Professional Documents
Culture Documents
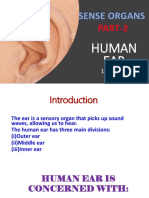
Ear Human Right Ear (Cropped) .JPG The Outer Portion of The Human Ear
Ear Human Right Ear (Cropped) .JPG The Outer Portion of The Human Ear
Uploaded by
arnel barawed0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageOriginal Title
scooter.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageEar Human Right Ear (Cropped) .JPG The Outer Portion of The Human Ear
Ear Human Right Ear (Cropped) .JPG The Outer Portion of The Human Ear
Uploaded by
arnel barawedCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
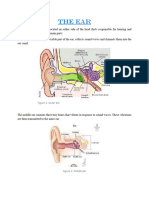
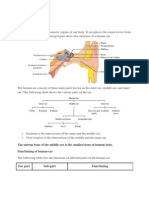
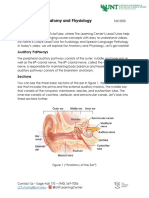
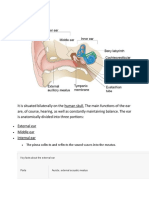
The ear is the organ of hearing and, in mammals, balance.
In mammals, the ear is usually
described as having three parts—the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. The
outer ear consists of the pinna and the ear canal. Since the outer ear is the only visible
portion of the ear in most animals, the word “ear” often refers to the external part alone.
[1] The middle ear includes the tympanic cavity and the three ossicles. The inner ear sits
in the bony labyrinth, and contains structures which are key to several senses: the
semicircular canals, which enable balance and eye tracking when moving; the utricle and
saccule, which enable balance when stationary; and the cochlea, which enables hearing.
The ears of vertebrates are placed somewhat symmetrically on either side of the head,
an arrangement that aids sound localisation.
Ear
Human right ear (cropped).jpg
The outer portion of the human ear
You might also like
- For Other Uses, See .: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument17 pagesFor Other Uses, See .: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchMichael FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Human EARDocument6 pagesHuman EARakNo ratings yet
- For Other Uses, See .: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument72 pagesFor Other Uses, See .: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediavishalsidankarNo ratings yet
- Research Task - Ear Anatomy Function-7Document2 pagesResearch Task - Ear Anatomy Function-7api-310554346No ratings yet
- Hearing Mechanism: Hearing, or Auditory Perception, Is The Ability To Perceive Sounds by Detecting VibrationsDocument2 pagesHearing Mechanism: Hearing, or Auditory Perception, Is The Ability To Perceive Sounds by Detecting VibrationsAnnabelle ArtiagaNo ratings yet
- The Human EarDocument13 pagesThe Human EarCalvo AdrianNo ratings yet
- Parts of EarsDocument15 pagesParts of EarsdizzybeeNo ratings yet
- Human Ear 08-05-2023Document3 pagesHuman Ear 08-05-2023Muhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Auditory System: Human Outer Ear and CultureDocument5 pagesAuditory System: Human Outer Ear and CulturejennyrosepamatNo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of The Ear Explicated With DiagramsDocument10 pagesStructure and Functions of The Ear Explicated With DiagramsemmanuelNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Ear PDFDocument5 pagesAnatomy of The Ear PDFPerry SinNo ratings yet
- A. The External Ear, C. The Inner EarDocument3 pagesA. The External Ear, C. The Inner EarLili M.No ratings yet
- Diagram of The Ear and Its FunctionsDocument14 pagesDiagram of The Ear and Its Functionsmcheche12No ratings yet
- Organs of Hearing and Tactile ResponsesDocument4 pagesOrgans of Hearing and Tactile ResponsesNarasimha MurthyNo ratings yet
- LEC-6 Structure of The Ear & Its Functions-1Document11 pagesLEC-6 Structure of The Ear & Its Functions-1Umais AmjadNo ratings yet
- Member of Group: Andre Setya Aji 5. Marditya Apin Fadila 6. Nindi Saputri Fenika Aprilia 7. Rika Nilam Ilham Wiratama 8. Utari Riyantini E.PDocument9 pagesMember of Group: Andre Setya Aji 5. Marditya Apin Fadila 6. Nindi Saputri Fenika Aprilia 7. Rika Nilam Ilham Wiratama 8. Utari Riyantini E.Pvika septiaNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Hearing Through Ear: Presented By: Seeza ENROLLMENT NUMBER: A044110521004 Submitted To: Dr. Sonal ChauhanDocument11 pagesPhysiology of Hearing Through Ear: Presented By: Seeza ENROLLMENT NUMBER: A044110521004 Submitted To: Dr. Sonal ChauhanMedical Physics2124No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: The Human EarDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: The Human Earclaudine_brionNo ratings yet
- EarDocument8 pagesEararpitsonone16No ratings yet
- Anatomy of EarDocument17 pagesAnatomy of Earkresha solankiNo ratings yet
- Human EarDocument2 pagesHuman EarKristine OlogNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of EarDocument3 pagesAnatomy of EarNitesh Kumar KarnaNo ratings yet
- Hearing SenseDocument13 pagesHearing SenseLuis NietoNo ratings yet
- Ear AntomyDocument19 pagesEar Antomyhadeelnazar12No ratings yet
- The Human EarDocument10 pagesThe Human Earvenkat kandukuriNo ratings yet
- Sense Organ-Human EarDocument22 pagesSense Organ-Human Earsaifulla dubaiNo ratings yet
- Research Task - Ear Anatomy FunctionDocument2 pagesResearch Task - Ear Anatomy Functionapi-308565443No ratings yet
- Sense Organ - EARSDocument29 pagesSense Organ - EARSshivangi ninamaNo ratings yet
- Hearing: The SensesDocument7 pagesHearing: The SensesSourav DasNo ratings yet
- The EarDocument2 pagesThe EaratangaremmyNo ratings yet
- EarDocument6 pagesEarDr.Mahesh kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Hearing: The SensesDocument20 pagesHearing: The SensesSourav DasNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The EarDocument6 pagesAnatomy of The Earanshu aroraNo ratings yet
- Human EarDocument2 pagesHuman Earisha890No ratings yet
- Anatomy: Sense Organ - EarDocument21 pagesAnatomy: Sense Organ - Earsaranya amuNo ratings yet
- Chronic TympanomastoiditisDocument25 pagesChronic Tympanomastoiditispatriciaberedo100% (1)
- Auditory SystemDocument8 pagesAuditory SystemRox SanNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of The Ear: Fact FileDocument5 pagesParts and Functions of The Ear: Fact FileJyoti MeenaNo ratings yet
- Bio ProjectDocument23 pagesBio Projectsoumya mazumdarNo ratings yet
- Ear Anatomy - TranscriptDocument5 pagesEar Anatomy - TranscriptSabeel KhalidNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The EarDocument8 pagesAnatomy of The EarDarkAngelNo ratings yet
- Ear Anatomy PDFDocument1 pageEar Anatomy PDFapi-279026508No ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Ear. AreteDocument12 pagesAnatomy of The Ear. AreteBrandon AreteNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EarDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The EarAurea Jasmine DacuycuyNo ratings yet
- HearingDocument15 pagesHearingdisha mangeNo ratings yet
- Human Ear PPTDocument10 pagesHuman Ear PPTsuman.sk3299No ratings yet
- April 29Document7 pagesApril 29api-292905822No ratings yet
- Anatomy Otitis MediaDocument4 pagesAnatomy Otitis MediaWayne N. LlanosNo ratings yet
- HearingDocument4 pagesHearingNatukunda DianahNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EarDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The EarGunel AliyevaNo ratings yet
- Special SensesDocument19 pagesSpecial SensesLord arainNo ratings yet
- Structure of Human EarDocument6 pagesStructure of Human EarAdnan QayumNo ratings yet
- Ear AnatomyDocument2 pagesEar Anatomyapi-311370707No ratings yet
- Human EarDocument38 pagesHuman Earshervlad75% (4)
- Anatomy of Ear 1Document18 pagesAnatomy of Ear 1VikrantNo ratings yet
- Finals TopicDocument22 pagesFinals TopicAbegail B. ManiquizNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of EarDocument2 pagesAnatomy of EarBellarmine JanellaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of EarDocument11 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of EarAriguna WijayaNo ratings yet
- PhysiologyDocument32 pagesPhysiologygraceprasanna207No ratings yet
- WitchcraftDocument2 pagesWitchcraftarnel barawedNo ratings yet
- VOMITDocument2 pagesVOMITarnel barawedNo ratings yet
- Types of Animal-WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesTypes of Animal-WPS Officearnel barawedNo ratings yet
- Blaw Parcor ReviewerDocument4 pagesBlaw Parcor Reviewerarnel barawedNo ratings yet
- INTAX ScandalDocument12 pagesINTAX Scandalarnel barawedNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Merchandising BusinessDocument27 pagesAccounting For Merchandising Businessarnel barawedNo ratings yet
- INTAX ScandalDocument12 pagesINTAX Scandalarnel barawedNo ratings yet