Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Surgical Instrumentation Return Demonstration PDF
Uploaded by
wokorow0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
333 views2 pagesOriginal Title
SURGICAL INSTRUMENTATION RETURN DEMONSTRATION.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
333 views2 pagesSurgical Instrumentation Return Demonstration PDF
Uploaded by
wokorowCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
SURGICAL INSTRUMENTATION RETURN DEMONSTRATION
I. GATHER THE MATERIALS
II. PURPOSES OF SURGICAL OPERATION
• DIAGNOSTIC- to confirm
• EXPLORATORY- to determine the extent
• CURATIVE- ABLATIVE- removal of an organ
• CURATIVE- CONSTRUCTIVE- repair of organ
• CURATIVE- RECONSTRUCTIVE- repair of damaged organ
• PALLIATIVE- relieve distressing signs
III. STAGES OF OPERATION
• PRE-OPERATIVE PHASE
• INTRAOPERATIVE PHASE
• POST-OPERATIVE PHASE
IV. FUNCTIONS OF SCRUB NURSE
• Maintain integrity, safety and efficiency of sterile field
• Prepare, arrange instrument supplies
• Assist in operation providing sterile instruments and supplies
V. FUNCTIONS OF CIRCULATING NURSE
• Application of nursing process, coordinating all team members
• Maintenance of a safe and comfortable environment for the patient
• Provision of assistance to any member of the OR team
• Maintenance of communication link between members
VI. PRINCIPLES OF STERILE TECHNIQUE
1. Only sterile items are used within the sterile field.
2. If you are in doubt about the sterility of anything, consider it unsterile.
3. Gowns are considered sterile ONLY from the waist to shoulder level in front and themselves.
4. sterile persons keep hands in sight and at or above waist level.
5. Hands are kept from the face and never held under the axillary’s region.
6. Changing table levels are avoided.
7. Items dropped below waist level are considered unsterile.
8. Tables are considered sterile only at table level.
9. Anything that extends below the table level is considered unsterile.
10. In unfolding sterile drape, the part that drops below the table level is considered unsterile.
11. Sterile persons touch only sterile items or areas, unsterile persons touch only unsterile items or
areas.
12. Unsterile persons should not directly get in contact with the sterile field. Use sterile transfer
forceps.
13. Unsterile persons a void reaching over a sterile field and sterile persons avoid leaning over an
unsterile field.
14. In pouring into a sterile field and sterile persons avoid leaning over the basin to avoid over
reaching.
15. The scrub nurse should set the basin or glasses to be filled at the edge of the sterile table.
16. Surgeons turn away from the sterile field and to have perspiration removed from the brow.
17. Sterile persons keep well within the sterile area.
18. Sterile persons pass each other back to back.
19. Sterile persons turn back to non-sterile person or area when passing.
20. Unsterile persons avoid sterile areas.
21. Unsterile person should maintain at least 1foot distance from any sterile area.
22. Unsterile persons never walk between 2 sterile areas.
VII. CLASSIFICATION OF INSTRUMENTS
• Cutting- knife,scalpel, scissors,
• Clamping and occluding- hemostatic forceps, mixter, Ochsner,
• Grasping and holding- adson forceps (toothted, toothless), thumb forceps, tissue forceps
• Exposing and retracting- self retaining (mastoid, gelpi,) non retaining (army navy,
Richardson)
VIII. IDENTIFICATION OF BLADES
• Blade number 10 11 12 15 is for handle number 3, cut delicate tissues
• Blade number 23 24 25 is for handle number 4, cut tough tissues
IX. PUT THE BLADE IN THE HOLDER
X. IDENTIFICATION OF INSTRUMENTS IN THE STERILE FIELD
XI. DISPOSE THE SHARPS AND WASH THE EQUIPMENT
You might also like
- Oral Suctioning With RationaleDocument3 pagesOral Suctioning With RationaleKaguraNo ratings yet
- DOH programs teaching guideDocument2 pagesDOH programs teaching guideCharissa Magistrado De LeonNo ratings yet
- Oxygen TherapyDocument3 pagesOxygen Therapymarie100% (3)
- Care of Elderly Patients: Role of NursesDocument2 pagesCare of Elderly Patients: Role of Nursespatel h100% (1)
- Malaria PosterDocument1 pageMalaria PosterTommaso ForzaNo ratings yet
- Cite One Role of The Community To Health and ExplainDocument3 pagesCite One Role of The Community To Health and ExplainAbegyl Nicole FiguraNo ratings yet
- And Standards of Practice EmphasizesDocument15 pagesAnd Standards of Practice EmphasizesKrizia R. PingkeNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 3-What's My LineDocument3 pagesWorksheet 3-What's My LineKate MassonNo ratings yet
- Community Phc2 RleDocument12 pagesCommunity Phc2 Rleefermin_lovely100% (1)
- Nurses Assigned in Rural ServicesDocument3 pagesNurses Assigned in Rural ServicescubezeroNo ratings yet
- Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State (HHS)Document21 pagesHyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State (HHS)Malueth AnguiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Research 1: Module 4: Conceptual Phase Week 6: The Research ProblemDocument4 pagesNursing Research 1: Module 4: Conceptual Phase Week 6: The Research ProblemLEMUEL GLENN BAUTISTANo ratings yet
- Group 4 NCM 114Document14 pagesGroup 4 NCM 114ESTELLE VERA O. VELEZNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Community Health NursingDocument8 pagesFundamentals of Community Health NursingAziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Family health nursing and malnutritionDocument5 pagesFamily health nursing and malnutritionLea TanNo ratings yet
- Lab Clin Clin Tasks Attempted 1 2 3 4 5 6 7: ST ND RD TH TH TH THDocument4 pagesLab Clin Clin Tasks Attempted 1 2 3 4 5 6 7: ST ND RD TH TH TH THRichard Patterson100% (1)
- Medical-Surgical Nursing 1: Pamantasan NG Lungsod NG MaynilaDocument3 pagesMedical-Surgical Nursing 1: Pamantasan NG Lungsod NG MaynilaAye DumpNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes NCM 119Document23 pagesLecture Notes NCM 119Angelie PantajoNo ratings yet
- COMMUNITY HEALTH NURSING CONCEPTS Topic 2Document25 pagesCOMMUNITY HEALTH NURSING CONCEPTS Topic 2Ciedelle Honey Lou DimaligNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 MidtermDocument25 pagesNCM 112 MidtermJan Charlie Sophia100% (1)
- Nur 111 Session 1 Sas 1Document8 pagesNur 111 Session 1 Sas 1Zzimply Tri Sha UmaliNo ratings yet
- A Beautiful Mind ReviewDocument1 pageA Beautiful Mind ReviewEmmanuel NacionNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Client With Life Threatening Conditions Acute Ill, Multi-Organ Problems High Acuity and Emergency SituationsDocument43 pagesNursing Care of Client With Life Threatening Conditions Acute Ill, Multi-Organ Problems High Acuity and Emergency SituationsGlaiza Fabia100% (1)
- Operating Room Instruments GuideDocument8 pagesOperating Room Instruments GuideVictoria Castillo TamayoNo ratings yet
- Activity IntoleranceDocument6 pagesActivity IntoleranceRaidis PangilinanNo ratings yet
- CA1 Module 4 Activities: Lesson 1Document6 pagesCA1 Module 4 Activities: Lesson 1Esmareldah Henry SirueNo ratings yet
- Guidelines in BedmakingDocument9 pagesGuidelines in Bedmakinglex aspira100% (1)
- OVERVIEW OF CHN CONCEPTSDocument15 pagesOVERVIEW OF CHN CONCEPTSChiz EscubuaNo ratings yet
- CHN 2Document10 pagesCHN 2gunn twothingNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary AngiographyDocument3 pagesPulmonary AngiographyBiway RegalaNo ratings yet
- Types of IncisionsDocument3 pagesTypes of IncisionsJenny Lyn LimosNo ratings yet
- Male CatheterizationDocument30 pagesMale CatheterizationJoeurielle CarteraNo ratings yet
- Checklist Preparing Medications From Vials and AmpulesDocument4 pagesChecklist Preparing Medications From Vials and AmpulesDenvic0% (1)
- Helping Filipinos achieve better healthDocument3 pagesHelping Filipinos achieve better healthGilbert Salacup0% (1)
- Sample Only Nso - Tracheostomy CareDocument5 pagesSample Only Nso - Tracheostomy CareNader Abdurasad100% (1)
- CHN Quiz Compilation FinalsDocument20 pagesCHN Quiz Compilation FinalsFayeann Vedor LoriegaNo ratings yet
- Disaster Nursing SAS Session 14Document6 pagesDisaster Nursing SAS Session 14Niceniadas CaraballeNo ratings yet
- Chest Tube Reflective EssayDocument2 pagesChest Tube Reflective EssayAnjae GariandoNo ratings yet
- Global Health SituationDocument6 pagesGlobal Health SituationFrancym R. BatengaNo ratings yet
- Sanaani Nur Hathi M. Nso Jugular Venous Oximetry Staff Nurse 1Document7 pagesSanaani Nur Hathi M. Nso Jugular Venous Oximetry Staff Nurse 1Nur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- NURSE-PATIENT INTERACTION: ASSESSING DEPRESSIONDocument9 pagesNURSE-PATIENT INTERACTION: ASSESSING DEPRESSIONPatricia VasquezNo ratings yet
- Write Each Utensil's According To The Arrangement in The Tray Service Hospital Set - UpDocument5 pagesWrite Each Utensil's According To The Arrangement in The Tray Service Hospital Set - UpChristine Joy MolinaNo ratings yet
- Community health nursing role in caring for clientsDocument3 pagesCommunity health nursing role in caring for clientsEthan Marcos GoNo ratings yet
- Nebulization Nursing Procedure at Ateneo de Zamboanga UniversityDocument9 pagesNebulization Nursing Procedure at Ateneo de Zamboanga UniversityMitzi BelamideNo ratings yet
- Operating Room: "Caring For Intraoperative Patients."Document42 pagesOperating Room: "Caring For Intraoperative Patients."Cath BrilNo ratings yet
- Handling Instruments During The Surgical ProcedureDocument4 pagesHandling Instruments During The Surgical ProcedureR-o-N-n-e-l100% (1)
- Digestive System 2Document32 pagesDigestive System 2Johnmer AvelinoNo ratings yet
- Leukemias: Care SettingDocument11 pagesLeukemias: Care SettingTinNo ratings yet
- Age Related ChangesDocument8 pagesAge Related ChangesEricson CandelariaNo ratings yet
- 5B Assessing Apical Pulse-2Document4 pages5B Assessing Apical Pulse-2Marky RoqueNo ratings yet
- Preboard Examination - NP5 STUDENTDocument11 pagesPreboard Examination - NP5 STUDENTAli IgnacioNo ratings yet
- De Leon, Charissa M. Legarda CA1: Management Guidlines Spontaneous AbortionDocument2 pagesDe Leon, Charissa M. Legarda CA1: Management Guidlines Spontaneous AbortionCharissa Magistrado De LeonNo ratings yet
- Surgical TeamDocument9 pagesSurgical Teamkarenkaren09No ratings yet
- Visual Impairment Nursing Care PlansDocument58 pagesVisual Impairment Nursing Care PlansMaria Garcia Pimentel Vanguardia IINo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPchesca_paunganNo ratings yet
- Asepsi S: SurgicalDocument47 pagesAsepsi S: Surgicalspongebob27No ratings yet
- UCSF Laboratory Animal Resource Center Guidelines For Aseptic Surgery (Non-Rodents)Document5 pagesUCSF Laboratory Animal Resource Center Guidelines For Aseptic Surgery (Non-Rodents)Leo PerezNo ratings yet
- Operating Room Orientation ManualDocument14 pagesOperating Room Orientation ManualHannah MercadoNo ratings yet
- OR Sitting and Sterile Technique GuideDocument50 pagesOR Sitting and Sterile Technique Guidetsega tilahunNo ratings yet
- NSC Assignment Group 1Document3 pagesNSC Assignment Group 1Idama FavourNo ratings yet
- Introduction PneuDocument2 pagesIntroduction PneuwokorowNo ratings yet
- CA Intro DXTX PDFDocument121 pagesCA Intro DXTX PDFwokorowNo ratings yet
- Nursing Pharmacology: Anti-Neoplastic Chemotherapeutic DrugsDocument42 pagesNursing Pharmacology: Anti-Neoplastic Chemotherapeutic DrugswokorowNo ratings yet
- Rodalyn Quilang Initial DatabaseDocument3 pagesRodalyn Quilang Initial DatabasewokorowNo ratings yet
- Jazzle George E. Oteyza NCMB 312 Rle BSN 3Y1-3A Lab Module Course TaskDocument3 pagesJazzle George E. Oteyza NCMB 312 Rle BSN 3Y1-3A Lab Module Course TaskwokorowNo ratings yet
- Understanding Pain Concepts and TreatmentDocument46 pagesUnderstanding Pain Concepts and TreatmentwokorowNo ratings yet
- Jazzle George E. Oteyza VRTS 113 BSN 3Y1-3A Week 5Document2 pagesJazzle George E. Oteyza VRTS 113 BSN 3Y1-3A Week 5wokorow100% (1)
- Cataguing High School Health CenterDocument1 pageCataguing High School Health CenterwokorowNo ratings yet
- Surgical Instruments GuideDocument70 pagesSurgical Instruments Guidewokorow100% (1)
- Case Scenario:: 6. Make A Pain and Comforting Cycle For Your Patient Using This Diagram: See The Diagram in Your ModuleDocument1 pageCase Scenario:: 6. Make A Pain and Comforting Cycle For Your Patient Using This Diagram: See The Diagram in Your ModulewokorowNo ratings yet
- PainDocument86 pagesPainslayah_08No ratings yet
- DengueDocument2 pagesDenguewokorowNo ratings yet
- Pain PDFDocument10 pagesPain PDFJanaica JuanNo ratings yet
- Identify Non-Modifiable and Modifiable Risk Factors For HypertensionDocument3 pagesIdentify Non-Modifiable and Modifiable Risk Factors For HypertensionwokorowNo ratings yet
- Jazzle George E. Oteyza VRTS 113 BSN 3Y1-3A Week 5Document2 pagesJazzle George E. Oteyza VRTS 113 BSN 3Y1-3A Week 5wokorow100% (1)
- Inflammation PDFDocument20 pagesInflammation PDFwokorowNo ratings yet
- Gerontology Lec 2Document7 pagesGerontology Lec 2wokorowNo ratings yet
- Basal Body Temperature SheetDocument1 pageBasal Body Temperature SheetwokorowNo ratings yet
- Cast Study EGGTOPIC FinalkunoDocument41 pagesCast Study EGGTOPIC FinalkunowokorowNo ratings yet
- Gerontology Lec 2Document7 pagesGerontology Lec 2wokorowNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy 2008Document28 pagesEctopic Pregnancy 2008Alleya SheeneNo ratings yet
- Warning Signs of Possible RuptureDocument2 pagesWarning Signs of Possible RupturewokorowNo ratings yet
- Case Study Bronchiolitis UpdatedDocument23 pagesCase Study Bronchiolitis UpdatedwokorowNo ratings yet
- Warning Signs of Possible RuptureDocument2 pagesWarning Signs of Possible RupturewokorowNo ratings yet
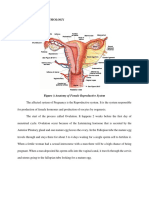
- Ii. Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument3 pagesIi. Anatomy and PhysiologywokorowNo ratings yet
- SAGE UK Style Guide ShortDocument10 pagesSAGE UK Style Guide ShortFernando MartinsNo ratings yet
- Tracheostomy Care - An Evidence-Based Guide - American Nurse TodayDocument4 pagesTracheostomy Care - An Evidence-Based Guide - American Nurse TodayZulaikah Nur IstiqomahNo ratings yet
- The History of Seventh-Day Adventist Church in Bangladesh by Sunil SarkarDocument45 pagesThe History of Seventh-Day Adventist Church in Bangladesh by Sunil SarkarSunil Sarkar86% (7)
- Drug Addict Treatment Center Khyber Medical Hospital Peshawar Field Work Report by Fakhre Alam Mohmand Dept of Social Work UOPDocument32 pagesDrug Addict Treatment Center Khyber Medical Hospital Peshawar Field Work Report by Fakhre Alam Mohmand Dept of Social Work UOPFakhrealamswNo ratings yet
- Mediland Pa88 UmDocument21 pagesMediland Pa88 UmSreejith SwaminathanNo ratings yet
- QUESTIONNAIRE "Stress Management Performed by The Level III Nursing Students of Nueva Ecija University of Science and Technology With Regards To Their Clinical Duties".Document4 pagesQUESTIONNAIRE "Stress Management Performed by The Level III Nursing Students of Nueva Ecija University of Science and Technology With Regards To Their Clinical Duties".Mark Anthony S. Castillo82% (11)
- City of Jefferson and Cole County Resource GuideDocument43 pagesCity of Jefferson and Cole County Resource GuideCassidyNo ratings yet
- (LIVE WEBINAR) China and Asia-Pacific - InviteDocument1 page(LIVE WEBINAR) China and Asia-Pacific - InviteMuralidhar RNo ratings yet
- Strategy Case: KPJ Healthcare Berhad: Prepared For: Dr. Dolhadi Zainudin Submission Date: 26 March 2014Document40 pagesStrategy Case: KPJ Healthcare Berhad: Prepared For: Dr. Dolhadi Zainudin Submission Date: 26 March 2014Yasushi Charles Teo100% (1)
- PRC Case Completion Form For Midwifery ExamsDocument2 pagesPRC Case Completion Form For Midwifery ExamsNoel83% (30)
- Weebly LCDocument3 pagesWeebly LCapi-376429631No ratings yet
- Assessing Capital Asset Realignment For Enhanced Services and The Future of The U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs' Health InfrastructureDocument94 pagesAssessing Capital Asset Realignment For Enhanced Services and The Future of The U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs' Health InfrastructureScribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Planned Structured of ActivitiesDocument8 pagesPlanned Structured of ActivitiesAnn Michelle TarrobagoNo ratings yet
- Perioperative Nursing 101Document2 pagesPerioperative Nursing 101Anthony Dema-ala0% (1)
- Unit 6. TelephoningDocument7 pagesUnit 6. TelephoningvivinNo ratings yet
- Case 3Document3 pagesCase 3Aman SankrityayanNo ratings yet
- Tick (/) The Correct Answer. 1. How Are You? Congratulations. You Re Very CleverDocument13 pagesTick (/) The Correct Answer. 1. How Are You? Congratulations. You Re Very CleverMOGANAPRIA A/P KALAICHELVAM MoeNo ratings yet
- Nur 4144 - Qi Project PaperDocument8 pagesNur 4144 - Qi Project Paperapi-391107694No ratings yet
- Poster IdsDocument4 pagesPoster Idsapi-250096168No ratings yet
- AHM Black White Boost FlexiDocument10 pagesAHM Black White Boost FlexiDani Kirky Ylagan100% (1)
- Report On OSDocument27 pagesReport On OSAjisha Kurian100% (1)
- 2019 Waiver Renewal PDFDocument401 pages2019 Waiver Renewal PDFAnne KelseyNo ratings yet
- Health Insurance Coverage ExplainedDocument18 pagesHealth Insurance Coverage ExplainedVenkat Reddy ArrabiriNo ratings yet
- Patient Care Delivery SystemDocument13 pagesPatient Care Delivery SystemAiza Apelada-NievaNo ratings yet
- DPR SPMCH HospitalDocument51 pagesDPR SPMCH HospitalhimdweepNo ratings yet
- Despersion NumericalsDocument15 pagesDespersion NumericalsShubhamNo ratings yet
- MNCHN Manual of OperationsDocument235 pagesMNCHN Manual of OperationsBenjo Dela Cruz100% (1)
- 350 Questions For The Situational Judgement TestDocument376 pages350 Questions For The Situational Judgement Testhairul80% (5)
- ASPE Vol3 Chapter2 PDFDocument56 pagesASPE Vol3 Chapter2 PDFAu C. GacotNo ratings yet
- AMP Vs Cemented Thompson 2010Document7 pagesAMP Vs Cemented Thompson 2010docpanchuNo ratings yet
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (17)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (78)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (403)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- 12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosFrom Everand12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (207)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo ratings yet
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesFrom EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (34)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (44)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementFrom EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (40)
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingFrom EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Algorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsFrom EverandAlgorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (722)
- Summary: How to Be an Adult in Relationships: The Five Keys to Mindful Loving by David Richo: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: How to Be an Adult in Relationships: The Five Keys to Mindful Loving by David Richo: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)