Professional Documents
Culture Documents
It Is of Two Types Natural Disaster Man - Made Disaster
It Is of Two Types Natural Disaster Man - Made Disaster
Uploaded by
Dimpal ChoudharyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
It Is of Two Types Natural Disaster Man - Made Disaster
It Is of Two Types Natural Disaster Man - Made Disaster
Uploaded by
Dimpal ChoudharyCopyright:
Available Formats
INTRODUCTION
A disaster is a serious disruption occurring over a short or long period of time that causes
widespread human, material, economic or environmental loss which exceeds the ability of the
affected community or society to cope using its own resources. Developing countries suffer the
greatest costs when a disaster hits – more than 95 percent of all deaths caused by hazards occur
in developing countries, and losses due to natural hazards are 20 times greater (as a percentage of
GDP) in developing countries than in industrialized countries No matter what society disasters
occur in, they tend to induce change in government and social life. They may even alter the
course of history by broadly affecting entire populations and exposing mismanagement or
corruption regardless of how tightly information is controlled in a society.
DEFINITION
A disaster is an occurrence disrupting the normal conditions of existence and causing a level of
suffering that exceeds the capacity of adjustment of the affected community.
A sudden accident or a natural catastrophe that causes great damage or loss of life.
CLASSIFICATION OF DISASTER
It is of two types
Natural disaster
Man –made disaster
NATURAL DISASTER –
A natural disaster is a natural process or phenomenon that may cause loss of life, injury or
other health impacts, property damage, loss of livelihoods and services, social and economic
disruption, or environmental damage.
Various phenomena like earthquakes, landslides, volcanic eruptions, floods, hurricanes,
tornadoes, blizzards, tsunamis, cyclones and pandemics are all natural hazards that kill
thousands of people and destroy billions of dollars of habitat and property each year.
However, the rapid growth of the world's population and its increased concentration often in
hazardous environments has escalated both the frequency and severity of disasters. With the
tropical climate and unstable landforms, coupled with deforestation, unplanned growth
proliferation, non-engineered constructions make the disaster-prone areas more vulnerable.
Natural disaster (earthquake)
MAN-MADE DISASTER –
Human-instigated disasters are the consequence of technological or human hazards.
Examples include stampedes, fires, transport accidents, industrial accidents, oil spills,
terrorist attacks, nuclear explosions/nuclear radiation. War and deliberate attacks may also be
put in this category.
Other types of induced disasters include the more cosmic scenarios of catastrophic global
warming, nuclear war, and bioterrorism.
One opinion argues that all disasters can be seen as human-made, due to human failure to
introduce appropriate emergency management measures.
ON THE BASIS OF SPEED OF ONSET
Sudden onset disaster
Slow onset disaster
PHASES OF DISASTER MANAGEMENT
You might also like
- Care Plan On PneumoniaDocument22 pagesCare Plan On PneumoniaDimpal Choudhary100% (4)
- Procedure On Chest PhysiotherapyDocument13 pagesProcedure On Chest PhysiotherapyDimpal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Disaster Notes ImpDocument30 pagesDisaster Notes Imppuneet017No ratings yet
- Disaster ManagementDocument3 pagesDisaster ManagementManpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Disaster ManagementDocument17 pagesDisaster ManagementThilaga SenthilmuruganNo ratings yet
- Geography Project: Introduction (Page 2)Document3 pagesGeography Project: Introduction (Page 2)Anisha MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Disaster ManagementDocument118 pagesDisaster ManagementParth SharmaNo ratings yet
- Mama Baby Care Cambridge SchoolDocument6 pagesMama Baby Care Cambridge SchoolRaahin RahimNo ratings yet
- Climate and Geology. NaturalDocument10 pagesClimate and Geology. NaturalDare RedevilNo ratings yet
- Types of DisastersDocument11 pagesTypes of DisastersKimberly Sheen Medina YamsonNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Disaster Management Concept and MeaningDocument8 pagesAn Introduction To Disaster Management Concept and MeaningReinan Ezekiel Sotto LlagasNo ratings yet
- Reference 2 - Natural DisasterousDocument20 pagesReference 2 - Natural DisasterousRohan G RaikarNo ratings yet
- Disaster Unit1Document30 pagesDisaster Unit1Sri Bala Vidyadhari ChintaNo ratings yet
- Foundation Course - Disaster Management NOTESDocument54 pagesFoundation Course - Disaster Management NOTESnandhu ragavanNo ratings yet
- Disaster Management. BS Psychology 4th Semester. University of Swat.Document6 pagesDisaster Management. BS Psychology 4th Semester. University of Swat.Fazle KhaliqNo ratings yet
- Disaster Management NOTESDocument56 pagesDisaster Management NOTESSanthya HarshithaNo ratings yet
- Meaning of Disaster:: Accidents Fires ExplosionsDocument43 pagesMeaning of Disaster:: Accidents Fires Explosionsjinalpanchal962No ratings yet
- DRRRDocument13 pagesDRRRCrezyle Jan CabibihanNo ratings yet
- NSTP 2 DisasterDocument1 pageNSTP 2 DisasterMae MendozaNo ratings yet
- 06 Chapter1Document12 pages06 Chapter1Shrey NirmalNo ratings yet
- Disaster ManagementDocument21 pagesDisaster ManagementShrinivas PrabhuneNo ratings yet
- DRRR ReviewerDocument12 pagesDRRR ReviewerJoanah AnogNo ratings yet
- Environmental Hazards Assignment Winter Quarter 2015-16Document32 pagesEnvironmental Hazards Assignment Winter Quarter 2015-16Muhammad AbbasNo ratings yet
- Lecture 33-40 Disaster ManagementDocument35 pagesLecture 33-40 Disaster Managementdave pitumenNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument20 pagesUnit INikitha Shinde100% (1)
- DRRR Lesson 1Document2 pagesDRRR Lesson 1corteztricia45No ratings yet
- DPPM Module 1Document15 pagesDPPM Module 1Dev KalraNo ratings yet
- Accidents, Fires, ExplosionsDocument3 pagesAccidents, Fires, ExplosionsPraveen Kumar JhaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science & Disaster ManagementDocument104 pagesEnvironmental Science & Disaster ManagementJyothis T SNo ratings yet
- CJC SummerDocument3 pagesCJC SummerMedelyn MoresNo ratings yet
- DRRR Mod 1 & 2Document5 pagesDRRR Mod 1 & 2Jazmin CruzNo ratings yet
- What Is Disaster ManagementDocument5 pagesWhat Is Disaster Management9536909268No ratings yet
- DPPM Unit 1 Study MaterialDocument46 pagesDPPM Unit 1 Study MaterialJyothi GNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument7 pagesUntitledLen ShaoxiNo ratings yet
- Narrative Report in NSTPDocument2 pagesNarrative Report in NSTPLenoj OlarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Disaster Prevention and Mitigation 001Document27 pagesChapter 8 Disaster Prevention and Mitigation 001Jamaica RamosNo ratings yet
- Natural Disaster Management FDocument134 pagesNatural Disaster Management FLords Porseena100% (1)
- Disaster Nursing: "Doing The Best For The Most, With The Least, by The Fewest"Document16 pagesDisaster Nursing: "Doing The Best For The Most, With The Least, by The Fewest"ChannelGNo ratings yet
- DRR 1-2Document11 pagesDRR 1-2MAFNo ratings yet
- Sean Lejee O. Bajan October 22, 2018 Grade 12 - Integrity Reflection PaperDocument2 pagesSean Lejee O. Bajan October 22, 2018 Grade 12 - Integrity Reflection PaperSeanLejeeBajanNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of Disaster and Disaster Risk: Prepared By: Mateo T. Tadong, LPTDocument19 pagesBasic Concept of Disaster and Disaster Risk: Prepared By: Mateo T. Tadong, LPTElia Saph MoonNo ratings yet
- Disaster MPH Sem1Document7 pagesDisaster MPH Sem1Manav MPHNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document104 pagesModule 4akhil krishnanNo ratings yet
- 1 ST HANDOUTDRRRDocument3 pages1 ST HANDOUTDRRRAljhon Matthew DizonNo ratings yet
- DRRRDocument26 pagesDRRRJemimah FV100% (1)
- A Project Report On EarthquakeDocument43 pagesA Project Report On EarthquakeBiswajit RouthNo ratings yet
- Disaster Risk Reduction: 2 Sem - 3 QuarterDocument2 pagesDisaster Risk Reduction: 2 Sem - 3 QuarterMaryNo ratings yet
- What Is DisasterDocument2 pagesWhat Is DisasterRabbit RibbitNo ratings yet
- Im MDM 3 J VCHRN 37 C F455Document88 pagesIm MDM 3 J VCHRN 37 C F455Jayanth ThammineniNo ratings yet
- Impacts of Natural HazardDocument3 pagesImpacts of Natural HazardCASTRO, JANELLA T.No ratings yet
- DRRR ReviewerDocument24 pagesDRRR ReviewerAnna SpadillaNo ratings yet
- DRRR PresentationDocument10 pagesDRRR Presentationleilay003No ratings yet
- A Disaster Is A SuddenDocument3 pagesA Disaster Is A Suddenzitadewi435No ratings yet
- Disaster Readiness and Risk Reduction 1and 2Document8 pagesDisaster Readiness and Risk Reduction 1and 2dianapanaga20No ratings yet
- ManDocument2 pagesManbhavsartejNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Climate Change and Disaster Risk ManagementDocument4 pagesBasic Concepts of Climate Change and Disaster Risk ManagementJuliet Alexia PamittanNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document8 pagesUnit 3Parth SharmaNo ratings yet
- Week 15 Drought ManagementDocument13 pagesWeek 15 Drought ManagementSahir SamiNo ratings yet
- Sayli SM Sem 2Document22 pagesSayli SM Sem 2SayliKadveNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of Disaster and Disaster RiskDocument31 pagesBasic Concept of Disaster and Disaster RiskCzarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- Disaster and Disaster RiskDocument34 pagesDisaster and Disaster RiskAudrey VicenteNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Artery Disease: Nikhil Vaishnav M.Sc. (Nursing)Document70 pagesPeripheral Artery Disease: Nikhil Vaishnav M.Sc. (Nursing)Dimpal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Goal Planning Rationale Implementation Evaluation Subjective DataDocument4 pagesNursing Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Goal Planning Rationale Implementation Evaluation Subjective DataDimpal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
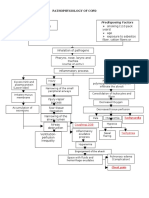
- Streptococcus Pneumonae: Pathophysiology of CopdDocument1 pageStreptococcus Pneumonae: Pathophysiology of CopdDimpal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of PneumoniaDimpal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Goal Planning Rationale Implementation Evaluation Subjective DataDocument5 pagesNursing Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Goal Planning Rationale Implementation Evaluation Subjective DataDimpal Choudhary100% (1)
- Procedure On Lumber PunctureDocument8 pagesProcedure On Lumber PunctureDimpal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
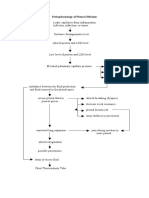
- Pathophysiology of Pleural EffusionDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Pleural EffusionDimpal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary FibrosisDocument4 pagesPulmonary FibrosisDimpal Choudhary100% (2)
- Lumber Puncture ProcedureDocument8 pagesLumber Puncture ProcedureDimpal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument82 pagesCongenital Heart DiseaseDimpal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Uninodular Goitre: One Thyroid Nodule Can Be Either Inactive, or Active (Toxic)Document6 pagesUninodular Goitre: One Thyroid Nodule Can Be Either Inactive, or Active (Toxic)Dimpal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Nursing EducationDocument19 pagesNursing EducationDimpal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Bladder IrrigationDocument5 pagesBladder IrrigationDimpal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Self-Directed LearningDocument18 pagesSelf-Directed LearningDimpal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Polycythemia Vera: What Are The Symptoms of Polycythemia?Document10 pagesPolycythemia Vera: What Are The Symptoms of Polycythemia?Dimpal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Preparation OF Group Work: Netaji Subhash College of NursingDocument7 pagesPreparation OF Group Work: Netaji Subhash College of NursingDimpal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Introduction-:: Time Specific Objective Content Av AidsDocument7 pagesIntroduction-:: Time Specific Objective Content Av AidsDimpal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Tsunami Research Paper ConclusionDocument7 pagesTsunami Research Paper Conclusionfyswvx5b100% (1)
- Explanation TextDocument8 pagesExplanation TextAi sholihahNo ratings yet
- MELC 2 - Day 6Document36 pagesMELC 2 - Day 6JUSTINE C. DE VILLANo ratings yet
- Presentation 6 Fukushima Nuclear Power Plant Accident Imperial College London Sae OchiDocument26 pagesPresentation 6 Fukushima Nuclear Power Plant Accident Imperial College London Sae OchiKlea RoseniNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Science Assessment TOS (2021-2022)Document2 pages2nd Quarter Science Assessment TOS (2021-2022)Mariel Grace JameroNo ratings yet
- Cucuta S Earthquake in 1881Document5 pagesCucuta S Earthquake in 1881Michell Fernanda López SierraNo ratings yet
- LEVEL 3 Interactive Display: Unit 8Document1 pageLEVEL 3 Interactive Display: Unit 8Damyan Alex Cuesta SalazarNo ratings yet
- Mindanao Community School: Lester Victor M.BendovalDocument3 pagesMindanao Community School: Lester Victor M.BendovalavinmanzanoNo ratings yet
- Geo Cala 3Document6 pagesGeo Cala 3MatizasucceedNo ratings yet
- Division of Iligan City Acelo C. Badelles Sr. Memorial High SchoolDocument1 pageDivision of Iligan City Acelo C. Badelles Sr. Memorial High SchoolJM Robles RemoladoNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering: Dr. Deepankar ChoudhuryDocument23 pagesGeotechnical Earthquake Engineering: Dr. Deepankar ChoudhuryadssadasdsadNo ratings yet
- Illuminati Freemason SecretsDocument5 pagesIlluminati Freemason SecretsChristopher Michael Simpson100% (2)
- Digital Seismic Network: To Map Himalayan Orogen and Seismic HazardDocument2 pagesDigital Seismic Network: To Map Himalayan Orogen and Seismic Hazardgeetika kharkwalNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Hazards: - Ground Shaking - Tsunami - Landslides and Rockfalls - LiquefactionDocument15 pagesEarthquake Hazards: - Ground Shaking - Tsunami - Landslides and Rockfalls - LiquefactionAnna Daniella LunaNo ratings yet
- Performance Based Seismic Design of Reinforced Concrete Structures With ACI 318-14Document9 pagesPerformance Based Seismic Design of Reinforced Concrete Structures With ACI 318-14mehdi taheriNo ratings yet
- Obadiah Final Manuscript 16 01Document50 pagesObadiah Final Manuscript 16 01Zenaida FeliasNo ratings yet
- Coupled Effective Stress Analysis of Sand Liquefaction For Petobo Site Post M 7.4 Palu EarthquakeDocument12 pagesCoupled Effective Stress Analysis of Sand Liquefaction For Petobo Site Post M 7.4 Palu EarthquakeDedi ApriadiNo ratings yet
- Design Criteria - International Water PowerDocument6 pagesDesign Criteria - International Water PowerMatthias GoltzNo ratings yet
- 1ST SUMMATIVE TEST FOR G10finalDocument2 pages1ST SUMMATIVE TEST FOR G10finalcherish austriaNo ratings yet
- PHIVOLCS Earthquake Intensity ScaleDocument2 pagesPHIVOLCS Earthquake Intensity ScaleZairah Ann BorjaNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes and EarthDocument4 pagesEarthquakes and EarthMarla Grace Estanda AbdulganiNo ratings yet
- 4 Exercise 15.1Document2 pages4 Exercise 15.1SHAFA AULIANo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document3 pagesChapter 8DANIEL DIBITAUNo ratings yet
- Perceptions of Post-Disaster Housing Safety in Future Typhoons and EarthquakesDocument30 pagesPerceptions of Post-Disaster Housing Safety in Future Typhoons and EarthquakesKaye OleaNo ratings yet
- NDRRMCDocument213 pagesNDRRMCJohn MichaelMackayNo ratings yet
- New Ormoc City National High School: Grade Level Content Standard Performance StandardDocument5 pagesNew Ormoc City National High School: Grade Level Content Standard Performance StandardMarifeNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 5esDocument16 pagesLesson Plan 5esEldrine Manzano BalberonaNo ratings yet
- Earthquake, Weathering and ErosionDocument61 pagesEarthquake, Weathering and ErosionPatricia Sofia DizonNo ratings yet
- San Andreas Fault ReportDocument6 pagesSan Andreas Fault Reportnokthor.tripura1No ratings yet
- Disaster Management (Vikrant)Document19 pagesDisaster Management (Vikrant)Vikrant ChaudharyNo ratings yet