Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP Anemia
Uploaded by
Aria0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
541 views2 pagesOriginal Title
NCP_Anemia.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
541 views2 pagesNCP Anemia
Uploaded by
AriaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
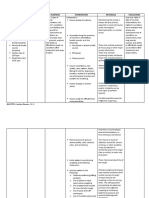
NURSING CARE PLAN
ASSESSMENT NURSING PLANNING NURSING RATIONALE EVALUATION
DIAGNOSIS INTERVENTION
Subjective: Anemia, related to Long term: Monitor Decreased RBC indexes Long term:
The client states that decreased After 3 days of hemoglobin, are associated with After 3 days of nursing
she is feeling tired hemoglobin as nursing intervention hematocrit, decreased oxygen- intervention the client
and has shortness of evidenced by the client will be able RBC counts, carrying capacity of the has been able to achieve
breath exertional to achieve improved and blood. It is critical to improved condition
discomfort or condition from risk reticulocyte compare serial from risk factor.
dyspnea. factor. counts. laboratory values to
Objective: Assist the evaluate progression or Short Term:
Abnormal Short term: client in deterioration in the After 15 minutes of
labs (CBC = After 15 minutes of planning and client and to identify nursing intervention the
decreased nursing interventions prioritizing changes before they client verbalized
RBC and the client verbalizes activities of become potentially life- understanding of risk
HGB) understanding of risk daily living threatening. factor
pale skin factor (ADL). This will allow the client
dizziness Assist the to maximize his/her time
dyspnea client in for accomplishing
fatigue developing a important activities. Not
headaches schedule for all self-care and hygiene
irritability daily activity activities need to be
and rest. completed i the
Stress the morning. Likewise, not
importance of all housework needs to
frequent rest be completed in one
periods. day.
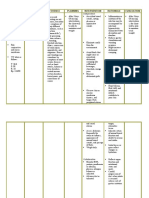
Educate Energy reserves may be
energy- depleted unless the
conservation client respects the
techniques. body’s need for
Instruct the increased rest. A plan
client about that balances periods of
medications activity with periods of
that may rest can help the client
stimulate RBC complete desired
production in activities without adding
the bone levels to fatigue.
marrow. Clients and caregivers
Provide may need to learn skills
supplemental for delegating task to
oxygen others, setting priorities,
therapy, as and clustering care to
needed. use available energy to
Anticipate the complete desired
need for the activities. Organization
transfusion of and time management
packed RBCs. can help the client
conserve energy and
reduce fatigue.
Recombinant human
erythropoietin, a
hematological growth
factor, increases
hemoglobin and
decreases the need for
RBC transfusions.
Oxygen saturation
should be kept at 90% or
greater.
Packed RBCs increase
oxygen-carrying capacity
of the blood.
You might also like
- Aubrey Rose A. Vidon BSN 3Y1-2 September 4, 2020 Course Task #2Document11 pagesAubrey Rose A. Vidon BSN 3Y1-2 September 4, 2020 Course Task #2Aria0% (1)
- Course Task #3: AnswerDocument5 pagesCourse Task #3: AnswerAria100% (3)
- MS Cu6Document1 pageMS Cu6AriaNo ratings yet
- MS CourseTask10Document2 pagesMS CourseTask10Aria67% (3)
- MS CourseUnit9Document2 pagesMS CourseUnit9Aria100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan 2Document6 pagesNursing Care Plan 2KM TopacioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Interaction Immediate Cause Goal: Effectivenes SDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan: Interaction Immediate Cause Goal: Effectivenes SCatherine Kaye Marquez RoxasNo ratings yet
- Body Weakness NCPDocument1 pageBody Weakness NCPtwicetrashNo ratings yet
- IBSDocument1 pageIBSIris MambuayNo ratings yet
- Lung Cancer (Nursing Care)Document5 pagesLung Cancer (Nursing Care)heiyuNo ratings yet
- NCP DMDocument6 pagesNCP DMstara123No ratings yet
- Nursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Hepatitis A PDFDocument2 pagesNursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Hepatitis A PDFswapnilazarusNo ratings yet
- ASSESSMENT HEALTH NURSING INTERVENTION EVALUATIONDocument3 pagesASSESSMENT HEALTH NURSING INTERVENTION EVALUATIONtflorenzNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument9 pagesNCPHendy Hency YunusNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective DataDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective DataAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Peptic UlcerDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Peptic UlcerJefferson Baluyot PalmaNo ratings yet
- SDL 1Document2 pagesSDL 1Duchess Juliane Jose MirambelNo ratings yet
- NCP DM and HCVDDocument3 pagesNCP DM and HCVDMAYBELINE OBAOB100% (1)
- Hepatitis A N C P BY BHERU LALDocument2 pagesHepatitis A N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalNo ratings yet
- NCP PryllDocument6 pagesNCP PryllpjcolitaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnisis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnisis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument4 pagesNCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceJet BautistaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study SARAHDocument2 pagesDrug Study SARAHirene Joy DigaoNo ratings yet
- NCP (Acute Pain)Document2 pagesNCP (Acute Pain)jennilois100% (1)
- NURSING Nursing Care Plan for Diabetes MellitusDocument3 pagesNURSING Nursing Care Plan for Diabetes MellitusYsun Espino100% (1)
- NCP 1Document1 pageNCP 1Rommelie CaballeroNo ratings yet
- NCP Pre EclampsiaDocument2 pagesNCP Pre EclampsiaFarrah Grace Birowa0% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanKath RubioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Patient with PruritusDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan for Patient with PruritusJachel Kathleen LaguioNo ratings yet
- Pre-Operative (Incision & Drainage of Abscess)Document6 pagesPre-Operative (Incision & Drainage of Abscess)Eunice MañalacNo ratings yet
- Healthcare - Nursing Care Plan - Excess Fluid VolumeDocument4 pagesHealthcare - Nursing Care Plan - Excess Fluid VolumeBenjamin CañalitaNo ratings yet
- Bowel incontinence diagnosis and interventionsDocument9 pagesBowel incontinence diagnosis and interventionsners_gun100% (1)
- NCP Ineffective Breastfeeding PDFDocument1 pageNCP Ineffective Breastfeeding PDFJACOB AQUINTEYNo ratings yet
- NCP Blood Glucose Imbalance 4thDocument2 pagesNCP Blood Glucose Imbalance 4thRainier IbarretaNo ratings yet
- Homework - Anxiety Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesHomework - Anxiety Nursing Care PlanmonaNo ratings yet
- NCP For ConcussionDocument3 pagesNCP For Concussiontamtam_antonio100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For LYING inDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For LYING inKarissa CiprianoNo ratings yet
- Davao Doctors College Nursing Care Plan for Patient ZDocument3 pagesDavao Doctors College Nursing Care Plan for Patient ZGicaDayap100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- NCP - ERDocument5 pagesNCP - ERAnnelore ArcayNo ratings yet
- NCP Arra AnemiaDocument2 pagesNCP Arra AnemiaShin GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Date/ Time/ Shift Cues Need Nursing Diagnosis With Rationale Objectives of Care Nursing Interventions With Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesDate/ Time/ Shift Cues Need Nursing Diagnosis With Rationale Objectives of Care Nursing Interventions With Rationale EvaluationPauleen Trisha SamparaniNo ratings yet
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationCharina AubreyNo ratings yet
- Fistula NCPDocument1 pageFistula NCPHasna LisnaNo ratings yet
- San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesDocument3 pagesSan Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, Philippineskuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPCamille VirayNo ratings yet
- FAMILY NURSING CARE PLANDocument3 pagesFAMILY NURSING CARE PLANSoniaMarieBalanayNo ratings yet
- NCP MRMDocument2 pagesNCP MRMKhloe Cristel Llanes Torres100% (1)
- Drug Study Pedia WardDocument2 pagesDrug Study Pedia WardCayanne ChuaNo ratings yet
- NCP Inactivity ToleranceDocument16 pagesNCP Inactivity ToleranceChrisTine M. MoralesNo ratings yet
- Ivf StudyDocument2 pagesIvf StudyDanePepitoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume DeficitDocument2 pagesFluid Volume DeficitpeternohibiNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance - PTBDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance - PTBIrish Eunice FelixNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan ADocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan ACrystal WyattNo ratings yet
- Activity IntoleranceDocument2 pagesActivity IntoleranceJaney Ceniza تNo ratings yet
- ESOMEPRAZOLEDocument6 pagesESOMEPRAZOLEGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Case Study NCP ActualDocument3 pagesCase Study NCP Actualdhamy florNo ratings yet
- Seizure NCPDocument2 pagesSeizure NCPChristine Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Impaired Physical MobilityDocument1 pageImpaired Physical MobilitySheena Yen de Pano-PagdalianNo ratings yet
- Assessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesAssessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationimnasNo ratings yet
- R.O. Appendicitis.: Nursing Care Plan (NCP)Document2 pagesR.O. Appendicitis.: Nursing Care Plan (NCP)Karen Joy ItoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Plan for Anemia ManagementDocument2 pagesNursing Plan for Anemia ManagementAriaNo ratings yet
- NcpFatigue Related To Decreased Hemoglobin and Diminished Oxygen-Carrying Capacity of The Blood.Document3 pagesNcpFatigue Related To Decreased Hemoglobin and Diminished Oxygen-Carrying Capacity of The Blood.The Right WayNo ratings yet
- NCP AnemiaDocument3 pagesNCP AnemiaJadeNo ratings yet
- Finding Your Ideal Length Of Time For Focused Work - Based On The Teachings Of Dr. Andrew Huberman: Unlocking Peak ProductivityFrom EverandFinding Your Ideal Length Of Time For Focused Work - Based On The Teachings Of Dr. Andrew Huberman: Unlocking Peak ProductivityNo ratings yet
- JKDocument3 pagesJKAriaNo ratings yet
- Microbial Diseases of Nervous SystemDocument11 pagesMicrobial Diseases of Nervous SystemAriaNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Sex Ed Study Benefits Parents Students ResearchersDocument2 pagesComprehensive Sex Ed Study Benefits Parents Students ResearchersAriaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAriaNo ratings yet
- Course Unit Task #3: Aubrey Rose A.Vidon September 15, 2020 BSN 3Y1 - 2 Ncmb312 LabDocument3 pagesCourse Unit Task #3: Aubrey Rose A.Vidon September 15, 2020 BSN 3Y1 - 2 Ncmb312 LabAriaNo ratings yet
- Compare and Contrast Two Obstructive Lung Disorders: Asthma vs COPDDocument1 pageCompare and Contrast Two Obstructive Lung Disorders: Asthma vs COPDAriaNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Sensory Changes in Older People: Chelsey Mae D. Rafael / Aubrey Rose A.Vidon BSN 3Y1 - 2Document4 pagesCase Study: Sensory Changes in Older People: Chelsey Mae D. Rafael / Aubrey Rose A.Vidon BSN 3Y1 - 2AriaNo ratings yet
- Identify A Teacher You Might Had in The Past Who Think Was A Good Teacher But Do NotDocument4 pagesIdentify A Teacher You Might Had in The Past Who Think Was A Good Teacher But Do NotAriaNo ratings yet
- NURES GanttChartDocument2 pagesNURES GanttChartAriaNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Gastrointestinal System of Older People Case Scenario: LapayDocument1 pageCase Study: Gastrointestinal System of Older People Case Scenario: LapayAriaNo ratings yet
- Aubrey Rose A. Vidon August 29, 2020 BSN 3Y1-2 Course Task #1Document2 pagesAubrey Rose A. Vidon August 29, 2020 BSN 3Y1-2 Course Task #1AriaNo ratings yet
- Group 2 EXAMDocument5 pagesGroup 2 EXAMAriaNo ratings yet
- Name of PatientDocument1 pageName of PatientAriaNo ratings yet
- LyricsDocument2 pagesLyricsAriaNo ratings yet
- Aubrey Rose A. Vidon BSN 3Y1 - 2Document2 pagesAubrey Rose A. Vidon BSN 3Y1 - 2Aria100% (1)
- Aubrey Rose A. Vidon BSN 3Y1 - 2 October 5, 2020 Course Task #3Document2 pagesAubrey Rose A. Vidon BSN 3Y1 - 2 October 5, 2020 Course Task #3AriaNo ratings yet
- Measuring Blood Pressure AccuratelyDocument3 pagesMeasuring Blood Pressure AccuratelyAriaNo ratings yet
- Aubrey Rose A. Vidon BSN 3Y1 - 2 October 20, 2020 TOPIC: An Evaluative Study of Bachelor of Science in Nursing Students of Our Lady of FatimaDocument2 pagesAubrey Rose A. Vidon BSN 3Y1 - 2 October 20, 2020 TOPIC: An Evaluative Study of Bachelor of Science in Nursing Students of Our Lady of FatimaAriaNo ratings yet
- MS CourseTask8Document3 pagesMS CourseTask8Aria100% (1)
- Nursing Plan for Anemia ManagementDocument2 pagesNursing Plan for Anemia ManagementAriaNo ratings yet
- Sexuality Education Research Impacts NursingDocument8 pagesSexuality Education Research Impacts NursingAriaNo ratings yet
- MS Discussion1Document1 pageMS Discussion1AriaNo ratings yet
- Aubrey Rose A. Vidon BSN 3Y1 - 2Document2 pagesAubrey Rose A. Vidon BSN 3Y1 - 2AriaNo ratings yet
- Group #4: Unit Task #1 (Nursing Research I)Document11 pagesGroup #4: Unit Task #1 (Nursing Research I)AriaNo ratings yet
- Bible Aromatherapy 2022Document39 pagesBible Aromatherapy 2022johanjacobvelosagomezNo ratings yet
- Week1 - NAILCARE (Sek)Document2 pagesWeek1 - NAILCARE (Sek)rhyzeneNo ratings yet
- Soal BIGDocument12 pagesSoal BIGRifNo ratings yet
- Class Test 3Document3 pagesClass Test 3Balakrishnan MarappanNo ratings yet
- Info - PathophysiologyDocument6 pagesInfo - PathophysiologyRupert BassigNo ratings yet
- Understand the Difference Between Omega-3 EPA and DHADocument7 pagesUnderstand the Difference Between Omega-3 EPA and DHASutanto TanakaNo ratings yet
- Etiology and Pathogenesis of The Congenital Pneumonia in Newborns Literature Review Part 1 PDFDocument4 pagesEtiology and Pathogenesis of The Congenital Pneumonia in Newborns Literature Review Part 1 PDFGolden DawnNo ratings yet
- DLL ObservationDocument5 pagesDLL ObservationBelinda LapsitNo ratings yet
- Baby Thesis RevisedDocument20 pagesBaby Thesis RevisedSanjoe Angelo ManaloNo ratings yet
- Journal - A Bracket Positioning OverviewDocument5 pagesJournal - A Bracket Positioning OverviewRetta GabriellaNo ratings yet
- Resume About NoiseDocument5 pagesResume About NoiseElsa MutiaraNo ratings yet
- Acute GlomerulonephritisDocument1 pageAcute GlomerulonephritisAyrheen FornolesNo ratings yet
- Rebecca Sunseri: Developing A Nutrition PlanDocument7 pagesRebecca Sunseri: Developing A Nutrition PlanBecca SunseriNo ratings yet
- Achigan-DakoTchokponhoueNDanikouetal 2015Document13 pagesAchigan-DakoTchokponhoueNDanikouetal 2015Juan Pablo Hernandez PaezNo ratings yet
- Phlebotomy Essentials 7th EditionDocument61 pagesPhlebotomy Essentials 7th Editioneric.rodriguez669100% (44)
- Lista Detaliata A Serviciilor Regina MariaDocument69 pagesLista Detaliata A Serviciilor Regina MariaAmreusit SaschimbnumeleNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Presentation MIOSHADocument77 pagesPowerpoint Presentation MIOSHAMD AZHER ULLAH BAIGNo ratings yet
- Running Head: QSEN 1Document11 pagesRunning Head: QSEN 1Mariam AbedNo ratings yet
- Professional Foundation Level Acupressure Training CourseDocument94 pagesProfessional Foundation Level Acupressure Training CourseLuis Del Valle TorregrosaNo ratings yet
- Pneumothoraks Jurnal RadiologiDocument9 pagesPneumothoraks Jurnal RadiologiRachmi MerrinaNo ratings yet
- VGO-411 Veterinary Gynaecology Question BankDocument7 pagesVGO-411 Veterinary Gynaecology Question BankSuryakantaRoulTuntunNo ratings yet
- Barangay Staff Accomplishment Report New LHDocument2 pagesBarangay Staff Accomplishment Report New LHUy HenryNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - 1. Research Overview TranscriptDocument13 pagesModule 2 - 1. Research Overview TranscriptpatrickfvlboltNo ratings yet
- DT Asa Bella-1Document12 pagesDT Asa Bella-1Bella Faradiska YuandaNo ratings yet
- Special Edition E-80 4Document2 pagesSpecial Edition E-80 4Ankit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Usb Powered Led Strip: User GuideDocument5 pagesUsb Powered Led Strip: User Guidespiritos123456789No ratings yet
- Week 3 (20!09!2021) Compe Law ProvisionsDocument18 pagesWeek 3 (20!09!2021) Compe Law ProvisionsNeil FrangilimanNo ratings yet
- Stree Rog 4Document11 pagesStree Rog 4Sambamurthi Punninnair NarayanNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation: Presenter: DR Amanda Lundah Date: 15/4/20Document25 pagesCase Presentation: Presenter: DR Amanda Lundah Date: 15/4/20King MazingaNo ratings yet
- CariesCare-International Consensus-Manuscript BDJ-corrected 12062019Document13 pagesCariesCare-International Consensus-Manuscript BDJ-corrected 12062019pocket4love4yeahNo ratings yet