Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IBS
Uploaded by
Iris Mambuay0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
242 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
242 views1 pageIBS
Uploaded by
Iris MambuayCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Cagayan de Oro College PHINMA Education Network
College of Allied Health Sciences
Nursing Department
BSN-3 Medical Surgical Nursing Activity Sheet
2nd Semester, Periodical 1, S.Y. 2020-2021
NAMES:__________MAMBUAY, IRIS JUNE F.__________________________________________ DATE:_02/09/2021______
SECTION:__C1-01___________ C.I:_MS. PHOEBE JAENN TAN, RN_________
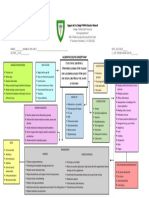
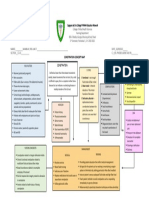
IBS (IRRITABLE BOWEL SYNDROME) CONCEPT MAP
IBS (IRRITABLE BOWEL SYNDROME) CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
RISK FACTORS
TYPES
Results from a functional disorder of intestinal motility, it is Occasional urgency
Women one of the most common GI problems in the large IBS-C - constipation Poor control of flatus
NURSING INTERVENTIONS Heredity intestines. Also defines as a chronic dysfunctional disorder
IBS-D – diarrhea Diarrhea or constipation
Psychological stress characterized by recurrent abdominal pain associated with
IBS-M – both Rectal bleeding
Promote diet and lifestyle Depression and anxiety disordered bowel movements which may include diarrhea,
IBS-U – unknown Weight loss
changes Diet high in fat and stimulating or irritating food constipation or both.
Instruct to avoid food triggers Migraine headaches
Alcohol consumption
Encourage eating of high-fiber Smoking ASSESSMENT/DX
diet and increase fluid intake Sleep deprivation
Management of stressors Surgery Diagnostic criteria: COMPLICATIONS S/SX
through assistance of SO a) Recurrent abdominal pain or discomfort for at least 3 days
Infections
Laxatives are suggested but a month in the past 3 mos., including two or more of the ff: Mood disorders Cramping
Diverticulitis
with careful use a) Improvement with defecation Depression Abdominal pain
Chronic fatigue syndrome
Frequent hand washing with b) Onset associated with change in frequency of stool Anxiety Bloating
Chronic pelvic pain
antibacterial soaps c) Onset associated with change in appearance Impacted bowel Gas
Fibromyalgia
To rule out other colon diseases: Food intolerance Mood changes
Interstitial cystitis
a) Stool studies Malnourishment Vomiting
GERD
b) Contrast x-ray studies Hemorrhoids Persistent pain that isn’t relieved by
c) Proctoscopy Pregnancy complications passing gas or bowel movement
Barium enema and colonoscopy
NURSING DIAGNOSES Manometry and electromyography
Imbalanced nutrition: less than body requirements related to MEDICAL/NURSING MANAGEMENT
altered absorption Restriction and then gradual reintroduction of foods that Participate in a stress or behaviour modification program
Acute pain related to abdominal muscle spasms are possibly irritating i.e beans, caffeinated beverages, Consumption of probiotics
Diarrhea secondary to IBS corn, wheat, dairy, fried foods, alcohol, spicy foods and Antidiarrheal agents, antidepressants and
Ineffective coping related to stress and anxiety secondary to IBS aspartame anticholinergic/antispasmodics
Risk for deficient fluid volume related to diarrhea Opt for high-fiber diet Artichoke leaf extract. Peppermint oil and caraway oil
Powerlessness related to current health condition Exercise Discourage smoking/alcohol
Deficient knowledge regarding lack of information Adequate rest and sleep Fluids should not be taken with meals
Fiber supplements
You might also like
- NCP DM and HCVDDocument3 pagesNCP DM and HCVDMAYBELINE OBAOB100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument24 pagesDrug Studyabulan100% (1)
- Chronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesChronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanRuva Oscass JimmyNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Peripheral Tissue Perfusion Related To Vasoconstriction Secondary To High Glucose Level.Document6 pagesIneffective Peripheral Tissue Perfusion Related To Vasoconstriction Secondary To High Glucose Level.SAROL, RYAN CHRISTIAN B.No ratings yet
- Generic Brand Class Therapeutic Pharmacologic Dosage: PPD's Better Pharmacy Drug Hand Book 9 Edition 2009Document4 pagesGeneric Brand Class Therapeutic Pharmacologic Dosage: PPD's Better Pharmacy Drug Hand Book 9 Edition 2009Crystal Queen MarquezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective DataDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective DataAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Colestipol Hydrochloride Nursing ConsiderationsDocument3 pagesColestipol Hydrochloride Nursing ConsiderationsAbby AngNo ratings yet
- Content: Outline Form Only Make A Separate Sheet For The Content. The Health Teaching Plan Should Focus On Home Care For Patients With Mood DisorderDocument4 pagesContent: Outline Form Only Make A Separate Sheet For The Content. The Health Teaching Plan Should Focus On Home Care For Patients With Mood DisorderRaffy Sebastian Seballos100% (1)
- Relationship Between CKD Stage and Pulmonary Edema on Chest X-RayDocument6 pagesRelationship Between CKD Stage and Pulmonary Edema on Chest X-RayAnnisa RabbaniNo ratings yet
- Lack of Knowledge On Diabetes Management or Blood Glucose ManagementDocument2 pagesLack of Knowledge On Diabetes Management or Blood Glucose ManagementDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan DiarrheaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan DiarrheaAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Actibile: Formulation: Drug InteractionsDocument1 pageActibile: Formulation: Drug InteractionsNxxxNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Obstructive JaundiceDocument11 pagesCase Study: Obstructive JaundiceZhy CaluzaNo ratings yet
- DuphalacDocument2 pagesDuphalacianecunarNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan UlcerDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Ulcerxrampley2100% (2)
- Impaired Physical MobilityDocument2 pagesImpaired Physical MobilityAbdelhafiz SusmiranNo ratings yet
- Actual NCPDocument2 pagesActual NCPbaki0146No ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Goal Interventions Expected Outcome: (List 5 Unique To The Given Nursing DX)Document3 pagesNursing Diagnosis Goal Interventions Expected Outcome: (List 5 Unique To The Given Nursing DX)joyrena ochondraNo ratings yet
- Drug AnalysisDocument3 pagesDrug AnalysisAnn Aquino100% (1)
- Assessment, Diagnosis, Planning, Intervention and Evaluation of a Client with Increased Airway SecretionsDocument3 pagesAssessment, Diagnosis, Planning, Intervention and Evaluation of a Client with Increased Airway SecretionsNicholas TagleNo ratings yet
- Case File GERDDocument9 pagesCase File GERDMutiara Shifa100% (1)
- Discharge Plan For AppendectomyDocument1 pageDischarge Plan For AppendectomyMyra AtuleNo ratings yet
- Renal Failure NCPDocument3 pagesRenal Failure NCPjsksNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (Acute Pain)Document1 pageNursing Care Plan (Acute Pain)kyaw100% (2)
- Drug Classification: Antacid & Antihistamine Student ReportDocument2 pagesDrug Classification: Antacid & Antihistamine Student ReportKish AmoreNo ratings yet
- NCP RheumatoidDocument5 pagesNCP RheumatoidJane Elizabeth Gonzales MacahiaNo ratings yet
- Discharge PlanDocument9 pagesDischarge PlanRheynel NietesNo ratings yet
- NCP PainDocument2 pagesNCP PainApril_Ivy_Raga_3835No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyMelody Forca FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal System Disorders NCLEX Practice - Quiz #2 - 50 Questions - NurseslabsDocument52 pagesGastrointestinal System Disorders NCLEX Practice - Quiz #2 - 50 Questions - NurseslabsGypsy Joan TranceNo ratings yet
- DP Discharge Plan@@@@@@@@Document6 pagesDP Discharge Plan@@@@@@@@Maemae SumalinogNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Disorder QuizDocument35 pagesCognitive Disorder QuizCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Rheumatoid ArthritisJashAnia MarIe EvArdo FloresNo ratings yet
- Case No 45: of Intermittent Abdominal Pain Abdominal Bloating and Nausea and Vomiting (NVDocument17 pagesCase No 45: of Intermittent Abdominal Pain Abdominal Bloating and Nausea and Vomiting (NVPremiums of the RoseNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlanCindy MariscotesNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndeoendentDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndeoendentDiane Sarino CabonceNo ratings yet
- "Nahadlok Naman Ko Sa Akong Gipambati, Ning-Undang Ko Sakong Work As QHSE and Training Manager, Nagdecide Ko Muuli Sa Pilipinas. Pag-Uli Nako Last Week, Ginabati Nako Mura Ko Makulbaan" AsDocument4 pages"Nahadlok Naman Ko Sa Akong Gipambati, Ning-Undang Ko Sakong Work As QHSE and Training Manager, Nagdecide Ko Muuli Sa Pilipinas. Pag-Uli Nako Last Week, Ginabati Nako Mura Ko Makulbaan" Ashanna caballoNo ratings yet
- NCP Blood Glucose Imbalance 4thDocument2 pagesNCP Blood Glucose Imbalance 4thRainier IbarretaNo ratings yet
- Risk For Activity Intolerance NCPDocument2 pagesRisk For Activity Intolerance NCPMike SoySauce LibrojoNo ratings yet
- Assessment, Diagnosis, Planning, Intervention and Evaluation for Decreased AppetiteDocument1 pageAssessment, Diagnosis, Planning, Intervention and Evaluation for Decreased AppetiteVanetNo ratings yet
- Ngo 2bsn1 Ncm109 Prelim NCPDocument7 pagesNgo 2bsn1 Ncm109 Prelim NCPAMIEL SIMON NGONo ratings yet
- Nursing Interventions for Effective Airway ManagementDocument2 pagesNursing Interventions for Effective Airway ManagementwaadNo ratings yet
- Final Case StudyDocument18 pagesFinal Case Studyapi-487702467100% (1)
- SDL 1Document2 pagesSDL 1Duchess Juliane Jose MirambelNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Tissue InjuryDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Tissue InjuryJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Examples of Therapeutic and Non Therapeutic Communication TechniquesDocument6 pagesExamples of Therapeutic and Non Therapeutic Communication TechniquesReya Mae OrcajadaNo ratings yet
- Primaxin (Imipenem - Cilistatin)Document2 pagesPrimaxin (Imipenem - Cilistatin)ENo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Peptic UlcerDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Peptic UlcerJefferson Baluyot PalmaNo ratings yet
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (Gerd) : By: Therese Jane TimbalopezDocument14 pagesGastroesophageal Reflux Disease (Gerd) : By: Therese Jane Timbalopezjoyrena ochondraNo ratings yet
- Student Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan AmputationDocument3 pagesStudent Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan AmputationNur faizah bt azmiNo ratings yet
- Rle Worksheet Nursing ProcessDocument6 pagesRle Worksheet Nursing ProcessMARVIE JOY BALUMA CABIOCNo ratings yet
- SLCN Gazette Magazine, Volume 1, Issue 1, 2019Document20 pagesSLCN Gazette Magazine, Volume 1, Issue 1, 2019Mayzelle RizNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanPrince Juzzel Banag100% (1)
- Name of The DrugDocument2 pagesName of The DrugSistine Rose LabajoNo ratings yet
- Nursing responsibilities for ampicillinDocument3 pagesNursing responsibilities for ampicillinCharlene Serino JavierNo ratings yet
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Causes, Symptoms and ManagementDocument6 pagesIrritable Bowel Syndrome: Causes, Symptoms and ManagementmynameNo ratings yet
- Concept Map For Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (Gerd)Document1 pageConcept Map For Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (Gerd)Iris MambuayNo ratings yet
- 14 (MANUSCRIPT) Irritable Bowel SyndromeDocument11 pages14 (MANUSCRIPT) Irritable Bowel Syndromekint manlangitNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1BSN 14 Group 1Document8 pagesNursing Care Plan 1BSN 14 Group 1Mikaella GacostaNo ratings yet
- CHOLELITHIASISDocument4 pagesCHOLELITHIASISKate ValdesNo ratings yet
- Crohn'S Disease Concept MapDocument1 pageCrohn'S Disease Concept MapIris MambuayNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer Disease (Pud) Concept Map PUDDocument1 pagePeptic Ulcer Disease (Pud) Concept Map PUDIris Mambuay0% (1)
- Ulcerative Colitis Concept MapDocument1 pageUlcerative Colitis Concept MapIris MambuayNo ratings yet
- Review of Digestive SystemDocument3 pagesReview of Digestive SystemIris MambuayNo ratings yet
- Concept Map For Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (Gerd)Document1 pageConcept Map For Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (Gerd)Iris MambuayNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea Concept MapDocument1 pageDiarrhea Concept MapIris MambuayNo ratings yet
- Viral Hepatitis (A) - DummyDocument3 pagesViral Hepatitis (A) - DummyIris MambuayNo ratings yet
- Code of Ethics for Filipino NursesDocument2 pagesCode of Ethics for Filipino NursesJessica Christel MaglalangNo ratings yet
- Ulcerative Colitis Concept MapDocument1 pageUlcerative Colitis Concept MapIris MambuayNo ratings yet
- Reflection On Webinar About Healthy Living During The PandemicDocument2 pagesReflection On Webinar About Healthy Living During The PandemicIris MambuayNo ratings yet
- PERIOPERATIVE NURSING BASICS: STERILE TECHNIQUEDocument10 pagesPERIOPERATIVE NURSING BASICS: STERILE TECHNIQUEIris MambuayNo ratings yet
- Constipation Concept MapDocument1 pageConstipation Concept MapIris MambuayNo ratings yet
- Practice ProblemsDocument1 pagePractice ProblemsIris MambuayNo ratings yet
- Nursing Research NotesDocument12 pagesNursing Research NotesIris MambuayNo ratings yet
- Practice ProblemsDocument1 pagePractice ProblemsIris MambuayNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Nursing Care: Managing Pain and Risk of InfectionDocument6 pagesPostpartum Nursing Care: Managing Pain and Risk of InfectionIris MambuayNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing QuestionnaireDocument5 pagesMaternal and Child Health Nursing QuestionnaireIris MambuayNo ratings yet
- Cognitive LearningDocument8 pagesCognitive LearningIris MambuayNo ratings yet
- MCN NCP3Document4 pagesMCN NCP3Iris MambuayNo ratings yet
- MCN NCP3Document4 pagesMCN NCP3Iris MambuayNo ratings yet
- Theories and Principles of Health EthicsDocument2 pagesTheories and Principles of Health EthicsIris MambuayNo ratings yet
- Pediatric DosesDocument17 pagesPediatric DosesIris MambuayNo ratings yet
- Pedia Meal PlanDocument2 pagesPedia Meal PlanIris MambuayNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing QuestionnaireDocument5 pagesMaternal and Child Health Nursing QuestionnaireIris MambuayNo ratings yet
- Theories and Principles of Health Ethics ExplainedDocument21 pagesTheories and Principles of Health Ethics ExplainedIris MambuayNo ratings yet
- Botulism: BSN Ii - ADocument11 pagesBotulism: BSN Ii - AIris MambuayNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Nursing Care: Managing Pain and Risk of InfectionDocument6 pagesPostpartum Nursing Care: Managing Pain and Risk of InfectionIris MambuayNo ratings yet
- Theories and Principles of Health EthicsDocument2 pagesTheories and Principles of Health EthicsIris MambuayNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet: Silica FumeDocument3 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: Silica FumeEzequiel BeitiaNo ratings yet
- The First Six Weeks by Midwife Cath (Extract)Document24 pagesThe First Six Weeks by Midwife Cath (Extract)Allen & Unwin14% (7)
- Saadat Hasan Manto, Partition, and Mental Illness Through The Lens of Toba Tek SinghDocument6 pagesSaadat Hasan Manto, Partition, and Mental Illness Through The Lens of Toba Tek SinghIrfan BalochNo ratings yet
- Deep Learning Based PET MR Radiomics For The ClassDocument8 pagesDeep Learning Based PET MR Radiomics For The ClassRon FranklinNo ratings yet
- 1 01 Foodborne IllnessDocument28 pages1 01 Foodborne Illnessapi-329321140No ratings yet
- Breach of Duty of CareDocument46 pagesBreach of Duty of CareJavier LimNo ratings yet
- Choice and Medication Benefits LeafletDocument3 pagesChoice and Medication Benefits LeafletrowanpurdyNo ratings yet
- Arogya Sanjeevani Policy, Star Health and Allied Insurance Co LTDDocument9 pagesArogya Sanjeevani Policy, Star Health and Allied Insurance Co LTDMANTUNo ratings yet
- Expository Essay: Name: Mistry R. Paut Class: Ii BDocument2 pagesExpository Essay: Name: Mistry R. Paut Class: Ii BMistry RfnrstyNo ratings yet
- Pahade Et Al 2021 Indian (Marathi) Version of The Shoulder Pain and Disability Index (Spadi) TranslatioDocument8 pagesPahade Et Al 2021 Indian (Marathi) Version of The Shoulder Pain and Disability Index (Spadi) TranslatioAnnisa Assyifa YustianNo ratings yet
- DEMet Advisory Curriculum Part OneDocument127 pagesDEMet Advisory Curriculum Part OnePeter BurnhamNo ratings yet
- Textual EvidenceDocument28 pagesTextual EvidenceGRECEL JOYCE M. ONGCONo ratings yet
- Mail For Uploading The VideoDocument1 pageMail For Uploading The VideoDr Subodh ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Disease Prediction Using Machine Learning Algorithms2020 PDFDocument7 pagesDisease Prediction Using Machine Learning Algorithms2020 PDFSumati BaralNo ratings yet
- Encefalitis LimbicaDocument11 pagesEncefalitis LimbicaRandy UlloaNo ratings yet
- IDSA Molnupiravir GuidelineDocument10 pagesIDSA Molnupiravir GuidelineJaz ButuyanNo ratings yet
- Gestational Diabetes Mellitus - : One Disease Two Lives at StakeDocument31 pagesGestational Diabetes Mellitus - : One Disease Two Lives at StakeSadia YousafNo ratings yet
- PC and NPC Creation Tables PDFDocument7 pagesPC and NPC Creation Tables PDFAut80% (5)
- OREO Personality TestDocument9 pagesOREO Personality TestJasmin de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Frontal Lobe SyndromeDocument67 pagesFrontal Lobe SyndromeVIJAYKUMAR HIREMATH100% (1)
- Advance Care Plan and Factors Related To Disease Progression in Patients With Spinocerebellar Ataxia Type 1: A Cross-Sectional Study in ThailandDocument6 pagesAdvance Care Plan and Factors Related To Disease Progression in Patients With Spinocerebellar Ataxia Type 1: A Cross-Sectional Study in ThailandJefe de Escuela PsicologiaNo ratings yet
- 111 Predatory UGC's Revised White List Has 111 More Predatory Journals - Science ChronicleDocument31 pages111 Predatory UGC's Revised White List Has 111 More Predatory Journals - Science ChronicleP meruguNo ratings yet
- Health Declaration FormDocument1 pageHealth Declaration FormAlintana JobelleNo ratings yet
- Krok Review: How To Prepare Krok TestDocument84 pagesKrok Review: How To Prepare Krok Testgaurav100% (2)
- Journal of The Neurological Sciences: SciencedirectDocument12 pagesJournal of The Neurological Sciences: SciencedirectBotez MartaNo ratings yet
- Disartria Infantil PDFDocument11 pagesDisartria Infantil PDFMaría Belén Soto AlarcónNo ratings yet
- How To Make Homemade Organic Body LotionDocument26 pagesHow To Make Homemade Organic Body LotionSuzaine MendozaNo ratings yet
- Medical Laboratory Tests: Tang PingDocument42 pagesMedical Laboratory Tests: Tang Pingapi-19916399No ratings yet
- 3 Year CPC October 8, 20202Document4 pages3 Year CPC October 8, 20202Raian SuyuNo ratings yet
- Unit Two The Health Benefits of Physical ActivityDocument10 pagesUnit Two The Health Benefits of Physical ActivityYoseph DefaruNo ratings yet