Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Azithromycin (1 G Azithromycin in Monodosis)
Azithromycin (1 G Azithromycin in Monodosis)
Uploaded by
inah krizia lague0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Azithromycin.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesAzithromycin (1 G Azithromycin in Monodosis)
Azithromycin (1 G Azithromycin in Monodosis)
Uploaded by
inah krizia lagueCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
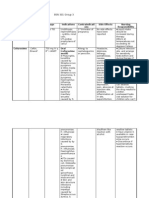
Azithromycin (1 g azithromycin in monodosis)
Classification - Therapeutic:agents for atypical mycobacterium, anti-infectives
Pharmacologic:macrolides
Action - Inhibits protein synthesis at the level of the 50S bacterial ribosome.
Indication - Treatment of the following infections due to susceptible organisms: Upper
respiratory tract infections, including streptococcal pharyngitis, acute bacterial exacerbations of
chronic bronchitis and tonsillitis, Lower respiratory tract infections, including bronchitis and
pneumonia, Acute otitis media, Skin and skin structure infections, Nongonococcal urethritis,
cervicitis, gonorrhea, and chancroid. Prevention of disseminated Mycobacterium avium
complex (MAC) infection in patients with advanced HIV infection. Extended-release suspension
(ZMax) Acute bacterial sinusitis and community-acquired pneumonia in adults.
Contraindication - Hypersensitivity to azithromycin, erythromycin, or othermacrolide anti-
infectives; History of cholestatic jaundice or hepatic dysfunction with prior use of azithromycin.;
QT interval prolongation, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, or bradycardia.; Concurrent use of
quinidine, procainamide, dofetilide, amiodarone, or sotalol.
Adverse Reaction - CNS: dizziness, seizures, drowsiness, fatigue, headache. CV: torsades de
pointes , chest pain, hypotension, palpitations, QT interval prolongation. GI: hepatoxicity,
pseudomembranous colitis, abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, cholestatic jaundice, qliver
enzymes, dyspepsia, flatulence, melena, oral candidiasis, pyloric stenosis. GU: nephritis,
vaginitis. Hemat: anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia. Derm: stevens-johnson syndrme,
toxic epidermal necrolysis , photosensitivity, rash. EENT: ototoxicity. F and E:
hyperkalemia.Misc: angioedema
Nursing Consideration –
Assess patient for infection (vital signs; appearance of wound, sputum, urine, and
stool; WBC) at beginning of and throughout therapy.
● Obtain specimens for culture and sensitivity before initiating therapy
● Observe for signs and symptoms of anaphylaxis (rash, pruritus, laryngeal edema, wheezing).
Notify health care professional immediately if
these occur.
● Assess patient for skin rash frequently during therapy.
● Lab Test Considerations: May causeqserum bilirubin, AST, ALT, LDH,
and alkaline phosphatase concentrations.
● May cause creatine phosphokinase, potassium, prothrombin time, BUN, serum
creatinine, and blood glucose concentrations.
● Instruct patients to take medication as directed and to finish the drug completely,
even if they are feeling better.
● Instruct patient not to take azithromycin with food or antacids.
● Caution patient to avoid driving or other activities requiring alertness until response to
medication is known.
You might also like
- Adult Infectious Disease Bulletpoints HandbookFrom EverandAdult Infectious Disease Bulletpoints HandbookRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- Discharge PlanDocument4 pagesDischarge PlanJennyLapitanNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime (Drug Study)Document2 pagesCefuroxime (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888100% (13)
- 100 Most Used Drugs in UKDocument4 pages100 Most Used Drugs in UKIndiraMarieAquinoEsguerraNo ratings yet
- Propanolol and Spironolactone Drug StudyDocument2 pagesPropanolol and Spironolactone Drug StudyLisette Castillo91% (11)
- Eritro Papulo Skuamosa 2021Document47 pagesEritro Papulo Skuamosa 2021Yolanda Agnesia Purba0% (1)
- ARI Control ProgrammeDocument13 pagesARI Control ProgrammeArun George44% (9)
- Ampicillin:: Treatment of The Following Infections: Skin and Skin Structure Infections, Soft-TissueDocument1 pageAmpicillin:: Treatment of The Following Infections: Skin and Skin Structure Infections, Soft-TissueGeorge FogNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyMaAngelica Tresha RaonNo ratings yet
- ADALIMUMAB (Humira)Document4 pagesADALIMUMAB (Humira)GLen CaniedoNo ratings yet
- Interim Guidance For Treatment of Monkeypox: CasesDocument5 pagesInterim Guidance For Treatment of Monkeypox: CasesRafael Rufino PioNo ratings yet
- Azithromycin (Drug Study)Document2 pagesAzithromycin (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse688893% (15)
- Cefixime: Suprax Class and CategoryDocument3 pagesCefixime: Suprax Class and CategoryArianne Joy SalvadorNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument3 pagesDrugsCzarina CamamaNo ratings yet
- Ciprofloxacin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesCiprofloxacin Drug StudyRosalie Delfin89% (9)
- Examination Card 10Document9 pagesExamination Card 10FUTURE DOCTORNo ratings yet
- Leptospirosis Case Study (Short)Document16 pagesLeptospirosis Case Study (Short)Liryc Ernest CuerboNo ratings yet
- Ther. Class: Antiulcer Pharm. Class: Proton Indications: CNS: DizzinessDocument5 pagesTher. Class: Antiulcer Pharm. Class: Proton Indications: CNS: DizzinessLorenzo Daniel AntonioNo ratings yet
- AmikacinDocument5 pagesAmikacinGregory LitangNo ratings yet
- Cefazolin Sodium AncefDocument1 pageCefazolin Sodium AncefKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- Infammatory Bowel Diseases: DR Yasser MahrousDocument32 pagesInfammatory Bowel Diseases: DR Yasser Mahrousmohamed hanyNo ratings yet
- Azimex SuspensionDocument7 pagesAzimex Suspensionelcapitano vegetaNo ratings yet
- CefuroximeDocument2 pagesCefuroximeReem NurNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyShiara Ruth EdrosoloNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document4 pagesDrug Study 2roxybabesNo ratings yet
- MethottexateDocument104 pagesMethottexateFarha Elein KukihiNo ratings yet
- MEDICATION: Garamycin, Garamycin Ophthalmic, Genoptic Classifications: Antiinfective Aminoglycoside Antibiotic ActionDocument4 pagesMEDICATION: Garamycin, Garamycin Ophthalmic, Genoptic Classifications: Antiinfective Aminoglycoside Antibiotic ActionLea Mae HandayanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Paracetamol Ambroxol Ascorbic Acid CefuroximeDocument6 pagesDrug Study Paracetamol Ambroxol Ascorbic Acid CefuroximeJaymark LambinoNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug: Ceftriaxone 2g/IVDocument3 pagesName of Drug: Ceftriaxone 2g/IVAllan DiazNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Effects: Death of Rapidly Replicating Cells, ParticularlyDocument3 pagesTherapeutic Effects: Death of Rapidly Replicating Cells, ParticularlyMarc Louise DatoyNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyKristine-Joy Legaspi FrancoNo ratings yet
- Microbiology, Infections, and Antibiotic Therapy: Elizabeth J. Rosen, MD Francis B. Quinn, MD March 22, 2000Document86 pagesMicrobiology, Infections, and Antibiotic Therapy: Elizabeth J. Rosen, MD Francis B. Quinn, MD March 22, 2000skmvicky1483No ratings yet
- Drugs ErDocument7 pagesDrugs EreyesidphNo ratings yet
- Pdoc - DS Inflagic 20Document3 pagesPdoc - DS Inflagic 20reshad reswaanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study-Ceftriaxone ClindamycinDocument2 pagesDrug Study-Ceftriaxone ClindamycinDavid VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study of Ceftriaxone & RowatinexDocument5 pagesDrug Study of Ceftriaxone & RowatinexLorina Lynne ApelacioNo ratings yet
- 2018 10 10 002356file1Document2 pages2018 10 10 002356file1Одончимэг СайханбаярNo ratings yet
- RebamipideDocument5 pagesRebamipidejunerubinNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Arthritis Osteoarthritis Ankylosing Spondylitis Gout PainDocument4 pagesRheumatoid Arthritis Arthritis Osteoarthritis Ankylosing Spondylitis Gout Paincicilvasquez0817No ratings yet
- Hydrocortisone Inj. (IV)Document2 pagesHydrocortisone Inj. (IV)zepoli_zepoly6232No ratings yet
- Infections in Immunocompromised Host CHRI ClassDocument26 pagesInfections in Immunocompromised Host CHRI Classmmkavitha98No ratings yet
- Drug Analysis: Submitted By: GALICINAO, Gretta Shalou GDocument9 pagesDrug Analysis: Submitted By: GALICINAO, Gretta Shalou GggalicinaoNo ratings yet
- Profort VialDocument8 pagesProfort Vialelcapitano vegetaNo ratings yet
- VIII. Pharmacology Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindi Cation Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesVIII. Pharmacology Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindi Cation Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesZau MacaraigNo ratings yet
- Approach To Antibiotics in SurgeryDocument30 pagesApproach To Antibiotics in SurgeryzahraaNo ratings yet
- RocephinDocument2 pagesRocephinianecunar100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyNajmah Saaban100% (1)
- Coagulase +ve Coagulase - VeDocument41 pagesCoagulase +ve Coagulase - Veshrutik91No ratings yet
- Gamutin Drug Study-PediatricsDocument6 pagesGamutin Drug Study-PediatricsJhulia GamutinNo ratings yet
- 2018 - 10 - 10 - 005732file1 2Document2 pages2018 - 10 - 10 - 005732file1 2Bogart McGregorNo ratings yet
- CiprofloxacinDocument2 pagesCiprofloxacinCee SanchezNo ratings yet
- Drug STUDY CefotaximeDocument5 pagesDrug STUDY CefotaximeJeffrey Calicdan Bucala75% (8)
- Acute Glomerulonephritis (AGN)Document35 pagesAcute Glomerulonephritis (AGN)jennalyn_dejelo100% (1)
- Drug Study, 1Document2 pagesDrug Study, 1ninjatechnique10No ratings yet
- Group-3-Ward-Class 20240213 182023 0000Document31 pagesGroup-3-Ward-Class 20240213 182023 0000Hanna CarsanoNo ratings yet
- LeukemiaDocument51 pagesLeukemiaCres Padua QuinzonNo ratings yet
- Agranulocytosis FinalDocument17 pagesAgranulocytosis FinalsanthiyasandyNo ratings yet
- Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: AetiologyDocument5 pagesToxic Epidermal Necrolysis: AetiologyreyhanrrNo ratings yet
- Clindamycin (Cleocin)Document2 pagesClindamycin (Cleocin)Erickson Caisido GarciaNo ratings yet
- Cancer Drug StudyDocument14 pagesCancer Drug StudyIamanamay Trinidad100% (1)
- CeftazidimeDocument1 pageCeftazidimePaulineNo ratings yet
- Antispasmodic Anticholinergic: Drug NameDocument13 pagesAntispasmodic Anticholinergic: Drug NameAngela Rose BaliteNo ratings yet
- The Perfect Neutropenic Diet Cookbook; The Complete Nutrition Guide To Reinstating Overall Health For General Wellness With Delectable And Nourishing RecipesFrom EverandThe Perfect Neutropenic Diet Cookbook; The Complete Nutrition Guide To Reinstating Overall Health For General Wellness With Delectable And Nourishing RecipesNo ratings yet
- BARRA HistoryDocument20 pagesBARRA Historyinah krizia lagueNo ratings yet
- Manyanita LyricsDocument4 pagesManyanita Lyricsinah krizia lagueNo ratings yet
- G9 Circulatory SystemDocument42 pagesG9 Circulatory Systeminah krizia lagueNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 - Beowulf RevisedDocument76 pagesGrade 9 - Beowulf Revisedinah krizia lagueNo ratings yet
- Generation of Evidence (8: Prepared byDocument1 pageGeneration of Evidence (8: Prepared byinah krizia lagueNo ratings yet
- Culture of Reading: Its Efficacy Towards The Pupils' Reading FluencyDocument11 pagesCulture of Reading: Its Efficacy Towards The Pupils' Reading Fluencyinah krizia lagueNo ratings yet
- Week 14 LFDDocument2 pagesWeek 14 LFDinah krizia lagueNo ratings yet
- Activity TagubaDocument1 pageActivity Tagubainah krizia lagueNo ratings yet
- Lague, Inah Krizia O. BSN 3DDocument7 pagesLague, Inah Krizia O. BSN 3Dinah krizia lagueNo ratings yet
- LAGUE - Teaching Plan PDFDocument3 pagesLAGUE - Teaching Plan PDFinah krizia lagueNo ratings yet
- Group 8 (Semblante, Lague, Peras, Rama) T-Test: ValueDocument11 pagesGroup 8 (Semblante, Lague, Peras, Rama) T-Test: Valueinah krizia lagueNo ratings yet
- Velez College College of Nursing: Bascon, Karl Niño D. Calunsag, Hazel Kate C. Lague, Inah Krizia ODocument7 pagesVelez College College of Nursing: Bascon, Karl Niño D. Calunsag, Hazel Kate C. Lague, Inah Krizia Oinah krizia lagueNo ratings yet
- Velez College - College of Nursing: F. Ramos ST., Cebu City S.Y. 2018 - 2019 Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesVelez College - College of Nursing: F. Ramos ST., Cebu City S.Y. 2018 - 2019 Lesson Planinah krizia lagueNo ratings yet
- NCP Autoimmune DisorderDocument4 pagesNCP Autoimmune Disorderinah krizia lagueNo ratings yet
- Week 1 & 2Document6 pagesWeek 1 & 2inah krizia lagueNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune DisordersDocument13 pagesAutoimmune Disordersinah krizia lagueNo ratings yet
- CHN 2 JournalDocument2 pagesCHN 2 Journalinah krizia lagueNo ratings yet
- Impaired Memory Teaching Plan: General ObjectivesDocument3 pagesImpaired Memory Teaching Plan: General Objectivesinah krizia lagueNo ratings yet
- Week 13 LFDDocument1 pageWeek 13 LFDinah krizia lagueNo ratings yet
- Sampling: By: Kachiri T. Salibio-MercadalDocument49 pagesSampling: By: Kachiri T. Salibio-Mercadalinah krizia lagueNo ratings yet
- Successful Aging: Attitude Is EverythingDocument7 pagesSuccessful Aging: Attitude Is Everythinginah krizia lagueNo ratings yet
- Lague, Inah Krizia O. Bsn-3DDocument9 pagesLague, Inah Krizia O. Bsn-3Dinah krizia lagueNo ratings yet
- Systemic Lupus Erythematous: Precipitating Factors: Environmental Drug-Induced InfectionDocument10 pagesSystemic Lupus Erythematous: Precipitating Factors: Environmental Drug-Induced Infectioninah krizia lagueNo ratings yet
- CHN 2 JournalDocument2 pagesCHN 2 Journalinah krizia lagueNo ratings yet
- Lague - Case Analysis ReportDocument43 pagesLague - Case Analysis Reportinah krizia lagueNo ratings yet
- Four Aspects of The Lived ExperienceDocument2 pagesFour Aspects of The Lived Experienceinah krizia lagueNo ratings yet
- CHN 2 JournalDocument2 pagesCHN 2 Journalinah krizia lagueNo ratings yet
- CHN 2 JournalDocument2 pagesCHN 2 Journalinah krizia lagueNo ratings yet
- HIV AIDS Opportunistic InfectionsDocument26 pagesHIV AIDS Opportunistic InfectionsLaylee ClareNo ratings yet
- Algen Healthcare Price List PDFDocument4 pagesAlgen Healthcare Price List PDFShashank Shray0% (1)
- Drug Study Paracetamol, Ibuprofen, Cotrimoxazole, AllopurinolDocument6 pagesDrug Study Paracetamol, Ibuprofen, Cotrimoxazole, Allopurinolpaupaulala89% (9)
- Scarlet FeverDocument4 pagesScarlet FeverJap NofuenteNo ratings yet
- Abruptio Placenta For StudentsDocument26 pagesAbruptio Placenta For Studentssonam MaclayNo ratings yet
- Flip Chart 06 IUDDocument12 pagesFlip Chart 06 IUDLamyaa Ali HasanNo ratings yet
- Form P (Weekly Reporting Format - IDSP) : Oriana Hospital PVT - LTDDocument2 pagesForm P (Weekly Reporting Format - IDSP) : Oriana Hospital PVT - LTDRavi ParmarNo ratings yet
- NSW Immunisation ScheduleDocument1 pageNSW Immunisation ScheduleKristinaNo ratings yet
- Toxic Shock SyndromeDocument10 pagesToxic Shock Syndromealice_lim01100% (1)
- 7.antiviral To MalariaDocument48 pages7.antiviral To MalariaSalih IntajNo ratings yet
- GlaucomaDocument15 pagesGlaucomaAmalliaPradisthaNo ratings yet
- Renal ColicDocument14 pagesRenal ColicIsabela OlgaNo ratings yet
- Syphilis Is An STD That Can Cause LongDocument3 pagesSyphilis Is An STD That Can Cause LongPaulyn BaisNo ratings yet
- HEMOPTYSISDocument21 pagesHEMOPTYSISYeny WijayantiNo ratings yet
- OSCE Skills 2013 1Document141 pagesOSCE Skills 2013 1Haseeb RayhanNo ratings yet
- Patient With RIF Pain: Differentials & ManagementDocument4 pagesPatient With RIF Pain: Differentials & ManagementgeotrophNo ratings yet
- Cefazolin and Dextrose USPDocument3 pagesCefazolin and Dextrose USPYaleswari Hayu PertiwiNo ratings yet
- 1 First Aid KitDocument27 pages1 First Aid KitDiji RakNo ratings yet
- MisoprostolDocument6 pagesMisoprostolMitchel Córdova LoaizaNo ratings yet
- No Nomor Kartu Nama Nomor SJP Poli Tujuan SJP Nama FKTPDocument3 pagesNo Nomor Kartu Nama Nomor SJP Poli Tujuan SJP Nama FKTPklinik dktNo ratings yet
- What Are The Symptoms of An Iron Deficiency?Document6 pagesWhat Are The Symptoms of An Iron Deficiency?Rei ChanNo ratings yet
- Case PresentationDocument13 pagesCase PresentationAnto BijuNo ratings yet
- Condensed ADULT DIABETIC KETOACIDOSIS (DKA) MANAGEMENT CHART Aug 2017Document2 pagesCondensed ADULT DIABETIC KETOACIDOSIS (DKA) MANAGEMENT CHART Aug 2017Zubair Mahmood KamalNo ratings yet
- Dr. Reckweg FormulaeDocument4 pagesDr. Reckweg FormulaeSatyendra RawatNo ratings yet
- Annual Medical ReportDocument6 pagesAnnual Medical ReportAnne Beatrice CarimpongNo ratings yet
- Harga Paten Feb 2017 (Sent)Document5 pagesHarga Paten Feb 2017 (Sent)khrisnagungNo ratings yet