Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pyrite: Pī'rīt Pīrī'tēz, PƏ-, Pī'rīts
Uploaded by
Zdravko VidakovicOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pyrite: Pī'rīt Pīrī'tēz, PƏ-, Pī'rīts
Uploaded by
Zdravko VidakovicCopyright:
Available Formats
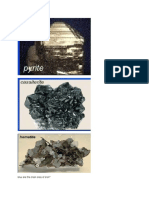
PYRITE
(pī'rīt) or iron pyrites (pīrī'tēz, pə–, pī'rīts) , pale brass-yellow mineral, the bisulfide of iron,
FeS2. It occurs most commonly in crystals (belonging to the isometric system and usually in the
form of cubes and pyritohedrons) but is also found in massive, granular, and stalactite form. In
spite of its nickname, “fool's gold,” it often is associated with true gold; auriferous pyrite is a
commercially important source of gold. Other metals that sometimes replace a part of the iron
are cobalt, nickel, arsenic, and copper. The most common sulfide mineral, pyrite is widely
distributed in rocks of all ages and types. Its chief use is as a source of sulfur in the manufacture
of sulfuric acid. The term pyrites is applied to any of a number of metallic sulfides that strike fire
with steel. Some minerals resembling pyrite in appearance or composition are arsenopyrite,
chalcopyrite (copper pyrites), cobaltite, marcasite (white iron pyrites or spear pyrites), and
pyrrhotite (magnetic pyrites).
You might also like
- Why Does Iron Taste Funny? Chemistry Book for Kids 6th Grade | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandWhy Does Iron Taste Funny? Chemistry Book for Kids 6th Grade | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Pyrite: The Real Story Behind "Fool's Gold"Document3 pagesPyrite: The Real Story Behind "Fool's Gold"Alejandro LavineNo ratings yet
- Past Tense Sentences in Mining ArticlesDocument3 pagesPast Tense Sentences in Mining ArticlesAkbar WidodoNo ratings yet
- IV. METAL ALLOYS: Common Types & UsesDocument8 pagesIV. METAL ALLOYS: Common Types & UsesDhina CasungcadNo ratings yet
- Sulfides: Pyrite and MarcasiteDocument3 pagesSulfides: Pyrite and Marcasitebijoy82No ratings yet
- Ferrous MetalsDocument2 pagesFerrous MetalsShubhi ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- MINERALSDocument15 pagesMINERALSBea Dacillo BautistaNo ratings yet
- Native Elements and Sulfides WSDocument36 pagesNative Elements and Sulfides WSMuhammad Firdaus RafqiNo ratings yet
- 9 IronDocument21 pages9 Ironahmedabdelaziz851647No ratings yet
- 5-1. Extraction of Metals 1Document40 pages5-1. Extraction of Metals 1teenoe21No ratings yet
- Processing Volcano-Related Gold, Silver and Copper Ores: Mineralogical AspectsDocument21 pagesProcessing Volcano-Related Gold, Silver and Copper Ores: Mineralogical AspectsFreddy MottaNo ratings yet
- Native Metals EMASDocument10 pagesNative Metals EMASHasbii PanthalassaNo ratings yet
- Iron and SteelDocument7 pagesIron and SteelaryannaldaNo ratings yet
- Iron Ore DepositsDocument11 pagesIron Ore Depositszunpwintzaw.161219999No ratings yet
- Identifying Archaeological Metal PDFDocument4 pagesIdentifying Archaeological Metal PDFadonisghlNo ratings yet
- Chemical ElementsDocument5 pagesChemical ElementsRofilR.AlbaoNo ratings yet
- Elementary IntroductionDocument7 pagesElementary IntroductionSyahrul RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Click icon to add metallic mineralsDocument8 pagesClick icon to add metallic mineralsAleena TariqNo ratings yet
- Nickel, gold, copper and other metals comparedDocument5 pagesNickel, gold, copper and other metals comparedRofilR.AlbaoNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Lesson 3 MineralsDocument36 pagesEarth and Life Lesson 3 MineralsMagdalena TagubaNo ratings yet
- Properties and Uses of MetalsDocument64 pagesProperties and Uses of MetalsVijay GohilNo ratings yet
- Iron Ores: Types and ClassificationDocument1 pageIron Ores: Types and ClassificationDeogratias LaurentNo ratings yet
- Mineralogy Gold RefractoryDocument1 pageMineralogy Gold RefractorySteven DziobaNo ratings yet
- Gold WikiDocument5 pagesGold WikigergerwgNo ratings yet
- Lectures Notes 2Document45 pagesLectures Notes 2Nitesh JainNo ratings yet
- Native Elements Group - Properties and UsesDocument5 pagesNative Elements Group - Properties and UsesBroadsageNo ratings yet
- Gold SourceDocument2 pagesGold SourceAjoc NoelNo ratings yet
- SPLM #2 (Copy 1)Document12 pagesSPLM #2 (Copy 1)adel antegraNo ratings yet
- What Are The Main Ores of IronDocument8 pagesWhat Are The Main Ores of IronGian Francis Eizeckel RomeroNo ratings yet
- Metallurgy lecture notes on principles of materials productionDocument40 pagesMetallurgy lecture notes on principles of materials productionNorman AdiNo ratings yet
- Ores and Economic Minerals - DR - Helen LangDocument5 pagesOres and Economic Minerals - DR - Helen LangLuis PaezNo ratings yet
- MetalsDocument2 pagesMetalssong MusicNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction - 2012 - Applied Welding Engineering V1Document3 pagesChapter 1 Introduction - 2012 - Applied Welding Engineering V1James LeonNo ratings yet
- Types of Ferrous and Non-Ferrous MetalsDocument4 pagesTypes of Ferrous and Non-Ferrous MetalsJerod RobertsNo ratings yet
- SGS MIN Tech Pub 2004 03 Process Mineralogy LR en 11 09Document16 pagesSGS MIN Tech Pub 2004 03 Process Mineralogy LR en 11 09Taeu YuNo ratings yet
- Advanced Geology of Ore DepositsDocument41 pagesAdvanced Geology of Ore DepositsPatchole Alwan TiarasiNo ratings yet
- NZ IronsandDocument16 pagesNZ IronsandSimon FidesNo ratings yet
- SulfideDocument1 pageSulfidetedy yidegNo ratings yet
- Application of MetalsDocument132 pagesApplication of MetalsMohammed Ashiq0% (1)
- Assignment CompioDocument4 pagesAssignment CompioDominic CompioNo ratings yet
- CH 4 Production of Iron and SteelDocument12 pagesCH 4 Production of Iron and SteelTadesse AyalewNo ratings yet
- Economic Geology: Silver and BerylliumDocument10 pagesEconomic Geology: Silver and BerylliumBARKAVENo ratings yet
- Rock Forming Minerals: RocksDocument3 pagesRock Forming Minerals: RocksUche S OsigweNo ratings yet
- Minerals ESLDocument27 pagesMinerals ESLJovan AbordajeNo ratings yet
- Identifying Archaeological MetalDocument4 pagesIdentifying Archaeological MetalAantchuNo ratings yet
- 5 Sulfides (GL 204 My Lecture) - HandoutDocument16 pages5 Sulfides (GL 204 My Lecture) - HandoutStanliNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project. RohitDocument23 pagesChemistry Project. Rohitprabinpandey.ogiNo ratings yet
- Study of Constituents of Alloys: Swarnprastha Public School Chemistry ProjectDocument13 pagesStudy of Constituents of Alloys: Swarnprastha Public School Chemistry Projectvineetsinghal83% (12)
- Feasible One To Employ.Document18 pagesFeasible One To Employ.Akhil SuseelNo ratings yet
- Origin and Classification of Iron Ore Deposits The Iron Ore Deposits of India Can Be Broadly Divided in To The Following Six Groups On The Basis of Mode of Occurrence and OriginDocument1 pageOrigin and Classification of Iron Ore Deposits The Iron Ore Deposits of India Can Be Broadly Divided in To The Following Six Groups On The Basis of Mode of Occurrence and OriginJewel AssociateNo ratings yet
- Iron Ore Deposits of IndiaDocument11 pagesIron Ore Deposits of IndiadeshmukhgeolNo ratings yet
- 03 - Kelompok Oksida Dan HidroksidaDocument59 pages03 - Kelompok Oksida Dan HidroksidaRoges tomara mahesaNo ratings yet
- OXIDESDocument6 pagesOXIDESayesha.brianne.de.guzmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05Document20 pagesChapter 05Khan MARCEL NjiNo ratings yet
- A Short History of MetalsDocument7 pagesA Short History of MetalsMichael Douglas Souza RamosNo ratings yet
- Iron and The EnvironmentDocument15 pagesIron and The EnvironmentIzzy ConceptsNo ratings yet
- Minerals Classification GuideDocument11 pagesMinerals Classification Guidesubham kunduNo ratings yet
- Little Rocks & Small Minerals! | Rocks And Mineral Books for Kids | Children's Rocks & Minerals BooksFrom EverandLittle Rocks & Small Minerals! | Rocks And Mineral Books for Kids | Children's Rocks & Minerals BooksRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- The Gold Rush: The Uses and Importance of Gold - Chemistry Book for Kids 9-12 | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandThe Gold Rush: The Uses and Importance of Gold - Chemistry Book for Kids 9-12 | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Fighting Tips and TricksDocument18 pagesFighting Tips and TricksZdravko VidakovicNo ratings yet
- What Is New in Delphi 5Document11 pagesWhat Is New in Delphi 5Zdravko VidakovicNo ratings yet
- Delphi 8 - Migrating Delphi Applications To The Microsoft .NET Framework With Delphi 8Document22 pagesDelphi 8 - Migrating Delphi Applications To The Microsoft .NET Framework With Delphi 8Remy MartinNo ratings yet
- By Marco Cantù (Free) Chapter 3: The Delphi LanguageDocument41 pagesBy Marco Cantù (Free) Chapter 3: The Delphi LanguageZdravko VidakovicNo ratings yet
- Self-Hypnosis Induction: by Charles E. Henderson, PH.DDocument5 pagesSelf-Hypnosis Induction: by Charles E. Henderson, PH.DZdravko VidakovicNo ratings yet
- Invar PRDocument2 pagesInvar PRZdravko VidakovicNo ratings yet
- T-72 Tank Barrel Bore Wear: Robert Jankovych and Stanislav BeerDocument8 pagesT-72 Tank Barrel Bore Wear: Robert Jankovych and Stanislav BeerZdravko VidakovicNo ratings yet
- Bolts (Japan Tower Association)Document9 pagesBolts (Japan Tower Association)Zdravko VidakovicNo ratings yet
- The Optics and Electrodynamics of Moving BodiesDocument37 pagesThe Optics and Electrodynamics of Moving BodiesZdravko VidakovicNo ratings yet
- DIN 824-Paper FoldingDocument1 pageDIN 824-Paper FoldingZdravko VidakovicNo ratings yet
- Lottery Mathematics - WikipediaDocument7 pagesLottery Mathematics - WikipediaZdravko VidakovicNo ratings yet
- Examples of Tower LoadingsDocument13 pagesExamples of Tower LoadingsZdravko VidakovicNo ratings yet
- FeldsparDocument2 pagesFeldsparZdravko VidakovicNo ratings yet
- T-72 Tank Barrel Bore Wear: Robert Jankovych and Stanislav BeerDocument8 pagesT-72 Tank Barrel Bore Wear: Robert Jankovych and Stanislav BeerZdravko VidakovicNo ratings yet
- Limestone: Limestone Is A Sedimentary Rock Composed Largely of The MineralDocument4 pagesLimestone: Limestone Is A Sedimentary Rock Composed Largely of The MineralZdravko VidakovicNo ratings yet
- Dark rock-forming silicate minerals found in igneous and metamorphic rocksDocument1 pageDark rock-forming silicate minerals found in igneous and metamorphic rocksZdravko VidakovicNo ratings yet
- U ChartsDocument21 pagesU ChartsjoelNo ratings yet
- Mudstone: Lyme Regis Sedimentary Rock Clays Muds Grain Size MM Clay Minerals FissilityDocument1 pageMudstone: Lyme Regis Sedimentary Rock Clays Muds Grain Size MM Clay Minerals FissilityZdravko VidakovicNo ratings yet
- Dolerite: Igneous Rock Plagioclase Labradorite Pyroxene Ophitic Stone and Stone ProductsDocument1 pageDolerite: Igneous Rock Plagioclase Labradorite Pyroxene Ophitic Stone and Stone ProductsZdravko VidakovicNo ratings yet
- SiltstoneDocument1 pageSiltstoneZdravko VidakovicNo ratings yet
- Caliche: A Soil Containing Impure LimestoneDocument1 pageCaliche: A Soil Containing Impure LimestoneZdravko VidakovicNo ratings yet
- GD&T Reference ChartDocument1 pageGD&T Reference ChartZdravko VidakovicNo ratings yet
- Hartbeesthoek 94 (The New South African Datum)Document15 pagesHartbeesthoek 94 (The New South African Datum)Zdravko VidakovicNo ratings yet
- Fastener glossary guideDocument32 pagesFastener glossary guideHugo RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Beam Deflection FormulaeDocument2 pagesBeam Deflection Formulae7575757575100% (6)
- GratingDocument36 pagesGratingRay Gong100% (1)
- Engineering Properties of MaterialsDocument6 pagesEngineering Properties of Materialspapilolo2008No ratings yet
- GratingDocument36 pagesGratingRay Gong100% (1)
- Lecture 17: Design and Static Strength of Welded JointsDocument36 pagesLecture 17: Design and Static Strength of Welded Jointssprashant5No ratings yet