Professional Documents
Culture Documents
International Marketing Environment
Uploaded by
Liliana OvandoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
International Marketing Environment
Uploaded by
Liliana OvandoCopyright:
Available Formats
It records all the financial
The Twentieth to It is the system of accounts that
First half of the Balance of transactions of its residents and
the Twenty-First records the international financial
20th century Payments the rest of the world during a
Century transactions of a nation.
specified period of time.
Worldwide
Currently there are greater Protectionism It can be classified into: 1. Protection of an infant industry
Economic
opportunities for international trade
Depression
that countries previously did not
have. 2. Protection of the home market
6. Conservation of natural resources
The last half of
the 20th century 3. Need to keep money at home
They have become economically
7. Industrialization of a low-wage nation
interdependent and with the
potential for high demands. 4.Encouragement of capital
There were struggles
8. Maintenance of employment and accumulation
between the countries
reduction of unemployment
adopting the socialist
After World War II
Marxist approach
5. Maintenance of the standard of
9. National defense living and real wages.
The United States
and those who
sets out to instill the
followed a democratic 10. Increase of business size
ideal of capitalism in
capitalist approach to
as much of the world
economic
as possible. 11. Etaliation and bargaining
development
Trade Barriers
The United States It helped rebuild
sets out to instill the Europe Tariffs Quotas and Import Licenses Voluntary Export Restraints
ideal of capitalism in
as much of the world It provided financial
as possible. and industrial Tax imposed by a A quota is a specific Is an agreement between
assistance for government on goods unit or dollar limit the importing country and
developmentEurope that enter through its applied to a particular the exporting country for a
The Marshall Plan borders. type of good. restriction on the volume
of exports.
Produced by: Liliana Ovando Pérez
Bibliographic:
Cateora, P.R., Gilly, M.C. y Graham, J.L. (2011) International Marketing. 15 ed. McGraw-Hill Irwin. Unit 2: “The Dynamic Environment of
International Trade” (p. 26-48)
Antidumping Penalties Standards Monetary Barriers Voluntary Export Restraints
It is a new non-tariff barrier They are standards or Are those imposed by the Is an absolute restriction
Easing Trade that emerged as a way to regulations designed to government, to regulate against the purchase and
Restrictions keep foreign products out protect the health, safety international trade importation of certain
of the market. and quality of the product goods and/or services
from other countries.
The Omnibus Trade
General Agreement General Agreement The International
and Competitiveness
on Tariffs and Trade on Tariffs and Trade Monetary Fund It plays an important role
Act
in the international trade
environment by helping to
maintain stability in
It is a global institution financial markets.
It is focused on helping The GATT treaty and It is an institution that created to help nations
companies become more subsequent meetings establishes many rules become and remain
competitive in world have produced governing trade among economically viable.
markets, as well as agreements significantly its 148 members,
correcting perceived reducing tariffs on a wide provides a panel of Helps countries seeking
injustice in business range of goods experts to hear and rule economic development
practices. on trade disputes Among its objectives is the and restructuring.
between members, and stabilization of exchange
issue binding decisions. rates
Protests against Among its objectives is the There is also the
Global Institutions stabilization of exchange establishment of freely
rates convertible currencies to
facilitate the expansion
and balanced growth of
It all started in 1999 due to Environmental concerns, worker
The IMF also lends money international trade.
unwanted consequences exploitation and domestic job losses,
of globalizationsovereignty cultural extinction, higher oil prices, and to members having
of nations diminished sovereignty of nations. trouble meeting financial
obligations to other
members.
Produced by: Liliana Ovando Pérez
Bibliographic:
Cateora, P.R., Gilly, M.C. y Graham, J.L. (2011) International Marketing. 15 ed. McGraw-Hill Irwin. Unit 2: “The Dynamic Environment of
International Trade” (p. 26-48)
You might also like
- The Objectives of the New International Economic Order: Pergamon Policy StudiesFrom EverandThe Objectives of the New International Economic Order: Pergamon Policy StudiesNo ratings yet
- Served As An Economic Lifeline For The Spaniards in ManilaDocument2 pagesServed As An Economic Lifeline For The Spaniards in ManilaMarianne Cristy Toledo DeiparineNo ratings yet
- IBT Reviewer PDFDocument6 pagesIBT Reviewer PDFKekekkeke KekkekekeNo ratings yet
- GlobalizationDocument6 pagesGlobalizationJOHN BEBON YAPNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument9 pagesUntitledVinuya, Alyza Mae S.No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 The Dynamic Environment of International TradeDocument49 pagesChapter 2 The Dynamic Environment of International Tradeklairesandoval989No ratings yet
- Intbust MidtermsDocument9 pagesIntbust MidtermsKisqhNo ratings yet
- Market-Integration GRP1Document29 pagesMarket-Integration GRP1Mark Wendel SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 PPT 3Document6 pagesLecture 3 PPT 3mgimogenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document4 pagesChapter 1Lee TeukNo ratings yet
- Contemporary World - Economic and Technological GlobalizationDocument2 pagesContemporary World - Economic and Technological GlobalizationRika MiyazakiNo ratings yet
- Global EconomyDocument3 pagesGlobal EconomyYna SarrondoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 DevelopmentDocument2 pagesChapter 10 DevelopmentSarah JungNo ratings yet
- BA316 International Business Trade Module 2Document19 pagesBA316 International Business Trade Module 2Pamela Rose CasenioNo ratings yet
- GE 3 The Contemporary World QUIZ 1Document3 pagesGE 3 The Contemporary World QUIZ 1wzialcitaNo ratings yet
- 07 Chapter-2 PDFDocument35 pages07 Chapter-2 PDFkartikeya gulatiNo ratings yet
- CONTEMP RevDocument12 pagesCONTEMP RevAlisa HernandezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Eco561Document32 pagesChapter 1 Eco561norshaheeraNo ratings yet
- GlobalizationDocument9 pagesGlobalizationmaruinaangelaNo ratings yet
- Final Reviewer Gen Ed 3Document4 pagesFinal Reviewer Gen Ed 3Jean Antonette Santos ManabatNo ratings yet
- Globalization Is A Curse On National Economic DevelopmentDocument3 pagesGlobalization Is A Curse On National Economic DevelopmentsoumilNo ratings yet
- Notes in ContemporaryDocument6 pagesNotes in ContemporarytriciamayanilaNo ratings yet
- Coffee Risk 2008Document18 pagesCoffee Risk 2008Kevin CoffeeNo ratings yet
- Ibt QuizzesDocument10 pagesIbt QuizzesKekekkeke KekkekekeNo ratings yet
- Labor Cases - Part 1Document44 pagesLabor Cases - Part 1LAW10101No ratings yet
- Titular Dianne L. Bsed1 D Ge103 Lesson 6Document4 pagesTitular Dianne L. Bsed1 D Ge103 Lesson 6John Mhielo NarzolesNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Exam - 5Document5 pagesMid Term Exam - 5david.samhon73No ratings yet
- GLOBALISATION Maurya SirDocument22 pagesGLOBALISATION Maurya Sirmonica pappiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Gec 3Document3 pagesChapter 2 Gec 3Al-Khan HadjailNo ratings yet
- Module 5-1Document13 pagesModule 5-1sumayiahkarshafudheen.9800No ratings yet
- The Globalization of Economic Relations: Prepared By: Marlon F. AdlitDocument22 pagesThe Globalization of Economic Relations: Prepared By: Marlon F. AdlitJazzie AlbaricoNo ratings yet
- Module 2 The Globalization of EconomyDocument3 pagesModule 2 The Globalization of EconomyNaruto UzumakiNo ratings yet
- General Education ReviewerDocument10 pagesGeneral Education ReviewerVincentNo ratings yet
- MarketIntegration 3Document11 pagesMarketIntegration 3Franz Althea BasabeNo ratings yet
- Course Note 1 - Dang Gia Vung - RA6127378Document6 pagesCourse Note 1 - Dang Gia Vung - RA6127378Gia Vững ĐặngNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document3 pagesLesson 2JuNo ratings yet
- Group 2 (Chapter 3 - Market Integration)Document15 pagesGroup 2 (Chapter 3 - Market Integration)MARLYN GUIANGNo ratings yet
- SecretDocument3 pagesSecretSUAREZ, Jessa M.No ratings yet
- The Contemporary World: Global EconomyDocument47 pagesThe Contemporary World: Global EconomyCristine Joy SalazarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (IBT)Document5 pagesChapter 2 (IBT)Nicolle CurammengNo ratings yet
- International Business: BBM Semester VI 4 Jan 2011Document38 pagesInternational Business: BBM Semester VI 4 Jan 2011Tripti SinghNo ratings yet
- BME 30 ReviewerDocument9 pagesBME 30 ReviewerKleiam ChumzyNo ratings yet
- Ibt Prelim ReviewerDocument8 pagesIbt Prelim ReviewerApril Mae LomboyNo ratings yet
- Economic GlobalizationDocument2 pagesEconomic GlobalizationFerly Ann BaculinaoNo ratings yet
- Contemporary World Hand OutDocument18 pagesContemporary World Hand OutArlyn GacillosNo ratings yet
- Ma29 GT#2Document8 pagesMa29 GT#2Nacion EstefanieNo ratings yet
- Global Trade Law PPT IDocument15 pagesGlobal Trade Law PPT Ismkamran.mbaNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 MCQDocument10 pagesChap 1 MCQS.M. YAMINUR RAHMANNo ratings yet
- Market Integration: Unit IIIDocument6 pagesMarket Integration: Unit IIICiony UgbaminNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 IntlBusTrdDocument2 pagesLesson 1 IntlBusTrdWerpa PetmaluNo ratings yet
- Ch2 The Law of Com. Adv.Document17 pagesCh2 The Law of Com. Adv.rifka funeduNo ratings yet
- The Globalization of World EconomicsDocument33 pagesThe Globalization of World EconomicsAngela YlaganNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - The Global EconomyDocument5 pagesUnit 2 - The Global EconomyHam BurgerNo ratings yet
- Zamora, Jaymel Chem 4B The Contemporary World - MarketIntegrationDocument14 pagesZamora, Jaymel Chem 4B The Contemporary World - MarketIntegrationJaymel ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Ibt 1&2revDocument5 pagesIbt 1&2revponchingmanansalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: International Business and TradeDocument4 pagesChapter 3: International Business and Tradegian reyesNo ratings yet
- Review e Ripe FinalDocument1 pageReview e Ripe FinalJhea Cabos GaradoNo ratings yet
- 022 Article A008 enDocument4 pages022 Article A008 enIbrahim AbidNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Globalization of World EconomiesDocument12 pagesWeek 2 Globalization of World EconomiesPaul CincoNo ratings yet
- VU Lesson 44 International Trade and Finance International TradeDocument5 pagesVU Lesson 44 International Trade and Finance International TradeSusheel KumarNo ratings yet
- My Social Program: "We Will Be Your Voice"Document9 pagesMy Social Program: "We Will Be Your Voice"Liliana OvandoNo ratings yet
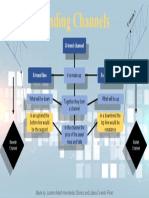
- Channel-Of-Distribution Structures Distribution PatternsDocument3 pagesChannel-Of-Distribution Structures Distribution PatternsLiliana OvandoNo ratings yet
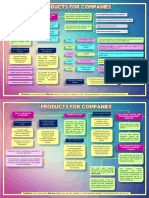
- Products For Companies Mapa ConceptualDocument2 pagesProducts For Companies Mapa ConceptualLiliana OvandoNo ratings yet
- Trending ChannelsDocument1 pageTrending ChannelsLiliana OvandoNo ratings yet
- What Is The Main Idea of The Video?: Title: "Learn A New Culture (2017) "Document2 pagesWhat Is The Main Idea of The Video?: Title: "Learn A New Culture (2017) "Liliana OvandoNo ratings yet
- Marketing and Economic DevelopmentDocument3 pagesMarketing and Economic DevelopmentLiliana OvandoNo ratings yet
- G.O OneDocument2 pagesG.O OneLiliana OvandoNo ratings yet
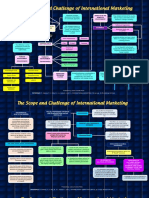
- The Scope and Challenge of International MarketingDocument3 pagesThe Scope and Challenge of International MarketingLiliana OvandoNo ratings yet
- Decision MakingDocument5 pagesDecision MakinganupsuchakNo ratings yet
- Unit-5 Mefa.Document12 pagesUnit-5 Mefa.Perumalla AkhilNo ratings yet
- Corporate Social ResponsibilityDocument8 pagesCorporate Social ResponsibilityJustin Miguel IniegoNo ratings yet
- SPMS Workshop Lectures PART IIDocument65 pagesSPMS Workshop Lectures PART IIrodrigo_iii_3100% (1)
- Heritage International Public SchoolDocument13 pagesHeritage International Public SchoolBKP KA CHELANo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Power System Economics: Daniel Kirschen Goran StrbacDocument5 pagesFundamentals of Power System Economics: Daniel Kirschen Goran StrbacGurdeep singh BaliNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship-11 12 Q2 SLM WK2Document6 pagesEntrepreneurship-11 12 Q2 SLM WK2MattNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - ProductDocument7 pagesLesson 6 - ProductShanley Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Itc14 mcp23Document8 pagesItc14 mcp23Lee TeukNo ratings yet
- 20170927090928talent Management W2Document19 pages20170927090928talent Management W2Bum MieNo ratings yet
- W. Edwards Deming's 14 PointsDocument4 pagesW. Edwards Deming's 14 PointsAr'anne ZabalaNo ratings yet
- Quantity Theory of MoneyDocument4 pagesQuantity Theory of MoneyNazmun BegamNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4 English Agricultural-MarketDocument29 pagesChapter-4 English Agricultural-MarketThach Nguyen Thi ThienNo ratings yet
- McDonalds Marketing SwotDocument4 pagesMcDonalds Marketing SwotHarsh AhujaNo ratings yet
- State Bank of India FinalDocument81 pagesState Bank of India FinalShaikh Shakeeb100% (1)
- Example White KnightDocument5 pagesExample White KnightDeepshikha BandebuccheNo ratings yet
- Role of Information and Communications Technology (ICT)Document13 pagesRole of Information and Communications Technology (ICT)Lianne LagromaNo ratings yet
- Why Do Financial Institutions ExistDocument44 pagesWhy Do Financial Institutions Existwaqar hattarNo ratings yet
- ACCN 101 ASSIGNMENT GROUP OF 1o.docx2Document37 pagesACCN 101 ASSIGNMENT GROUP OF 1o.docx2Simphiwe KarrenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Mathematics of Finance: Nguyen Thi Minh TamDocument30 pagesChapter 3: Mathematics of Finance: Nguyen Thi Minh TamPhương Anh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- IELTS Task 1Document12 pagesIELTS Task 1saidur183No ratings yet
- Work Order: Add: IGST Add: SGST Add: CGST 0.00 5,022.00 5,022.00Document1 pageWork Order: Add: IGST Add: SGST Add: CGST 0.00 5,022.00 5,022.00VinodNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Analyzing Recording TransactionsDocument6 pagesLesson 1 Analyzing Recording TransactionsklipordNo ratings yet
- Joint Report by JP Morgan and Oliver Wyman Unlocking Economic Advantage With Blockchain A Guide For Asset ManagersDocument24 pagesJoint Report by JP Morgan and Oliver Wyman Unlocking Economic Advantage With Blockchain A Guide For Asset ManagersJuan JesúsNo ratings yet
- Ateneo de Davao University Philippine Popular CultureDocument8 pagesAteneo de Davao University Philippine Popular CultureLoida BicoNo ratings yet
- Globalization's Wrong TurnDocument8 pagesGlobalization's Wrong TurnAna TamaritNo ratings yet
- 42 42 Characteristics of Working CapitalDocument22 pages42 42 Characteristics of Working Capitalpradeepg8750% (2)
- Week Five:: Reporting andDocument38 pagesWeek Five:: Reporting andIzham ShabdeanNo ratings yet
- Value Chain IPLDocument1 pageValue Chain IPLShivaen KatialNo ratings yet
- 4a - Long Term Sources of FinanceDocument12 pages4a - Long Term Sources of FinanceSudha AgarwalNo ratings yet