Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is A Cotyledon
Uploaded by
VictoriaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is A Cotyledon
Uploaded by
VictoriaCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is a Cotyledon?
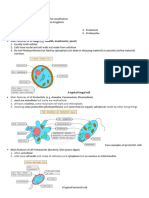
A cotyledon is part of the embryo within the seed of a plant. Often when the seed germinates, or
begins to grow, the cotyledon may become the first leaves of the seedling. Botanists use the number
of cotyledons present in the seed of a plant as a means of classification. Monocots are seeds that
have only one cotyledon, while dicots are plants with two cotyledons. The cotyledons are formed
during the process of embryogenesis along with the roots and shoots of the plant prior to
germination.
Function of Cotyledon
In dicot plants, the cotyledons are photosynthetic and function like leaves. The cotyledons are the
first part of the plant to emerge from the soil. Some cotyledons last only days after growing from the
soil and give way for other plant growth, while some cotyledons can last for years. The cotyledons
are important for the new plant as it begins to grow because they contain the stored food reserves
from the seed to give the plant its initial burst of energy to grow.
Types of Cotyledon
Botanists typically classify cotyledons as epigeal or hypogeal. Epigeal cotyledons expand after the
germination of the seed, rise above the ground, and become photosynthetic. Hypogeal
cotyledons remain below the ground after they emerge from the seed and do not become
photosynthetic. Hypogeal cotyledons typically serve as a food storage organ, providing nourishment
for the growing plant.
You might also like
- How Do Plants Grow? Botany Book for Kids | Children's Botany BooksFrom EverandHow Do Plants Grow? Botany Book for Kids | Children's Botany BooksNo ratings yet
- Science - Life Cycle of A PlantDocument31 pagesScience - Life Cycle of A PlantSetyo NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Plant Life Cycle (How Plants Grow): 2nd Grade Science Workbook | Children's Botany Books EditionFrom EverandPlant Life Cycle (How Plants Grow): 2nd Grade Science Workbook | Children's Botany Books EditionNo ratings yet
- Monocot vs. DicotDocument2 pagesMonocot vs. DicotRonalynNo ratings yet
- II. Seed-GerminationDocument49 pagesII. Seed-GerminationAndrew GatesNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in PlantsDocument12 pagesNutrition in Plantsdvrao_chowdaryNo ratings yet
- Growing Tomato ExperimentDocument6 pagesGrowing Tomato ExperimentPatrick Regidor83% (6)
- Monocot and Dicot SeedsDocument1 pageMonocot and Dicot SeedsSamuel LuNo ratings yet
- Seed Germination Inquiry Pre-Inquiry InvestigationDocument19 pagesSeed Germination Inquiry Pre-Inquiry InvestigationjeetuckNo ratings yet
- GerminationDocument14 pagesGerminationPhoo Pyae Pyae KyawNo ratings yet
- Fruits and SeedsDocument4 pagesFruits and Seedscornaga WirayudhaNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter Biology Note Grade 10Document7 pages3rd Quarter Biology Note Grade 10G and B Family buildingNo ratings yet
- Process of Seed GerminationDocument4 pagesProcess of Seed Germinationalya.chandhokNo ratings yet
- Daryl GuinayenDocument9 pagesDaryl GuinayenEmmanuel GallidoNo ratings yet
- Seeds: Germination Is When A Seed Embryo Goes From A DormantDocument3 pagesSeeds: Germination Is When A Seed Embryo Goes From A DormantAurea Jasmine DacuycuyNo ratings yet
- Notes - Growth and DevelopmentDocument4 pagesNotes - Growth and DevelopmentNathan mwapeNo ratings yet
- LabandpaulDocument12 pagesLabandpaulAr Ar PadzNo ratings yet
- The Structure of Dicot Seed:: Icse Class:9 Biology GerminationDocument3 pagesThe Structure of Dicot Seed:: Icse Class:9 Biology GerminationjaswanthNo ratings yet
- Agr122 Lab Report 4Document8 pagesAgr122 Lab Report 4Nur AthirahNo ratings yet
- Seeds and Germination - : Seed StructureDocument1 pageSeeds and Germination - : Seed StructureSundari Murugan50% (2)
- Plant Production Importance of PlantsDocument5 pagesPlant Production Importance of PlantsAiza T. VegaNo ratings yet
- Seed Report OutlineDocument2 pagesSeed Report OutlineAshlee JornadalNo ratings yet
- Seedstructure 130129220104 Phpapp01Document16 pagesSeedstructure 130129220104 Phpapp01Rehana PillayNo ratings yet
- Handouts-Lect. 29 - Introduction To Kingdom Plantae PDFDocument6 pagesHandouts-Lect. 29 - Introduction To Kingdom Plantae PDFRizwan BalochNo ratings yet
- KOlomi 65 e 8 B Ve CEt JES1Document11 pagesKOlomi 65 e 8 B Ve CEt JES1mahender106yoNo ratings yet
- Monocot and Dicot Grade 4Document22 pagesMonocot and Dicot Grade 4Jenefer MagoraNo ratings yet
- GerminationDocument1 pageGerminationJagdeesh GosineNo ratings yet
- Seed GerminationDocument7 pagesSeed Germinationganeshbalak2000No ratings yet
- Monocot and Dicot 4Document21 pagesMonocot and Dicot 4Jenefer MagoraNo ratings yet
- Seeds: Strategic Intervention Materials in Science by Dr. AaaDocument9 pagesSeeds: Strategic Intervention Materials in Science by Dr. AaajoseNo ratings yet
- 14.1.1.introduction To Measurement of GrowthDocument11 pages14.1.1.introduction To Measurement of GrowthALPHONCE ODHIAMBONo ratings yet
- Ansh Malik Holiday HomeworkDocument7 pagesAnsh Malik Holiday HomeworkRavi KetavNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and MorphologyDocument8 pagesAnatomy and MorphologyminichelNo ratings yet
- Growing PlantsDocument5 pagesGrowing PlantsCamila CervantesNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Seeds and Its GerminationDocument18 pagesParts of The Seeds and Its GerminationNova Estrada KionisalaNo ratings yet
- Final SLM OA11, Quarter 3, Week2Document2 pagesFinal SLM OA11, Quarter 3, Week2l.a. lopezNo ratings yet
- Plant DevelopmentDocument2 pagesPlant DevelopmentPrincess Keith RiveraNo ratings yet
- 1506231856511463Document3 pages1506231856511463chikenbiriyanieaterNo ratings yet
- Seed Germination in PlantsDocument49 pagesSeed Germination in PlantsbridgetnicolelimNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument10 pagesProjectRoseNo ratings yet
- How Plant Grow and ReproduceDocument6 pagesHow Plant Grow and ReproduceFrinces Mae CristalNo ratings yet
- Germination Green Bean Media Cotton Wet: BackgroundDocument8 pagesGermination Green Bean Media Cotton Wet: BackgroundlessyNo ratings yet
- Grdae VII-Biology - Nutrition in Plants - NotesDocument6 pagesGrdae VII-Biology - Nutrition in Plants - NotesDEBENDRA NATH CHOUDHURYNo ratings yet
- Plants & Seeds: Prior KnowledgeDocument60 pagesPlants & Seeds: Prior KnowledgeGurpreet Bedi0% (1)
- Effect of Urea On Plants GrowthDocument21 pagesEffect of Urea On Plants Growthtamal mondalNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Seed: ObjectiveDocument4 pagesParts of The Seed: ObjectiveJoan Rayos PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Critical Factors Affecting GerminationDocument6 pagesCritical Factors Affecting GerminationIzza AmirNo ratings yet
- Gr12 - Reproduction in PlantsDocument14 pagesGr12 - Reproduction in PlantsZelNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in ScienceDocument8 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in ScienceRegine MalanaNo ratings yet
- Bio 205 GerminationDocument6 pagesBio 205 GerminationadebolaabdulghalibNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 1 Nutrition in PlantsDocument5 pagesCBSE Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plantsgtbit.cse.aashishNo ratings yet
- Seed Parts and FertilizationDocument10 pagesSeed Parts and FertilizationYasmin MiroNo ratings yet
- Aaua SIWES Report Compiled by OLATUNJI ODocument51 pagesAaua SIWES Report Compiled by OLATUNJI OAyodeleNo ratings yet
- SeedsDocument6 pagesSeedsLawrence KasambaNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument9 pagesAnatomymomina tayyabNo ratings yet
- CONTENTSDocument11 pagesCONTENTSAyushmaan MaithaniNo ratings yet
- Features of OrganismsDocument3 pagesFeatures of OrganismsDarlene BellesiaNo ratings yet
- Seed Antatomy and Germination Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesSeed Antatomy and Germination Lesson Planapi-600991950No ratings yet
- Grade 8 Agriculture Science Week 2 Lesson 1Document5 pagesGrade 8 Agriculture Science Week 2 Lesson 1Balram HaroldNo ratings yet
- Exercise 5Document4 pagesExercise 5Cindy jabilloNo ratings yet