Professional Documents
Culture Documents
American Government - 1
American Government - 1
Uploaded by
Daisy Aquino0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageThe document outlines 6 basic principles of government: popular sovereignty establishes that government is created by and subject to the people's will; limited government restricts the governing powers of leaders without other branches' approval; separation of powers vests legislative, executive, and judicial powers in separate bodies; checks and balances allows each branch to amend or veto other branches to prevent too much power; judicial review allows courts to examine other branches' consistency with the constitution; and federalism distributes power between a central authority and constituent parts.
Original Description:
Original Title
American Government -1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document outlines 6 basic principles of government: popular sovereignty establishes that government is created by and subject to the people's will; limited government restricts the governing powers of leaders without other branches' approval; separation of powers vests legislative, executive, and judicial powers in separate bodies; checks and balances allows each branch to amend or veto other branches to prevent too much power; judicial review allows courts to examine other branches' consistency with the constitution; and federalism distributes power between a central authority and constituent parts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageAmerican Government - 1
American Government - 1
Uploaded by
Daisy AquinoThe document outlines 6 basic principles of government: popular sovereignty establishes that government is created by and subject to the people's will; limited government restricts the governing powers of leaders without other branches' approval; separation of powers vests legislative, executive, and judicial powers in separate bodies; checks and balances allows each branch to amend or veto other branches to prevent too much power; judicial review allows courts to examine other branches' consistency with the constitution; and federalism distributes power between a central authority and constituent parts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
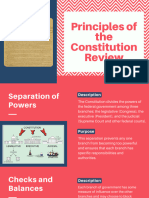
Government
Basic Principles of Government
Constitution = “supreme law of the land”
Popular Sovereignty
A doctrine in political theory that government is created by
and subject to the will of the people
Limited Government
System in which the primary leaders have very little
governing powers over the decisions and laws that are
created without approval from other branches or leaders
within the government
Separation of Powers
An act of vesting the legislative, executive, and judicial powers
of government in separate bodies
Checks and Balance
A system that allows each branch of the government to amend or
veto acts of another branch so as to prevent any one brand from
exerting too much power
Judicial Review
Power of the courts of a country to examine the actions of the
legislative, executive, and administrative arms of the government to
determine whether such actions are consistent with the constitution
Federalism
The distribution of power in an organization (such as government)
between a central authority (Federal Government) and the constituent
You might also like
- Outline A - The Law Pertaining To The State and Its Relationship With Its CitizensDocument69 pagesOutline A - The Law Pertaining To The State and Its Relationship With Its CitizensAngelic BorjaNo ratings yet
- Separation of PowerDocument40 pagesSeparation of PowerYong MgdnglNo ratings yet
- Cooley's Constitutional Limitations, Volume I at Page 224: Delegated LegislationDocument23 pagesCooley's Constitutional Limitations, Volume I at Page 224: Delegated LegislationArchana Shanker0% (1)
- CJ Admin Reviewer PDFDocument21 pagesCJ Admin Reviewer PDFSophiaFrancescaEspinosaNo ratings yet
- Judicial Fortitude: The Last Chance to Rein In the Administrative StateFrom EverandJudicial Fortitude: The Last Chance to Rein In the Administrative StateNo ratings yet
- Separation of PowerDocument25 pagesSeparation of PowerKuber JaishiNo ratings yet
- Constitutionalism Dr. S.K. BoseDocument2 pagesConstitutionalism Dr. S.K. BoseDr SK BoseNo ratings yet
- Unitary and Federal GovernmentDocument5 pagesUnitary and Federal Governmentariah janeNo ratings yet
- ADMINISTRATIVE LAW ReviewerDocument53 pagesADMINISTRATIVE LAW Reviewerrain100% (1)
- NOTES - 1987 Constitution of The PhilippinesDocument8 pagesNOTES - 1987 Constitution of The PhilippinesJenny Lyn MahinayNo ratings yet
- Doctrine of Separation of PowersDocument10 pagesDoctrine of Separation of PowerspriyaNo ratings yet
- What Is The Reason For The Development of Admin Law?Document11 pagesWhat Is The Reason For The Development of Admin Law?Mary Fatima Tolibas BerongoyNo ratings yet
- The PHILIPPINE GOVERNMENT - Executive, Legislative and JudiciaryDocument31 pagesThe PHILIPPINE GOVERNMENT - Executive, Legislative and JudiciaryIkkinNo ratings yet
- Constitution I: 4. Separation of PowersDocument21 pagesConstitution I: 4. Separation of PowersMarco Ramon100% (1)
- Constitutionalism My NotesDocument3 pagesConstitutionalism My NotesTrupti GowdaNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Law1Document10 pagesConstitutional Law1Her SheNo ratings yet
- Administrative Law 2018 Thursdays, 6:30-8:30 P.M.: Class: LLB 2B Lecturer: Atty. Sahara Alia J. SilonganDocument14 pagesAdministrative Law 2018 Thursdays, 6:30-8:30 P.M.: Class: LLB 2B Lecturer: Atty. Sahara Alia J. SilongansakuraNo ratings yet
- Judicial Review: Course TeacherDocument68 pagesJudicial Review: Course TeacherSanket Jamuar HNLU Batch 2018No ratings yet
- Notes On Political Law: I. Basic Principles of Political Law A. Separation of PowersDocument37 pagesNotes On Political Law: I. Basic Principles of Political Law A. Separation of PowersHamza MidsalipagNo ratings yet
- Article 6 NotesDocument22 pagesArticle 6 NotesAllisonNo ratings yet
- Constitutional SupremacyDocument1 pageConstitutional SupremacyIgnatius LingNo ratings yet
- Sources and PrincipalDocument9 pagesSources and PrincipalSo NuNo ratings yet
- Castillo-Word MeaningsDocument2 pagesCastillo-Word MeaningsJascha CastilloNo ratings yet
- 1 Definitions of ConstitutionDocument4 pages1 Definitions of ConstitutionAngel Jimmy George100% (1)
- LUIS RODRIGUEZ - Principles of Limited Gov - 2021Document2 pagesLUIS RODRIGUEZ - Principles of Limited Gov - 2021LUIS RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- CCH 302 Lesson 2 Constitutional Terminologies in GovernanceDocument7 pagesCCH 302 Lesson 2 Constitutional Terminologies in Governanceantony omondiNo ratings yet
- IJCRT1812758Document14 pagesIJCRT1812758DaisyNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument3 pagesDocumentMaricel PalawanNo ratings yet
- Statutory Construction Sualog ReviewerDocument36 pagesStatutory Construction Sualog Reviewerdeguia2340027No ratings yet
- Delegated LegislationDocument50 pagesDelegated LegislationSARIKANo ratings yet
- 4564654654Document2 pages4564654654sovxxxNo ratings yet
- The Principle of Separation of Powers - Constitutional GuaranteeDocument5 pagesThe Principle of Separation of Powers - Constitutional GuaranteeAndreea PopescuNo ratings yet
- Separation of PowersDocument28 pagesSeparation of PowersAnam ShoaibNo ratings yet
- 4 PDFDocument15 pages4 PDFAshish SinghNo ratings yet
- Admin Law Class (Atty. Alejandria) : Handout #1 Date Posted: Jan. 30Document12 pagesAdmin Law Class (Atty. Alejandria) : Handout #1 Date Posted: Jan. 30Juliefer Ann GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Shorya JuyalDocument2 pagesShorya Juyalshaurya juyalNo ratings yet
- A Country May Have A But Not Necessarily: Constitution ConstitutionalismDocument10 pagesA Country May Have A But Not Necessarily: Constitution ConstitutionalismasilahNo ratings yet
- Separation of PowersDocument5 pagesSeparation of PowersAqib ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Bill of RightsDocument2 pagesBill of RightsFerdinand BernardoNo ratings yet
- Challenges To Seperation of PowerDocument3 pagesChallenges To Seperation of PowerHARSHVARDHAN NLUJANo ratings yet
- Mewujudkan Dalam Penyus Nan Undang Undang: H Ks and BalancesDocument10 pagesMewujudkan Dalam Penyus Nan Undang Undang: H Ks and BalancesSinta YunitaNo ratings yet
- Narang A.S., India Political System, Process and Development, Gitanjali Publishing House, New Delhi, 2015, P. 672 - 674Document26 pagesNarang A.S., India Political System, Process and Development, Gitanjali Publishing House, New Delhi, 2015, P. 672 - 674saif aliNo ratings yet
- ConstitutionalismDocument2 pagesConstitutionalismAminaNo ratings yet
- Definition of Separation of PowerDocument4 pagesDefinition of Separation of PowerraymondkuNo ratings yet
- Check and BalanceDocument9 pagesCheck and Balancemodicam oloyaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Government and Polotics 2Document3 pagesComparative Government and Polotics 2leoleicristinorNo ratings yet
- Sources of Administrative LawDocument9 pagesSources of Administrative LawAkshat TennetiNo ratings yet
- Principles of The Constitution ReviewDocument11 pagesPrinciples of The Constitution Reviewkaiswaggy2No ratings yet
- MOOCs-Separation of Powers-E TextDocument13 pagesMOOCs-Separation of Powers-E TextPulakNo ratings yet
- Admin LawDocument6 pagesAdmin LawmangalagowrirudrappaNo ratings yet
- Separation of PowersDocument6 pagesSeparation of PowersarloNo ratings yet
- Constiutionalism SelfDocument19 pagesConstiutionalism SelfAbhinay BhalotiyaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Constitutionalism & Constitutional SpiritDocument31 pagesAssignment Constitutionalism & Constitutional SpiritSurabhi DesaiNo ratings yet
- Applicability of Sepration of Power in India Administrative LawDocument9 pagesApplicability of Sepration of Power in India Administrative Lawsparsh lalNo ratings yet
- Week 011-Module The LegislativeDocument7 pagesWeek 011-Module The LegislativeDoty AcasioNo ratings yet
- Administrative Law NotesDocument64 pagesAdministrative Law Noteskarishma kapoorNo ratings yet
- Judicial Power - The Power of The Court To: Sagisag vs. OchoaDocument8 pagesJudicial Power - The Power of The Court To: Sagisag vs. Ochoasam baysaNo ratings yet
- Separation of Power: Submitted To Dr. Nurul Huda Sakib (Sir)Document16 pagesSeparation of Power: Submitted To Dr. Nurul Huda Sakib (Sir)Shah RinNo ratings yet
- And Is Supreme in Matters Falling Within Its Own Constitutionally Allocated SphereDocument2 pagesAnd Is Supreme in Matters Falling Within Its Own Constitutionally Allocated SphereMark Angelo CabilloNo ratings yet
- 4 - Separation of Powers - Check and BalanceDocument13 pages4 - Separation of Powers - Check and BalanceBhuwan SharmaNo ratings yet