Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Features of Organisms
Uploaded by
Darlene Bellesia0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views3 pages1) The five kingdoms are animals, plants, fungi, protoctists, and prokaryotes.
2) Fungi are usually multicellular and feed by absorbing nutrients from dead or living material. Protoctists include single-celled and multicellular organisms with nuclei and sometimes cell walls or chloroplasts. Prokaryotes like bacteria are typically single-celled without nuclei.
3) Plants are distinguished by their green pigment chlorophyll. Flowering plants reproduce sexually using flowers and seeds, and can be divided into monocotyledons and dicotyledons which differ in leaf veins and flower structures.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) The five kingdoms are animals, plants, fungi, protoctists, and prokaryotes.
2) Fungi are usually multicellular and feed by absorbing nutrients from dead or living material. Protoctists include single-celled and multicellular organisms with nuclei and sometimes cell walls or chloroplasts. Prokaryotes like bacteria are typically single-celled without nuclei.
3) Plants are distinguished by their green pigment chlorophyll. Flowering plants reproduce sexually using flowers and seeds, and can be divided into monocotyledons and dicotyledons which differ in leaf veins and flower structures.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views3 pagesFeatures of Organisms
Uploaded by
Darlene Bellesia1) The five kingdoms are animals, plants, fungi, protoctists, and prokaryotes.
2) Fungi are usually multicellular and feed by absorbing nutrients from dead or living material. Protoctists include single-celled and multicellular organisms with nuclei and sometimes cell walls or chloroplasts. Prokaryotes like bacteria are typically single-celled without nuclei.
3) Plants are distinguished by their green pigment chlorophyll. Flowering plants reproduce sexually using flowers and seeds, and can be divided into monocotyledons and dicotyledons which differ in leaf veins and flower structures.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Features of Organisms
The Five Kingdoms :
The first division of living things in the classification
System is to put them into one of five kingdoms
They are :
1. Animals 4. Protoctists
2. Plants 5. Prokaryotes
3. Fungi
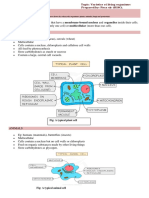
Main features of all fungi (e.g. moulds, mushrooms, yeast)
1. Usually multi cellular
2. Cells have nuclei and cell walls not made from cellulose
3. Do not Photosynthesize but feed by saprophytic (on dead or decaying material) or parasitic (onlive material)
nutrition
A typical fungal cell
Main features of all Protoctists (e.g. Amoeba, Paramecium, Plasmodium)
1. most are unicellular but some are multicellular
2. all have a nucleus, some may have cell walls and chloroplasts
3. meaning some protoctists photosynthesise and some feed on organic substances made by other living things
Two examples of protoctist cells
Main features of all Prokaryotes (bacteria, blue-green algae)
1. often unicellular
2. cells have cell walls (not made of cellulose) and cytoplasm but no nucleus or mitochondria
A typical bacterial cell
The Plant Kingdom
At least some parts of any plant are green, caused by the presence of the pigment chlorophyll which absorbs energy
from sunlight for the process of photosynthesis
The plant kingdom includes organisms such as ferns and flowering plants
Ferns
Have leaves called fronds
Do not produce flowers but instead reproduce by spores produced on the underside of fronds
Ferns reproduce by spores found in the underside of their fronds
Flowering plants
Reproduce sexually by means of flowers and seeds
Seeds are produced inside the ovary found at the base of the flower
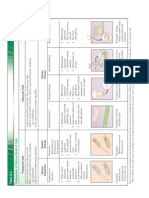
Can be divided into two groups – monocotyledons and dicotyledons
Wheat plants are monocotyledons Sunflowers are dycotyledons
How do you distinguish between monocotyledons and dicotyledons?
1) Flowers
Flowers from monocotyledons contain petals in multiples of 3
Flowers from dicotyledons contain petals in multiples of 4 or 5
2) Leaves
Leaves from monocotyledons have parallel leaf veins
Leaves from dicotyledons have reticulated leaf veins (meaning that they are all interconnected and form a web-
like network throughout the leaf)
Comparing Monocots and Dicots
Viruses
Viruses are not part of any classification system as they are not considered living things
They do not carry out the seven life processes for themselves, instead they take over a host cell’s metabolic
pathways in order to make multiple copies of themselves
Virus structure is simply genetic material (RNA or DNA) inside a protein coat
Structure of a typical virus
You might also like
- Classification NotesDocument13 pagesClassification NotesAli Usman AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Living Organisms: All Vertebrates Have A Backbone. There Are 5 Classes of VertebratesDocument4 pagesCharacteristics of Living Organisms: All Vertebrates Have A Backbone. There Are 5 Classes of VertebratesKrish PatelNo ratings yet
- Extended Only: CHP 1 Characteristics of Living Organisms: BasicsDocument21 pagesExtended Only: CHP 1 Characteristics of Living Organisms: BasicsX GamerNo ratings yet
- 1-Characteristics of Living OrganismsDocument19 pages1-Characteristics of Living OrganismsLulwa KhaskiehNo ratings yet
- How Organisms Are Classified: ClassificationDocument13 pagesHow Organisms Are Classified: ClassificationRahil BhavanNo ratings yet
- Classification of OrganismsDocument15 pagesClassification of OrganismssaadNo ratings yet
- Classification: How Organisms Are Classified?: OffspringDocument9 pagesClassification: How Organisms Are Classified?: OffspringFarah LangrialNo ratings yet
- Biology PretestDocument2 pagesBiology PretestJanice AthaliaNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument13 pagesBiology NotesHeinzNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Life-Plant KingdomDocument14 pagesAn Overview of Life-Plant KingdomUbaid Ur rahmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 (Varieties of Living Organism)Document3 pagesChapter-2 (Varieties of Living Organism)ToXicNo ratings yet
- Life Science StudyGuideDocument113 pagesLife Science StudyGuideNthabeleng RamotseoaNo ratings yet
- Module III - Unit 3 - THE NATURE AND COMPOSITION OF PLANTSDocument10 pagesModule III - Unit 3 - THE NATURE AND COMPOSITION OF PLANTSRechel SamontinaNo ratings yet
- Ch-1 ClassificationDocument27 pagesCh-1 ClassificationHaziq KhanNo ratings yet
- Year 9 RevisionDocument9 pagesYear 9 Revisionsamuel.kucharskyNo ratings yet
- Variety of Living OrganismDocument60 pagesVariety of Living OrganismThaw ThawNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes IGCSEDocument107 pagesBiology Notes IGCSERachel Adams100% (2)
- Olevels Biology Featuress of Five KingdomsDocument5 pagesOlevels Biology Featuress of Five KingdomskasshafemmanNo ratings yet
- Botany InformationDocument19 pagesBotany InformationJana Mohamed Mohamed Asaad Ibrahim AwadNo ratings yet
- Integrated Science NotesDocument17 pagesIntegrated Science NotesannmarieNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument20 pagesBiology NotesDannesa ValenciaNo ratings yet
- New World International School Biology Igcse Notes Chapter - 1Document15 pagesNew World International School Biology Igcse Notes Chapter - 1Noor Samir100% (1)
- Biology Ch#1Document14 pagesBiology Ch#1Farzan ButtNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes by Vasumitra GajbhiyeDocument59 pagesBiology Notes by Vasumitra GajbhiyeketamineNo ratings yet
- Bio NotesDocument101 pagesBio NotesMichelle HlungwaniNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Chapter 1 NotesDocument22 pagesForm 5 Chapter 1 NotesEeJun Lee50% (2)
- Unit 1 MICROORGANISMSDocument68 pagesUnit 1 MICROORGANISMSNatayNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Characteristic Eample 1 - Monera Prokaryotic Bacteria Actinomycetes Protozoa Fungi Plants, Algae Arthropods Mammals ManDocument17 pagesKingdom Characteristic Eample 1 - Monera Prokaryotic Bacteria Actinomycetes Protozoa Fungi Plants, Algae Arthropods Mammals Manبلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Cell Parts and FunctionDocument60 pagesLecture 3 Cell Parts and FunctionEsther Suan-LancitaNo ratings yet
- 1.1 - 1.8Document39 pages1.1 - 1.8gracy jNo ratings yet
- Biology 10Document3 pagesBiology 10Levi Yiwei PanNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument120 pagesBiologyMoch. Choirul Anam,S.SiNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Assignment Gr. 3Document26 pagesCell Biology Assignment Gr. 3Lamin N CeesayNo ratings yet
- 2 The Variety of Living OrganismsDocument10 pages2 The Variety of Living Organismsahasna.bandaraNo ratings yet
- Biology Igcse SummaryDocument86 pagesBiology Igcse SummaryTarun PatelNo ratings yet
- All ZnotesDocument158 pagesAll ZnotesaakashchandraniisNo ratings yet
- Period 4 Ch1Document14 pagesPeriod 4 Ch1sarashehab678No ratings yet
- Anatomy Physiology Plant ReproductionDocument23 pagesAnatomy Physiology Plant ReproductionAndrea Nicole BalaresNo ratings yet
- 1 Characteristics and Classification of Living OrganismsDocument6 pages1 Characteristics and Classification of Living OrganismsTumbikani Yamikani E NjovuNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IGCSE Biology: Topic 1: The Nature and Variety of Living OrganismsDocument4 pagesEdexcel IGCSE Biology: Topic 1: The Nature and Variety of Living OrganismsNoor-E-Khadiza ShamaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - 3Document32 pagesUnit 1 - 3Sunita SharmaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 10 The Simplest Living BeingsDocument8 pagesUNIT 10 The Simplest Living BeingsAnitaNo ratings yet
- The Five Kingdoms BiologyDocument13 pagesThe Five Kingdoms BiologyMuhtasim RafidNo ratings yet
- The Nature and Variety of Living OrganismsDocument1 pageThe Nature and Variety of Living OrganismsDinangaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Prokaryotes, EukaryotesDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Prokaryotes, EukaryotesMetchie Rico RafaelNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Living OrganismsDocument21 pagesCharacteristics of Living OrganismsSamaira JainNo ratings yet
- Tabla 2Document1 pageTabla 2Liseth Johanna Cristancho FlorezNo ratings yet
- Biological ScienceDocument2 pagesBiological Sciencebleary06mindNo ratings yet
- SN Chapter 1Document25 pagesSN Chapter 1Mohd Razin F2025No ratings yet
- 5 KingdomsDocument6 pages5 KingdomszhensenNo ratings yet
- The Cell/ All About CellsDocument35 pagesThe Cell/ All About CellsJandrew Gomez DimapasocNo ratings yet
- Biology Short NotesDocument7 pagesBiology Short NotesyusufNo ratings yet
- UP Diliman - Geol 130 Plants ReportDocument94 pagesUP Diliman - Geol 130 Plants ReportMac ServitoNo ratings yet
- BiodiversityDocument12 pagesBiodiversityDeejay BeekayNo ratings yet
- Unit 0 - The CellDocument5 pagesUnit 0 - The CellDavid ToledanoNo ratings yet
- Assignment No.2 Chapter 4: Acellular and Prokaryotic Microbes Chapter No. & TitleDocument4 pagesAssignment No.2 Chapter 4: Acellular and Prokaryotic Microbes Chapter No. & TitleBridgette ArandilaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology NotesDocument50 pagesIGCSE Biology NotesRumaisa AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Living OrganismsDocument15 pagesCharacteristics of Living Organismswahab.7803No ratings yet
- A Review of The Plant KingdomDocument5 pagesA Review of The Plant KingdomVincent OmondiNo ratings yet
- Microbiology: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideFrom EverandMicrobiology: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- 5 Complex Numbers 2Document29 pages5 Complex Numbers 2Darlene BellesiaNo ratings yet
- Latihan Math Trigono New Klas 11 HSTKB 31 Jul 2023 - SplitDocument1 pageLatihan Math Trigono New Klas 11 HSTKB 31 Jul 2023 - SplitDarlene BellesiaNo ratings yet
- 002 Ionic BondingDocument23 pages002 Ionic BondingDarlene BellesiaNo ratings yet
- Mechanos 1 CH 3Document7 pagesMechanos 1 CH 3Darlene BellesiaNo ratings yet
- Ips 1Document6 pagesIps 1Darlene BellesiaNo ratings yet
- Mechanos 1 CH 2Document8 pagesMechanos 1 CH 2Darlene BellesiaNo ratings yet
- Mechanic 4.2 - 2021 MSDocument6 pagesMechanic 4.2 - 2021 MSDarlene BellesiaNo ratings yet
- VECTORDocument13 pagesVECTORDarlene BellesiaNo ratings yet
- CT REVIEW Term 3 - Differentiation and GradientDocument2 pagesCT REVIEW Term 3 - Differentiation and GradientDarlene BellesiaNo ratings yet
- Number, X Frequency, F X.FDocument2 pagesNumber, X Frequency, F X.FDarlene BellesiaNo ratings yet
- Height (CM) Number of Student X X.FDocument3 pagesHeight (CM) Number of Student X X.FDarlene BellesiaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/12Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/12Darlene BellesiaNo ratings yet
- S15 - 41Document2 pagesS15 - 41Darlene BellesiaNo ratings yet
- Ex 1A PG 9Document6 pagesEx 1A PG 9Darlene BellesiaNo ratings yet
- Ex 1B PG 17Document2 pagesEx 1B PG 17Darlene BellesiaNo ratings yet
- Current ESSAI 1 MrkschemeDocument6 pagesCurrent ESSAI 1 MrkschemeDarlene BellesiaNo ratings yet
- MIX 123 Pure MathDocument3 pagesMIX 123 Pure MathDarlene BellesiaNo ratings yet
- Mix Pure Math 1-2-3 MarkschemeDocument5 pagesMix Pure Math 1-2-3 MarkschemeDarlene BellesiaNo ratings yet
- S15 - 43Document3 pagesS15 - 43Darlene BellesiaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Mathematics 9709/21Document12 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Mathematics 9709/21Darlene BellesiaNo ratings yet
- Mix Pure Math 1-2-3Document2 pagesMix Pure Math 1-2-3Darlene BellesiaNo ratings yet
- S15 - 42Document3 pagesS15 - 42Darlene BellesiaNo ratings yet
- MIX 123 Pure Math MarkschemeDocument8 pagesMIX 123 Pure Math MarkschemeDarlene BellesiaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Mathematics 9709/13Document20 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Mathematics 9709/13Darlene BellesiaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Mathematics 9709/22Document16 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Mathematics 9709/22Darlene BellesiaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument20 pagesCambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDarlene BellesiaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Mathematics 9709/12Document20 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Mathematics 9709/12Darlene BellesiaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Mathematics 9709/11Document20 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Mathematics 9709/11Darlene BellesiaNo ratings yet
- Morphological and Anatomical Studies On Some Monocot Xerophytes of District Karak, PakistanDocument9 pagesMorphological and Anatomical Studies On Some Monocot Xerophytes of District Karak, PakistanNanda ayu SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- JS 1 Agriculture 3ird Term Exam 2020Document9 pagesJS 1 Agriculture 3ird Term Exam 2020praiseforever90100% (1)
- Sbi3u Plants Unit NotesDocument22 pagesSbi3u Plants Unit NotesSaddi MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Plant TaxonomyDocument7 pagesPlant TaxonomySiaNo ratings yet
- LaporanDocument21 pagesLaporanAnnisa FitriNo ratings yet
- Virtual Garden Lab Report: By: Morgan Farlow Date: 7/1/20Document6 pagesVirtual Garden Lab Report: By: Morgan Farlow Date: 7/1/20jhjhkhkNo ratings yet
- CRS Laboratory Exercise No.2aDocument12 pagesCRS Laboratory Exercise No.2aBaisa A. UsmanNo ratings yet
- What Are Angiosperms?Document5 pagesWhat Are Angiosperms?Yolo WoloNo ratings yet
- Types of PlantsDocument2 pagesTypes of PlantsArt Justin SahagunNo ratings yet
- Takhtajan System of ClassificationDocument8 pagesTakhtajan System of Classificationshazeen shoaibNo ratings yet
- Activity 6 Plant Morphology Group 6 1Document9 pagesActivity 6 Plant Morphology Group 6 1Alyka Lee VictorinoNo ratings yet
- Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDocument31 pagesClick To Edit Master Subtitle StyleMA Orejas RamosNo ratings yet
- LET Reviewer in BIOLOGICAL SCIENCE Part 11 PDFDocument1 pageLET Reviewer in BIOLOGICAL SCIENCE Part 11 PDFaileen a. maputeNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy PDFDocument5 pagesTaxonomy PDFMd AshfaqueNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 Plant Classification PrinciplesDocument32 pagesCHAPTER 1 Plant Classification PrinciplesDarwiis Khama100% (3)
- USA NPN Botany PrimerDocument79 pagesUSA NPN Botany Primermillian0987100% (2)
- Virtual Garden Lab: Row Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4 Day 5 Day 6 Day 7 Day 8 Day 9Document6 pagesVirtual Garden Lab: Row Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4 Day 5 Day 6 Day 7 Day 8 Day 9Josalin RiveraNo ratings yet
- Bentham and Hooker's System of Classification Drpunamjeswal bsc-IIDocument4 pagesBentham and Hooker's System of Classification Drpunamjeswal bsc-IIShreyas SNo ratings yet
- DLP Second Quarter Science 4Document63 pagesDLP Second Quarter Science 4Manelyn Taga100% (9)
- An Introduction To Plant TaxanomyDocument187 pagesAn Introduction To Plant TaxanomyNazimah Maqbool100% (1)
- Act 4 PearlasDocument5 pagesAct 4 PearlasAlyssa Pauline PalacioNo ratings yet
- Hello ScribeDocument6 pagesHello ScribeYogesh BagadNo ratings yet
- 25MonocotOrigin PDFDocument62 pages25MonocotOrigin PDFPragyaNo ratings yet
- Dicot Monocot Comparison Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesDicot Monocot Comparison Lesson Planapi-373491715No ratings yet
- Characteristics-and-classification-of-living-organisms-Paper 2 Classified Solved Question CIE IGCSE GCSE OLevel BiologyDocument32 pagesCharacteristics-and-classification-of-living-organisms-Paper 2 Classified Solved Question CIE IGCSE GCSE OLevel BiologyIGCSE Physics & ChemistryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Part 1) - Plant Anatomy & Physiology PDFDocument89 pagesChapter 1 (Part 1) - Plant Anatomy & Physiology PDFMohammed Ridzuwan94% (16)
- Variety of Living Things and Their ClassificationDocument11 pagesVariety of Living Things and Their ClassificationAyuni100% (1)
- Plant Classification PDFDocument31 pagesPlant Classification PDFtresnaNo ratings yet
- Bio Names Last DinDocument7 pagesBio Names Last DinGette GarciaNo ratings yet
- Production and Evaluation of Cement-Bonded Particle Board Using Cogon Grass As ConstituentDocument9 pagesProduction and Evaluation of Cement-Bonded Particle Board Using Cogon Grass As ConstituentAnthony YapNo ratings yet