boniva) Inhibits resorption of • Extremely long half life
bone by osteoclasts • Administration
without other drugs,
food – with a plain
glass of water, patient
to remain upright
after
• Usually reassessed
after 5 years of use
Methadone (Methadose) Binds, activates mu-opioid • Addiction/dependence
receptor risk
• Respiratory
depression
• Constipation
Clotrimazole + Betamethasone Combination antifungal • Fungal infections can
(Lotrisone) and topical corticosteroid take a while to treat
• Skin thinning with
prolonged use
• Skin irritation
Sumatriptan (Imitrex) Serotonin agonist at • Caution in patients at
5HT1D receptors – high risk of
thought to cause cardiovascular
vasoconstriction, but concerns
maybe a little more • Treatment of acute
unknown now? migraine
• CNS adverse effects
like confusion
Nifedipine (Procardia) Blocks the entry of • Edema
calcium into smooth • No action on the heart
muscle, causing (compared to
vasodilation diltiazem, verapamil)
• Used to help prevent
angina and manage
blood pressure
Famotidine (Pepcid) Histamine 2 Receptor • Slightly less potent
Antagonist which reduces than the PPI’s
gastric acid secretion
leading to relief of • Can accumulate in
heartburn and GI kidney disease
symptoms • Tend to work a little
quicker than the PPI’s
Finasteride (Proscar) Inhibits 5 alpha reductase • Sexual dysfunction
which prevent side effect
dihydrotestosterone • Can be used for hair
formation which growth in baldness
contributes to • Takes months to
enlargement of the shrink prostate
prostate
Ferrous Sulfate (Feosol) Iron replacement • Deficiency can cause
anemia and RLS
• GI upset
• Constipation
Terazosin (Hytrin) Blocks alpha receptors • Orthostasis risk
which causes smooth • Not selective for
muscle relaxation of the bladder so can be
bladder neck and prostate used for HTN and BPH
and vasodilation • Usually dosed at night
Fish Oil (Lovaza) Not well understood, but • Burping/fish taste
can help reduce • GI upset
triglycerides and increase • Rare potential to
HDL interfere with platelet
aggregation (usually
help around surgery)
Tizanidine (Zanaflex) Central alpha-2 receptor • Sedation
agonist which inhibits • Dizziness
motor neurons and • Maybe a little better
reduces spasticity tolerated in the
elderly than
cyclobenzaprine
Risedronate (Actonel) Inhibits resorption of • Extremely long half life
bone by osteoclasts • Administration
without other drugs,
food – with a plain
glass of water, patient
to remain upright
after
• Usually reassessed
after 5 years of use
Memantine (Namenda) Inhibition of N-methyl-d- • CNS side effects like
aspartate (NMDA) sedation, confusion
receptors • Dose adjusted in
kidney impairment
• Used in delaying
progression of
dementia
Insulin Aspart (Novolog) Rapid acting insulin • Hypoglycemia
analog • Weight gain
• Targets post-prandial
elevations in blood
sugars
Aspirin Non-selective inhibitor of • Risk of Reye’s
cyclooxygenase (COX) – syndrome in pediatrics
which ultimately reduces • Typically used for
the production of cardiovascular
prostaglandins which are protection as low dose
involved in 81-325 mg once daily
pain/inflammation • GI bleed risk
Clobetasol (Temovate) Topical corticosteroid that • Skin thinning
can reduce inflammation, • Possible systemic
redness and itching effects with large
quantities over longer
periods of times
• Used for psoriasis and
dermatitis
Bisoprolol (Zebeta) Blocks beta-1 receptors • Pulse monitoring
(found primarily in the • Can blunt beta-agonist
heart); prevents activity of activity (potentially
sympathetic nervous exacerbate asthma,
system leading to COPD)
reduction in heart rate • Can block signs of
and BP hypoglycemia
(exception sweating)
Nitroglycerin (NitroStat) Relaxes vascular smooth • Dizziness
muscle and dilates • Headache
arteries and veins • Use for acute chest
pain (angina);
administer 3 tablets
over 15 minutes, call
911 if still having chest
pain
Varenicline (Chantix) Partial nicotine agonist • Vivid dreams and
which prevents nicotine nightmares
from binding and reduces • GI upset
reward sensation from • Insomnia
smoking
Raloxifene (Evista) Selective estrogen • DVT/PE risk
receptor modifier; blocks • Hot flashes
activity at some estrogen • Vaginal dryness
receptors and helps at
others in management of
reducing breast cancer
risk and can help in
osteoporosis
Olanzapine (Zyprexa) Blockade of dopamine 2 • Sedation and
receptors is primary orthostasis risk
mechanism • Extrapyramidal
symptoms
• Metabolic syndrome
and QTc prolongation
risk
Ondansetron (Zofran) Inhibits 5-HT3 (serotonin) • Rare QTc prolongation
receptors in the risk
chemoreceptor trigger • Often used in patient
zone to reduce nausea receiving emetogenic
chemotherapy
• CNS side effects
Ropinirole (Requip) Dopamine agonist that • Edema
can be used for • Obsessive behaviors
Parkinson’s where there is like excessive
a shortage of dopamine; gambling, eating
more commonly used in • GI side effects
RLS
Dicyclomine (Bentyl) Anticholinergic that can • Constipation
be helpful in managing • Dry eyes/dry mouth
diarrhea and relaxing • Confusion
smooth muscle in patients
with GI spasms and pain
Insulin Lispro (Humalog) Rapid acting insulin • Hypoglycemia
analog • Weight gain
• Targets post-prandial
blood sugars
Nabumetone (Relafen) Non-selective inhibitor of • Increase GI Bleed risk;
cyclooxygenase (COX) – take with food
which ultimately reduces • Exacerbates
the production of CHF/edema
prostaglandins which are • Inhibits platelet
involved in activity
pain/inflammation
Clarithromycin (Biaxin) Binds 50s ribosomal • Numerous CYP3A4
subunit and prevents drug interactions
protein synthesis (inhibitor)
• GI adverse effects
• Rare risk for QTc
prolongation
Lidocaine patch (Lidoderm) Binds to neuronal • Local pain relieving
membrane receptors and effects
inhibits sodium ion • 12 hours on/12 off
influxes and prevents cell • Systemic side effects
action potential usually minimal
Dutasteride (Avodart) Inhibits 5 alpha reductase • Sexual dysfunction
which prevent side effect
dihydrotestosterone • Fatigue
formation which • Takes months to
contributes to shrink prostate
enlargement of the
prostate
Phenytoin (Dilantin) Not well understood, • Ataxia, CNS changes
possibly blocking voltage with toxicity
gated sodium channels • Highly protein bound
drug, low albumin can
increase toxicity risk
• Enzyme inducing type
effect on CYP3A4 and
others
Colchicine (Colcrys) Binds to tubulin and • Diarrhea
prevents microtubule • Rare indication for
polymerization – reduces prophylaxis and
a gout flare and prevents treatment
it as well • Dose adjusted with
poor kidney function
Moxifloxacin (Avelox) Inhibits DNA gyrase in • Risk of spontaneous
bacteria which prevents tendonitis or tendon
DNA separation and cell rupture
division • Considered a
respiratory
fluoroquinolone only
• Binding interaction
with iron and calcium
can reduce absorption
Baclofen (Lioresal) Not well understood; • Used in management
skeletal muscle relaxant of spasms
• Sedation, confusion
• Can be used on an as
needed basis
Hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil) Not well understood, • Eye exams required
originally was used as • LFT/CBC monitoring
antimalarial drug, in US, • Takes a while to begin
primarily used as DMARD working (not a quick
in RA and Lupus acting medication in
RA or Lupus)
Enoxaparin (Lovenox) Increases activity of • Injection
antithrombin that • Bleed risk
ultimately inactivates • Risk of heparin
factor 10a; some activity induced
against clotting factor 2a thrombocytopenia
(thrombin), but less than
heparin
Atomoxetine (Strattera) Possible inhibition of • Insomnia, anxiety,
norepinephrine weight loss
transporter – used in • Not a controlled
ADHD substance (compared
to methylphenidate
and amphetamine
derivatives)
• Can worsen agitation,
irritability and possibly
cause suicidal
thoughts
Diphenhydramine (Benadryl) H1 receptor antagonist • Anticholinergic effects
which leads to relief of • Used for itching, mild
allergy symptoms and to moderate allergic
causes sedation reactions
• Over the counter
availability
Ketoconazole (Nizoral) Inhibits fungal • 3A4 drug interactions
cytochrome P450 enzyme (amiodarone,
14alpha-demthylase phenytoin, warfarin,
etc.)
• Primarily used as
topical agent (if so,
side effects are pretty
minimal)
• Liver concerns
Nortriptyline (Pamelor) Inhibits norepinephrine • Highly anticholinergic
and serotonin reuptake, (sedation, confusion,
leading to increased dry eye, etc.)
concentrations in the • Can be used for pain
synapse syndromes (migraines,
fibromyalgia, etc.)
• Higher risk of cardiac
concerns in overdose
compared to SSRI’s so
less often used for
depression
Benztropine (Cogentin) Anticholinergic that is • Anticholinergic side
centrally acting and can effects like dry eyes,
inhibit dopamine uptake dry mouth, confusion,
in the synapse – used to sedation
prevent EPS from • If patients are
antipsychotics and benefitting from
possible benefit in antipsychotics but
Parkinson’s experiencing EPS, this
drug may be used
• Not well tolerated in
elderly
Minocycline (Minocin) Inhibits bacterial protein • Increases sensitivity to
synthesis by binding to sunburn
the 30s ribosomal subunit • Binding interactions
with calcium and iron
• Most often used for
skin disorders (i.e.
acne)
Pantoprazole (Protonix) Inhibits H+/K+ ATPase • Short term only
pump in gastric parietal recommended for
cells (reduces hydrogen GERD
ion – stomach acid • Associated with low
concentration in stomach) magnesium and B12
• Most potent acid
blocking medication
class
Cefuroxime (Ceftin) Inhibits penicillin binding • Diarrhea
protein which prevents • Nausea/Vomiting
bacterial cell wall • broader spectrum
synthesis coverage than
cephalexin
Oxybutynin (Ditropan) Antagonist at muscarinic • Dry mouth
receptors which helps in • Confusion
the management of • Can exacerbate
overactive bladder urinary retention
Levetiracetam (Keppra) Not well known; possible • Sedation
anti-seizure activity due to • Confusion
inhibition of presynaptic • Can accumulate in
calcium channels kidney disease
Hydralazine (Apresoline) Not well understood, • Dosed multiple times
direct vasodilator, reduces per day
blood pressure • Can exacerbate, cause
Lupus
• Low blood pressure,
dizziness risk
Liraglutide (Victoza) Acts like human incretin • Weight loss effect as
(GLP-1 agonist) which can well as lowering blood
aid in promoting fullness, sugars
decrease appetite and • Injection, GI side
possibly stimulate insulin effects
release • Avoid in patients
who’ve had thyroid
cancer
Prasugrel (Effient) Blocks binding of ADP to • Bleed risk
the P2Y12 receptor; by • Often used in
doing this, it prevents combination with
platelet aggregation aspirin following
stenting
• Costlier than
clopidogrel
Mirabegron (Myrbetriq) Acts as an agonist at Beta- • Increase in blood
3 type receptors which pressure
causes detrusor smooth • Increase heart rate
muscle relaxation and can • Unique mechanism
help with overactive from anticholinergic
bladder medication used for
OAB
Canagliflozin (Invokana) Inhibits SGLT-2 which • Risk of urinary tract
helps keep glucose in the infections
urine – so ultimately • Mild diuretic effect
reduces blood sugar • Monitor kidney
function
Apixaban (Eliquis) Inhibits clotting factor 10a • Dose adjustments based on
to prevent blood clots and age, weight, and kidney
stroke function
• Alternative to warfarin
without routine INR
requirement
• Bleed risk
Tradjenta (Linagliptin) DPP-4 inhibitor – DPP-4 • Rare pancreatitis risk
breaks down incretins like • GI side effects
GLP-1 which are • Low risk of hypoglycemia
hormones that can reduce when used alone
blood sugars by
promoting fullness
Dulaglutide (Trulicity) Acts like human incretin • Weight loss effect as well as
(GLP-1 agonist) which can lowering blood sugars
aid in promoting fullness, • Injection (once
decrease appetite and weekly), GI side effects
possibly stimulate insulin • Avoid in patients
release who’ve had thyroid
cancer
Morphine (MS Contin) Binds, activates mu-opioid • Addiction/dependence risk
receptor • Respiratory
depression
• Constipation
Empagliflozin (Jardiance) Inhibits SGLT-2 which • Risk of urinary tract
helps keep glucose in the infections
urine – so ultimately • Mild diuretic effect
reduces blood sugar • Monitor kidney
function
Rivaroxaban (Xarelto) Inhibits clotting factor 10a • Dose adjustments based on
to prevent blood clots and age, weight, and kidney
stroke function
• Alternative to warfarin
without routine INR
requirement
• Bleed risk
Amiodarone (Cordarone) Class 3 antiarrhythmic; • LFT monitoring
likely inhibits potassium • TSH monitoring
and sodium channels • Can cause pulmonary fibrosis
which increase the
duration of ventricular
and atrial muscle
contraction
Carbamazepine (Tegretol) Sodium channel • Potent enzyme inducer, lots
antagonist used in the of drug interactions
management of seizure, • LFT monitoring
bipolar, and trigeminal • Hyponatremia risk
neuralgia
You might also like
- Pharmacology of Cardiac Diseases MINEDocument3 pagesPharmacology of Cardiac Diseases MINEMitu Miressa تNo ratings yet
- Top 200 Drug Study Reference RLPDocument31 pagesTop 200 Drug Study Reference RLPYathrika YathrikaNo ratings yet
- Brand Generic Class Other: NAPLEX ReviewDocument72 pagesBrand Generic Class Other: NAPLEX Reviewbapimirab654No ratings yet
- Drug of Choice and First Line of TreatmentDocument2 pagesDrug of Choice and First Line of Treatmentprinz1mendezNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Drug Chart: Drug Name Receptor Therapeutic Uses Adverse EffectsDocument18 pagesPharmacology Drug Chart: Drug Name Receptor Therapeutic Uses Adverse EffectsPadmavathy Naidu Chokkapu100% (2)
- Neuro Psych - Antiepileptic Drug ChartDocument5 pagesNeuro Psych - Antiepileptic Drug ChartMonica J Ortiz Pereira100% (1)
- Drug ListsDocument10 pagesDrug ListsAmber Merritt100% (1)
- Top 200 Drug ExamDocument1 pageTop 200 Drug ExamUyen V. NguyenNo ratings yet
- Antiepileptic Drugs AED: D' DI Disadv SE AdvDocument1 pageAntiepileptic Drugs AED: D' DI Disadv SE Advrayooona88No ratings yet
- Antiplatelet and anticoagulant drug comparison chartDocument10 pagesAntiplatelet and anticoagulant drug comparison chartDrashtibahen PatelNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Classification & Indications OverviewDocument16 pagesAntibiotic Classification & Indications Overviewdaven100% (1)
- OTC Exam 2 Study GuideDocument32 pagesOTC Exam 2 Study GuideDave WinNo ratings yet
- What 2 StudyDocument2 pagesWhat 2 StudyWil Lester100% (1)
- Common infections and recommended antibioticsDocument3 pagesCommon infections and recommended antibioticsNicole BerryNo ratings yet
- Required Formulas Look ThruDocument6 pagesRequired Formulas Look Thrukaylakmills_10135868No ratings yet
- Naplex NotesDocument226 pagesNaplex NotesløzanNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy Law Exam Review GuideDocument3 pagesPharmacy Law Exam Review Guidetiffanievo05100% (1)
- Chapter 32 - Pulmonary Arterial HypertensionDocument3 pagesChapter 32 - Pulmonary Arterial HypertensionDrashtibahen PatelNo ratings yet
- Pain and Inflammation Med ChartsDocument4 pagesPain and Inflammation Med Chartssurviving nursing school100% (1)
- Infectious Diseases IDocument7 pagesInfectious Diseases ITiff VoNo ratings yet
- Top 200 Drugs To MemorizeDocument6 pagesTop 200 Drugs To MemorizeJuan Fran HernandezNo ratings yet
- Northern Ireland Management of Infection Guidelines For Primary and Community Care 2016Document48 pagesNorthern Ireland Management of Infection Guidelines For Primary and Community Care 2016dreneavalentinstefanNo ratings yet
- Licensing and Compliance Requirements for Pharmacy OperationsDocument5 pagesLicensing and Compliance Requirements for Pharmacy OperationsHitomi Shiroshita100% (1)
- Study GuideDocument6 pagesStudy GuideFidelis MusicGroupNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology ChartDocument6 pagesPharmacology ChartPaula67% (3)
- Opioids PDFDocument2 pagesOpioids PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeNo ratings yet
- Naplex 1Document7 pagesNaplex 1baniyoNo ratings yet
- Drugs Interactions PDFDocument2 pagesDrugs Interactions PDFArne BorgerNo ratings yet
- REVIEW MATH, ROMAN NUMERALS, APOTHECARY, CONCENTRATIONSDocument9 pagesREVIEW MATH, ROMAN NUMERALS, APOTHECARY, CONCENTRATIONSEnzo VasquezNo ratings yet
- Math Formulas For NAPLEX CalculationsDocument1 pageMath Formulas For NAPLEX CalculationsNasru DiinNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics Fate of Drugs ADMEDocument63 pagesPharmacokinetics Fate of Drugs ADMERabie YahfoufiNo ratings yet
- Total Pharmacy Notes TPN For EEDocument1,601 pagesTotal Pharmacy Notes TPN For EEClaire Cura100% (1)
- Naplex MpjeDocument35 pagesNaplex MpjeAtlantis ManNo ratings yet
- Chapter 35 AsthmaDocument4 pagesChapter 35 AsthmaDrashtibahen PatelNo ratings yet
- Drug Cards CNSDocument23 pagesDrug Cards CNSChristine Schroeder100% (2)
- Pharmacy Law Final Study GuideDocument21 pagesPharmacy Law Final Study Guidetohomas100% (1)
- PK Equations To Know For NaplexDocument1 pagePK Equations To Know For NaplexNasru DiinNo ratings yet
- PERIOPERATIVE ANTIBIOTICS AND MENINGITIS GUIDELINESDocument10 pagesPERIOPERATIVE ANTIBIOTICS AND MENINGITIS GUIDELINESDrashtibahen PatelNo ratings yet
- 6 PharmacologyDocument5 pages6 PharmacologyIbrahimFikryNo ratings yet
- Classification of AntibioticsDocument5 pagesClassification of AntibioticsdenaNo ratings yet
- Top 200 Expanded 1Document27 pagesTop 200 Expanded 1Dean HarperNo ratings yet
- Drug Cards (PDF Library)Document5 pagesDrug Cards (PDF Library)Jim Stewart0% (2)
- TPN CalculationDocument3 pagesTPN CalculationSARANYANo ratings yet
- First-Line BP Meds in Pregnancy & Allergy Drug CautionsDocument1 pageFirst-Line BP Meds in Pregnancy & Allergy Drug CautionsMaxwell Bentley LeeNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Disorders Treatment OptionsDocument5 pagesAnxiety Disorders Treatment OptionsJohn HolmesNo ratings yet
- MULTISTATE PHARMACY JURISPRUDENCE EXAMINATION (MPJE): Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandMULTISTATE PHARMACY JURISPRUDENCE EXAMINATION (MPJE): Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- Anti-psychotic Drugs GuideDocument4 pagesAnti-psychotic Drugs GuideDrSamia El WakilNo ratings yet
- Family Names of DrugsDocument1 pageFamily Names of DrugsangelNo ratings yet
- Warfarin Sodium: INR Levels 4.0 or Less Ok To Carry Out Procedure Test Atleast 72 Hrs Prior To ProcedureDocument6 pagesWarfarin Sodium: INR Levels 4.0 or Less Ok To Carry Out Procedure Test Atleast 72 Hrs Prior To ProcedureVimi GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Drug of Choice in Various Diseases - Candidiasis - PharmacologyDocument1 pageDrug of Choice in Various Diseases - Candidiasis - PharmacologyPragnesh ParmarNo ratings yet
- A-Autonomic Drugs: 1) CholinergicDocument28 pagesA-Autonomic Drugs: 1) CholinergicMahmoud Ahmed MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Medical Suffixes Cheat SheetDocument1 pagePharmacology Medical Suffixes Cheat SheetPattyNo ratings yet
- Vancomycin Pharmacology Indications, Mechanism, and Side Effects! PDFDocument1 pageVancomycin Pharmacology Indications, Mechanism, and Side Effects! PDFFrancis PasayNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Calculation Volume 2Document4 pagesPharmaceutical Calculation Volume 2Tony AnsahNo ratings yet
- Top 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)From EverandTop 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Revision Guide Made Simple For Pharmacy Technicians 2nd EditionFrom EverandRevision Guide Made Simple For Pharmacy Technicians 2nd EditionNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology for Student and Pupil Nurses and Student Pharmacy TechniciansFrom EverandPharmacology for Student and Pupil Nurses and Student Pharmacy TechniciansNo ratings yet
- Advanced Pharm From QuizletDocument62 pagesAdvanced Pharm From QuizletBetsy Brown Byersmith100% (1)
- AMA On Medical Marijuana, Recreational Cannabis and Cardiovascular HealthDocument22 pagesAMA On Medical Marijuana, Recreational Cannabis and Cardiovascular HealthBetsy Brown ByersmithNo ratings yet
- Drug Template 9Document1 pageDrug Template 9Betsy Brown ByersmithNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System SheetDocument11 pagesCardiovascular System SheetBetsy Brown ByersmithNo ratings yet
- AcutePrescribingLimits FINALDocument1 pageAcutePrescribingLimits FINALBetsy Brown ByersmithNo ratings yet
- Study Guide for NLN RN Pharmacology Exam Drugs and Their UsesDocument64 pagesStudy Guide for NLN RN Pharmacology Exam Drugs and Their UsesRichard BakerNo ratings yet
- Major functions of adrenergic and cholinergic receptorsDocument77 pagesMajor functions of adrenergic and cholinergic receptorsBetsy Brown Byersmith100% (1)
- Cardiovascular System SheetDocument11 pagesCardiovascular System SheetBetsy Brown ByersmithNo ratings yet
- NervousSystem - ANS and NMJ - PharmacologyDocument14 pagesNervousSystem - ANS and NMJ - PharmacologyBetsy Brown ByersmithNo ratings yet
- Diuretics For CardiacDocument6 pagesDiuretics For CardiacBetsy Brown ByersmithNo ratings yet
- FNP Review - AANP Immunization PearlsDocument94 pagesFNP Review - AANP Immunization PearlsJamila Ziyaeva100% (14)
- Gynecology PDFDocument54 pagesGynecology PDFgabriela_toma2009No ratings yet
- DRUG Card FormDocument4 pagesDRUG Card FormBetsy Brown ByersmithNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Meds For Nurse PractionerDocument139 pagesCardiac Meds For Nurse PractionerBetsy Brown ByersmithNo ratings yet
- Anemia ChartDocument1 pageAnemia ChartBetsy Brown ByersmithNo ratings yet
- Gynecology PDFDocument54 pagesGynecology PDFgabriela_toma2009No ratings yet
- Abx FlashDocument3 pagesAbx FlashBetsy Brown ByersmithNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System SheetDocument11 pagesCardiovascular System SheetBetsy Brown ByersmithNo ratings yet
- Test Bank Lehne S Pharmacotherapeutics For Advanced Practice Nurses and Physician Assistants 2nd EdiDocument479 pagesTest Bank Lehne S Pharmacotherapeutics For Advanced Practice Nurses and Physician Assistants 2nd EdiBetsy Brown Byersmith89% (133)
- WK 5 Rash Decision TreeDocument1 pageWK 5 Rash Decision TreeBetsy Brown ByersmithNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic TableDocument7 pagesAntibiotic TablenkuligowskiNo ratings yet
- Brain Dump SheetDocument2 pagesBrain Dump SheetBetsy Brown ByersmithNo ratings yet
- Study Guide for NLN RN Pharmacology Exam Drugs and Their UsesDocument64 pagesStudy Guide for NLN RN Pharmacology Exam Drugs and Their UsesRichard BakerNo ratings yet
- FNP Review - AANP Immunization PearlsDocument94 pagesFNP Review - AANP Immunization PearlsJamila Ziyaeva100% (14)
- Mark A. Riddle - Pediatric Psychopharmacology FOR PRIMARY CARE-American Academy of Pediatrics (2016) PDFDocument230 pagesMark A. Riddle - Pediatric Psychopharmacology FOR PRIMARY CARE-American Academy of Pediatrics (2016) PDFBetsy Brown ByersmithNo ratings yet
- Exam Tips for Medical StudentsDocument21 pagesExam Tips for Medical StudentsBetsy Brown ByersmithNo ratings yet
- Hypertension and Cardiology GuideDocument40 pagesHypertension and Cardiology GuideAnne Lowry92% (13)
- Guidelines For Complete SOAP2Document2 pagesGuidelines For Complete SOAP2Betsy Brown Byersmith100% (1)
- Diabetes Meds From PreceptorDocument4 pagesDiabetes Meds From PreceptorBetsy Brown ByersmithNo ratings yet
- Know Common Disease ManagementDocument14 pagesKnow Common Disease Managementcdx25No ratings yet
- Antianginal Drugs Lecture NotesDocument10 pagesAntianginal Drugs Lecture NotesPrincewill SeiyefaNo ratings yet
- AmlodipineDocument2 pagesAmlodipineMika Kudo100% (2)
- DM Type II Case StudyDocument28 pagesDM Type II Case StudyRichard Sy67% (3)
- Amlodipine AtenololDocument7 pagesAmlodipine AtenololBidhur Chakma 1935371673No ratings yet
- Cardio Lab MedsDocument11 pagesCardio Lab MedsDianne Erika MeguinesNo ratings yet
- Acp Dipiro Eg Hypertension FinalDocument83 pagesAcp Dipiro Eg Hypertension FinalAlberto CombiNo ratings yet
- AbecabDocument3 pagesAbecabMohimin Hossain Rahat 2016156673No ratings yet
- Grand Rounds PresentationDocument40 pagesGrand Rounds Presentationapi-610941700No ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical chemistry-II: Antihypertensive DrugsDocument5 pagesPharmaceutical chemistry-II: Antihypertensive DrugsMONIKA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Systemic Hypertension Associated With Kidney DiseaseDocument6 pagesTreatment of Systemic Hypertension Associated With Kidney DiseaseDr.Lázár AttilaNo ratings yet
- AnginaDocument16 pagesAnginaMc_Lopez_1761No ratings yet
- Cardiac Drugs 2nd Edition 2015 PDFDocument550 pagesCardiac Drugs 2nd Edition 2015 PDFditairinaNo ratings yet
- Amlodipine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAmlodipine Drug StudyJoseph Dann Enero Jr.100% (3)
- Case Study - ESRD (DS, NCP)Document8 pagesCase Study - ESRD (DS, NCP)Zhy CaluzaNo ratings yet
- Studi Kasus MK Konsep Terapi Genap 2019.2020 - UkbDocument8 pagesStudi Kasus MK Konsep Terapi Genap 2019.2020 - UkbYossi KhrismaeniNo ratings yet
- Iron Supplement for PregnancyDocument8 pagesIron Supplement for PregnancySarie LevitaNo ratings yet
- Basic Drug Cards 1Document13 pagesBasic Drug Cards 1Sara Sabra100% (1)
- Amniodarone (Norvasc) Drug SummDocument1 pageAmniodarone (Norvasc) Drug SummWarrenNo ratings yet
- Pharma Cardio Respi and Repro NclexdocxDocument8 pagesPharma Cardio Respi and Repro NclexdocxJhayneNo ratings yet
- Types of Hypertension Pathophysiology Aims and Objectives Drugs Mechanism of Action Literature Review Materials AND MethodsDocument14 pagesTypes of Hypertension Pathophysiology Aims and Objectives Drugs Mechanism of Action Literature Review Materials AND MethodsMaram RanadeepNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Table - GonzalesDocument14 pagesPharmacology Table - GonzalesMark Angelo PonferradoNo ratings yet
- Exam Drug Sem 2 - 2021Document6 pagesExam Drug Sem 2 - 2021Achi Beridze100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyAngeli A EstilloreNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching Plan: Effective?) - The Blood Pressure WillDocument3 pagesHealth Teaching Plan: Effective?) - The Blood Pressure WillphoebeNo ratings yet
- Amcardia 5mg, 10mg (Amlodipine)Document4 pagesAmcardia 5mg, 10mg (Amlodipine)Bhakti A MagdalenaNo ratings yet
- Esrd Ppt. - Alex (Final)Document109 pagesEsrd Ppt. - Alex (Final)Shoixi ⎝⓿⏝⓿⎠No ratings yet
- Prescription Analysis1Document21 pagesPrescription Analysis1Rizzalaine CaringalNo ratings yet
- Cost Comparison Charts PDFDocument78 pagesCost Comparison Charts PDFMaskedUpNinjaNo ratings yet
- Hospital's Drug Formulary (2nd Edition)Document96 pagesHospital's Drug Formulary (2nd Edition)henry omacheNo ratings yet