Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Maslow's Hierarchy of Educational Objectives
Uploaded by
comelec carmenOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Maslow's Hierarchy of Educational Objectives
Uploaded by
comelec carmenCopyright:
Available Formats
ARTCHELYN R.
AGUA
TCC
PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION
EDUC 10
1. How can you make assessments precise, accurate and dependable?
Answer:
Assessment can be made precise, accurate and dependable only if what are to be
achieved are clearly stated and feasible. The learning targets, involving knowledge,
reasoning, skills, products and effects, need to be stated in behavioural terms which
denote something which can be observed through the behaviour of the students.
2. Discuss Maslow’s Hierarchy of educational objectives at the
educational level. Give examples.
Answer:
Starting at the bottom of the pyramid (Figure 1), physiological needs are the first
priority and must be satisfied first. These needs include nourishment, sleep, clothing, and
shelter. People must have these basic needs met in order to focus on anything else –
otherwise, their actions will focus solely on meeting these physiological requirements.
They are the top priority and are therefore the most important driving factor for human
beings. If a person is hungry, they will ignore any other wants or wishes to focus on
satisfying their hunger. If a student is hungry, they could exhibit distracting or rule-
breaking behavior because education is not their priority – hunger is. A student might fall
asleep in class instead of working on their assignments because they lost sleep the
previous night. In this example, the student would naturally prioritize sleep over
education.
Once physiological needs are satisfied, the next priority is safety. Safety needs are
usually environmental, which includes a student’s home environment, school
environment, and any other environment they’re regularly a part of. If the student is
having personal issues at home (for example, arguing parents, parents struggling with
addiction, lack of parental structure, etc.) or they live in a dangerous area, they will have
difficulty learning because their basic safety needs have not been met. Similarly, if the
student is being bullied or if they don’t feel accepted and liked by their educator, they
will struggle to learn and complete their work. Their priority will be acquiring safety.
Students thrive on predictability and structure, and they associate these factors with a
feeling of safety. They do best with no disruptions in their routines. If they lack a routine,
or if there are factors threatening their routines, they may feel unsafe and apprehensive.
This can cause the student to perform poorly.
After physiological and safety requirements have been met, love and a sense of
belonging become the priority. This applies to family and friend relationships. A student
may develop their sense of belonging through joining clubs, volunteering, participating in
church groups, or making other group-centered commitments. When a person does not
feel loved or does not feel like they belong, they crave affection or acceptance in group
settings. The need for love and belonging may be forgotten, but it can be just as critical to
a student as their physiological requirements.
Self-esteem is the next need that must be met. Self-esteem involves individuality, respect
for others, accomplishment, and confidence. Most people are extremely critical of
themselves, which stems from their own evaluation of self-accomplishment and potential.
Self-esteem can be two-fold. First, people will crave accomplishment, confidence,
competence, and fortitude. Secondly, they will yearn for importance, appreciation,
acknowledgment, and status. When all of these needs are met, people will feel adequate,
capable, strong, and worthy. If these needs are not satisfied, people will feel incompetent,
unprotected, and unimportant.
These first four needs can all be considered deprivation needs. If these needs are not
satisfied, those shortcomings will motivate people to focus on meeting their highest-
priority needs. One more need follows these deprivation needs, and that is self-
actualization. This is an aspiration to fulfill one’s own potential. This need is not driven
by inadequacy, but instead by a craving for self-improvement. Maslow suggests that very
few people ever attain this level. Self-actualized people tend to be impulsive,
independent, analytical, and realistic.
3. Differentiate between skills, competencies and abilities target,
product, output, and project targets.
Answer:
A major difference between skills and competencies is one of scope. Skills are
specific to a task, while competencies incorporate a set of skills with abilities and
knowledge. Skills are just one of three facets that make up a competency; the other two
are knowledge and abilities.
Products, Outputs and Projects Targets are no differences because they are both
tangible and concrete evidence of a student’s ability. A clear target for products and
projects need to clearly specify the level of workmanship of such projects.
4. How can you determine an appropriate assessment procedure or
method?
Answer:
Assessment methods have to be appropriate all the time. This is not a choice but a
must in order to make assessment valid. Appropriateness of Assessment Methods
Appropriateness of Assessment determines if an assessment tool is suitable for the type
of topic used as learning target the following are the kinds of assessment methods
1) Written-Response Method
2) Product Rating Scales
3) Performance Tests
4) Oral Questioning
5) Observation and Self Reports.
This method may require short answers or answers which expresses the thoughts of the
students through written formats while delivery of question may occur as written or
orally.
5. Construct a table of specification and indicate its part.
6. A test may be reliable but not necessarily valid. Is it possible for a test
to be valid but not reliable, discuss.
Answer:
If the scale is reliable it tells you the same weight every time you step on it as
long as your weight has not actually changed. However, if the scale is not working
properly, this number may not be your actual weight. If that is the case, this is an
example of a scale that is reliable, or consistent, but not valid. For the scale to be valid
and reliable, not only does it need to tell you the same weight every time you step on the
scale, but it also has to measure your actual weight.
Switching back to testing, the situation is essentially the same. A test can be reliable,
meaning that the test-takers will get the same score no matter when or where they take it,
within reason of course. But that doesn't mean that it is valid or measuring what it is
supposed to measure. A test can be reliable without being valid. However, a test cannot
be valid unless it is reliable.
7. Compare analytic versus holistic rubric.
Answer:
Depending on your goals as you evaluate papers, you'll want to consider whether to
assign a "holistic score" to a paper or to analyze specific elements of students writing to
give more detailed response. In brief, holistic scoring gives students a single, overall
assessment score for the paper as a whole. Analytic scoring provides students with at
least a rating score for each criterion, though often the rubric for analytic scoring offers
teachers enough room to provide some feedback on each criterion.
8. Explain extensively process oriented learning competencies.
Answer:
Process-oriented performance-based assessment is concerned with the actual task
performance rather than the output or product of the activity. Learning Competencies are
defined as groups or clusters of skills and abilities needed for a particular task
9. Discuss the most effective and reliable assessment.
Answer:
The most effective and reliable assessment are Reliability and Validity because It is
common among instructors to refer to types of assessment, whether a selected response
test (i.e. multiple-choice, true/false, etc.) or a constructed response test that requires
rubric scoring (i.e. essays, performances, etc.) as being reliable and valid. Technically, it
is not the test itself but rather the resulting test score or rubric score that must have a high
degree of reliability and validity. Reliability refers to the degree to which scores from a
particular test are consistent from one use of the test to the next. Validity refers to the
degree to which a test score can be interpreted and used for its intended purpose.
Reliability is a very important piece of validity evidence. A test score could have high
reliability and be valid for one purpose, but not for another purpose.
10.What is assessment? Explain extensively.
Answer:
In education, the term assessment refers to the wide variety of methods or tools
that educators use to evaluate, measure, and document the academic readiness, learning
progress, skill acquisition, or educational needs of students.
You might also like
- Evaluation Activity: in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements in The Course MSE GE 222 (Advance Educational Psychology)Document7 pagesEvaluation Activity: in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements in The Course MSE GE 222 (Advance Educational Psychology)Ruztom John TamayoNo ratings yet
- Educ 5 1Document5 pagesEduc 5 1Eulimer LoayonNo ratings yet
- 3761 EaDocument17 pages3761 EaM Noaman AkbarNo ratings yet
- Educ 106 Module-3Document31 pagesEduc 106 Module-3Roderick Viloria MiloNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Principles of High Quality AssessmentDocument22 pagesModule 3 Principles of High Quality AssessmentJasmine Nicole OsallaNo ratings yet
- Learning Module 3 ASSESSMENT IN LEARNING 1Document22 pagesLearning Module 3 ASSESSMENT IN LEARNING 1Galutera, Rachel Ann B.No ratings yet
- Importance of Affective Assessments: Item Writing GuidelinesDocument11 pagesImportance of Affective Assessments: Item Writing GuidelinesMariaceZette RapaconNo ratings yet
- Principle of Language Assessment 2003Document6 pagesPrinciple of Language Assessment 2003Esteban ManzanaresNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Authentic Assessment in The Classroom.Document16 pagesModule 1 Authentic Assessment in The Classroom.Analisa SalangusteNo ratings yet
- Educ 8 NotesDocument6 pagesEduc 8 Notesiancarlo824No ratings yet
- School TestingDocument7 pagesSchool TestingEva Noviana BudiyantiNo ratings yet
- Student-Centered Classroom Assessment MethodsDocument3 pagesStudent-Centered Classroom Assessment MethodsQotrun NadaNo ratings yet
- Midterm ReviewerDocument7 pagesMidterm Reviewerjhonmichaelatienza3No ratings yet
- 679 - How Learning WorksDocument5 pages679 - How Learning Worksapi-301951044No ratings yet
- POINTERS FOR TEST 311 PrelimDocument20 pagesPOINTERS FOR TEST 311 PrelimMary DenizeNo ratings yet
- Educ. 6 - Pearl Joy C. AntonaDocument2 pagesEduc. 6 - Pearl Joy C. AntonaPearl Joy AntonaNo ratings yet
- 6507-1.pdf MA PDFDocument19 pages6507-1.pdf MA PDFNazia ZamanNo ratings yet
- Fair Assessment Practices: Giving Students Equitable Opportunties To Demonstrate LearningDocument6 pagesFair Assessment Practices: Giving Students Equitable Opportunties To Demonstrate LearningWinie Jane LizardoNo ratings yet
- Importance of Validity and Reliability in Classroom AssessmentsDocument13 pagesImportance of Validity and Reliability in Classroom AssessmentsCacai PhotosNo ratings yet
- Activity 2sir BenDocument4 pagesActivity 2sir BenGenesis AbrasaldoNo ratings yet
- Subjective and ObjectiveDocument5 pagesSubjective and Objectiveعباس معنى100% (2)
- LECTURE NOTES 7B - Importance of Validity and Reliability in Classroom AssessmentsDocument13 pagesLECTURE NOTES 7B - Importance of Validity and Reliability in Classroom AssessmentsTheresa Nova Dologmandin-VillaesterNo ratings yet
- Weebly Act 3Document2 pagesWeebly Act 3api-264280897No ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Reflection 2 1 2Document4 pagesLesson 2 - Reflection 2 1 2Mikken Casing0% (1)
- Brother NathanDocument13 pagesBrother NathanNathaniel MingoNo ratings yet
- Authentic AssessmentDocument12 pagesAuthentic AssessmentRitzmund Diaz100% (2)
- Assess Student Learning in TestsDocument5 pagesAssess Student Learning in TestscherylpuebloNo ratings yet
- Assessment Learning 1Document4 pagesAssessment Learning 1rieann leonNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 06 APRIL 2018 UNIQUE NUMBER: 694117Document5 pagesAssignment 2 06 APRIL 2018 UNIQUE NUMBER: 694117Ntokozo MthantiNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Learning 1 Arnold B. Salazar MODULE 2, Lesson 2Document12 pagesAssessment of Learning 1 Arnold B. Salazar MODULE 2, Lesson 2Karen Mae Sarmiento TanNo ratings yet
- Mother TongueDocument8 pagesMother TongueLyra MoncadaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Element Reliability and Validity: Instructions and Answers For TeachersDocument26 pagesLesson Element Reliability and Validity: Instructions and Answers For TeachersNhatran93No ratings yet
- Buku Kompen (123 141)Document19 pagesBuku Kompen (123 141)Moch Aira SoemiratNo ratings yet
- M1authenticassessmentintheclassroom 1 230126022923 90e287a4Document33 pagesM1authenticassessmentintheclassroom 1 230126022923 90e287a4Marjorie MalvedaNo ratings yet
- Authentic AssessmentDocument7 pagesAuthentic AssessmentSafaa Mohamed Abou KhozaimaNo ratings yet
- AOLDocument7 pagesAOLjimwelluismagno27No ratings yet
- What Is Authentic Assessment?Document4 pagesWhat Is Authentic Assessment?Maribeth CuestaNo ratings yet
- Psychological TestingDocument7 pagesPsychological TestingjoyesmonpulickalNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Difference Between Assessment and EvaluationDocument20 pagesUnderstanding the Difference Between Assessment and EvaluationDivyaNo ratings yet
- Cep2 Content Module 13Document23 pagesCep2 Content Module 13Melanie TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Evaluating Our Instruction: SurveysDocument24 pagesEvaluating Our Instruction: SurveysGanesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Module 25Document5 pagesUnit 4 Module 25jhonrainielnograles52No ratings yet
- CST Students with Disabilities: New York State Teacher CertificationFrom EverandCST Students with Disabilities: New York State Teacher CertificationNo ratings yet
- What is Authentic Assessment? Defining Attributes and ExamplesDocument14 pagesWhat is Authentic Assessment? Defining Attributes and ExamplesNarthaniel PameronNo ratings yet
- What Is Authentic AssessmentDocument5 pagesWhat Is Authentic AssessmentBrian Brangzkie TorresNo ratings yet
- AOL 2 RHONADocument6 pagesAOL 2 RHONAjimwelluismagno27No ratings yet
- Module 2Document9 pagesModule 2cherry ann lubidNo ratings yet
- Assessment Module 2Document16 pagesAssessment Module 2Angelica BautistaNo ratings yet
- Marking, Grading and Giving FeedbackDocument18 pagesMarking, Grading and Giving FeedbackLiss Cabanilla GarcíaNo ratings yet
- AIL 1 Activity 1Document2 pagesAIL 1 Activity 1johnkennethdelacruz003No ratings yet
- Gallavan (Sec) Chapter 1Document18 pagesGallavan (Sec) Chapter 1Ryan Mag-usaraNo ratings yet
- Performance-Based Assessment for 21st-Century SkillsFrom EverandPerformance-Based Assessment for 21st-Century SkillsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- Educational Measurement and Evaluation: Leonila P. Santiago Portia O. VillavicencioDocument85 pagesEducational Measurement and Evaluation: Leonila P. Santiago Portia O. VillavicencioFerlyn Claire Basbano LptNo ratings yet
- Content Assessments For 10th Grade World HistoryDocument9 pagesContent Assessments For 10th Grade World Historyapi-680031225No ratings yet
- What Is Item AnalysisDocument3 pagesWhat Is Item AnalysisjolaiNo ratings yet
- Gose Educ 105Document19 pagesGose Educ 105api-569343867No ratings yet
- Principles of High Quality Assessment ExplainedDocument3 pagesPrinciples of High Quality Assessment ExplainedJulie Ann ParicaNo ratings yet
- Kepy - 01 - 06 - 24 - EtextDocument10 pagesKepy - 01 - 06 - 24 - Etextmradul guptaNo ratings yet
- Passing Exams with Confidence Strategies for Study Habit ImprovementFrom EverandPassing Exams with Confidence Strategies for Study Habit ImprovementRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Groups of Students Are Consistently Scoring Lower On Standardized English Tests? If A School Is Treat Different Types of Students Unequally?Document7 pagesGroups of Students Are Consistently Scoring Lower On Standardized English Tests? If A School Is Treat Different Types of Students Unequally?Sardar Ahsan suduzaiNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippine1Document4 pagesRepublic of The Philippine1comelec carmenNo ratings yet
- Quarterly Status Report On ID (Annex F)Document1 pageQuarterly Status Report On ID (Annex F)comelec carmenNo ratings yet
- QUARTERLY REPORT On Indigenuos People and Internally Displaced PersonsDocument1 pageQUARTERLY REPORT On Indigenuos People and Internally Displaced Personscomelec carmenNo ratings yet
- Statistical Data of Registration 21OCT2019Document1 pageStatistical Data of Registration 21OCT2019comelec carmenNo ratings yet
- Number of Detainee Registered VotersDocument1 pageNumber of Detainee Registered Voterscomelec carmenNo ratings yet
- January 6Document1 pageJanuary 6comelec carmenNo ratings yet
- ROADSHOW Program Page 2Document1 pageROADSHOW Program Page 2comelec carmenNo ratings yet
- Minutes of The Election Registration Board (Erb) Meeting On October 21, 2019 Cortes, Surigao Del SurDocument2 pagesMinutes of The Election Registration Board (Erb) Meeting On October 21, 2019 Cortes, Surigao Del Surcomelec carmenNo ratings yet
- Rooad Show Program Openning RemarksDocument1 pageRooad Show Program Openning Remarkscomelec carmenNo ratings yet
- Tarpauline SizeDocument1 pageTarpauline Sizecomelec carmenNo ratings yet
- Sangguniang Kabataan ApplicantDocument1 pageSangguniang Kabataan Applicantcomelec carmenNo ratings yet
- MR of Koppel 2HP Office AirconDocument4 pagesMR of Koppel 2HP Office Airconcomelec carmenNo ratings yet
- Property Issue Slip: QTY Description Date of Property Unit Value Total Value Purchase NumberDocument1 pageProperty Issue Slip: QTY Description Date of Property Unit Value Total Value Purchase Numbercomelec carmenNo ratings yet
- Report On Waste Materials - 1hp Panasonic AirconDocument2 pagesReport On Waste Materials - 1hp Panasonic Airconcomelec carmenNo ratings yet
- Common Poster AreasDocument1 pageCommon Poster Areascomelec carmenNo ratings yet
- Marjoricar A. Navarro 55-77-51-95-03-81-11-02Document1 pageMarjoricar A. Navarro 55-77-51-95-03-81-11-02comelec carmenNo ratings yet
- Task Force Tear DownDocument1 pageTask Force Tear Downcomelec carmenNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Appearance: Office of The Election OfficerDocument1 pageCertificate of Appearance: Office of The Election Officercomelec carmenNo ratings yet
- Peace and Order Situation Report For The Month of November 2012Document1 pagePeace and Order Situation Report For The Month of November 2012comelec carmenNo ratings yet
- Cortes PWD ReportDocument1 pageCortes PWD Reportcomelec carmenNo ratings yet
- LGU Casual RequestDocument1 pageLGU Casual Requestcomelec carmenNo ratings yet
- Logbook of Filed Certificate of Candidacy: Office of The Election OfficerDocument1 pageLogbook of Filed Certificate of Candidacy: Office of The Election Officercomelec carmenNo ratings yet
- Certification: Republic of The Philippines Commission On Elections Office of The Election Officer Cortes, Surigao Del SurDocument1 pageCertification: Republic of The Philippines Commission On Elections Office of The Election Officer Cortes, Surigao Del Surcomelec carmenNo ratings yet
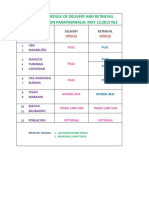
- BEIs PROPOSED DELIVERY N RETRIEVAL MAY132013NLEDocument1 pageBEIs PROPOSED DELIVERY N RETRIEVAL MAY132013NLEcomelec carmenNo ratings yet
- Application For Leave - EADocument1 pageApplication For Leave - EAcomelec carmenNo ratings yet
- Blank Cert. of AppearanceDocument1 pageBlank Cert. of Appearancecomelec carmenNo ratings yet
- Application For Leave - EODocument1 pageApplication For Leave - EOcomelec carmenNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Appearance: Office of The Election OfficerDocument1 pageCertificate of Appearance: Office of The Election Officercomelec carmenNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Appearance: Office of The Election OfficerDocument1 pageCertificate of Appearance: Office of The Election Officercomelec carmenNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Appearance: Office of The Election OfficerDocument1 pageCertificate of Appearance: Office of The Election Officercomelec carmenNo ratings yet
- 30DayWM Call17 With Dr. Joe RubinoDocument35 pages30DayWM Call17 With Dr. Joe Rubinolisa252100% (1)
- Overcoming barriers to effective communicationDocument4 pagesOvercoming barriers to effective communicationMary Grace YañezNo ratings yet
- Calista RoyDocument16 pagesCalista RoyKyla A. CasidsidNo ratings yet
- Validity and ReliabilityDocument6 pagesValidity and Reliabilitywedad jumaNo ratings yet
- BearsinthenightDocument8 pagesBearsinthenightAntwain UtleyNo ratings yet
- Leson Planning Think 5A/5BDocument3 pagesLeson Planning Think 5A/5BDavid NerioNo ratings yet
- Tactile Defensiveness PDFDocument7 pagesTactile Defensiveness PDFCristi BacuNo ratings yet
- Ashtavakra GitaDocument47 pagesAshtavakra GitaSwami Hanuman DasNo ratings yet
- FIDP for Fundamentals of Accountancy, Business and ManagementDocument3 pagesFIDP for Fundamentals of Accountancy, Business and ManagementByerus Tv100% (4)
- English KSSR Year 5Document2 pagesEnglish KSSR Year 5Anita LeeNo ratings yet
- Articulo - Ntersection of Ubuntu Pedagogy and Social Justice +Document8 pagesArticulo - Ntersection of Ubuntu Pedagogy and Social Justice +Jesus GuillermoNo ratings yet
- History of OBDocument44 pagesHistory of OBSaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- The Seven-Step Process in The Hypothetico-Deductive MethodDocument3 pagesThe Seven-Step Process in The Hypothetico-Deductive MethodALI KHANNo ratings yet
- Triad Color TestDocument37 pagesTriad Color TestC.O.M.A research -stopalienabduction-0% (1)
- Lesson Plan Form: Ccss - Ela-Literacy - Rf.K.1 Ccss - Ela-Literacy - Rf.K.1.ADocument4 pagesLesson Plan Form: Ccss - Ela-Literacy - Rf.K.1 Ccss - Ela-Literacy - Rf.K.1.Aapi-511791998No ratings yet
- Final Summative TaskDocument6 pagesFinal Summative TaskKanan PatelNo ratings yet
- Singular VS Plural and Present Progressive (Maha)Document3 pagesSingular VS Plural and Present Progressive (Maha)Psych 0216No ratings yet
- Structure and Grammar GuideDocument4 pagesStructure and Grammar GuideRaden Dicky Wirawan ListiandokoNo ratings yet
- Cochlear ImplantsDocument53 pagesCochlear ImplantsSovitJungBaralNo ratings yet
- Methods of Teaching MathematicsDocument13 pagesMethods of Teaching MathematicsSadiq Merchant94% (53)
- Subject ComplementsDocument2 pagesSubject Complementsedithaenriquez0% (1)
- Key A2 Basic Level English Exam PDFDocument4 pagesKey A2 Basic Level English Exam PDFakhilesh sahooNo ratings yet
- Raa-EDDE210-Module2 Activity2-4 Principles of Online LearningDocument1 pageRaa-EDDE210-Module2 Activity2-4 Principles of Online LearningfilipinianaNo ratings yet
- Kindergarten Fine Motor SkillsDocument94 pagesKindergarten Fine Motor SkillsVero MoldovanNo ratings yet
- Tecnology Humanities PDFDocument57 pagesTecnology Humanities PDFMaya ErnieNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 10 e 6 Mar 2019Document7 pagesLesson Plan 10 e 6 Mar 2019Sabina Lucia GrapiniNo ratings yet
- Elaina Katz - Ilp Teacher Leadership ProjectDocument6 pagesElaina Katz - Ilp Teacher Leadership Projectapi-417029122No ratings yet
- Evaluation Rating Sheet For Nonprint LRsDocument9 pagesEvaluation Rating Sheet For Nonprint LRsAriel PalerNo ratings yet
- Kant-Critique of JudgmentDocument3 pagesKant-Critique of JudgmentDavid Fernyhough0% (2)
- Prepositions ExplainedDocument27 pagesPrepositions ExplainedVanshNo ratings yet