Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tense Cheat Sheets
Uploaded by
johnstonOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tense Cheat Sheets
Uploaded by
johnstonCopyright:
Available Formats
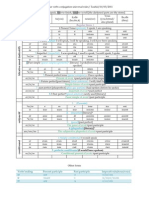
Simple Past Present Perfect Present Future Past Future
indicatif passé antérieur
(indicatif passé simple) (passé composé) (indicatif présent) (indicatif futur simple) (indicatif futur antérieur)
I had spoke j'eus parlé I spoke je parlai I have spoken J'ai parlé I speak je parle I will speak je parlerai I will have spoken J'aurai parlé
you (fam) tu eus parlé you (fam) tu parlas you (fam) tu as parlé you (fam) tu parles you (fam) tu parleras you (fam) tu auras parlé
he/she/it il/elle eut parlé he/she/it il parla he/she/it il a parlé he/she/it il parle he/she/it il parlera he/she/it il aura parlé
we nous eûmes parlé we nous parlâmes we nous avons parlé we nous parlons we nous parlerons we nous aurons parlé
you (unfam/pl) vous eûtes parlé you (unfam/pl) vous parlâtes you (unfam/pl) vous avez parlé you (unfam/pl) vous parlez you (unfam/pl) vous parlerez you (unfam/pl) vous aurez parlé
they ils/elles eurent parlé they ils parlèrent they ils ont parlé they ils parlent they ils parleront they ils auront parlé
If the verb uses être (to be): -ir verbs: -is,-is,-it,-imes,-ites,-irent If the verb uses être (to be): -ir verbs: -s,-s,-t,-ssons,-ssez,-ssent Keep the verb ending and add: If the verb uses être (to be):
fus,fus,fut,fûmes,fûtes,furent -re verbs: -is,-is,-it,-imes,-ites,-irent suis,es,est,sommes,êtes,sont -re verbs: -s,-s,--,-ons,-ez,-ent -ir verbs: -ai,-as,-a,-ons,-ez,-ont serai,seras,sera,serons,serez,seront
plus past particle plus past particle -re verbs: -ai,-as,-a,-ons,-ez,-ont plus past particle
The French past anterior is the literary Most common passé composé verbs
equivalent of the past perfect. Used in The passé simple, simple past or w/ être: advenir, aller, arriver,
often follows: après que (after),
literature and historical accounts to indicate preterite, also called the passé défini is décéder, descendre, devenir, entrer, Note: To conjugate French compound
aussitôt que (as soon as), dès
an action in the past that occurred before the literary equivalent of the passé intervenir, monter, mourir, naître, French has around 300 irregular verbs tenses, you need an auxiliary verb, usually
que (as soon as), espérer que (to
another action in the past. Because it is a composé in the French language, used partir, passer, parvenir, provenir, (or "group 3"). avoir (to have) or être (to be), plus the past
hope that), lorsque (when), quand
literary tense, you don't need to practice predominantly in formal writing (including redevenir, remonter, renaître, rentrer, participle of the desired verb.
(when), une fois que (once), etc.
conjugating it, but it is important for you to history and literature) and formal speech. ressortir, rester, retourner, revenir,
be able to recognize it sortir, survenir, tomber, venir.
<---------------------------------------------------------------- PAST ---------------------
INDICATIVE
PRESENT------> FUTURE----------------------------------->
Pluperfect Imperfect Past Imperative Present Imperative Present Participle Past Conditional
(indicatif plus-que-parfait) (indicatif imparfait) (impératif passé) (impératif) (participe présent) (Second Past)
I had spoken J'avais parlé I was speaking je parlais aie parlé! sois tu parle! I had spoken j'eusse parlé
parlant
you (fam) tu avais parlé you (fam) tu parlais ayons parlé! soyons nous parlons! you (fam) tu eusses parlé
he/she/it il avait parlé he/she/it il parlait ayez parlé! soyez vous parlez! Past Participle he/she/it il eût parlé
we nous avions parlé we nous parlions (participe passé) we nous eussions parlé
In French, the imperative mood expresses an order, request, or
you (unfam/pl) vous aviez parlé you (unfam/pl) vous parliez you (unfam/pl) vous eussiez parlé
directive and is created with regular verbs by using the verb directly.
they ils avaient parlé they ils parlaient parlé ayant parlé they ils eussent parlé
The imperative drops the subject, uses the present tense of a verb and
If the verb uses être (to be): -ir verbs: -ais,-ais,-ait,-ions,-iez,-aient uses the conjugations of three subject pronouns: tu (familiar), vous
Past Participle (reg verbs) formed by dropping infinitive ending of a verb
étais,étais,était,étions,étiez,étaient plus (unfamiliar), and nous (when including yourself in the group). Regular -
-re verbs: -ais,-ais,-ait,-ions,-iez,-aient and adding: [é] for –ER verbs, [i] for –IR verbs, [u] for –RE verbs
past particle er, -ir, and -re verbs follow the same pattern in commands.
Past Imperfect irregular verbs to know (past participle): acquérir
One of the clauses shows a Yellow indicates 1st year students must know these tenses (acquis), apprendre (appris), atteindre (atteint), avoir (eu), boire (bu),
The subjunctive is needed when the Wish/will, Emotion, Impersonal and conjugations. Ex: comprendre (compris), conduire (conduit), connaître (connu), craindre
sentence contains two different clauses Present
expressions, Recommendations, & Imperfect of these 2 auxiliary verbs (craint), croire (cru), découvrir (découvert), devoir (dû), dire (dit), écrire
(a dependent and a main clause) with have: avoir (to have) ai,as,a,avons,avez,ont
Doubt/desire/denial, or one of the (écrit), être (été), faire (fait), finir (fini), instruire (instruit), joindre (joint),
two different subjects. The clauses are clauses requires the subjunctive in
am/is/are: être (to be) suis,es,est,sommes,êtes,sont lire (lu), mettre (mis), ouvrir (ouvert), paraître (paru), parler (parlé),
joined by que (that) or, by qui (who) --> some other respect. had: avoir (to have) avais,avais,avait,avions,aviez,avaient peindre (peint), pouvoir (pu), prendre (pris), produire (produit), savoir
Memory Aid: (WEIRD) was/were: être (to be) étais,étais,était,étions,étiez,étaient (su), souffrir (souffert), suivre (suivi), tenir (tenu), vendre (vendu), venir
(venu), voir (vu), vouloir (voulu).
<----------------------------------------------------------------------------- PAST -------------------
PRESENT------> CONDITIONAL
Pluperfect Subjunctive Imperfect Subjunctive Past Subjunctive Present Subjunctive Conditional Past Conditional
(subjonctif plus-que-parfait) (subjonctif imparfait) (subjonctif passé) (subjonctif présent) (conditionnel présent) (First Past)
that...I had
spoken que j'eusse parlé that I spoke que je parlasse that I had spoke que j'aie parlé that I speak que je parle I would speak je parlerais I would have spoken J'aurais parlé
SUBJUNCTIVE
that you (fam) que tu eusses parlé that you (fam) que tu parlasses that you (fam) que tu aies parlé that you (fam) que tu parles you (fam) tu parlerais you (fam) tu aurais parlé
that he/she/it qu'il eût parlé that he/she/it qu'il parlât that he/she/it qu'il ait parlé that he/she/it qu'il parle he/she/it il parlerait he/she/it il aurait parlé
que nous ayons
that we que nous eussions parlé that we que nous parlassions that we parlé that we que nous parlions we nous parlerions we nous aurions parlé
que vous ayez
that you que vous eussiez parlé that you que vous parlassiez that you parlé that you que vous parliez you (unfam/pl) vous parleriez you (unfam/pl) vous auriez parlé
that they qu'ils eussent parlé that they qu'ils parlassent that they qu'ils aient parlé that they qu'ils parlent they ils parleraient they ils auraient parlé
-ir and -er verbs: same endings If the verb uses être (to be): Keep the verb ending and add: Keep the verb ending and add: If the verb uses être (to be):
-ir / -er verbs:
-isse,-isses,-ît,-issions,-issiez,-issent sois,sois,soit,soyons,soyez,soient -ir verbs: same -ir verbs: same serais,serais,serait,serions,seriez,seraient
plus past particle -re verbs: same -re verbs: same plus past particle
You might also like
- Latin Verb-Conjugations: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideFrom EverandLatin Verb-Conjugations: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- The SubjunctiveDocument11 pagesThe Subjunctiveandreea.dimasNo ratings yet
- Passé Composé - EtreDocument4 pagesPassé Composé - EtreAvani KukrejaNo ratings yet
- Frases Comunes Antes Del SubjuntivoDocument3 pagesFrases Comunes Antes Del SubjuntivoVanessa TrujilloNo ratings yet
- Texs French GrammarDocument136 pagesTexs French Grammarnedaftt100% (1)
- Tex's French GrammarDocument136 pagesTex's French GrammarRaluca BalanNo ratings yet
- Passé ComposéDocument5 pagesPassé Composéalex1971No ratings yet
- Passé Composé - AvoirDocument4 pagesPassé Composé - AvoirAvani KukrejaNo ratings yet
- Passé Composé - AvoirDocument4 pagesPassé Composé - AvoirAvani KukrejaNo ratings yet
- Le Passé Composé........ PastDocument8 pagesLe Passé Composé........ PastSamira YağlıcaNo ratings yet
- Portuguese/Contents/Irregular Verbs: TensesDocument3 pagesPortuguese/Contents/Irregular Verbs: TensesMiguel Angel Galvan Higuera JrNo ratings yet
- Sum Active IndicativeDocument1 pageSum Active Indicativearcheogirl100% (1)
- Week 3 Notes The Three Conjugations of The Present Indicative of Regular Verbs Ending in Ar Er and IrDocument6 pagesWeek 3 Notes The Three Conjugations of The Present Indicative of Regular Verbs Ending in Ar Er and IrJohnmarcNo ratings yet
- Guidelines On Verbs and Tense 2Document3 pagesGuidelines On Verbs and Tense 2sonal benganiNo ratings yet
- Introduction Into Basic StructureDocument4 pagesIntroduction Into Basic StructureUcha Mutiara AnggelaNo ratings yet
- Le Passe ComposeDocument13 pagesLe Passe Composemalr86No ratings yet
- French, Italian, Spanish GrammarDocument9 pagesFrench, Italian, Spanish GrammarJustin Morgan100% (8)
- SpanishDocument11 pagesSpanishJohn Mark LoberanesNo ratings yet
- 02 - Imperative MoodDocument6 pages02 - Imperative MoodVajresh N.No ratings yet
- Quick Recap On French Past Tense: Avoir or ÊtreDocument8 pagesQuick Recap On French Past Tense: Avoir or Êtreayshen gahramanovaNo ratings yet
- Passe ComposeDocument5 pagesPasse ComposeAnjel EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Passato ProssimoDocument3 pagesPassato ProssimovmarinelliNo ratings yet
- Passé Composé (Avoir) PDFDocument4 pagesPassé Composé (Avoir) PDFEla DasNo ratings yet
- FR 106 French Verb ReviewDocument20 pagesFR 106 French Verb Reviewjoy PrinceNo ratings yet
- Spanish Verb ConjugationsDocument4 pagesSpanish Verb ConjugationsScottNo ratings yet
- The Imparfait: NotesDocument3 pagesThe Imparfait: NotesAnish Kantheti100% (1)
- Passé Composé (French PronunciationDocument10 pagesPassé Composé (French PronunciationAnonymous 54AmhqqNo ratings yet
- Spanish Grammar For English SpeakersDocument30 pagesSpanish Grammar For English Speakersbiffin100% (1)
- SpanishDocument11 pagesSpanishJohn Mark LoberanesNo ratings yet
- Verb TenseDocument16 pagesVerb Tensemp SinghNo ratings yet
- Present Tense of Regular VerbsDocument6 pagesPresent Tense of Regular VerbsbobNo ratings yet
- Latin Participles Grammar PDFDocument3 pagesLatin Participles Grammar PDFDbishNo ratings yet
- Fola 312 Prelim Reviewer PDFDocument16 pagesFola 312 Prelim Reviewer PDFcarlalacayangaNo ratings yet
- Passé Composé Avec Être: Remember Which Verbs Use Être? Continue ReadingDocument3 pagesPassé Composé Avec Être: Remember Which Verbs Use Être? Continue ReadingAshutosh HNo ratings yet
- Verb Conjugation #7 Present With A Future Value: Lesson NotesDocument4 pagesVerb Conjugation #7 Present With A Future Value: Lesson NotesTamim RahmanNo ratings yet
- Verb TenseDocument16 pagesVerb TenseRose Bt MustafhaNo ratings yet
- French DuoDocument26 pagesFrench DuoDaniela CascoNo ratings yet
- Week 13 Time and TenseDocument5 pagesWeek 13 Time and TenseMihaela Codrina AntonNo ratings yet
- List of Irregular Subjunctive VerbsDocument7 pagesList of Irregular Subjunctive VerbsShanta MathaiNo ratings yet
- Le Joual Quebec Slang WikiDocument12 pagesLe Joual Quebec Slang WikiThe CheetahNo ratings yet
- Appendix SBPDocument33 pagesAppendix SBPMaged LamiyNo ratings yet
- The Most Common SuffixesDocument49 pagesThe Most Common SuffixesMi MiNo ratings yet
- Zeit For MenDocument2 pagesZeit For MenEXO-L J.M.No ratings yet
- Principal Parts of Greek VerbsDocument2 pagesPrincipal Parts of Greek VerbsLuis BravoNo ratings yet
- French NotesDocument9 pagesFrench NotesLuna DollyNo ratings yet
- French Regular Verbs Conjugation Universal RulesDocument2 pagesFrench Regular Verbs Conjugation Universal RulesMd. Makhjanul Islam Tauhid100% (1)
- Understanding Passe Compose Fact FileDocument2 pagesUnderstanding Passe Compose Fact FileruthbitutuogotiNo ratings yet
- Za OIB 58991531150Document21 pagesZa OIB 58991531150jopa_cvitkovicNo ratings yet
- Verb ReviewDocument16 pagesVerb Reviewga3farahmadoni100% (1)
- Jenny Spanish Preterito Indefinido 277-281Document5 pagesJenny Spanish Preterito Indefinido 277-281George SmithNo ratings yet
- Conversational Past - Separable Prefix Verbs Grimm: Verbs Das Perfekt - Trennbare VerbenDocument5 pagesConversational Past - Separable Prefix Verbs Grimm: Verbs Das Perfekt - Trennbare VerbenRam Sharat Reddy BNo ratings yet
- Verbs TensesDocument2 pagesVerbs TensesInés Sevillano BorobioNo ratings yet
- Le Futur SimpleDocument3 pagesLe Futur SimpleElouise FourieNo ratings yet
- El Presente de Indicativo - Verbos RegularesDocument7 pagesEl Presente de Indicativo - Verbos RegularesMadalina DobindaNo ratings yet
- Avoir Et Être Cours GrammaireDocument31 pagesAvoir Et Être Cours GrammaireSafae NassifNo ratings yet
- Passe SimpleDocument4 pagesPasse SimpleAnjel EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Online Notebook by SlidesgoDocument49 pagesOnline Notebook by SlidesgoIvy Mie SagangNo ratings yet
- Research II: Quarter 1 - Module 4: Methods in Scientific Research Reports (IMRAD)Document28 pagesResearch II: Quarter 1 - Module 4: Methods in Scientific Research Reports (IMRAD)johnston100% (1)
- Research II: Quarter 1 - Module 4: Methods in Scientific Research Reports (IMRAD)Document28 pagesResearch II: Quarter 1 - Module 4: Methods in Scientific Research Reports (IMRAD)johnston100% (1)
- Sponges, Cnidarians, EchinodermsDocument8 pagesSponges, Cnidarians, EchinodermsjohnstonNo ratings yet
- Golden Apple Snail Infestation On The Rice Bowl Capitals of The Philippines Preview - PDFDocument5 pagesGolden Apple Snail Infestation On The Rice Bowl Capitals of The Philippines Preview - PDFjohnstonNo ratings yet
- 9.5 .R SpaceReviewDocument17 pages9.5 .R SpaceReviewRusherNo ratings yet
- Captain - Marvel.2019.HDTC .X264-AdsFreeDocument124 pagesCaptain - Marvel.2019.HDTC .X264-AdsFreejohnstonNo ratings yet
- All The World's A StageDocument2 pagesAll The World's A StagejohnstonNo ratings yet
- The Positive and Negative Impact of Inclusive LeadershipDocument9 pagesThe Positive and Negative Impact of Inclusive LeadershipAmbreen ZainebNo ratings yet
- The Challenge To Live According To The Gospel: 21 February 2021 1st Sunday of Lent Year BDocument4 pagesThe Challenge To Live According To The Gospel: 21 February 2021 1st Sunday of Lent Year BSam MaestroNo ratings yet
- SN Quick Reference 2018Document6 pagesSN Quick Reference 2018pinakin4uNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Tle Grade 8Document4 pagesFinal Exam Tle Grade 8John leo Claus67% (3)
- Tea Board of India PDFDocument18 pagesTea Board of India PDFDebasish RazNo ratings yet
- New Criticism Hills Like White Elephants FinalDocument4 pagesNew Criticism Hills Like White Elephants Finalapi-313631761No ratings yet
- Pengaruh PH Ekstraksi Terhadap Rendemen, Sifat Fisiko-Kimia Dan Fungsional Konsentrat Protein KACANG GUDE (Cajanus Cajan (L.) Millsp.)Document11 pagesPengaruh PH Ekstraksi Terhadap Rendemen, Sifat Fisiko-Kimia Dan Fungsional Konsentrat Protein KACANG GUDE (Cajanus Cajan (L.) Millsp.)Rezaa RezNo ratings yet
- HLSS 310 Critical Infrastructure ProtectionDocument12 pagesHLSS 310 Critical Infrastructure ProtectionMoffat HarounNo ratings yet
- Mutant ChroniclesDocument3 pagesMutant ChroniclesZoth BernsteinNo ratings yet
- Alup Allegro 37 AC IE3 400V 4-13bar 50Hz Metric Technical Data ENDocument2 pagesAlup Allegro 37 AC IE3 400V 4-13bar 50Hz Metric Technical Data ENBosznay ZoltánNo ratings yet
- Understanding EarsDocument1 pageUnderstanding EarsmerkyworksNo ratings yet
- Certified Vendors As of 6 17 22Document18 pagesCertified Vendors As of 6 17 22Harry ConnerNo ratings yet
- MikroC PRO For DsPIC30Document9 pagesMikroC PRO For DsPIC30ivcal20No ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in English 2Document9 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in English 2RENELYN PANSIPANSI100% (1)
- Chemistry For Engineers - Week 4 and 5 - Chemical BondDocument162 pagesChemistry For Engineers - Week 4 and 5 - Chemical BondHồng NhungNo ratings yet
- Gopesh Obalappa Pilot ResumeDocument3 pagesGopesh Obalappa Pilot ResumeGopesh ObalappaNo ratings yet
- ADCD LowDocument8 pagesADCD LowrahulmultivisionNo ratings yet
- BLE Catalogue 2013Document21 pagesBLE Catalogue 2013Shahina Parvin ShaikNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan Ke 12 - The Passive VoiceDocument5 pagesPertemuan Ke 12 - The Passive VoiceZarNo ratings yet
- PlayStation MagazineDocument116 pagesPlayStation MagazineFrank Costello67% (3)
- Group 6G Revised Research Manuscript 1Document57 pagesGroup 6G Revised Research Manuscript 1Mc Rollyn VallespinNo ratings yet
- Tahmina Ferdousy Jhumu: HND Btec Unit 15 Psychology For Health and Social CareDocument29 pagesTahmina Ferdousy Jhumu: HND Btec Unit 15 Psychology For Health and Social CareNabi BoxNo ratings yet
- AQA Power and Conflict GCSE Revision Guide LADocument49 pagesAQA Power and Conflict GCSE Revision Guide LAderaw11557No ratings yet
- Activate My Win 7 Pro Product KeyDocument4 pagesActivate My Win 7 Pro Product KeydoktauNo ratings yet
- SIP Debugging Commands Overview - Cisco CommunityDocument5 pagesSIP Debugging Commands Overview - Cisco CommunitysenthilNo ratings yet
- 18TE72 - Wireless Communication Experiential Learning ReportDocument10 pages18TE72 - Wireless Communication Experiential Learning ReportRitika BakshiNo ratings yet
- A Lonely Quest For Facts On Genetically Modified CropsDocument5 pagesA Lonely Quest For Facts On Genetically Modified Cropsbrkica2011No ratings yet
- Prakhar Gupta Epics and Empires-Game of Thrones Make Up EssayDocument5 pagesPrakhar Gupta Epics and Empires-Game of Thrones Make Up EssayGat DanNo ratings yet
- 978-0393617542 Research MethodsDocument18 pages978-0393617542 Research MethodsReccebacaNo ratings yet
- Screen 2014 Uricchio 119 27Document9 pagesScreen 2014 Uricchio 119 27NazishTazeemNo ratings yet