Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pharmacology Antidepressants - UpToDate
Uploaded by
MelissandreCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pharmacology Antidepressants - UpToDate
Uploaded by
MelissandreCopyright:
Available Formats
Official reprint from UpToDate®
© 2020 UpToDate, Inc. and/or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved.www.uptodate.com
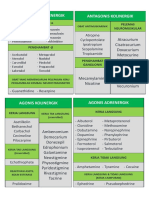
Unipolar depression in adults: Antidepressant doses*
Usual total starting Usual total dose per Extreme daily dose
Drug dose per day day range
(mg) ¶ (mg) (mg) ¶
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
Citalopram 20 20 to 40 Δ 10 to 40 Δ
Escitalopram 10 10 to 20 5 to 30
Fluoxetine 20 20 to 60 10 to 80
Fluvoxamine 50 50 to 200 25 to 300
Fluvoxamine CR 100 100 to 200 100 to 300
Paroxetine 20 20 to 40 10 to 50
Paroxetine CR 25 25 to 50 12.5 to 62.5
Sertraline 50 50 to 200 25 to 300
Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors
Desvenlafaxine 25 to 50 50 to 100 50 to 400 ◊
Duloxetine 30 to 60 60 30 to 120 §
Levomilnacipran 20 40 to 80 20 to 120
Milnacipran 12.5 100 to 200 50 to 300
Venlafaxine 37.5 to 75 75 to 375 75 to 375
Venlafaxine XR 37.5 to 75 75 to 225 75 to 375
Atypical agents
Agomelatine § (not 25 25 to 50 25 to 50
available in United States)
Bupropion 200 300 (maximum single dose 100 to 450
150 mg)
Bupropion SR 12 hour 150 300 (maximum single dose 150 to 400
200 mg)
Bupropion XL 24 hour 150 300 150 to 450 (United States)
150 to 300 (Europe)
Bupropion hydrobromide 174 348 174 to 522
24 hour
Mirtazapine 15 15 to 45 7.5 to 60
Serotonin modulators
Nefazodone ‡ 200 300 to 600 50 to 600
Trazodone 100 200 to 400 100 to 600
Vilazodone 10 40 10 to 40
Vortioxetine 10 20 5 to 20
Tricyclics and tetracyclics †
Amitriptyline 25 150 to 300 10 to 300
Amoxapine 25 200 to 300 25 to 400
Clomipramine 25 100 to 250 25 to 300
Desipramine 25 150 to 300 25 to 300
Doxepin 25 100 to 300 10 to 300
Imipramine 25 150 to 300 10 to 300
Maprotiline 25 100 to 225 25 to 225
Nortriptyline 25 50 to 150 10 to 150
Protriptyline 10 15 to 60 5 to 60
Trimipramine 25 150 to 300 25 to 300
Monamine oxidase inhibitors †
Isocarboxazid 10 10 to 40 10 to 60
Phenelzine 15 15 to 90 7.5 to 90
Selegiline transdermal 6 mg/24 hour patch 6 to 12 mg/24 hour patch 6 to 12 mg/24 hour patch
Tranylcypromine 10 30 to 60 10 to 60
* Total daily oral doses shown in table may need to be given as two or three equally divided doses per day, depending on specific
antidepressant and other factors. For additional detail, refer to individual Lexicomp drug monographs included with UpToDate.
¶ Lower end doses may be useful for initiating or maintaining elderly, medically compromised (eg, renal or hepatic illness), or drug
sensitive patients, as well as patients with a low body mass index. High doses may be used for medications that are well tolerated
but ineffective at lower doses.
Δ Maximum recommended dose of citalopram is 20 mg for patients >60 years of age, with significant hepatic insufficiency, or
taking interacting medications that can increase citalopram levels. For more information refer to the UpToDate topic on unipolar
depression in adults and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors.
◊ Although desvenlafaxine doses up to 400 mg per day have been studied, there is no evidence that doses >50 mg per day provide
any additional benefit.
§ Although doses >60 mg/day did not confer additional benefit in clinical trials, individual patients may benefit from dose escalation
up to a maximum of 120 mg/day.
¥ Agomelatine may be hepatotoxic and is contraindicated with any degree of liver impairment. Transaminase monitoring is
required according to the product information.
‡ Caution: can cause liver failure. Not available in Europe, Canada, and several other countries.
† Conservative starting doses shown in table are lower than starting doses shown in some other references. For additional
information, refer to UpToDate topics on unipolar depression in adults and cyclic antidepressants and monoamine oxidase
inhibitors for treatment of adults with depression.
Data from:
1. The American Psychiatric Publishing Textbook of Psychopharmacology, 4th edition. Schatzberg AF, Nemeroff CB (eds); American
Psychiatric Publishing, Inc. Washington, D.C. (2009).
2. Labbate LA, Fava M, Rosenbaum JF, Arana GW. Drugs for the treatment of depression. In: Handbook of Psychiatric Drug Therapy,
6th ed, Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia 2010. p.54.
3. Gartlehner G, Thaler K, Hill S, Hansen RA. How should primary care doctors select which antidepressants to administer? Curr
Psychiatry Rep 2012; 14:360.
4. Lexicomp Online. Copyright © 1978-2020 Lexicomp, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Graphic 53818 Version 30.0
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5796)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Methamphetamine Use Disorder - Epidemiology, Clinical Manifestations, Course, Assessment, and Diagnosis - UpToDate PDFDocument16 pagesMethamphetamine Use Disorder - Epidemiology, Clinical Manifestations, Course, Assessment, and Diagnosis - UpToDate PDFMelissandre100% (1)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Late Complications of Bariatric Surgical Operations - UpToDateDocument46 pagesLate Complications of Bariatric Surgical Operations - UpToDateMelissandreNo ratings yet
- CatinoneDocument32 pagesCatinoneanon_703837948100% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- APA - DSM5 - Severity Measure For Social Anxiety Disorder Adult PDFDocument3 pagesAPA - DSM5 - Severity Measure For Social Anxiety Disorder Adult PDFMelissandreNo ratings yet
- Atypical Antidepressants - Pharmacology, Administration, and Side Effects - UpToDateDocument16 pagesAtypical Antidepressants - Pharmacology, Administration, and Side Effects - UpToDateMelissandreNo ratings yet
- APA - DSM5 - Severity of Acute Stress Symptoms Adult PDFDocument3 pagesAPA - DSM5 - Severity of Acute Stress Symptoms Adult PDFMelissandreNo ratings yet
- APA - DSM5 - Severity Measure For Separation Anxiety Disorder Adult PDFDocument3 pagesAPA - DSM5 - Severity Measure For Separation Anxiety Disorder Adult PDFMelissandreNo ratings yet
- APA - DSM5 - Level 2 Repetitive Thoughts and Behaviors Adult PDFDocument3 pagesAPA - DSM5 - Level 2 Repetitive Thoughts and Behaviors Adult PDFMelissandreNo ratings yet
- APA - DSM5 - Severity Measure For Agoraphobia Adult PDFDocument3 pagesAPA - DSM5 - Severity Measure For Agoraphobia Adult PDFMelissandreNo ratings yet
- APA - DSM5 - Severity Measure For Specific Phobia Adult PDFDocument3 pagesAPA - DSM5 - Severity Measure For Specific Phobia Adult PDFMelissandreNo ratings yet
- APA - DSM5 - Clinician Rated Severity of Conduct Disorder PDFDocument2 pagesAPA - DSM5 - Clinician Rated Severity of Conduct Disorder PDFMelissandreNo ratings yet
- Prescription Stimulants' Effects On Healthy Inhibitory Control, Working Memory, and Episodic Memory - A Meta-AnalysisDocument23 pagesPrescription Stimulants' Effects On Healthy Inhibitory Control, Working Memory, and Episodic Memory - A Meta-AnalysisMelissandreNo ratings yet
- APA - DSM5 - Severity Measure For Panic Disorder Adult PDFDocument3 pagesAPA - DSM5 - Severity Measure For Panic Disorder Adult PDFMelissandreNo ratings yet
- How You Can Train Working MemoryDocument1 pageHow You Can Train Working MemoryMelissandreNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Biases: I Knew It All Along!Document5 pagesCognitive Biases: I Knew It All Along!MelissandreNo ratings yet
- Sound Manipulation: How You Can TrainDocument1 pageSound Manipulation: How You Can TrainMelissandreNo ratings yet
- Obat Klinik 2022-2023Document96 pagesObat Klinik 2022-2023jeane rahmanNo ratings yet
- Blanko Stok OpnameDocument24 pagesBlanko Stok OpnameBinti WibowoNo ratings yet
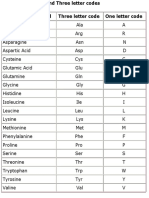
- Amino Acid CodesDocument1 pageAmino Acid Codesmorzan ortizNo ratings yet
- Olahan Maret Untuk LapiDocument232 pagesOlahan Maret Untuk LapiMedika AntapaniNo ratings yet
- Psikofarmaka Nama Obat Sediaan Merk Obat Nama Pabrik Anti PsikosisDocument4 pagesPsikofarmaka Nama Obat Sediaan Merk Obat Nama Pabrik Anti PsikosisClarissa AndersonNo ratings yet
- Perencanaan Pembelian Obat Dan BHPDocument11 pagesPerencanaan Pembelian Obat Dan BHPmayarita dilucaselNo ratings yet
- PKPADocument22 pagesPKPAYola SafitriNo ratings yet
- Orange BookDocument109 pagesOrange BookkayabaNo ratings yet
- List of Schedule I Drugs (US) - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument7 pagesList of Schedule I Drugs (US) - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaterterdgdfgdfgdfgfdgNo ratings yet
- Buspirone (Buspar) - Snorting ExperienceDocument11 pagesBuspirone (Buspar) - Snorting Experienceraven krowNo ratings yet
- AJINOMOTO 2013 Ideal Amino Acid Profile For PigletsDocument28 pagesAJINOMOTO 2013 Ideal Amino Acid Profile For PigletsFreddy Alexander Horna Morillo100% (1)
- EXISTENCIASDocument41 pagesEXISTENCIASadolfo pinoNo ratings yet
- USP Related CompoundsDocument8 pagesUSP Related CompoundsBoureghda FayçalNo ratings yet
- Latihan Analisis ABC (Pareto)Document11 pagesLatihan Analisis ABC (Pareto)Ekwan Prasetyo AzlinNo ratings yet
- LAPORAN PEMAKAIAN FARMASI 2019 (Autosaved) (Autosaved) FixDocument520 pagesLAPORAN PEMAKAIAN FARMASI 2019 (Autosaved) (Autosaved) FixEnrawani DamanikNo ratings yet
- ABC, STOCK, PENGADAAN - Copy-DikonversiDocument13 pagesABC, STOCK, PENGADAAN - Copy-DikonversiBayuSetiaNo ratings yet
- Antihistamines 101 Munich 06-05Document15 pagesAntihistamines 101 Munich 06-05pentruNo ratings yet
- PsychopharmacologyDocument1 pagePsychopharmacologypayumoNo ratings yet
- Pain JuniDocument36 pagesPain JuniNi Putu Ari FebriantariNo ratings yet
- Sas 2013Document8 pagesSas 2013api-252561013No ratings yet
- 12Document45 pages12Halimatun SyadyahNo ratings yet
- Daftar Harga April 2021 TerbaruDocument92 pagesDaftar Harga April 2021 TerbarulylywaternuryndahsaryNo ratings yet
- Daftar Obat Pengobatan MassalDocument7 pagesDaftar Obat Pengobatan MassalChristian Hasudungan NainggolanNo ratings yet
- Antagonis Kolinergik Antagonis AdrenergikDocument8 pagesAntagonis Kolinergik Antagonis AdrenergikmarsellaNo ratings yet
- PricelistDocument4 pagesPricelistMAYMART CASABANo ratings yet
- Rencana Distribusi Obat PuskesmasDocument58 pagesRencana Distribusi Obat PuskesmasLita Rahma YulitaNo ratings yet
- PhikalDocument4 pagesPhikalDennis OptionalNo ratings yet
- Daftar Obat Yang Dimusnahkan Tahun 2020Document10 pagesDaftar Obat Yang Dimusnahkan Tahun 2020Agie ArieNo ratings yet
- Nama Obat Jumlah Order DistributorDocument22 pagesNama Obat Jumlah Order DistributorNdaa NandaNo ratings yet