Professional Documents
Culture Documents
C =Kc C =Kc: B) Ө= 18.6°C, P*=819.7 Kpa
Uploaded by
Perak HanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
C =Kc C =Kc: B) Ө= 18.6°C, P*=819.7 Kpa
Uploaded by
Perak HanCopyright:
Available Formats
RESPONSI SOLID SURFACE (2)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY RESPONSI SOLID SURFACE (2)
CHEMICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
UNIVERSITAS KATOLIK PARAHYANGAN CHEMICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT
UNIVERSITAS KATOLIK PARAHYANGAN
1. A monolayer of CO molecules (effective area 0.165 nm 2) is 1. A monolayer of CO molecules (effective area 0.165 nm 2) is
adsorbed on the surface of 1.00 g of an Fe/Al 203 catalyst at 77 K, adsorbed on the surface of 1.00 g of an Fe/Al 203 catalyst at 77 K,
the boiling point of liquid nitrogen. Upon warming, the carbon the boiling point of liquid nitrogen. Upon warming, the carbon
monoxide occupies 4.25 cm3 at O0Cand 1.00 bar. What is the monoxide occupies 4.25 cm3 at O0Cand 1.00 bar. What is the
surface area of the catalyst? surface area of the catalyst?
2. The data for the adsorption of ammonia on barium fluoride are 2. The data for the adsorption of ammonia on barium fluoride are
reported below. Confirm that they fit a BET isotherm and find reported below. Confirm that they fit a BET isotherm and find
values of C and Vmon! values of C and Vmon!
a) Ө= 0°C, p*=429.6 kPa c) Ө= 0°C, p*=429.6 kPa
p/kPa 14.0 37.6 65.6 79.2 82.7 100.7 106.4 p/kPa 14.0 37.6 65.6 79.2 82.7 100.7 106.4
V/cm3 11.1 13.5 14.9 16.0 15.5 17.3 16.5 V/cm3 11.1 13.5 14.9 16.0 15.5 17.3 16.5
b) Ө= 18.6°C, p*=819.7 kPa d) Ө= 18.6°C, p*=819.7 kPa
p/kPa 5.3 8.4 14.4 29.2 62.1 74.0 80.1 102.0 p/kPa 5.3 8.4 14.4 29.2 62.1 74.0 80.1 102.0
V/cm3 9.2 9.8 10.3 11.3 12.9 13.1 13.4 14.1 V/cm3 9.2 9.8 10.3 11.3 12.9 13.1 13.4 14.1
3. A. Akgerman and M. Zardkoohi (J. Chem. Eng. Data 41,185 (1996)) 3. A. Akgerman and M. Zardkoohi (J. Chem. Eng. Data 41,185 (1996))
examined the adsorption of phenol from aqueous solution on to fly examined the adsorption of phenol from aqueous solution on to fly
ash at 20°C. They fitted their observations to a Freundlich isotherm ash at 20°C. They fitted their observations to a Freundlich isotherm
of the form c ads = K C1/soln where Cads is the concentration of of the form c ads = K C1/soln where Cads is the concentration of
adsorbed phenol and Csol is the concentration of aqueous phenol. adsorbed phenol and Csol is the concentration of aqueous phenol.
Among the data reported are the following: Among the data reported are the following:
Csol/(mg g-1) 8.26 15.63 25.43 31.74 40.00 Csol/(mg g-1) 8.26 15.63 25.43 31.74 40.00
Cads/(mg g-1) 4.4 19.2 35.2 52.0 67.2 Cads/(mg g-1) 4.4 19.2 35.2 52.0 67.2
Determine the constants K and n. What further information would Determine the constants K and n. What further information would
be necessary in order to express the data in terms of fractional be necessary in order to express the data in terms of fractional
coverage, Ө? coverage, Ө?
4. The release of petroleum products by leaky underground storage 4. The release of petroleum products by leaky underground storage
tanks is a serious threat to clean ground water. BTEX compounds tanks is a serious threat to clean ground water. BTEX compounds
(benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and xylenes) are of primary (benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and xylenes) are of primary
concern due to their ability to cause health problems at low concern due to their ability to cause health problems at low
concentrations. D.S. Kershaw, B.C. Kulik, and S. Pamukcu (J. concentrations. D.S. Kershaw, B.C. Kulik, and S. Pamukcu (J.
Geotech. & Geoenvir. Engrg. 123,324(1997)) have studied the Geotech. & Geoenvir. Engrg. 123,324(1997)) have studied the
ability of ground tyre rubber to sorb (adsorb and absorb) benzene ability of ground tyre rubber to sorb (adsorb and absorb) benzene
and 0-xylene. Though sorption involves more than surface and 0-xylene. Though sorption involves more than surface
interactions, sorption data are usually found to fit one of the interactions, sorption data are usually found to fit one of the
adsorption isotherms. In this study, the authors have tested how adsorption isotherms. In this study, the authors have tested how
well their data fit the linear (q =KCeq), Freundlich (q =KF Ceq1/n), and well their data fit the linear (q =KCeq), Freundlich (q =KF Ceq1/n), and
Langmuir (q =KLMCeq/(1 +KLCeq) type isotherms, where q is the mass Langmuir (q =KLMCeq/(1 +KLCeq) type isotherms, where q is the mass
of solvent sorbed per gram of ground rubber (in milligrams per of solvent sorbed per gram of ground rubber (in milligrams per
gram), the Ks and M are empirical constants, and c eq the gram), the Ks and M are empirical constants, and ceq the
equilibrium concentration of contaminant in solution (in milligrams equilibrium concentration of contaminant in solution (in milligrams
per litre). per litre).
(a) Determine the units of the empirical constants. (a) Determine the units of the empirical constants.
(b) Determine which of the isotherms best fits the data in the table (b) Determine which of the isotherms best fits the data in the table
below for the sorption of benzene on ground rubber. below for the sorption of benzene on ground rubber.
Ceq (mg dm-3) 97.10 36.10 10.40 6.51 6.21 2.48 Ceq (mg dm-3) 97.10 36.10 10.40 6.51 6.21 2.48
q/ (mg g-1) 7.13 4.60 1.80 1.10 0.55 0.31 q/ (mg g-1) 7.13 4.60 1.80 1.10 0.55 0.31
(c) Compare the sorption efficiency of ground rubber to that of (c) Compare the sorption efficiency of ground rubber to that of
granulated activated charcoal, which for benzene has been granulated activated charcoal, which for benzene has been
shown to obey the Freundlich isotherm in the form shown to obey the Freundlich isotherm in the form
q = 1.0 Ceq 1.6 with coefficient of determination R2 = 0.94. q = 1.0 Ceq 1.6 with coefficient of determination R2 = 0.94.
You might also like
- Ө= 0°C, P*=429.6 Kpa: Geotech. & Geoenvir. Engrg. 123,324 (1997) ) Have Studied TheDocument1 pageӨ= 0°C, P*=429.6 Kpa: Geotech. & Geoenvir. Engrg. 123,324 (1997) ) Have Studied TheKevin SanjayaNo ratings yet
- Bài tập Hoá lý 2 (Physical Chemistry 2 - Homework)Document10 pagesBài tập Hoá lý 2 (Physical Chemistry 2 - Homework)anhxuan03102001No ratings yet
- HCMUT Physical Chemistry 2 Homework AnswersDocument10 pagesHCMUT Physical Chemistry 2 Homework AnswersBích NgọcNo ratings yet
- Reactivity of CaoDocument5 pagesReactivity of CaoAlberto Moreno GomezNo ratings yet
- Stable Carbon Isotope Composition of Atmospheric Methyl BromideDocument4 pagesStable Carbon Isotope Composition of Atmospheric Methyl BromideAlessandra CincinelliNo ratings yet
- Cipc 2009-105Document5 pagesCipc 2009-105Ralf JonesNo ratings yet
- 2017, kumar-ZnCl2-YADocument42 pages2017, kumar-ZnCl2-YAElvis BoniNo ratings yet
- 10.1016@0304 42037590027 4Document15 pages10.1016@0304 42037590027 4Mun CongNo ratings yet
- 2011 Main Exam (WSTVL)Document4 pages2011 Main Exam (WSTVL)Thembinkosi ThobekaNo ratings yet
- IR Spectroscopy Determines CO2 in WaterDocument4 pagesIR Spectroscopy Determines CO2 in Watersm_carvalhoNo ratings yet
- CARBON ISOTOPE AS GEOCHEMICAL TRACERDocument7 pagesCARBON ISOTOPE AS GEOCHEMICAL TRACERNdeye Khady NdiayeNo ratings yet
- Preboard Exam Day1 SET ADocument12 pagesPreboard Exam Day1 SET AJeanne Cortez0% (1)
- Conway 2014Document10 pagesConway 2014John Jairo RamosNo ratings yet
- Great: Chemical Engineering Science, Vol. 47, No. 9-l I. Pp. 2437-2442Document6 pagesGreat: Chemical Engineering Science, Vol. 47, No. 9-l I. Pp. 2437-2442kaltoumNo ratings yet
- Applsci 09 03354Document17 pagesApplsci 09 03354Kenny SamNo ratings yet
- Carbon Dioxide Thermodynamic Properties Handbook: Covering Temperatures from -20° to 250°C and Pressures up to 1000 BarFrom EverandCarbon Dioxide Thermodynamic Properties Handbook: Covering Temperatures from -20° to 250°C and Pressures up to 1000 BarNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument1 pageAssignmentMani JhariyaNo ratings yet
- Adsorption of CO On Molecular Sieves and Activated CarbonDocument6 pagesAdsorption of CO On Molecular Sieves and Activated CarbonFernando AmoresNo ratings yet
- Sorption: Is Sorption A Transfer or Transform Reaction ? Transfer ReactionDocument23 pagesSorption: Is Sorption A Transfer or Transform Reaction ? Transfer ReactionMostafaNo ratings yet
- Role of Hydrate Phases of Calcium Carbonate On The Scaling PhenomenonDocument10 pagesRole of Hydrate Phases of Calcium Carbonate On The Scaling PhenomenonSaurav BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Kinetics and Mass Transfer of Carbon Dioxide Absorption Into Aqueous AmmoniaDocument8 pagesKinetics and Mass Transfer of Carbon Dioxide Absorption Into Aqueous AmmoniaGuido PalazzoNo ratings yet
- 0021-95172990378-1Document10 pages0021-95172990378-1ulsakNo ratings yet
- Absorption of Carbonyl Sulphide in Aqueous PiperazineDocument9 pagesAbsorption of Carbonyl Sulphide in Aqueous PiperazineBlack PearlNo ratings yet
- ChE426 Final Exam 2005Document2 pagesChE426 Final Exam 2005احمد الدلالNo ratings yet
- Shear Viscosity Measurements of Liquid Carbon Dioxide: IP: 130.89.98.137 On: Sat, 29 Nov 2014 18:50:59Document6 pagesShear Viscosity Measurements of Liquid Carbon Dioxide: IP: 130.89.98.137 On: Sat, 29 Nov 2014 18:50:59fabrizzio_vakeroNo ratings yet
- Vol2 n11 349-3581Document10 pagesVol2 n11 349-3581farah al-sudaniNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions With AnswersDocument7 pagesPractice Questions With AnswersYan YuetNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Products of The Carbonation of Portland Cement sn1136Document55 pagesThe Ultimate Products of The Carbonation of Portland Cement sn1136Bruno HuetNo ratings yet
- CFD Simulation of CO2 Sorption in A Circulating Fluidized Bed Using The Deactivation Kinetic ModelDocument8 pagesCFD Simulation of CO2 Sorption in A Circulating Fluidized Bed Using The Deactivation Kinetic Modelziglat2004No ratings yet
- Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry: Amin Alamdari, Abdolmohammad Alamdari, Dariush MowlaDocument7 pagesJournal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry: Amin Alamdari, Abdolmohammad Alamdari, Dariush MowlaLux Olan ReyesNo ratings yet
- Elsevier Science Publishers B.V., Amsterdam - Printed in The NetherlandsDocument6 pagesElsevier Science Publishers B.V., Amsterdam - Printed in The NetherlandsRENATO JAIR COSTA MINGANo ratings yet
- F Iller-Elastomer Interactions: Influence of Oxygen Plasma Treatment On Surface and Mechanical Properties of Carbon Black / Rubber CompositesDocument6 pagesF Iller-Elastomer Interactions: Influence of Oxygen Plasma Treatment On Surface and Mechanical Properties of Carbon Black / Rubber CompositesAmina DinariNo ratings yet
- Reduction of CaO-Fe2O3 Series Compounds by CODocument10 pagesReduction of CaO-Fe2O3 Series Compounds by COSaumit PalNo ratings yet
- Physico-Chemical Characterization of Aphron-Based Drilling FluidsDocument7 pagesPhysico-Chemical Characterization of Aphron-Based Drilling Fluidsmohammad teimuriNo ratings yet
- Experimental Mutual Solubilities of Co and H O in Pure Water and Nacl SolutionsDocument6 pagesExperimental Mutual Solubilities of Co and H O in Pure Water and Nacl SolutionszibaNo ratings yet
- Separation of Carbon Dioxide From Flue Gas Using Adsorption On Porous SolidsDocument25 pagesSeparation of Carbon Dioxide From Flue Gas Using Adsorption On Porous SolidsMARUFNo ratings yet
- Activated Carbon With NaclDocument4 pagesActivated Carbon With NaclhughsalgadoNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Exam 2022 Part 2Document6 pagesComprehensive Exam 2022 Part 2Annie LNo ratings yet
- Spectrophotometric Analysis of Copper in a PennyDocument12 pagesSpectrophotometric Analysis of Copper in a PennyLauren BoersmaNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry of A Biomimetic and Rubisco-Inspired CO Capture System From AirDocument14 pagesThermochemistry of A Biomimetic and Rubisco-Inspired CO Capture System From AirAhdanNo ratings yet
- ERT 208/4 Reaction Engineering: Identifying the Rate Limiting StepDocument33 pagesERT 208/4 Reaction Engineering: Identifying the Rate Limiting StepAasim ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Palandri, 1993 (J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis)Document12 pagesPalandri, 1993 (J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis)Alberto Moreno GomezNo ratings yet
- Molecules: Adsorption of CD (II) On Modified Granular Activated Carbons: Isotherm and Column StudyDocument17 pagesMolecules: Adsorption of CD (II) On Modified Granular Activated Carbons: Isotherm and Column StudyAditya sharmaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0304389420320847 MainDocument9 pages1 s2.0 S0304389420320847 MainclaudiacarranzafNo ratings yet
- CP302 Separation Process Principles Mass Transfer / Set 2 (Worked) Examples in Interface Mass Transfer, Mass Transfer Coefficients, Overall Coefficients and Transfer UnitsDocument4 pagesCP302 Separation Process Principles Mass Transfer / Set 2 (Worked) Examples in Interface Mass Transfer, Mass Transfer Coefficients, Overall Coefficients and Transfer Unitsأثير عبد الباري يعقوبNo ratings yet
- S0016702923110034Document13 pagesS0016702923110034pradyumna singhNo ratings yet
- Biosorption of Mno in Aqueous Solutions Using Pinus InsularisDocument9 pagesBiosorption of Mno in Aqueous Solutions Using Pinus InsularisAYAUWU LOVEDAYNo ratings yet
- Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular SpectrosDocument8 pagesSpectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular SpectrosHassan TalebiNo ratings yet
- JMR 1997 0316 PDFDocument5 pagesJMR 1997 0316 PDFMarcus Hoseth BentzenNo ratings yet
- Behaviour of Geopolymer Reinforced Concrete BeamsDocument84 pagesBehaviour of Geopolymer Reinforced Concrete BeamsHarish T S Gowda100% (1)
- Understanding Carbonate Equilibria by MeasuringDocument16 pagesUnderstanding Carbonate Equilibria by MeasuringJohn Jairo RamosNo ratings yet
- Progress in Nuclear Energy Leaching BehaviorDocument5 pagesProgress in Nuclear Energy Leaching BehaviorAnonymous 6tg80e6BqANo ratings yet
- Modelling Co Solubility in Pure Water and Nacl-Type Waters From 0 To 300 8C and From 1 To 300 Bar Application To The Utsira Formation at SleipnerDocument13 pagesModelling Co Solubility in Pure Water and Nacl-Type Waters From 0 To 300 8C and From 1 To 300 Bar Application To The Utsira Formation at SleipnerzibaNo ratings yet
- Model NSR Catalysts Fabrication and Reactivity of Barium at Room TemperatureDocument16 pagesModel NSR Catalysts Fabrication and Reactivity of Barium at Room TemperatureSabri AeroChemNo ratings yet
- Of In: The Kinetics Carbonyl Formation AsphaltDocument8 pagesOf In: The Kinetics Carbonyl Formation AsphaltArief Fath100% (1)
- Quantifying Methane Emissions From Anaerobic DigestersDocument8 pagesQuantifying Methane Emissions From Anaerobic DigestersIbrahim Al-MutazNo ratings yet
- Adsorption and Pore Condensation of Krypton On MesoporousDocument7 pagesAdsorption and Pore Condensation of Krypton On MesoporousSibnath KayalNo ratings yet
- GCL INTERACTION STUDYDocument9 pagesGCL INTERACTION STUDYMario WhoeverNo ratings yet
- Enggen 140 2023 s1 - Mock Test 2-3Document16 pagesEnggen 140 2023 s1 - Mock Test 2-3KingstanIINo ratings yet
- 1995-Kinetics of absorption of CO2 into aqueous solutions of 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanolDocument12 pages1995-Kinetics of absorption of CO2 into aqueous solutions of 2-amino-2-methyl-1-propanolbaohongqian2020No ratings yet
- GSS5 Rising Main Condition Assessment and Risk Management ManualDocument2 pagesGSS5 Rising Main Condition Assessment and Risk Management ManualNickNo ratings yet
- Time Management - Anthony RobbinsDocument55 pagesTime Management - Anthony RobbinsWind100% (24)
- (Journal) AN INNER QUALITY APPROACH TO REDUCINGDocument9 pages(Journal) AN INNER QUALITY APPROACH TO REDUCINGMery SanavieNo ratings yet
- Examples of Biography EssaysDocument5 pagesExamples of Biography Essayshyyaqmaeg100% (2)
- Macbeth PerformanceDocument4 pagesMacbeth Performanceapi-541677543No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 1Document9 pagesChapter 1 1Janine BordarioNo ratings yet
- BP B1 Tests Unit1Document6 pagesBP B1 Tests Unit1JovanaNo ratings yet
- Vision IAS CSP21T30S FLT6Document39 pagesVision IAS CSP21T30S FLT6AvanishNo ratings yet
- Eh TW5825Document2 pagesEh TW5825Lim Hendra Kurniawan Halim (Hendra)No ratings yet
- Croft LeafletDocument2 pagesCroft Leafletece142No ratings yet
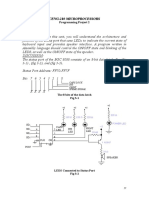
- Ceng-280 Microprocessors: Programming Project 2Document6 pagesCeng-280 Microprocessors: Programming Project 2kwstas vrotzisNo ratings yet
- Kinematic Structure of Machine ToolsDocument23 pagesKinematic Structure of Machine ToolswagoheNo ratings yet
- Designing Test Suites: Design A Test Suite For The Following ProblemDocument2 pagesDesigning Test Suites: Design A Test Suite For The Following ProblemAndroid Sourvivors sNo ratings yet
- Year 4 Geography Field Trip BookletDocument4 pagesYear 4 Geography Field Trip Bookletapi-357287502No ratings yet
- Gen Eoli de D AlDocument7 pagesGen Eoli de D AlCarlos J Duran ForeNo ratings yet
- Cowin E7 Manual PDFDocument10 pagesCowin E7 Manual PDFPaylish100% (1)
- ROSS FRL LubricatorsDocument16 pagesROSS FRL LubricatorsDavid Antonio Vargas CastilloNo ratings yet
- TD Tip Tinner PDFDocument2 pagesTD Tip Tinner PDFbehzadNo ratings yet
- Gate 2 K 13 PosterDocument1 pageGate 2 K 13 Poster7killers4uNo ratings yet
- History of AsphaltDocument3 pagesHistory of AsphaltRonald CostalesNo ratings yet
- Control Manual 30RB - RQ - LR 1Document36 pagesControl Manual 30RB - RQ - LR 1Iwan SetiawanNo ratings yet
- EQUIPMENT DATA SHEET Self Propelled Skidding SystemsDocument15 pagesEQUIPMENT DATA SHEET Self Propelled Skidding Systemsmathew1965No ratings yet
- BiologyDocument6 pagesBiologySuraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Minilab SpecsDocument5 pagesMinilab SpecsFrancisco DesiderioNo ratings yet
- CBC-Tailoring NC IIDocument66 pagesCBC-Tailoring NC IICharmaine Mae RetizaNo ratings yet
- Women EmpowermentDocument14 pagesWomen EmpowermentProfessor HappyNo ratings yet
- Surface Safety Products CatalogDocument37 pagesSurface Safety Products CatalogZaid AlahmedNo ratings yet
- Manual E7370Document12 pagesManual E7370Carlos Rodríguez MartínNo ratings yet
- SWIFTgpi Newsflash August Application Providers FinalDocument7 pagesSWIFTgpi Newsflash August Application Providers FinalSushma V KumarNo ratings yet
- Taper Roller BearingDocument130 pagesTaper Roller BearingAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet