Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Response Problems Crystal Defects
Uploaded by
Yustinus LazuardiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Response Problems Crystal Defects
Uploaded by
Yustinus LazuardiCopyright:
Available Formats
CRYSTAL DEFECTS
RESPONSE PROBLEMS
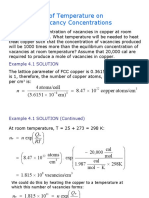
1. Calculate the vacancy fraction in copper (Cu) at (a) 20 C and (b) the melting point, 1085 C. Measurements have
determined the values of the enthalpy of vacancy formation, Hv , to be 1.03 eV and the entropic prefactor, A, to be 1.1.
2. In iridium (Ir), the vacancy fraction, nv/N, is 3.091 105 at 1234 C and 5.26 103 at the melting point. Calculate the
enthalpy of vacancy formation, Hv.
3. A formation energy of 2.0 eV is required to create a vacancy in a particular metal. At 800 C there is one vacancy for
every 10,000 atoms.
(a) At what temperature will there be one vacancy for every 1,000 atoms?
(b) Repeat the calculation, but this time with an activation energy of 1.0 eV. Note the big change in the temperature
interval necessary to obtain the same change in vacancy concentration as was the case with an activation energy of
2.0 eV.
4. In iron (Fe) the energy associated with the generation of a vacancy is 1.05 eV. At what temperature (T) in °C will one out
of 105 lattice sites be vacant?
5. On appropriate schematic drawings show the generation and characteristics of Schottky defects in (a) a closed-packed
metal, (b) an ionic crystal and (c) a semiconductor.
6. In NaCl, the cations are more mobile than the anions. What effect, if any, do you expect small amounts of the following
impurities to have on the conductivity of NaCl crystals: (a) AgCl, (b) MgCl2, (c) NaBr, (d) Na2O?
7. Confirm the presence of iron vacancies for a sample of wustite which has a unit cell dimension of 428.2 pm, an Fe:O ratio
of 0.910 and an experimental density of 5.613 × 103 kg m−3.
8. How would you expect charge neutrality to be maintained in TiO1.25?
9. An ionic crystal of the MX2 type forms Schottky defects, for which the energy of formation is 200 kJ/mole. By how much
should the temperature be reduced from 2000 K in order to reduce the concentration of anion vacancies by a factor of
10?
10. How would you expect the formation of colour centres to affect the density of the crystal?
11. Stoichiometric titanium (II) oxide and magnesium oxides have densities of 4.93 and 3.58 g cm 3 respectively. X-ray
diffraction studies have shown that both have the NaCl structure, with unit cell edges of 416.2 and 421.2 pm respectively.
Assume that the presence of vacancies does not affect the cell edge lengths. Estimate the percentage of vacancies in
these solids.
12. From theoretical considerations it is concluded that the (activation) energy required to form an interstitial atom in copper
(Cu) is about 4 eV. Assuming this value to be correct, determine the equilibrium concentration of these defects
(defects/cm3) at 1350 K.
13. Undoped β-alumina demonstrates a maximum conductivity and minimum activation energy when the sodium excess is
around 20 to 30 mole%. Thereafter, further increase in the sodium content causes the conductivity to decrease. By
contrast, β-alumina crystals doped with Mg2+ have a much higher conductivity than do undoped crystals. Explain these
observations.
You might also like
- Even Better than Eden: Nine Ways the Bible's Story Changes Everything about Your StoryFrom EverandEven Better than Eden: Nine Ways the Bible's Story Changes Everything about Your StoryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (20)
- Electrochemistry One-shot Practice SheetDocument4 pagesElectrochemistry One-shot Practice SheetYasir Karim100% (1)
- ElectrochemistryDocument5 pagesElectrochemistryNeel SiddhpuraNo ratings yet
- Endohedral Metallofullerenes: Fullerenes with Metal InsideFrom EverandEndohedral Metallofullerenes: Fullerenes with Metal InsideNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCHEMISTRYDocument5 pagesELECTROCHEMISTRYsarahNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument2 pagesElectrochemistryaashish100% (1)
- Practice ProblemsDocument2 pagesPractice Problemsanon_915449609No ratings yet
- ch4 ExamplesDocument11 pagesch4 ExamplesSary KilanyNo ratings yet
- 2.electrochemistry QB (2023-24)Document6 pages2.electrochemistry QB (2023-24)Shana Chandran 18083No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document34 pagesChapter 4XNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument2 pagesElectrochemistrySaksham SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 ElectrochemistryDocument7 pagesUnit 3 ElectrochemistrySapna 2704No ratings yet
- Electrochemistry 12th - CHEMISTRYDocument12 pagesElectrochemistry 12th - CHEMISTRYRakesh RanjanNo ratings yet
- Sainik School Chemistry AssignmentDocument5 pagesSainik School Chemistry AssignmentSenthil KumarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry TestDocument4 pagesChemistry TestCarrie PerryNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCHEMISTRYDocument1 pageELECTROCHEMISTRYsanjarm099No ratings yet
- 12 Electrochemistry Assignment-1Document4 pages12 Electrochemistry Assignment-1Yashraj NarwariyaNo ratings yet
- UEME 1122 Material Science Tutorial 1Document2 pagesUEME 1122 Material Science Tutorial 1JamesNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Chemistry Numerical Set 1Document1 pageClass Xii Chemistry Numerical Set 1sudeep26No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry ElectrochemistryDocument2 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry ElectrochemistryMagic Mind. TamilNo ratings yet
- C12SB760Document2 pagesC12SB760Tish BarnesNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: R Cell RDocument15 pagesElectrochemistry: R Cell RSsNo ratings yet
- HomeworkDocument6 pagesHomeworkmyalyaNo ratings yet
- Class Room Problems: Based On ElectrolysisDocument3 pagesClass Room Problems: Based On ElectrolysisAmudala HemashviniNo ratings yet
- 3 Electrochemistry Assignment 1Document9 pages3 Electrochemistry Assignment 1Unknown GamerNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Past Papers 2022-14Document4 pagesElectrochemistry Past Papers 2022-14Venugopal JujhavarappuNo ratings yet
- Faraday's Law On ElectrolysisDocument2 pagesFaraday's Law On ElectrolysisFavourNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Past Papers 2022-14Document4 pagesElectrochemistry Past Papers 2022-1410 A Pratyush Dubey0% (1)
- Kinetics of Materials HomeworksDocument11 pagesKinetics of Materials Homeworks魏碧儜No ratings yet
- Unit 3 ElectrochemisrtyDocument7 pagesUnit 3 ElectrochemisrtyRahgul M.S.50% (2)
- Seminario 1Document5 pagesSeminario 1Javier FrancoNo ratings yet
- H2 Chemistry QuestionsDocument56 pagesH2 Chemistry Questionskitonium100% (2)
- XIIElectrochemistryDocument3 pagesXIIElectrochemistryAyush KumarNo ratings yet
- 12TH Grade Electrochemistry Worksheet-1Document3 pages12TH Grade Electrochemistry Worksheet-1Amen RaipurNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Board Questions 2010-2020Document4 pagesElectrochemistry Board Questions 2010-2020amone nNo ratings yet
- Chepter Wise QuestionsDocument240 pagesChepter Wise QuestionsVinay Tyagi100% (1)
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Worksheet - ElectrochemistryDocument4 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Worksheet - ElectrochemistryArya VermaNo ratings yet
- Electro RevisionDocument2 pagesElectro RevisionShubham KumarNo ratings yet
- Ionic Theory and Electrolysis Problems1Document8 pagesIonic Theory and Electrolysis Problems1Juma BwaiNo ratings yet
- Tutorials PT 1 - Materials ScienceDocument19 pagesTutorials PT 1 - Materials ScienceVassish DassagneNo ratings yet
- QuizDocument5 pagesQuizSikander AzamNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument2 pagesElectrochemistryKuldeep SharmaNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument48 pagesChemistryDeepan KumarNo ratings yet
- Chem 12Document1 pageChem 12JakeNo ratings yet
- Tipo Test Tilley PDFDocument7 pagesTipo Test Tilley PDFJesus27No ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: 2 303 G - RtlogkDocument7 pagesElectrochemistry: 2 303 G - RtlogkSnehashis BoseNo ratings yet
- Nov 1stDocument2 pagesNov 1stsarahNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Concepts and CalculationsDocument7 pagesElectrochemistry Concepts and CalculationsParam SoniNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 E FDocument2 pagesAssignment 1 E FSudhananda MallickNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Assignment-1Document2 pagesElectrochemistry Assignment-1Anubhav SinghNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document117 pagesLecture 4Sam ThorNo ratings yet
- CHE1010 Introductory Chemistry Tutorial Sheet 5Document4 pagesCHE1010 Introductory Chemistry Tutorial Sheet 5Chimuka Onson MapikiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Test 11 Chap 1-5Document2 pagesChemistry Test 11 Chap 1-5Sabitra RudraNo ratings yet
- Unit Test (Set-1) Class-Xii SUBJECT-chemistry (043) General InstructionDocument2 pagesUnit Test (Set-1) Class-Xii SUBJECT-chemistry (043) General InstructionShivansh TripathiNo ratings yet
- Tugas Mandiri NewDocument2 pagesTugas Mandiri NewHany KusumawatiNo ratings yet
- Questions On Transition MetalsDocument3 pagesQuestions On Transition MetalscpliamNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY Holiday Homework - 12-1Document3 pagesCHEMISTRY Holiday Homework - 12-1Ashif AbhasNo ratings yet
- Chemistry (Class - XII) (Unit 1 To 3) Time: 1.00 Hrs MM: 25 MDocument1 pageChemistry (Class - XII) (Unit 1 To 3) Time: 1.00 Hrs MM: 25 MKamal AnandNo ratings yet
- Electro Chemistry (QB)Document4 pagesElectro Chemistry (QB)Akshith ReddyNo ratings yet
- 3Document2 pages3Yustinus LazuardiNo ratings yet
- Free PPT Templates: Insert The Title of Your Presentation HereDocument36 pagesFree PPT Templates: Insert The Title of Your Presentation HereFinsaria FidiyantiNo ratings yet
- Presentasi Kelompok 2 FixDocument25 pagesPresentasi Kelompok 2 FixYustinus LazuardiNo ratings yet
- N Vacancies M N Lattice Site M N Lattice Site M T Q Joule Mol Q Joule Mol K 1, 38 ×10 Joule KDocument2 pagesN Vacancies M N Lattice Site M N Lattice Site M T Q Joule Mol Q Joule Mol K 1, 38 ×10 Joule KYustinus LazuardiNo ratings yet
- 1Document1 page1Yustinus LazuardiNo ratings yet
- Kinetika Web 6 Reaksi KompleksDocument16 pagesKinetika Web 6 Reaksi KompleksYustinus LazuardiNo ratings yet
- Ch23 LipidsDocument33 pagesCh23 LipidsridhaNo ratings yet
- DFSDDocument35 pagesDFSDYustinus LazuardiNo ratings yet
- Biokim Kelas CDocument22 pagesBiokim Kelas CYustinus LazuardiNo ratings yet
- DFSDDocument35 pagesDFSDYustinus LazuardiNo ratings yet
- Kanggo KomputasiDocument2 pagesKanggo KomputasiYustinus LazuardiNo ratings yet
- KJDocument2 pagesKJYustinus LazuardiNo ratings yet
- SsDocument38 pagesSsYustinus LazuardiNo ratings yet
- Enzim - Part2 2019Document21 pagesEnzim - Part2 2019Candra Agung RamadanNo ratings yet
- A Study On Scanning Electron Microscopy in AdsorptionDocument2 pagesA Study On Scanning Electron Microscopy in AdsorptionNataraj Naik Banavath ch20m025No ratings yet
- Current Electricity. MiaDocument42 pagesCurrent Electricity. MiaVerla MfeerNo ratings yet
- HDL ZnAl Como AnodoDocument6 pagesHDL ZnAl Como AnodoDaniely Carlos Henrique Carlos HenriqueNo ratings yet
- Tailoring Composite MaterialsDocument23 pagesTailoring Composite MaterialsRama Rifqi100% (1)
- Talc in Plastics Enhances Strength and PerformanceDocument8 pagesTalc in Plastics Enhances Strength and Performancemusmanghani70scribdNo ratings yet
- Bobinas HansenDocument4 pagesBobinas HansenJose Ignacio Figueroa CortesNo ratings yet
- Solution For 1.4 and 1Document4 pagesSolution For 1.4 and 1lieu_hyacinth0% (1)
- Physics Practice Paper 1 - STD X PDFDocument8 pagesPhysics Practice Paper 1 - STD X PDFRachit SinghNo ratings yet
- Lecture on Slender Column Design and AnalysisDocument35 pagesLecture on Slender Column Design and AnalysisEmanoAceNo ratings yet
- Electron Beam WeldingDocument19 pagesElectron Beam WeldingSahil DhimanNo ratings yet
- Grand Test 4Document28 pagesGrand Test 4Dr. Pradeep SakeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-Material-Properties & BehaviourDocument17 pagesChapter 3-Material-Properties & BehaviourMohd Azizi100% (1)
- Mars RuleDocument32 pagesMars RuleRadha Krishnan R100% (3)
- PN Junction Diode: I-V Characteristics: Sung June KimDocument42 pagesPN Junction Diode: I-V Characteristics: Sung June KimasadNo ratings yet
- Arvay 2012Document21 pagesArvay 2012KaustubhNo ratings yet
- Implement Turbulence ModelDocument20 pagesImplement Turbulence ModelAlexandros HafNo ratings yet
- Varactor Diode PDFDocument3 pagesVaractor Diode PDFLackith Chandimal HettiarachchiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Structural Imperfections Kingery Introducción A Los Materiales CerámicosDocument27 pagesChapter 4 - Structural Imperfections Kingery Introducción A Los Materiales CerámicosLaura BárbaroNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 6Document17 pagesWorksheet 6Sumair Khan MasoodNo ratings yet
- MBBSBDS PHY Mock TestDocument7 pagesMBBSBDS PHY Mock TestBoluwatifeNo ratings yet
- Soran UniversityDocument7 pagesSoran UniversityHama Star100% (1)
- Dimensions Dimensions: DC Standard Inductive Proximity SensorsDocument1 pageDimensions Dimensions: DC Standard Inductive Proximity SensorsDwi SaputroNo ratings yet
- Mid Sem PresentationDocument15 pagesMid Sem PresentationdivyaNo ratings yet
- Gulf Harmony: Premium Quality Rust & Oxidation (R&O) Inhibited Multipurpose Lubricating OilsDocument1 pageGulf Harmony: Premium Quality Rust & Oxidation (R&O) Inhibited Multipurpose Lubricating Oilsatripathi2009No ratings yet
- Mass Production of High Quality Graphene An Analysis of Worldwide PatentsDocument12 pagesMass Production of High Quality Graphene An Analysis of Worldwide PatentsSrramNo ratings yet
- Low Yellowing ProductsDocument1 pageLow Yellowing ProductsPOINTERNo ratings yet
- Gusset Plate Connection DesignDocument3 pagesGusset Plate Connection DesignMin Khant KyawNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Metal FormingDocument37 pagesFundamentals of Metal FormingDeepak LambaNo ratings yet
- Francois Sears & Gerhard Salinger 'Thermodynamics, Kinetic Theory of Gasses and Statistical Mechanics' PDFDocument462 pagesFrancois Sears & Gerhard Salinger 'Thermodynamics, Kinetic Theory of Gasses and Statistical Mechanics' PDFanon_25384875991% (55)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidFrom EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1395)
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceFrom EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (51)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldFrom EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (64)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessFrom EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingFrom EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesFrom EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2193)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismFrom EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (500)
- The Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceFrom EverandThe Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (23)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayFrom EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (125)
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Paradox: The Nine Greatest Enigmas in PhysicsFrom EverandParadox: The Nine Greatest Enigmas in PhysicsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (57)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowFrom EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (48)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeFrom EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeNo ratings yet
- Black Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseFrom EverandBlack Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)From EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (155)
- Quantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishFrom EverandQuantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceFrom EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldFrom EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (54)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterFrom EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (409)
- Too Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldFrom EverandToo Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- Starry Messenger: Cosmic Perspectives on CivilizationFrom EverandStarry Messenger: Cosmic Perspectives on CivilizationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (158)