Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biology: Are You Familiar With The Four O'clock Flower?
Uploaded by
Pamela Andrea De Justo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageWhen a red-flowered variety of four o'clock flower is cross-pollinated with a white-flowered variety, the resulting heterozygous offspring produces pink flowers rather than either the red or white parental varieties. This is an example of incomplete dominance, where neither parental trait is fully dominant and the traits blend in the offspring. Codominance is also exhibited in cattle coat color and human blood types, where both parental alleles are simultaneously expressed in heterozygous individuals rather than one being dominant over the other.
Original Description:
Original Title
BIO 2 PT 2 3RD PERIO
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentWhen a red-flowered variety of four o'clock flower is cross-pollinated with a white-flowered variety, the resulting heterozygous offspring produces pink flowers rather than either the red or white parental varieties. This is an example of incomplete dominance, where neither parental trait is fully dominant and the traits blend in the offspring. Codominance is also exhibited in cattle coat color and human blood types, where both parental alleles are simultaneously expressed in heterozygous individuals rather than one being dominant over the other.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageBiology: Are You Familiar With The Four O'clock Flower?
Uploaded by
Pamela Andrea De JustoWhen a red-flowered variety of four o'clock flower is cross-pollinated with a white-flowered variety, the resulting heterozygous offspring produces pink flowers rather than either the red or white parental varieties. This is an example of incomplete dominance, where neither parental trait is fully dominant and the traits blend in the offspring. Codominance is also exhibited in cattle coat color and human blood types, where both parental alleles are simultaneously expressed in heterozygous individuals rather than one being dominant over the other.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
BIOLOGY
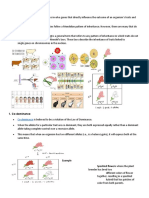
INCOMPLETE DOMINANCE AND are crossed, the resulting heterozygous
CODOMINANCE offspring is roan. Some of the offspring’s
hairs are red while others are white.
Are you familiar with the four o’clock
flower? The ABO blood type is another
example of two alleles, I A and IB, being
It is locally called rosas de alas
simultaneously expressed in a heterozygous
cuatro and scientifically known as Mirabilis
individual. This pattern is referred to as
jalapa.
codominace.
How many colors of its flower have you
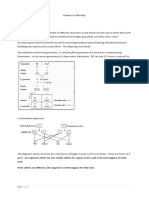
EX: In some kind of cattle, there are
seen?
two alleles for coat color, R for red and r for
The most common variety produces white. When an allele for white and one
red (or purple) flowers. Another variety allele for red combine, the coat is spotted
produces white flowers. with red and white, also called roan. Predict
the possible offspring of homozygous red
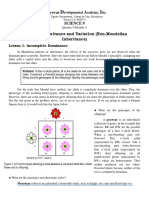
A biologist cross- pollinated a red – cow and roan cow.
flower variety with a white – flower variety.
Then the seeds from the flowers produced
flowers that were neither red nor white but
pink.
How is this different from Mendel’s
observations?
In Mendel’s crosses, when the genes
for contrasting characters are present in the
same individual, only the dominant
character appears; the recessive character
does not appear.
Thus, with respect to seed color, a
heterozygous individual (Gg) produces
yellow seeds only. We say yellow seed is
dominant and green is recessive. Mirabilis
presents a different case: the heterozygous
individual produces flowers that are pink – a
blending of red and white. Neither red nor
white flower color is dominant. Biologist
refer to this phenomenon as incomplete
dominance or no dominance.
Fur color in cattle is due to
codominant alleles that are simultaneously
expressed in heterozygous individuals.
When red – furred and white-furred animal
You might also like
- Inheritance PatternsDocument23 pagesInheritance PatternsKevin XueNo ratings yet
- Incomplete DominanceDocument2 pagesIncomplete DominanceRodrick RamosNo ratings yet
- Genetics 2.0Document42 pagesGenetics 2.0Micah Denise Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Handouts For Week 3Document8 pagesHandouts For Week 3Angel rose OrbeNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Week 5 Lesson 1Document5 pagesGen Bio Week 5 Lesson 1Gabriel SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Definition of CodominanceDocument4 pagesDefinition of Codominancemarjorie acsoncamachoNo ratings yet
- Incomplete Dominance & CodominanceDocument12 pagesIncomplete Dominance & CodominanceShaker MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes - NonmendelianDocument5 pagesSummary Notes - NonmendelianBonachita YamNo ratings yet
- Non-Mendelian Patterns of Heredity: Prepared by Imelda A. YganDocument38 pagesNon-Mendelian Patterns of Heredity: Prepared by Imelda A. YganJeestin Kent GabineraNo ratings yet
- Heridity, Inheritance and VariationDocument101 pagesHeridity, Inheritance and Variationdiana liberatoNo ratings yet
- Incomplete Dominance and CodominanceDocument13 pagesIncomplete Dominance and CodominanceSuccess MentorNo ratings yet
- Non-Mendelian Notes EditedDocument3 pagesNon-Mendelian Notes EditedJessa BarreraNo ratings yet
- Principles of Inheritance and Variation One Mark QuestionsDocument10 pagesPrinciples of Inheritance and Variation One Mark QuestionsRituNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument62 pagesGeneticsgwormtalaveraNo ratings yet
- Mendelian and Modern Genetics: General Biology IiDocument28 pagesMendelian and Modern Genetics: General Biology IiLesterNo ratings yet
- Complete Incomplete DominanceDocument25 pagesComplete Incomplete Dominancemohit tanwaniNo ratings yet
- Incomplete Dominance and CodominanceDocument9 pagesIncomplete Dominance and Codominancestefani anindyaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Osama Al-Amer: Chapter Iii: Extension To Mendelian GeneticsDocument29 pagesDr. Osama Al-Amer: Chapter Iii: Extension To Mendelian GeneticsBnDeRNo ratings yet
- HeredityDocument45 pagesHeredityLevy GerpacioNo ratings yet
- Honors Genetics Take Home 2009Document3 pagesHonors Genetics Take Home 2009abrook_ghsNo ratings yet
- 3.4 - Non-Mendelian Traits - Incomplete and Co-Dominance, Multiple AllelesDocument15 pages3.4 - Non-Mendelian Traits - Incomplete and Co-Dominance, Multiple AllelesJude GNo ratings yet
- Genetics II Answered Review F 07Document10 pagesGenetics II Answered Review F 07Sadhin SaleemNo ratings yet
- GENE INTERACTION (Autosaved) 4Document34 pagesGENE INTERACTION (Autosaved) 4Sana AkramNo ratings yet
- Non Mendellian For DiscussionDocument70 pagesNon Mendellian For DiscussionKate KatNo ratings yet
- Non-Mendelian Inheritance2Document41 pagesNon-Mendelian Inheritance2Jeremy Christian MendozaNo ratings yet
- InheritanceDocument50 pagesInheritanceLawrence MarquezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5-NOTESDocument25 pagesChapter 5-NOTESMujib Ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Johann Gregor Mendel: " The Father of Genetics"Document6 pagesJohann Gregor Mendel: " The Father of Genetics"Shiba TatsuyaNo ratings yet
- Geneticsor HeredityDocument4 pagesGeneticsor HereditychavaebreNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 18-Jul-2022Document9 pagesAdobe Scan 18-Jul-2022Deeps DeepanNo ratings yet
- Science Lecture NotesDocument6 pagesScience Lecture NotesJohn Renz CastilloNo ratings yet
- CHP 5 - Principles of Inheritance and VariationDocument68 pagesCHP 5 - Principles of Inheritance and VariationAbhishek ratnoo100% (1)
- Mendel's Laws of InheritanceDocument15 pagesMendel's Laws of InheritanceChristine Joy PatagNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 InheritanceDocument121 pagesChapter 22 Inheritancebhskardu83100% (2)
- Principles of Inheritance and Variation (Class-12) - 1Document9 pagesPrinciples of Inheritance and Variation (Class-12) - 1Ashok KumarNo ratings yet
- Strategic Intervention MaterialsDocument17 pagesStrategic Intervention MaterialsJordan Cardillo100% (1)
- Live Online TutoringDocument8 pagesLive Online TutoringAnsh BarmanNo ratings yet
- Section 5 Genes and InheritanceDocument100 pagesSection 5 Genes and InheritanceCAYTANO JIMENEZ ARELLYNo ratings yet
- Non-Mendelian Notes EditedDocument2 pagesNon-Mendelian Notes EditedMary Grace SunioNo ratings yet
- Principles of Inheritance and VariationDocument11 pagesPrinciples of Inheritance and VariationTRAP ZOIDNo ratings yet
- Dominance: Complete Dominance: If Two Alleles Have A Complete Dominance Relationship, TheDocument2 pagesDominance: Complete Dominance: If Two Alleles Have A Complete Dominance Relationship, TheSallyAceNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Week 4Document16 pagesScience 9 Week 4lenNo ratings yet
- Non-Mendelian Inheritance: Principles of BiologyDocument18 pagesNon-Mendelian Inheritance: Principles of BiologyJelly OrtizNo ratings yet
- Name Department::: Aiman AmjadDocument9 pagesName Department::: Aiman AmjadMuhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Patterns of InheritanceDocument27 pagesModule 3 Patterns of InheritancePapi0% (1)
- 10 Genetics I Mendelian Law-1Document58 pages10 Genetics I Mendelian Law-1Kresentia SetinNo ratings yet
- Heredity: Inheritance and VariationDocument6 pagesHeredity: Inheritance and VariationJendie BayanNo ratings yet
- Non-Mendelian Patterns of Inheritance 1Document23 pagesNon-Mendelian Patterns of Inheritance 1Jolly RiveraNo ratings yet
- To Our MIC206 Presentation: WelcomeDocument23 pagesTo Our MIC206 Presentation: WelcomeSuraiya Siraj NehaNo ratings yet
- Non Mendelian Patterns of InheritanceDocument39 pagesNon Mendelian Patterns of InheritanceRichiel Angulo SungaNo ratings yet
- GENETICS Is The Study of Inherited Characteristics Called TRAITS. in Natural Populations All TheDocument7 pagesGENETICS Is The Study of Inherited Characteristics Called TRAITS. in Natural Populations All TheDaniel BerryNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument8 pagesPhysics ProjectAanya SachdevaNo ratings yet
- Mendel PlusDocument23 pagesMendel PluslofisoulmusicNo ratings yet
- Lesson-Co1Document39 pagesLesson-Co1JOCELYN MATIGANo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument49 pagesGeneticsKenia AvilaNo ratings yet
- 3 Genetics Notes - VocabulariespptDocument48 pages3 Genetics Notes - VocabulariespptVickyNo ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN Introduction To HeredityDocument20 pagesLESSON PLAN Introduction To HeredityAnshika AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Agrarian ReformDocument15 pagesAgrarian ReformPamela Andrea De JustoNo ratings yet
- 1 Report PH HisortyDocument65 pages1 Report PH HisortyPamela Andrea De JustoNo ratings yet
- Round 12Document13 pagesRound 12Pamela Andrea De JustoNo ratings yet
- Mil 4th PrelimsDocument4 pagesMil 4th PrelimsPamela Andrea De JustoNo ratings yet
- Mil 4th PrelimsDocument4 pagesMil 4th PrelimsPamela Andrea De JustoNo ratings yet
- Media and Information LiteracyDocument4 pagesMedia and Information LiteracyPamela Andrea De JustoNo ratings yet
- Bio 2Document3 pagesBio 2Pamela Andrea De JustoNo ratings yet
- Religious Studies: 1. Mary, Model of Faithful Disciple and Witness 2. Church As A Community of DisciplesDocument2 pagesReligious Studies: 1. Mary, Model of Faithful Disciple and Witness 2. Church As A Community of DisciplesPamela Andrea De JustoNo ratings yet
- Biology: Mendel's Law of Independent Assortments of Genes - States That The InheritanceDocument4 pagesBiology: Mendel's Law of Independent Assortments of Genes - States That The InheritancePamela Andrea De JustoNo ratings yet