0% found this document useful (0 votes)
226 views2 pagesPneumonia Pathophysiology (Patient Based) : Non-Modifiable: Modifiable
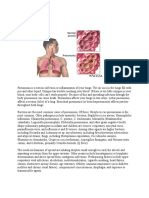
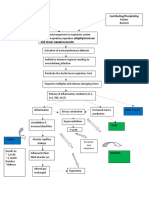
This document summarizes the pathophysiology of pneumonia. Pneumonia can be caused by both non-modifiable factors like age and weather, as well as modifiable factors like environment, socioeconomic status, and oral hygiene. The disease process begins when microbes are aspirated or inspired into the lungs and the body's defenses fail, allowing invasion of the lower respiratory tract. This triggers an immune response involving B-cells, antibodies, and chemical mediators that cause vasodilation, increased blood flow, congestion, fluid accumulation in the alveoli, and ultimately lung consolidation and difficulty breathing. Pneumonia results and requires medical management of symptoms.
Uploaded by
YVETTE CLAIRE BORRESCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
226 views2 pagesPneumonia Pathophysiology (Patient Based) : Non-Modifiable: Modifiable
This document summarizes the pathophysiology of pneumonia. Pneumonia can be caused by both non-modifiable factors like age and weather, as well as modifiable factors like environment, socioeconomic status, and oral hygiene. The disease process begins when microbes are aspirated or inspired into the lungs and the body's defenses fail, allowing invasion of the lower respiratory tract. This triggers an immune response involving B-cells, antibodies, and chemical mediators that cause vasodilation, increased blood flow, congestion, fluid accumulation in the alveoli, and ultimately lung consolidation and difficulty breathing. Pneumonia results and requires medical management of symptoms.
Uploaded by
YVETTE CLAIRE BORRESCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd