Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Study Note No. 4
Uploaded by
Caren Gay Gonzales TalubanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Study Note No. 4
Uploaded by
Caren Gay Gonzales TalubanCopyright:
Available Formats
STUDY NOTE NO.
Subject: Practical Research 1
Week: 2 Day: 3-4
Content Standard: Quantitative and Qualitative Research
Learning Competency: The learner describes characteristics, processes, and ethics of research.
Qualitative research gathers information that is not in numerical form. For example, diary accounts, open-ended
questionnaires, unstructured interviews and unstructured observations. Qualitative data is typically descriptive data and as
such is harder to analyze than quantitative data.
Qualitative research is useful for studies at the individual level, and to find out, in depth, the ways in which people think
or feel (e.g. case studies).
Analysis of qualitative data is difficult and requires an accurate description of participant responses, for example, sorting
responses to open questions and interviews into broad themes. Quotations from diaries or interviews might be used to
illustrate points of analysis. Expert knowledge of an area is necessary to try to interpret qualitative data and great care
must be taken when doing so, for example, if looking for symptoms of mental illness.
Quantitative research gathers data in numerical form which can be put into categories, or in rank order, or
measured in units of measurement. This type of data can be used to construct graphs and tables of raw data.
Experiments typically yield quantitative data, as they are concerned with measuring things. However, other research
methods, such as observations and questionnaires can produce both quantitative and qualitative information.
For example, a rating scale or closed questions on a questionnaire would generate quantitative data as these produce either
numerical data or data that can be put into categories (e.g. “yes”, “no” answers). Whereas open-ended questions would
generate qualitative information as they are a descriptive response.
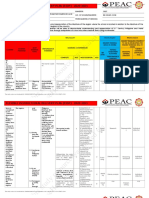
Qualitative Methods Quantitative Methods
Methods include focus groups, in-depth interviews, Surveys, structured interviews & observations, and
and reviews of documents for types of themes reviews of records or documents for numeric
information
Primarily inductive process used to formulate Primarily deductive process used to test pre-
theory or hypotheses specified concepts, constructs, and hypotheses that
make up a theory
More subjective: describes a problem or condition More objective: provides observed effects
from the point of view of those experiencing it (interpreted by researchers) of a program on a
problem or condition
Text-based Number-based
More in-depth information on a few cases Less in-depth but more breadth of information
across a large number of cases
Unstructured or semi-structured response options Fixed response options
No statistical tests Statistical tests are used for analysis
Can be valid and reliable: largely depends on skill Can be valid and reliable: largely depends on the
and rigor of the researcher measurement device or instrument used
Time expenditure lighter on the planning end and Time expenditure heavier on the planning phase and
heavier during the analysis phase lighter on the analysis phase
Less generalizable More generalizable
References:
https://www.orau.gov/cdcynergy/soc2web/Content/phase05/phase05_step03_deeper_qualitative_and_quantitative.
htm
http://www.simplypsychology.org/qualitative-quantitative.html
You might also like
- So What Is The Difference Between Qualitative Research and Quantitative ResearchDocument2 pagesSo What Is The Difference Between Qualitative Research and Quantitative ResearchAbdishakur Dahir MuseNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Research and Quantitative Research: Snap Survey Software Is The IdealDocument2 pagesQualitative Research and Quantitative Research: Snap Survey Software Is The IdealNatukunda DianahNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Qualitative and Quantitative Research MethodsDocument2 pagesDifferences Between Qualitative and Quantitative Research MethodsAli ShahNo ratings yet
- Quantitive and Qualitatitve Research MethodsDocument2 pagesQuantitive and Qualitatitve Research MethodsmahanteshkuriNo ratings yet
- Social Natural Sciences Market Research MethodsDocument6 pagesSocial Natural Sciences Market Research MethodsSaulo SauloNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Research Methods: Methods For Collecting DataDocument5 pagesAn Introduction To Research Methods: Methods For Collecting DataJulius MacaballugNo ratings yet
- Quantitative and QualitativeDocument7 pagesQuantitative and QualitativeTifanny Shaine TomasNo ratings yet
- Q1. W1. The Characteristics, Strengths, Weaknesses, and Kinds of Quantitative ResearchDocument7 pagesQ1. W1. The Characteristics, Strengths, Weaknesses, and Kinds of Quantitative ResearchDazzleNo ratings yet
- Methods For Collecting Data: Research Design ResearchDocument4 pagesMethods For Collecting Data: Research Design Researchzyra carmel caballeroNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Research MethodsDocument6 pagesAn Introduction To Research Methodskhaled merashliNo ratings yet
- What Exactly Research Methodology Means What Qualitative, Quantitative and Mixed Methodologies Are How To Choose Your Research MethodologyDocument8 pagesWhat Exactly Research Methodology Means What Qualitative, Quantitative and Mixed Methodologies Are How To Choose Your Research MethodologyKayz ShamuNo ratings yet
- Quantative and Qualitative ResearchDocument3 pagesQuantative and Qualitative ResearchOliver Cayetano IINo ratings yet
- Differences Between Qualitative and Quantitative Research MethodsDocument2 pagesDifferences Between Qualitative and Quantitative Research MethodsJonathan Wilder100% (4)
- Quantitative and QualitativeDocument7 pagesQuantitative and QualitativeCindyhhhoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document6 pagesChapter 3Faye EbuenNo ratings yet
- Notes QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE METHODSDocument4 pagesNotes QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE METHODSDavid LomentigarNo ratings yet
- Qualitative and Quantitative Research MethodsDocument12 pagesQualitative and Quantitative Research MethodssukhNo ratings yet
- BRM Unit 2 PPTDocument64 pagesBRM Unit 2 PPTAmol KareNo ratings yet
- BSN 3-1 Group 1 - Research InstrumentsDocument19 pagesBSN 3-1 Group 1 - Research InstrumentsAnabelle RicoNo ratings yet
- Prac Research Module 2Document12 pagesPrac Research Module 2Dennis Jade Gascon NumeronNo ratings yet
- 1) Explain The Importance of Market ResearchDocument2 pages1) Explain The Importance of Market ResearchCesca TambisNo ratings yet
- Baseline Data Collection TrainingDocument61 pagesBaseline Data Collection TrainingHaika AndrewNo ratings yet
- Research in Daily Life 2: Week 3Document10 pagesResearch in Daily Life 2: Week 3Abegail PanangNo ratings yet
- MSC 4 RMDocument56 pagesMSC 4 RMDr. Mamta SinghNo ratings yet
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative ResearchDocument6 pagesQualitative vs. Quantitative ResearchChristia Abdel HayNo ratings yet
- PR2 Lessons 1 3 Study GuideDocument9 pagesPR2 Lessons 1 3 Study GuideDiana OrdanezaNo ratings yet
- Qualitative and Quantitative ResearchDocument46 pagesQualitative and Quantitative ResearchShivaditya VermanNo ratings yet
- Educational Research Refers To The Systematic Collection andDocument3 pagesEducational Research Refers To The Systematic Collection andMaria Peeva MahseyaNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 SLM Q1 W1Document8 pagesPractical Research 2 SLM Q1 W1Sean LaguitNo ratings yet
- Assesment 1 - : Identify A Broad Problem AreaDocument7 pagesAssesment 1 - : Identify A Broad Problem AreaTwinkle RastogiNo ratings yet
- Qualitative and Quantitative Methods-1Document14 pagesQualitative and Quantitative Methods-1Simra MuzaffarNo ratings yet
- Different Kinds of ResearchDocument11 pagesDifferent Kinds of ResearchAlfatah muhumedNo ratings yet
- Qualitative and Quantitative ResearchDocument5 pagesQualitative and Quantitative ResearchDanielle Rose Jalagat100% (1)
- Practical Research 1Document10 pagesPractical Research 1Mindanao Community School100% (5)
- PDF Document PawsDocument3 pagesPDF Document PawsCarlo ReyesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6. Qualitative and Quantitative Research MethodsDocument5 pagesChapter 6. Qualitative and Quantitative Research MethodsMariana BarreraNo ratings yet
- Division Enhancement On Senior High School Inquiries Investigation and ImmersionDocument63 pagesDivision Enhancement On Senior High School Inquiries Investigation and ImmersionAshley Jade Hanna FloresNo ratings yet
- Sep-Dec 2022 COHORT RESEARCH METHODS NOTESDocument62 pagesSep-Dec 2022 COHORT RESEARCH METHODS NOTESAlice UmutoniNo ratings yet
- Research Methods ApproachesDocument3 pagesResearch Methods ApproachesxedrichandreiNo ratings yet
- RM-UNIT 4 Basic InstrumentationDocument139 pagesRM-UNIT 4 Basic Instrumentationaniruddha_parabNo ratings yet
- Data Collection MethodsDocument39 pagesData Collection MethodssasNo ratings yet
- Prelim Exam Coverage Practical Research 2Document3 pagesPrelim Exam Coverage Practical Research 2Janelie RojasNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3 Difference Between Qualitative and Qunatitative ResearchDocument6 pagesLESSON 3 Difference Between Qualitative and Qunatitative ResearchUlzzang girlNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction PDFDocument6 pagesChapter 1 Introduction PDFDaniela ArceoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Prac1 - SecondqDocument2 pagesReviewer in Prac1 - SecondqCeline GalizaNo ratings yet
- What Are The Research Methods: Techniques or Tools Techniques or ToolsDocument2 pagesWhat Are The Research Methods: Techniques or Tools Techniques or ToolsRamsi DowellNo ratings yet
- 9 ResearchDocument15 pages9 ResearchGrace PascualNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Methods - Introduction: Instructional Material For StudentsDocument23 pagesQuantitative Methods - Introduction: Instructional Material For StudentsArt IjbNo ratings yet
- Research MethodsDocument41 pagesResearch Methodsharismoten12No ratings yet
- Data GatheringDocument10 pagesData GatheringKylie Adrianna Bernabe SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Research Design: For Social ScienceDocument26 pagesResearch Design: For Social ScienceAhmad HafizanNo ratings yet
- Data CollectionDocument15 pagesData CollectionElena Beleska100% (1)
- QM Module1Document22 pagesQM Module1Kaneki kenNo ratings yet
- Research MethodsDocument31 pagesResearch Methodsaliyan hayderNo ratings yet
- Resesarch ReviewerDocument3 pagesResesarch ReviewerMa Jollie Mae BereNo ratings yet
- Group6 131118071738 Phpapp02 PDFDocument38 pagesGroup6 131118071738 Phpapp02 PDFAngel ArmogilaNo ratings yet
- Different Research Methodology PDFDocument19 pagesDifferent Research Methodology PDFCyndy Villapando100% (1)
- Research Methods SeraDocument70 pagesResearch Methods SeraYieli wal ChanNo ratings yet
- Research MethodologyDocument10 pagesResearch MethodologyMuthu ManikandanNo ratings yet
- Observation Sheet MTDocument1 pageObservation Sheet MTCaren Gay Gonzales Taluban100% (1)
- Study Note No. 1Document1 pageStudy Note No. 1Caren Gay Gonzales TalubanNo ratings yet
- Study Note No. 6Document3 pagesStudy Note No. 6Caren Gay Gonzales TalubanNo ratings yet
- What I Know What'S in What'S New What Is It Independent Assessment 3 EnvironmentDocument3 pagesWhat I Know What'S in What'S New What Is It Independent Assessment 3 EnvironmentCaren Gay Gonzales TalubanNo ratings yet
- Study Note No. 5Document3 pagesStudy Note No. 5Caren Gay Gonzales TalubanNo ratings yet
- Study Note No. 2Document1 pageStudy Note No. 2Caren Gay Gonzales TalubanNo ratings yet
- Research, As A General Rule Does Not Contain Hypothesis But Assumptions Based From Specific Questions AreDocument2 pagesResearch, As A General Rule Does Not Contain Hypothesis But Assumptions Based From Specific Questions AreCaren Gay Gonzales TalubanNo ratings yet
- Economics of EducationDocument23 pagesEconomics of EducationCaren Gay Gonzales TalubanNo ratings yet
- Study Note No. 1Document1 pageStudy Note No. 1Caren Gay Gonzales TalubanNo ratings yet
- Human Capital Development: Impact On Teachers' Work Engagement, Performance and Community EngagementDocument14 pagesHuman Capital Development: Impact On Teachers' Work Engagement, Performance and Community EngagementCaren Gay Gonzales TalubanNo ratings yet
- Research ProcessDocument14 pagesResearch ProcessCaren Gay Gonzales TalubanNo ratings yet
- Importance of ResearchDocument13 pagesImportance of ResearchCaren Gay Gonzales TalubanNo ratings yet
- Chapter6a AccelerationDocument47 pagesChapter6a AccelerationCaren Gay Gonzales TalubanNo ratings yet
- The Philosophical Movements in EducationDocument59 pagesThe Philosophical Movements in EducationCaren Gay Gonzales Taluban80% (5)
- Social Stratification: Presenter: Caren Gay Gonzales-TalubanDocument40 pagesSocial Stratification: Presenter: Caren Gay Gonzales-TalubanCaren Gay Gonzales TalubanNo ratings yet
- Finaloutline StatisticsDocument3 pagesFinaloutline StatisticsCaren Gay Gonzales TalubanNo ratings yet
- Reporter's RatingRating Sheet SheetDocument2 pagesReporter's RatingRating Sheet SheetCaren Gay Gonzales TalubanNo ratings yet
- Finaloutline StatisticsDocument3 pagesFinaloutline StatisticsCaren Gay Gonzales TalubanNo ratings yet
- 1541-Article Text-3558-1-10-20211119Document11 pages1541-Article Text-3558-1-10-20211119Luna EdeelweysNo ratings yet
- COMM 162 - Reading and Writing Test 3Document11 pagesCOMM 162 - Reading and Writing Test 3Karlos SoteloNo ratings yet
- Egyptian ArabicDocument2 pagesEgyptian ArabicIyesusgetanewNo ratings yet
- List of State Nursing Council Recognised Institutions Offering NURSE PRACTITIONER IN CRITICAL CARE (NPCC) Programme Inspected Under Section 13 and 14 of INC Act For The Academic Year 2020-2021Document5 pagesList of State Nursing Council Recognised Institutions Offering NURSE PRACTITIONER IN CRITICAL CARE (NPCC) Programme Inspected Under Section 13 and 14 of INC Act For The Academic Year 2020-2021Anmol GuptaNo ratings yet
- Quick Teacher Cover LetterDocument2 pagesQuick Teacher Cover Lettersolangi_naeemNo ratings yet
- BIMAS-2 A Two Page IntroductionDocument2 pagesBIMAS-2 A Two Page IntroductionSarah GracyntiaNo ratings yet
- PWC Application Form 2011Document3 pagesPWC Application Form 2011Ngoc NhuNo ratings yet
- International Talent Development Institute9 BTEC HND in Aviation Management Airport OperationsDocument4 pagesInternational Talent Development Institute9 BTEC HND in Aviation Management Airport OperationsSUNILNo ratings yet
- University of Vermont Diversity and Inclusion Action Plan SurveyDocument17 pagesUniversity of Vermont Diversity and Inclusion Action Plan SurveyThe College FixNo ratings yet
- GR 5 Term 1 2019 Ns T Lesson PlanDocument172 pagesGR 5 Term 1 2019 Ns T Lesson PlanLorraine NoloNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Physical EducationDocument4 pagesLesson Plan in Physical EducationGemmalyn DeVilla De CastroNo ratings yet
- En How To Use Chatgpt Beginners GuideDocument5 pagesEn How To Use Chatgpt Beginners GuideAlok TripathiNo ratings yet
- Healthmeans 20 Ways To Build Resilience UpdatedDocument23 pagesHealthmeans 20 Ways To Build Resilience UpdatedSofia BouçadasNo ratings yet
- A Man From Planet EarthDocument317 pagesA Man From Planet EarthsmaniacNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was Shared Via: Flexible Instructional Delivery Plan (Fidp) 2020-2021Document5 pagesThis Study Resource Was Shared Via: Flexible Instructional Delivery Plan (Fidp) 2020-2021Sa Le HaNo ratings yet
- Week 6 - Module 5-Staffing The Engineering OrganizationDocument9 pagesWeek 6 - Module 5-Staffing The Engineering OrganizationJitlee PapaNo ratings yet
- The Choice of Instructional Medium by The Selected Grade 10 Students of Don Gerardo Ouano Memorial National Highschool S.Y. 2022-2023Document22 pagesThe Choice of Instructional Medium by The Selected Grade 10 Students of Don Gerardo Ouano Memorial National Highschool S.Y. 2022-2023ljbebanco42No ratings yet
- PFS Paper # 1 Part A - InstructionsDocument3 pagesPFS Paper # 1 Part A - InstructionsElijah GeniesseNo ratings yet
- Activity Learning Sheets in Oral - Com - TYPES OF SPEECH CONTEXT - Guinsaugon High SchoolDocument5 pagesActivity Learning Sheets in Oral - Com - TYPES OF SPEECH CONTEXT - Guinsaugon High SchoolCatzMacedaMeekNo ratings yet
- ElectricalDocument56 pagesElectricalManoj Illangasooriya100% (1)
- 5 Steps To Use The Memory Palace TechniqueDocument6 pages5 Steps To Use The Memory Palace TechniqueAnisha Priya De Luxe100% (1)
- Lessons From Good Language Learner Part2 ContentsDocument3 pagesLessons From Good Language Learner Part2 ContentsMegabiteUQNo ratings yet
- Colleges Affiliated by Shah Abdul Latif UniversityDocument4 pagesColleges Affiliated by Shah Abdul Latif UniversitySindh Jobs Helper0% (2)
- Importance of Philippine HistoryDocument2 pagesImportance of Philippine HistoryJoyce Peñaescocia100% (2)
- Chapter One: Introduction To Marketing ResearchDocument29 pagesChapter One: Introduction To Marketing Researchmurthy1234567No ratings yet
- 2011 EngDocument15 pages2011 Eng비바525No ratings yet
- 10 Quality Engineer Interview Questions and AnswersDocument7 pages10 Quality Engineer Interview Questions and AnswersniensjvrNo ratings yet
- Books - MY - JOURNEY - IN - SCIENCE - Autobiography - of - An Indian Scientist - Hardev Singh Virk PDFDocument216 pagesBooks - MY - JOURNEY - IN - SCIENCE - Autobiography - of - An Indian Scientist - Hardev Singh Virk PDFHarjinder Singh DhaliwalNo ratings yet
- English ProjectDocument15 pagesEnglish Projectpranit.saluja.ps.2324No ratings yet
- Asha NRHM HryDocument8 pagesAsha NRHM Hrynareshjangra397No ratings yet