0% found this document useful (0 votes)
126 views6 pagesSlab and Footing Load Distribution Analysis
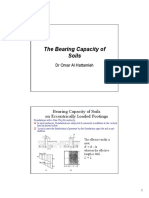
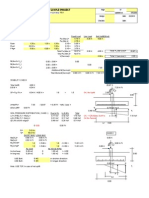
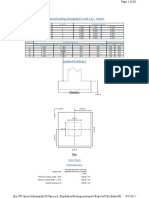
This document discusses slab load distribution and footing design for a combined footing. It calculates the total load, required footing area, center of gravity, and eccentricity. It then checks the allowable bearing capacity considering soil conditions. It also calculates values for a scenario where land is unavailable for the full footing length, and checks column capacities. The key results are: the required footing area is 190 sqft, the eccentricity is 0.37ft, and the allowable bearing capacity is greater than the calculated capacity of 2.2 ksf given in the soil report.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
126 views6 pagesSlab and Footing Load Distribution Analysis
This document discusses slab load distribution and footing design for a combined footing. It calculates the total load, required footing area, center of gravity, and eccentricity. It then checks the allowable bearing capacity considering soil conditions. It also calculates values for a scenario where land is unavailable for the full footing length, and checks column capacities. The key results are: the required footing area is 190 sqft, the eccentricity is 0.37ft, and the allowable bearing capacity is greater than the calculated capacity of 2.2 ksf given in the soil report.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd