Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Probability PDF
Uploaded by
Gerald S. FernandezOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Probability PDF
Uploaded by
Gerald S. FernandezCopyright:
Available Formats
Gerald S.
Fernandez
BSCE-3D
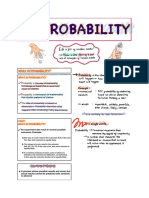
Probabilityis a numerical representation of the likelihood of occurrence of a
given event. It is a number between 0 and 1, assigning a probability of 1 if we are
certain that the event will happen, a probability of 0 if we are sure that the event will not
happen and 0.5 if we are only half-sure that the event will happen.
Basic Rules of Probability:
The Addition Rule
The probability of two events is the sum of the probability that either event
will happen subtracted by the probability that both will happen.
P(A or B)=P(A)+P(B)-P(A and B)
Complementary Rule
The sum of probabilities of the event and its complement must be equal to
1. P(A)+P(A’)=1
Conditional Rule
The probability that an event B occurs when it is known that some event
A has occurred.
P(B, Given A)= P(A and B)/P(A)
Multiplication Rule
Events A and B both occur is equal to the probability that event A occurs
times the probability that event B occurs, given event A already occurred.
P(A and B)=P(A)xP(B, Given A)
You might also like
- 01 Probability TheoryDocument15 pages01 Probability Theorymotivationmindset076No ratings yet
- 25-27 Statistical Reasoning-Probablistic Model-Naive Bayes ClassifierDocument35 pages25-27 Statistical Reasoning-Probablistic Model-Naive Bayes ClassifierDaniel LivingstonNo ratings yet
- FsafsdDocument2 pagesFsafsdJyotirmaya MaharanaNo ratings yet
- Laws of Probability: EventsDocument5 pagesLaws of Probability: EventsRamya GoudNo ratings yet
- Session - 2 - Conditional ProbabilityDocument17 pagesSession - 2 - Conditional ProbabilityPiyush PoddarNo ratings yet
- Conditional ProbabilityDocument9 pagesConditional ProbabilityDeva RaghulNo ratings yet
- Lec 2Document27 pagesLec 2DharamNo ratings yet
- Probability: TopicDocument30 pagesProbability: TopickakeroteNo ratings yet
- 1probability & Probability DistributionDocument45 pages1probability & Probability DistributionapurvaapurvaNo ratings yet
- Correlation Coefficients Are Used To Measure The Strength of The Relationship Between Two VariablesDocument2 pagesCorrelation Coefficients Are Used To Measure The Strength of The Relationship Between Two VariablesRileyNo ratings yet
- Engineering Data and Analysis - Notes 9Document3 pagesEngineering Data and Analysis - Notes 9Chou Xi MinNo ratings yet
- MicroprocessorDocument12 pagesMicroprocessorMd AsaduzzamanNo ratings yet
- ProbabilityDocument8 pagesProbabilityLyrics World РусскийNo ratings yet
- Section 4.2Document7 pagesSection 4.2modeNo ratings yet
- AP Statistics Chapter 5 - Probability: What Are The Chances? 5.1: Randomness, Probability and SimulationDocument3 pagesAP Statistics Chapter 5 - Probability: What Are The Chances? 5.1: Randomness, Probability and SimulationRhivia LoratNo ratings yet
- Conditional ProbabilityDocument3 pagesConditional ProbabilityTing HooiNo ratings yet
- Robiel H. Statistics For ManagementDocument18 pagesRobiel H. Statistics For ManagementtemedebereNo ratings yet
- 04 ProbabilityDocument54 pages04 Probabilityayham omariNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Relationships of Probability PDFDocument10 pagesSome Basic Relationships of Probability PDFJhasmin Orhel SagumNo ratings yet
- Probability Concepts and ApplicationsDocument10 pagesProbability Concepts and ApplicationsOrlando85% (13)
- Probability and StatisticsDocument4 pagesProbability and StatisticsNicholas M BandaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Rules in ProbabilityDocument41 pagesLecture 3 Rules in ProbabilityCllyan ReyesNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 AiDocument24 pagesUnit-3 AiMohit ThakurNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence: Enrique Peláez PH.DDocument20 pagesArtificial Intelligence: Enrique Peláez PH.DdavidchavezcevallosNo ratings yet
- PPT01 - Introduction To Probability TheoryDocument32 pagesPPT01 - Introduction To Probability TheoryAmbar SariNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document8 pagesUnit 3AaryaNo ratings yet
- Bayes's TheoremDocument2 pagesBayes's TheoremDivyanshi DubeyNo ratings yet
- 2022 07 22 ProbabilityDistributionsDocument88 pages2022 07 22 ProbabilityDistributionsJeedi SrinuNo ratings yet
- Bayesian Updating: Odds Class 12, 18.05 Jeremy Orloff and Jonathan BloomDocument8 pagesBayesian Updating: Odds Class 12, 18.05 Jeremy Orloff and Jonathan BloomMd CassimNo ratings yet
- Classical Probability Is Often Called A Priori Probability Because If We Keep Using OrderlyDocument6 pagesClassical Probability Is Often Called A Priori Probability Because If We Keep Using OrderlyNAVYA SHIVHARENo ratings yet
- Reyes, Jose Luis Alfonso S. Bsba-Bm Mg2A Portfolio Dr. John Irish Lira Probability and StatisticsDocument6 pagesReyes, Jose Luis Alfonso S. Bsba-Bm Mg2A Portfolio Dr. John Irish Lira Probability and StatisticsRenee San Gabriel ReyesNo ratings yet
- Probability Week 3Document28 pagesProbability Week 3lovesh kumarNo ratings yet
- 1 Week 4 Rules 2021Document3 pages1 Week 4 Rules 2021MeriDurglishviliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - ProbabilityDocument11 pagesChapter 3 - ProbabilityNik Muhammad Irfan Nik Mohd AmiruddinNo ratings yet
- ITS662 Chapter 4 - Bayes TheoremDocument14 pagesITS662 Chapter 4 - Bayes Theoremthegam852No ratings yet
- Addition Theorem, Multiplication Theorem, Baye's TheoremDocument29 pagesAddition Theorem, Multiplication Theorem, Baye's TheoremArun MishraNo ratings yet
- ProbabilityDocument7 pagesProbabilityWidiNo ratings yet
- Read ... The Probability of B Given A.: Example 1: A Bag Contains 12 Red M&MS, 12 Blue M&MS, and 12 GreenDocument5 pagesRead ... The Probability of B Given A.: Example 1: A Bag Contains 12 Red M&MS, 12 Blue M&MS, and 12 GreenYogendra RajavatNo ratings yet
- Probability & Probability DistributionDocument45 pagesProbability & Probability DistributionVinamra SinghNo ratings yet
- 2020 Odds RatioDocument4 pages2020 Odds RatioAkash GautamNo ratings yet
- Basic Probability ConceptsDocument2 pagesBasic Probability ConceptsThe lakkarsNo ratings yet
- ProbabilityDocument26 pagesProbabilityEyota AynalemNo ratings yet
- ProbabilityDocument2 pagesProbabilityhedina5402No ratings yet
- 1 Learning Objectives: MGMT 402 Data & Decisions Fall 2020 Lecture 1 NotesDocument24 pages1 Learning Objectives: MGMT 402 Data & Decisions Fall 2020 Lecture 1 NotesPablo SagionNo ratings yet
- 16 ProbabiltyDocument3 pages16 ProbabiltymanishNo ratings yet
- ProbabilityDocument10 pagesProbabilityVinayak Bhustalimath100% (1)
- Mutually Exclusive EventsDocument36 pagesMutually Exclusive EventsMl Phil100% (1)
- ProbabilityDocument4 pagesProbabilityMara Amei Marín RodenhorstNo ratings yet
- 留学生 第1.2课( 1.2 version2019. 9.18)Document12 pages留学生 第1.2课( 1.2 version2019. 9.18)Omar RefayNo ratings yet
- Biostatistics1718 2 PDFDocument27 pagesBiostatistics1718 2 PDFSamNo ratings yet
- EUBS QBM Lecture Notes 1Document2 pagesEUBS QBM Lecture Notes 1Rajdeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Probability Topic SummaryDocument1 pageProbability Topic SummaryPerson GainableNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Intro To Proba DistDocument31 pages2.2 Intro To Proba DistQuỳnh Anh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Probability Theory: Probability - Models For Random PhenomenaDocument116 pagesProbability Theory: Probability - Models For Random PhenomenasanaNo ratings yet
- Bayes Law by AHMDocument48 pagesBayes Law by AHMMaverickNo ratings yet
- Probabilistic Thinking: Nur Aini MasrurohDocument29 pagesProbabilistic Thinking: Nur Aini MasrurohFujiwara AndrieNo ratings yet
- CH 13 Guided Notes KEYDocument2 pagesCH 13 Guided Notes KEYHashbrownNo ratings yet
- Probability: TerminologyDocument7 pagesProbability: TerminologyGauri PhadkeNo ratings yet
- Yawa Nga ReviewerDocument16 pagesYawa Nga ReviewerGerald S. FernandezNo ratings yet
- Untitled Document PDFDocument1 pageUntitled Document PDFGerald S. FernandezNo ratings yet
- Name: Date: Plate #: Rating:: INSTRUCTOR: Engr - Jobel Hyles CabahugDocument1 pageName: Date: Plate #: Rating:: INSTRUCTOR: Engr - Jobel Hyles CabahugGerald S. FernandezNo ratings yet
- Gerald S. Fernandez: LocationDocument1 pageGerald S. Fernandez: LocationGerald S. FernandezNo ratings yet
- C12-Electromagnetic WavesDocument74 pagesC12-Electromagnetic WavesGerald S. FernandezNo ratings yet
- Aerobics: Muscle and Bone Strengthening ActivitiesDocument9 pagesAerobics: Muscle and Bone Strengthening ActivitiesGerald S. FernandezNo ratings yet