Professional Documents
Culture Documents
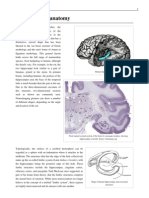
Neuroanatomy: Efig. 9.104B Efig. 9.105
Uploaded by
Nora Maricela Cavazos MendozaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Neuroanatomy: Efig. 9.104B Efig. 9.105
Uploaded by
Nora Maricela Cavazos MendozaCopyright:
Available Formats
Neuroanatomy
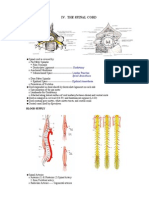
A second afferent pathway from the entorhinal cortex together medially, they form a bundle referred to as the
to the hippocampal formation is through the alvear pathway. fimbria of the fornix. The fornix then emerges from the hip-
Axons in the alvear pathway project directly on to CA1 and pocampal formation and curves under the corpus callosum
CA3 of the hippocampus (eFig. 9.104B). Similar to the before coursing medially to run adjacent to the midline (eFig.
perforant pathway, axons leaving the alvear pathway primar- 9.105). At the anterior commissure, the fornix divides into
ily originate from CA1 and CA3, which then project to the a precommissural fornix and postcommissural fornix to
subiculum. reach the nucleus accumbens, septal nuclei, medial frontal
Efferent axons leaving the hippocampal formation primar- cortex, mammillary nucleus, ventromedial nucleus of the
ily exit from the subiculum and form the fornix (Latin for hypothalamus, and anterior nucleus of the dorsal thalamus
“arch”), a white matter structure that arches over the (eFig. 9.95).
ventricular system (eFig. 9.95). The fornix begins with axons Through this section we have described a collection of
exiting the hippocampus to form the alveus along the anatomical structures and defined their connections with
ventricular surface of the hippocampus. As the axons come other areas of the brain and brainstem without exploring
Head of caudate nucleus Anterior horn of Crus of fornix Thalamus
lateral ventricle
A B
Inferior horn of lateral ventricle Choroid plexus Hippocampus Fimbria
eFig. 9.105 Hippocampus–fimbria–fornix system. Superior view of brain. The cerebral cortex, corpus callosum, and surrounding white matter
have been removed to expose the lateral ventricle. A. Choroid plexus in the lateral ventricle. B. choroid plexus removed. (From Crossman A.
e80 Neuroanatomy. 5th ed., Fig. 16.15. Philadelphia: Elsevier; 2015.)
booksmedicos.org
You might also like
- Jurnal - Christopher Muhamad Zildan Holliday - 215090107111029 - Kelas ADocument17 pagesJurnal - Christopher Muhamad Zildan Holliday - 215090107111029 - Kelas AChristopher Muhamad Zildan HNo ratings yet
- Fisiopatologia de La EpilepsiaDocument18 pagesFisiopatologia de La EpilepsiaVíctor ManuelNo ratings yet
- Assignment#4 Clinical Neuro Sciences: TOPIC: Describe Briefly The Clinical Testing of All Cranial NervesDocument3 pagesAssignment#4 Clinical Neuro Sciences: TOPIC: Describe Briefly The Clinical Testing of All Cranial NervesAlina ShaukatNo ratings yet
- Review Article: Mohammad SarwarDocument17 pagesReview Article: Mohammad SarwarRuslan MilevskyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Mental and Neurobehavior DisordersDocument57 pagesAnatomy of The Mental and Neurobehavior DisordersiqiqiqiqiqNo ratings yet
- Trans - Physio (The Limbic System) PDFDocument8 pagesTrans - Physio (The Limbic System) PDFJoher Jr. MendezNo ratings yet
- Hippocampus AnatomyDocument6 pagesHippocampus AnatomyravnoorNo ratings yet
- Limbic SystemDocument0 pagesLimbic SystemSeshadri Sekhar ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- BRAINSTEMDocument17 pagesBRAINSTEMaroosadilbar27No ratings yet
- Monteagudo 2007Document28 pagesMonteagudo 2007yngallo910No ratings yet
- Articulo DX Semana 14Document7 pagesArticulo DX Semana 14Valeria Garcia QuijanoNo ratings yet
- 48 Hour Chick Reviewer PDFDocument5 pages48 Hour Chick Reviewer PDFSheanna May FuriaNo ratings yet
- White Matter of The Cerebral HemispheresDocument50 pagesWhite Matter of The Cerebral HemispheresSandy MonirNo ratings yet
- UERM GROSS Cerebrum Cerebellum and CT ScanDocument82 pagesUERM GROSS Cerebrum Cerebellum and CT Scanroxanne.viriNo ratings yet
- Vana 2210 Lab 14-15Document18 pagesVana 2210 Lab 14-15Christalie Bea FernandezNo ratings yet
- Ant 325materialDocument13 pagesAnt 325materialDestiny BlissNo ratings yet
- 48 & 72 HR Chick PDFDocument3 pages48 & 72 HR Chick PDFpinky peachNo ratings yet
- The CerebellumDocument5 pagesThe CerebellumAndrew BarryNo ratings yet
- The Ventricular SystemDocument6 pagesThe Ventricular SystemM Arsalan TariqNo ratings yet
- The Posterior Fossa Cisterns: Albert L. Rhoton, JR., M.DDocument12 pagesThe Posterior Fossa Cisterns: Albert L. Rhoton, JR., M.DIndra HadianditeNo ratings yet
- Cerebellum LesionsofbrainstemDocument50 pagesCerebellum LesionsofbrainstemAira LorenzoNo ratings yet
- EmbryologyDocument92 pagesEmbryologyLoveena SteadmanNo ratings yet
- Brain Stem Part 1Document6 pagesBrain Stem Part 1ZED AlanaziNo ratings yet
- Brain Stem FullDocument25 pagesBrain Stem FullCosplay AccountNo ratings yet
- Exercise 14 Whole Mount of A 24 Hour Chick Embryo PDFDocument3 pagesExercise 14 Whole Mount of A 24 Hour Chick Embryo PDFMichaela FayeNo ratings yet
- 1040IMRI - Imri 25 59Document17 pages1040IMRI - Imri 25 59Juan Carlos LazoNo ratings yet
- Exercise 17 Serial Transverse Section of A 33 Hour Chick Embryo PDFDocument4 pagesExercise 17 Serial Transverse Section of A 33 Hour Chick Embryo PDFMichaela FayeNo ratings yet
- Spinocerebelar Tract-2Document20 pagesSpinocerebelar Tract-2Vijayasekhar VempalliNo ratings yet
- The Anatomy of The Ventricular SystemDocument6 pagesThe Anatomy of The Ventricular Systemalex soaresNo ratings yet
- Embryology Summary of Development Part 1 - 2019 - CNS, Axial SK, SK Muscle, SkinDocument9 pagesEmbryology Summary of Development Part 1 - 2019 - CNS, Axial SK, SK Muscle, Skindr.mumtaz09No ratings yet
- Arteries and Veins of The Cerebellum: Original PaperDocument33 pagesArteries and Veins of The Cerebellum: Original PaperCan EkerNo ratings yet
- Learn Neuroscience & Anatomy 23Document3 pagesLearn Neuroscience & Anatomy 23rajad100% (2)
- Cerebelo: Dr. J.J. Colon R6 C.M.N. La RazaDocument74 pagesCerebelo: Dr. J.J. Colon R6 C.M.N. La RazaJose Jesus ColonNo ratings yet
- MVST IB Head and Neck Anatomy: Ntroduction To The Ranial ErvesDocument4 pagesMVST IB Head and Neck Anatomy: Ntroduction To The Ranial ErvesSaffronMaeNo ratings yet
- L20-Thalamus & Limbic SystemDocument33 pagesL20-Thalamus & Limbic SystemSk JsNo ratings yet
- Axilla and Brachial PlexusDocument22 pagesAxilla and Brachial Plexusromaisa akhtarNo ratings yet
- Exercise 18 Whole Mount Section of A 48 Hour Chick Embryo PDFDocument4 pagesExercise 18 Whole Mount Section of A 48 Hour Chick Embryo PDFMichaela FayeNo ratings yet
- TA Lab 5 BrainDocument9 pagesTA Lab 5 BrainHajira NusretNo ratings yet
- Exercise 16 Whole Mount of A 33 Hour Chick Embryo PDFDocument3 pagesExercise 16 Whole Mount of A 33 Hour Chick Embryo PDFMichaela FayeNo ratings yet
- Capitulo 4Document12 pagesCapitulo 4Carla MonteroNo ratings yet
- Brainstem: External and Internal FeaturesDocument57 pagesBrainstem: External and Internal FeaturesJoaquin GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Secti On: Osteology of Head and NeckDocument102 pagesSecti On: Osteology of Head and NeckMarie GdlNo ratings yet
- Department of Anatomy College of Medicine University of Ibadan Neuroanatomy Dissection of The BrainDocument22 pagesDepartment of Anatomy College of Medicine University of Ibadan Neuroanatomy Dissection of The BrainAbdulateef AdebisiNo ratings yet
- Iv. The Spinal Cord: Cordotomy Lumbar PunctureDocument0 pagesIv. The Spinal Cord: Cordotomy Lumbar PunctureAnonymous t5TDwdNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan THTDocument9 pagesPemeriksaan THTAtikah MuhamadNo ratings yet
- Essay Solution On Space in The SkullDocument21 pagesEssay Solution On Space in The SkullEmmanuel IshiomaNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves 2016-36782Document51 pagesCranial Nerves 2016-36782Danu PostolacheNo ratings yet
- Medullar Oblongata (Myelencephalon) Gastrointestinal MotilityDocument10 pagesMedullar Oblongata (Myelencephalon) Gastrointestinal Motilitymurali_bharadwazNo ratings yet
- Author 'S Accepted ManuscriptDocument46 pagesAuthor 'S Accepted ManuscriptRaul DoctoNo ratings yet
- Spinal Tracts: DR - Krishna Madhukar Dept. of Orthopaedics Bharati HospitalDocument65 pagesSpinal Tracts: DR - Krishna Madhukar Dept. of Orthopaedics Bharati HospitalKrishna Madhukar100% (1)
- Callosotopy: Leg Motor Connections Illustrated by Fiber DissectionDocument7 pagesCallosotopy: Leg Motor Connections Illustrated by Fiber DissectionMarinaGuerraNo ratings yet
- Head FactoidsDocument17 pagesHead FactoidsENo ratings yet
- Anatomy - UPPER LIMB - 3 Muscles, Innervation and Compartments of The Upper Limb PDFDocument20 pagesAnatomy - UPPER LIMB - 3 Muscles, Innervation and Compartments of The Upper Limb PDFDr Ahmed NabilNo ratings yet
- Modul 2 (SSP)Document18 pagesModul 2 (SSP)citradlNo ratings yet
- Cerebellum TextDocument7 pagesCerebellum TextJean Pierre Chastre LuzaNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy Revision Notes PDFDocument7 pagesNeuroanatomy Revision Notes PDFTanya Tanu100% (1)
- The 55 Hour Chick EmbryoDocument6 pagesThe 55 Hour Chick EmbryoAndrei AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The External EarDocument28 pagesAnatomy of The External EarhamaNo ratings yet
- B 22-Rs-Anatomy - Saq AnswersDocument22 pagesB 22-Rs-Anatomy - Saq Answersapi-516879364No ratings yet
- Allen Science M T Class 10Document14 pagesAllen Science M T Class 10krishnaNo ratings yet
- Notice: Agency Information Collection Activities Proposals, Submissions, and ApprovalsDocument2 pagesNotice: Agency Information Collection Activities Proposals, Submissions, and ApprovalsJustia.comNo ratings yet
- The Til Pat YearsDocument1 pageThe Til Pat Yearsrajkumarvpost6508No ratings yet
- Binder1 CARENCRODocument27 pagesBinder1 CARENCROAddisu TsehayNo ratings yet
- Carnatic Music NotationDocument6 pagesCarnatic Music Notationksenthil kumar100% (1)
- Title To GoodsDocument2 pagesTitle To GoodsrrsinhanhpcNo ratings yet
- Amma Vun - Bala AshtagamDocument4 pagesAmma Vun - Bala AshtagamSHIV RAMNo ratings yet
- Fume Cup BrochureDocument2 pagesFume Cup Brochuremfisol2000No ratings yet
- Softwash ComparatorDocument5 pagesSoftwash ComparatorFaheem MushtaqNo ratings yet
- 2406 Final ExamDocument10 pages2406 Final ExamChandan GargNo ratings yet
- Birhane, E. 2014. Agroforestry Governance in Ethiopa Report WP 5Document50 pagesBirhane, E. 2014. Agroforestry Governance in Ethiopa Report WP 5woubshetNo ratings yet
- College Physics Global 10th Edition Young Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesCollege Physics Global 10th Edition Young Solutions ManualSaraSmithdgyj100% (57)
- Monthly Film Bulletin: 1T1IcqDocument12 pagesMonthly Film Bulletin: 1T1IcqAlfred_HitzkopfNo ratings yet
- 2019 National Innovation PoliciesDocument98 pages2019 National Innovation PoliciesRashmi SinghNo ratings yet
- List of Mines in IndiaDocument4 pagesList of Mines in IndiaNAMISH MAHAKULNo ratings yet
- Eva Braun Life With Hitler PDFDocument2 pagesEva Braun Life With Hitler PDFPamela0% (1)
- Topic 4 Qualitative Lectures 3Document28 pagesTopic 4 Qualitative Lectures 3JEMABEL SIDAYENNo ratings yet
- Online Book Store System: Bachelor of Computer EngineeringDocument31 pagesOnline Book Store System: Bachelor of Computer Engineeringkalpesh mayekarNo ratings yet
- Al-Arafah Islami Bank Limited: Prepared For: Prepared By: MavericksDocument18 pagesAl-Arafah Islami Bank Limited: Prepared For: Prepared By: MavericksToabur RahmanNo ratings yet
- AKSINDO (Mr. Ferlian), 11 - 13 Mar 2016 (NY)Document2 pagesAKSINDO (Mr. Ferlian), 11 - 13 Mar 2016 (NY)Sunarto HadiatmajaNo ratings yet
- Manusia LemahDocument8 pagesManusia LemahKhoirul MubinNo ratings yet
- The Watchmen Novel AnalysisDocument10 pagesThe Watchmen Novel AnalysisFreddy GachecheNo ratings yet
- 1416490317Document2 pages1416490317Anonymous sRkitXNo ratings yet
- Las Math 2 Q3 Week 1Document6 pagesLas Math 2 Q3 Week 1Honeyjo Nette100% (7)
- The Perception of Veggie Nilupak To Selected Grade 11 Students of Fort Bonifacio High SchoolDocument4 pagesThe Perception of Veggie Nilupak To Selected Grade 11 Students of Fort Bonifacio High SchoolSabrina EleNo ratings yet
- Socratic Sales The 21 Best Sales Questions For Mastering Lead Qualification and AcceDocument13 pagesSocratic Sales The 21 Best Sales Questions For Mastering Lead Qualification and Acceutube3805100% (2)
- ECB Priority III: Deutz - Starter MotorDocument7 pagesECB Priority III: Deutz - Starter MotorMarcelo OlivaresNo ratings yet
- Real Number System.Document7 pagesReal Number System.samuel1436No ratings yet
- Family Advent Devotions 1Document3 pagesFamily Advent Devotions 1collingdalenazNo ratings yet
- Tiny House 2020: Less House, More HomeDocument11 pagesTiny House 2020: Less House, More HomeVanshika SpeedyNo ratings yet