Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cholinoreceptor Blockers and Cholinesterase Regenerators: Submitted By: Aggabao, Ivy D. MED-2 Assignment #2 9/17/20
Uploaded by
Ivy AggabaoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cholinoreceptor Blockers and Cholinesterase Regenerators: Submitted By: Aggabao, Ivy D. MED-2 Assignment #2 9/17/20
Uploaded by
Ivy AggabaoCopyright:
Available Formats
SUBMITTED BY: AGGABAO, IVY D.
MED-2
ASSIGNMENT #2 9/17/20
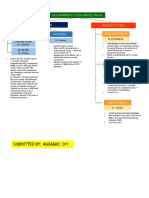
CHOLINORECEPTOR BLOCKERS AND
CHOLINESTERASE REGENERATORS
ANTICHOLINERGIC DRUGS CHOLINESTERASE REGENERATORS
ANTIMUSCARINIC ANTINICOTINIC OXIMES
Ex. Pralidoxime
M1-SELECTIVE GANGLION BLOCKERS
MOA: Reactivates the enzyme
Ex. Pirenzepine Ex. Mecamylamine cholinesterase by cleaving the
phosphate-ester bond formed between
the organophosphate and
MOA: Binds to the M1 muscarinic MOA: competitively block nicotinic
acetylcholinesterase→relieve skeletal
acetylcholine receptor→ inhibition cholinoreceptors on postganglionic
muscle end plate block.
of adenylate cyclase→ breakdown neurons in both sympathetic and
of phosphoinositides→ modulation parasympathetic ganglia in the
of potassium channels through the autonomic nervous system.
action of G proteins→ reduce
gastric acid secretion. NEUROMUSCULAR
BLOCKERS
DEPOLARIZING NON-DEPOLARIZING
NON-SELECTIVE Ex. Succinylcholine Ex. Rocuronium
Ex. Atropine
MOA: MOA:
Phase 1 (depolarizing) Act predominantly at the nicotinic
MOA: Acts centrally and peripherally to React w/ nicotinic receptor to receptor site by competing with
bind competitively to muscarinic open channel→ depolarization of acetylcholine→enter pore of ion
receptors→ prevents actions such as motor end plate→ spread to adjacent channel →produce more intense
the release of inositol trisphosphate membrane→ contractions of muscle motor blockade →weaken
neuromuscular transmission
(IP3) and the inhibition of adenylyl motor unit.
→diminish ability of
cyclase caused by muscarinic agonists→ Phase 2 (desensitizing)
acetylcholinesterase inhibitors to
prevent acetylcholine from Prolonged exposure→ initial end
antagonize the effect of
binding→reduce activity of the GI tract. plate depolarization decreases → nondepolarizing muscle relaxants.
membrane becomes repolarized.
tract.
You might also like
- Submitted By: Aggabao. Ivy D.: Cholinomimetic (Cholinergic) Drugs Direct-Acting Muscarinic Nicotinic Indirect ActingDocument1 pageSubmitted By: Aggabao. Ivy D.: Cholinomimetic (Cholinergic) Drugs Direct-Acting Muscarinic Nicotinic Indirect ActingIvy AggabaoNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument17 pagesAutonomic Nervous SystemKC PalattaoNo ratings yet
- Cholinoceptor-Activating, Cholinesterase-Inhibiting Drugs and Cholinoceptor-Blocking DrugsDocument6 pagesCholinoceptor-Activating, Cholinesterase-Inhibiting Drugs and Cholinoceptor-Blocking DrugsCarlos NiñoNo ratings yet
- Parasympathomimetic AgentsDocument26 pagesParasympathomimetic Agentsrushikesh ugaleNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of P-A Mediators Lecture Notes 12-13Document20 pagesPharmacology of P-A Mediators Lecture Notes 12-13Fikadu GidiNo ratings yet
- Harmacology: Brief Review On Cholinergic Receptors and TransmissionDocument10 pagesHarmacology: Brief Review On Cholinergic Receptors and TransmissionMa. Mil Adrianne PamaNo ratings yet
- Prelim Reviewer PcolDocument37 pagesPrelim Reviewer Pcol11Lag2Carisma II, Jose P.No ratings yet
- Resume KBK FarmakologiDocument4 pagesResume KBK FarmakologiWendy Wijaya100% (1)
- Cholinergic AntagonistsDocument7 pagesCholinergic AntagonistsFrances Lau Yee ChinNo ratings yet
- Whole Pharmacology ReviewDocument17 pagesWhole Pharmacology ReviewEslam khedrNo ratings yet
- PHARMA SupertableDocument2 pagesPHARMA SupertablelpanatalioNo ratings yet
- NMJ 1Document40 pagesNMJ 1Zainab AshroffNo ratings yet
- Harmacology: (Trans) Autonomic Pharmacology Topic OutlineDocument7 pagesHarmacology: (Trans) Autonomic Pharmacology Topic OutlineMa. Mil Adrianne PamaNo ratings yet
- Pcol Finals CompreDocument17 pagesPcol Finals CompreAbby LumanglasNo ratings yet
- Materi KolinergikDocument62 pagesMateri KolinergikWira KrisnaNo ratings yet
- (Cholinergic System) Model Questions and AnswersDocument45 pages(Cholinergic System) Model Questions and AnswersAjay SinghNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic Agents: Cholinergic Receptors Types of Receptor Muscarinic Receptor Nicotinic ReceptorDocument4 pagesCholinergic Agents: Cholinergic Receptors Types of Receptor Muscarinic Receptor Nicotinic ReceptorDonkeyManNo ratings yet
- Pcol 2Document9 pagesPcol 2cyk7xcdsj4No ratings yet
- Cholinergic Drugs - TablesDocument7 pagesCholinergic Drugs - TablesThuan Tăng NguyenNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology - Section 05 - Cholinergic Transmission 1 (Cholinomimetics and Antimuscarinics)Document5 pagesPharmacology - Section 05 - Cholinergic Transmission 1 (Cholinomimetics and Antimuscarinics)Pathalee ThalpavilaNo ratings yet
- 1 Ans - Intro DR DubeyDocument28 pages1 Ans - Intro DR Dubeyecc bafNo ratings yet
- Week 6 - Autonomic PharmacologyDocument19 pagesWeek 6 - Autonomic PharmacologyJayla Marie100% (1)
- NSAIDDocument1 pageNSAIDShubhangiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument17 pagesLecture 6 Autonomic Nervous SystemakramuddaulaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of PUDDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of PUDLEAH LUZADANo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of NSAIDsDocument82 pagesPharmacology of NSAIDsMuhammad Masoom Akhtar100% (1)
- Cholinergic DrugsDocument22 pagesCholinergic Drugsmug ashNo ratings yet
- Part 2Document7 pagesPart 2MYKRISTIE JHO MENDEZNo ratings yet
- PharmarespiDocument19 pagesPharmarespiMark Lorenz NaldozaNo ratings yet
- Autonomic PharmacologyDocument73 pagesAutonomic PharmacologyambiliNo ratings yet
- ANSDocument42 pagesANSRakshan T100% (1)
- Pharm Core List + Memory TricksDocument8 pagesPharm Core List + Memory TrickswenyouNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Solved Past PapersDocument10 pagesPharmacology Solved Past Papersfatima aghaNo ratings yet
- Crisp 2EDocument11 pagesCrisp 2EElavarasan0% (3)
- Pharmacology Trans ANS Drugs IDocument20 pagesPharmacology Trans ANS Drugs IPrincess Mara DuranNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S147226151730002X Main 2Document6 pages1 s2.0 S147226151730002X Main 2Cristhian BastidasNo ratings yet
- MKH 002Document6 pagesMKH 002Tatiana FlorianNo ratings yet
- Pharma Rapid Review FOCUSDocument85 pagesPharma Rapid Review FOCUSKeelNo ratings yet
- Drug Book List-1Document3 pagesDrug Book List-1Anushri ManeNo ratings yet
- Name of Medication Brand Name Generic Name Action 1. Dilantin 2. MannitolDocument4 pagesName of Medication Brand Name Generic Name Action 1. Dilantin 2. Mannitoleliza luisNo ratings yet
- Neuromuscular Blocking DrugsDocument3 pagesNeuromuscular Blocking DrugsYogi drNo ratings yet
- Pharma Super TableDocument56 pagesPharma Super TableMarco Paulo Reyes NaoeNo ratings yet
- Cholinoceptor-Activating & Cholinesterase - Inhibiting DrugsDocument27 pagesCholinoceptor-Activating & Cholinesterase - Inhibiting DrugsShashi kumarNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Neuromuscular Blocking DrugsDocument7 pagesPharmacology of Neuromuscular Blocking DrugsYader Enrique Altamirano RamirezNo ratings yet
- Materi 1 Asthma by Prof - Dr.barmawi Hisyam SP - PD-KPDocument38 pagesMateri 1 Asthma by Prof - Dr.barmawi Hisyam SP - PD-KPSri Ariantini AriantiniNo ratings yet
- AntifungalagentsDocument52 pagesAntifungalagentsspriyansh202No ratings yet
- Table of Antidotes PDFDocument2 pagesTable of Antidotes PDFhassen zabalaNo ratings yet
- Farmakologi Analgetik NSAID (Dr. Atina)Document56 pagesFarmakologi Analgetik NSAID (Dr. Atina)RidhaNo ratings yet
- PHARMACOLOGYDocument21 pagesPHARMACOLOGYAllisson BeckersNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Common Drugs and AntidotesDocument2 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Common Drugs and AntidotesAnaliza Kitongan LantayanNo ratings yet
- b8 - Ache InhibitorsDocument16 pagesb8 - Ache InhibitorsNav ThiranNo ratings yet
- Common Drugs and AntidotesDocument2 pagesCommon Drugs and AntidotesreynoldNo ratings yet
- Common Drugs and Antidotes: Antidote Indication Mode of ActionDocument2 pagesCommon Drugs and Antidotes: Antidote Indication Mode of ActionPiny CesarNo ratings yet
- Table of Antidotes PDFDocument2 pagesTable of Antidotes PDFAmirah AndresNo ratings yet
- Anticancer Drug TherapyDocument9 pagesAnticancer Drug TherapyMuhammad Shahbaz khanNo ratings yet
- Pharma-lc32-Drugs With Important Actions On Smooth Muscles Part 2Document6 pagesPharma-lc32-Drugs With Important Actions On Smooth Muscles Part 2Siva RamanNo ratings yet
- 2cholinergic Drugs - MahDocument56 pages2cholinergic Drugs - Mahعلي الكوافيNo ratings yet
- Class 1 Pharmacology of Cholinergic SystemDocument30 pagesClass 1 Pharmacology of Cholinergic SystemDr.U.P.Rathnakar.MD.DIH.PGDHMNo ratings yet
- Toxic Phosphorus Esters: Chemistry, Metabolism, and Biological EffectsFrom EverandToxic Phosphorus Esters: Chemistry, Metabolism, and Biological EffectsNo ratings yet
- Small Molecular Immunomodifiers of Microbial Origin: Fundamental and Clinical Studies of BestatinFrom EverandSmall Molecular Immunomodifiers of Microbial Origin: Fundamental and Clinical Studies of BestatinHamao UmezawaNo ratings yet
- Covid19 Report PDFDocument18 pagesCovid19 Report PDFIvy AggabaoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 PhysioDocument2 pagesExperiment 4 PhysioIvy AggabaoNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid MetabolismDocument10 pagesNucleic Acid MetabolismIvy AggabaoNo ratings yet
- Psychological and Behavioral Effects of Hyperinsulinism in GoldfishDocument3 pagesPsychological and Behavioral Effects of Hyperinsulinism in GoldfishIvy Aggabao100% (1)
- Geker Fier AP Psychology Unit 3 VocabDocument3 pagesGeker Fier AP Psychology Unit 3 Vocabyuchen zhangNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System 3rd Year Medicine Cerebellum & Basal GangliaDocument17 pagesCentral Nervous System 3rd Year Medicine Cerebellum & Basal GangliaGroup 14100% (1)
- Veterinary: Prathmesh DeshmukhDocument1 pageVeterinary: Prathmesh DeshmukhFaizan SheikhNo ratings yet
- Serif Newsletter 2Document3 pagesSerif Newsletter 2api-451663411No ratings yet
- Critical Care ChallengesDocument17 pagesCritical Care ChallengesYnaffit Alteza UntalNo ratings yet
- The History of Human Neuropsychology: January 2020Document27 pagesThe History of Human Neuropsychology: January 2020shamimNo ratings yet
- Tapsa THE EARDocument4 pagesTapsa THE EARgalileeNo ratings yet
- Abstracts Book - 1623231029Document158 pagesAbstracts Book - 1623231029DennyNo ratings yet
- Hallucinations PresentationDocument14 pagesHallucinations PresentationAbeer salehNo ratings yet
- Cognitive P. Chapter 2Document4 pagesCognitive P. Chapter 2May AloNo ratings yet
- Case Study CVDDocument49 pagesCase Study CVDzerpthederpNo ratings yet
- Attention To Attention Les FehmiDocument36 pagesAttention To Attention Les Fehmifundo100% (1)
- Histology of GangliaDocument18 pagesHistology of GangliaTahir AzizNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Colour-2599Document3 pagesThe Effect of Colour-2599Ana Maria EchimovNo ratings yet
- Masdar Muid Lab/SMF. Ilmu Kesehatan Anak FK. Unibraw / RSU Dr. Saiful Anwar MalangDocument7 pagesMasdar Muid Lab/SMF. Ilmu Kesehatan Anak FK. Unibraw / RSU Dr. Saiful Anwar MalangputriNo ratings yet
- Behaviorism: Unit 3.1 Behaviorist PerspectiveDocument15 pagesBehaviorism: Unit 3.1 Behaviorist Perspectivejade tagab100% (1)
- Febrile SeizureDocument25 pagesFebrile SeizureNagham HaddaraNo ratings yet
- ABCs of Neuroimaging - Ali YIKILMAZDocument45 pagesABCs of Neuroimaging - Ali YIKILMAZRanintha SurbaktiNo ratings yet
- Serotinin and DopamineDocument3 pagesSerotinin and DopamineshangsyndromeNo ratings yet
- Rachel Zahn - Embodied, Disembodied and Re-Embodied CognitionDocument6 pagesRachel Zahn - Embodied, Disembodied and Re-Embodied Cognitionalejandra_ferreiro_2No ratings yet
- Group1 Bipolar DisorderDocument145 pagesGroup1 Bipolar DisorderEula Angelica OcoNo ratings yet
- Bi Support Groups1Document6 pagesBi Support Groups1api-301357752No ratings yet
- Bulimia and AnorexiaDocument10 pagesBulimia and AnorexiaArleen PerezNo ratings yet
- 12vi. Vertigo Guidelines (Barts Health 2015)Document6 pages12vi. Vertigo Guidelines (Barts Health 2015)Rizky AmandaNo ratings yet
- AP 1 Transcription Factor As Precursor of PostZika and MS SymptomsDocument22 pagesAP 1 Transcription Factor As Precursor of PostZika and MS SymptomsElton MatsushimaNo ratings yet
- Semester 3 PBL Student Casebook 2022 23Document26 pagesSemester 3 PBL Student Casebook 2022 23zalsoud2002No ratings yet
- DMIT Software - Midbrain Activation - DMIT - Midbrain SoftwareDocument16 pagesDMIT Software - Midbrain Activation - DMIT - Midbrain Softwarevin100% (1)
- The Brain's Sense of Movement - Alan BerthozDocument352 pagesThe Brain's Sense of Movement - Alan BerthozKaroline MarxNo ratings yet
- Memory and The Human Lifespan by Steve JoordensDocument130 pagesMemory and The Human Lifespan by Steve Joordenseva100% (2)
- CH3 Attention and ConsciousnessDocument32 pagesCH3 Attention and ConsciousnessJainne Ann BetchaidaNo ratings yet