33% found this document useful (3 votes)
3K views13 pagesImpact Test ASME IX
1. The document discusses requirements for impact testing of materials according to ASME codes IX and B31.3. It outlines general guidelines, criteria for acceptance, test coupon preparation and testing procedures.
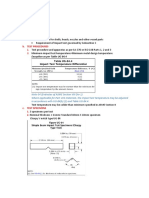
2. Tables and figures are presented showing minimum temperature limits for listed materials with and without impact testing, as well as requirements for low temperature toughness tests of different materials.
3. Procedures for impact testing methods and acceptance criteria are defined, including test specimens, test temperatures and conducting impact tests in accordance with various ASTM specifications.
Uploaded by
bounatiro HatemCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
33% found this document useful (3 votes)
3K views13 pagesImpact Test ASME IX
1. The document discusses requirements for impact testing of materials according to ASME codes IX and B31.3. It outlines general guidelines, criteria for acceptance, test coupon preparation and testing procedures.
2. Tables and figures are presented showing minimum temperature limits for listed materials with and without impact testing, as well as requirements for low temperature toughness tests of different materials.
3. Procedures for impact testing methods and acceptance criteria are defined, including test specimens, test temperatures and conducting impact tests in accordance with various ASTM specifications.
Uploaded by
bounatiro HatemCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Exigence Impact Test ASME IX
- Exigence Impact Test ASME B31.3 2016
- Requirements Table and Notes
- Minimum Temperatures and Exemption Curves
- Impact Testing Methods and Criteria