Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Care Plan 1 Med Surge
Uploaded by
ania ojedaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Care Plan 1 Med Surge
Uploaded by
ania ojedaCopyright:
Available Formats
NURSING
CAREPLAN TEMPLATE
Patient Data Collection Form
American Medical Academy School of Nursing
Student Name: Ania Lobeto Date: 10/29/2020 Culture/Ethnicity:
Patient Dirst and last initial: Health Insurance:Obama Religion: Christian
MS Care
Age: 67 Weight: 150 IB Language:English
Sex: Female Height: 5,6 Current Work Status:
Retired
Allergies: No known Marital Status: Widowed Occupation: N/A
allergies
Education: High School Support system: N/A
Chief Complaint:
Shortness of breath Headache
Current Diagnoses (minimum of three with citations):
Acute COPD exacerbation
Hypertension
Hyperlipidemia
Revised September 18, 2018
NURSING CAREPLAN TEMPLATE
Pathophysiology of Diagnoses (all):
The pathophysiology of severe COPD exacerbations requiring mechanical
ventilation is now well understood. Increased airways resistance, usually as a
result of worsening airway inDlammation, results in critical EFL and DH with
dramatically increased loading and functional weakness of the inspiratory
muscles.
The pathophysiology of hypertension Increased systemic vascular resistance,
increased vascular stiffness, and increased vascular responsiveness to stimuli are
central to the pathophysiology of hypertension. Morbidity and mortality
attributable to hypertension result from target organ involvement.
The pathophysiology of primary hyperlipidemia involve the idiopathic
hyperchylomicronemia in which defect in lipid metabolism leads to
hypertriglyceridemia and hyperchylomicronemia caused by a defect in lipoprotein
lipase activity or the absence of the surface apoprotein CII31
Diagnostic Procedures:
AST ALT
Medical History: Diabetes
Surgical History: Hip replacement 2005
Immunization History:
Flu Shot
Social History:She is widowed and is a retired school teacher. She lives alone but her
famil︎y visits her of︎ten︎ Smokes︎︎ ︎only 3︎ ︎-4︎ cigare︎︎ttes︎︎ per da︎y
Vital Signs Time: 0938 Respiration Rate: 28 breaths
per min
Temperature: 37 Pulse: 95 Blood Pressure: 156/92
Glucometer Reading: N/A
Safety Precautions:N/A
Revised September 18, 2018
NURSING CAREPLAN TEMPLATE
Limitations/Prosthetic devices: N/A
Patient Assessment Form
American Medical Academy School of Nursing
Neurological/ Neuromuscular
Overall Appearance:Good
LOC:Patient is alert and oriented to person, place, and time. Mood & Affect:Stability
(stable, Dixed, labile)
Mood & Affect:Stability (stable, Dixed, labile)
Sleep:Regular
Pain: N/A Location: N/A Duration: N/A Triggers: N/A Numeric Scale
0-10: 0
Paralysis/Paresis:N/A
Review of Cranial Nerves:Cranial Nerves II, III, IV, VI, VII, VIII, IX, X, XI, XII intact.
Glasgow Coma Score:15
Activity Tolerance: N/A Restrictions: N/A
ROM:Full ROM of all extremities.
Gait:Walks normal and steady
Cardiovascular
Pulses: 95 high heart rate Location: N/A
Capillary ReDill:N/A
Heart Sounds:Coarse crackles heard at the beginning of inspiration murmur is heard
while squatting or upon releaseof valsalva, standing or during valsalva strain.
Murmurs: no
Edema Score: no lower extremity edema
EKG:EKG showed sinus rhythm with a rate of 94 without RVH.
IV access (include gauge, Dluid type, and rate of Dluids):N/A
Revised September 18, 2018
NURSING CAREPLAN TEMPLATE
Respiratory
Oxygenation: O2 95% on 2L L/M via mask
Lung Assessment:Wheezes and rhonchi are present bilaterally without crackles. Using
auxiliary muscles to breathe.
Blood Gas: N/A
GI
Nutrition (diet):Regular
Restrictions: Sugar-sweetened beverages (soda, fruit drinks, sports drinks)
Appetite: Normal food intake
Type of Feeding: N/A Rate:N/A
Bowel Sounds: soft, positive bowel sounds
Abdominal Assessment: Inspection: Normal Palpation: Normal no pain Percussion:
Normal Auscultation: Hyperactive bowel sounds
GU
Last Bowel Movement: 10/28/2020 1030
Ostomy: N/A Output Description:Pt was incontinent of large amount of
brown bm
Site Assessment: N/A
Last Urine Void: 10/28/2020 1100 Output Description:Normal urine output
Bladder Assessment: Normal
Catheter:N/A
Type: Size:
Date of Insertion:
Integumentary
Color: N/A Temperature: 37c Turgor:Normal
Wounds: N/A
Drains: N/A
IV site: N/A
Type of Dressing:N/A
Last Dressing Change: N/A
Intake (12 Hours) Total: 2000mL Output Total (12 Hours):1000mL
Revised September 18, 2018
NURSING CAREPLAN TEMPLATE
Oral: 2000mL Voiding:N/A
IV:N/A Tubes/ Drains: N/A
Tubes: N/A Dressing: N/A
Patient Data Collection Form
American Medical Academy School of Nursing
Nursing Diagnosis (minimum of three and Explain rationale for priority ordering
list in priority order) (include behavior and relevant stimuli)
1. 1. Exacerbations can be severe and life
Acute COPD exacerbation threatening. At the Dirst sign of symptoms, a
person should seek immediate medical
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease care. Depending on the severity and cause,
(COPD) is deDined as “a preventable and people experiencing a COPD exacerbation
treatable disease with some signiDicant will often need to stay in the hospital. COPD
extrapulmonary effects that may is terminal. People with COPD who do not
contribute to the severity in individual die from another condition will usually die
patients. Its pulmonary component is from COPD. COPD who currently smokes
characterized by airDlow limitation that tobacco has the following reductions in life
expectancy, depending on stage of COPD:
is not fully reversible.
stage 1: 0.3 years. stage 2: 2.2 years. stage 3
or 4: 5.8 years
Revised September 18, 2018
NURSING CAREPLAN TEMPLATE
2. 2. It's important to treat hyperglycemia,
because if left untreated, hyperglycemia can
become severe and lead to serious
Hyperlipidemia is most commonly complications requiring emergency care,
associated with high-fat diets, a such as a diabetic coma. In the long term,
sedentary lifestyle, obesity and diabetes. persistent hyperglycemia, even if not
There are also genetic causes. Familial severe, can lead to complications affecting
hypercholesterolemia, one form of your eyes, kidneys, nerves and heart. The
hyperlipidemia, is the most common brain is very resistant to protracted
neuroglycopenia, and from anecdotal
dominantly inherited genetic disorder in
accounts it would appear that you need to
humans worldwide. have at least 6 hours of exposure to very
deep hypoglycemia before you get
permanent brain damage and subsequent
death.
3. 3. Early on, you may not notice symptoms of
Hypertension High blood pressure is a high blood pressure, so you may not be too
common condition in which the long- concerned. However, in the long run high
term force of the blood against your blood pressure can kill you. Normally, your
artery walls is high enough that it may heart beats regularly, pumping blood
eventually cause health problems, such through the vessels all over your body. It
as heart disease. can lead to severe health complications and
increase the risk of heart disease, stroke,
and sometimes death. Blood pressure is the
force that a person's blood exerts against
the walls of their blood vessels. If left
untreated, a blood pressure of 180/120 or
higher results in an 80% chance of death
within one year, with an average survival
rate of ten months.
Revised September 18, 2018
NURSING CAREPLAN TEMPLATE
Patient Data Collection Form
American Medical Academy School of Nursing
Medication Dose Route/Time Rationale for Nursing
Name (include Administration Implications
both trade/
generic name)
Revised September 18, 2018
NURSING CAREPLAN TEMPLATE
40 mg 1 tab PO To increase If patient
Atorvastatin daily levels of good” develops muscle
cholesterol and tenderness
(Lipitor) to lower during therapy,
triglycerides and CPK levels should
to treat the be monitored. If
symptoms of CPK levels are 10
high cholesterol times the upper
limit of normal or
myopathy occurs,
therapy should
be discontinued.
Monitor for signs
and symptoms of
immune-
mediated
necrotizing
myopathy
(IMNM)
(proximal muscle
weakness
andqserum
creatine kinase),
persisting despite
discontinuation
of statin therapy.
Perform muscle
biopsy to
diagnose; shows
necrotizing
myopathy
without
signiDicant
inDlammation.
Treat with
immunosuppress
ive agents.
Revised September 18, 2018
NURSING CAREPLAN TEMPLATE
750 mg 1 tab PO To treat the nausea, vomiting,
symptoms of anorexia,
Prednisone acute asthma, lethargy,
(Deltasone) arthritis, allergic confusion,
reactions, restlessness)
respiratory before and
illness, periodically
during therapy.
Monitor intake
and output ratios
and daily
weights.
Revised September 18, 2018
NURSING CAREPLAN TEMPLATE
50 mcg 1inhalation Used for COPD Inhaln: Once
orally twice removed from
salmeterol a day, foil overwrap,
approximat discard diskus
ely 12 when every
hours blister has been
apart. used or 6 wk
have passed,
whichever comes
Dirst. Do not use a
spacer with
powder for
inhalation. Use
Cautiously in:
Cardiovascular
disease
(including angina
and
hypertension);
Seizure
disorders;
Diabetes;
Glaucoma;
Hyperthyroidism;
Pheochromocyto
ma; Excessive use
(may lead to
tolerance and
paradoxical
bronchospasm);
Revised September 18, 2018
NURSING CAREPLAN TEMPLATE
81 mg 1 tab PO lower high blood Assess patient for
daily pressure signs of bleeding
(petechiae,
Asprin ecchymosis,
bloody or black
stools, bleeding
gums). Drink
adequate Dluids
while taking
aspirin. Advise
patient to avoid
alcohol when
prescribed high
doses of aspirin.
20 mg 1 tab PO For prevention PO: Administer
of once daily in the
cardiovascular evening. May be
disease and to administered
Pravastatin treat without regard to
(Pravachol) hyperlipidemia food. Avoid
grapefruit and
grapefruit juice
during therapy;
may increase risk
of toxicity. If
administered in
conjunction with
bile acid
sequestrants
(cholestyramine,
colestipol),
administer 1 hr
before or 4 hr
after bile acid
sequestrant.
Revised September 18, 2018
NURSING CAREPLAN TEMPLATE
Patient Data Collection Form
American Medical Academy School of Nursing
Revised September 18, 2018
NURSING CAREPLAN TEMPLATE
Patient education and discharge teaching:
You have been diagnosed with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Take your medicines exactly as directed. Don't skip doses.
Protect yourself from infectionWash your hands often. Do your best to keep your
hands away from your face. Most germs are spread from your hands to your
mouth.
Get a Dlu shot every year. Also ask your provider about pneumonia vaccines.
Stay away from crowds. It's especially important to do this in the winter when
more people have colds and Dlu.To stay healthy, get enough sleep, exercise
regularly, and eat a balanced diet. You should:Get about 8 hours of sleep every
night.Try to exercise for at least 30 minutes on most days.Have healthy foods
including fruits and vegetables, 100% whole grains, lean meats and Dish, and low-
fat dairy products. Try to stay away from foods high in fats and sugarYou have been
diagnosed with Hypertension.
Stay at a healthy weight. Get help to lose any extra pounds. Often times meeting
with a dietitian can help you identify changes that can be made to your diet to help
with weight loss. Learn to measure your own blood pressure. Keep a record of your
results. Ask your doctor which readings mean that you need medical attention.
Take your blood pressure medicine exactly as directed. Don’t skip doses. Missing
doses can cause your blood pressure to get out of control. The American Heart
Association (AHA) says the ideal amount of sodium is no more than 1,500 mg a
day. But because Americans eat so much salt, you can make a positive change by
cutting back to even 2,300 mg of sodium a day (1 teaspoon). You have been
diagnosed with Hyperlipidemia.
Maintain a healthy weight. Ask your healthcare provider how much you should
weigh. Ask him or her to help you create a weight loss plan if you are overweight.
Weight loss can decrease your cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
Exercise as directed. Exercise lowers your cholesterol levels and helps you
maintain a healthy weight. Get 30 minutes or more of aerobic exercise 4 to 6 days
each week. You can split your exercise into four 10-minute workouts instead of 30
minutes at one time. Examples of aerobic exercises include walking briskly,
swimming, or riding a bike. Work with your healthcare provider to plan the best
exercise program for you. Do not smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes
and cigars can increase your risk for a heart attack and stroke. Ask your healthcare
provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes
or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your healthcare provider before
you use these products. Eat heart-healthy foods. Talk to your dietitian about a
heart-healthy diet. The following will help you manage hyperlipidemia:Decrease
the total amount of fat you eat. Choose lean meats, fat-free or 1% fat milk, and low-
fat dairy products, such as yogurt and cheese. Limit or do not eat red meat. Red
meats are high in fat and cholesterol
Revised September 18, 2018
NURSING CAREPLAN TEMPLATE
Procedures/Imaging (Please include results):
Nor Clie
Chemistry Normal Client’s Date Hematolo mal nt’s Date
Value gy Val Valu
ue e
Sodium 135-145 136 10/28/ RBC 4.5-5.0 4.5 10/28/
mEq/L 2020 2020
Potassium 3.5-5.0 4.3 10/28/ HGB 12-15 g/ 10 10/28/
mEq/L 2020 dL 2020
Chloride 95-105 101 10/28/ HCT 35-47 % 37 10/28/
mEq/L 2020 2020
C02 23-29 16 10/28/ MCV 78-102 94.4 10/28/
mEq/L 2020 μm3 2020
Calcium 8.5-10.5 8.7 10/28/ MCH 25-35pg 26 10/28/
mg/dL 2020 2020
Phosphorus 1.8-2.6 4.3 10/28/ MCHC 31-37% 32 10/28/
mEq/L 2020 2020
Cholesterol Less than 250 10/28/ WBC 4,500 to 5,000 10/28/
200 mg/dL 2020 11,00 2020
Albumin 3.4-5.4 3.7 10/28/ Neutrophil 55-70% 92% 10/28/
g/dL 2020 s 2020
Revised September 18, 2018
NURSING CAREPLAN TEMPLATE
BUN 8 to 25 27 10/28/
mg/dL 2020 Bands
Creatinine 0.6 to 1.3 1.25 10/28/ Eosinophil 1-4% 0.2 10/28/
mg/dL 2020 s 2020
Uric Acid Lymphocy 20-40% 3.7 10/28/
tes 2020
Magnesiu 1.6 to 2.6 2.3 10/28/ Basophils 0-2% 1.0 10/28/
m mg/dl 2020 2020
Bilirubin 0.3-1.0 1.2 10/28/ Monocytes 2-8% 2.2 10/28/
mg/dl 2020 2020
Amylase 25 to 151 27 10/28/ Platelets 150,000 to 354,000 10/28/
2020 400,000 2020
Lipase
Other
PTT
PTINR
Other:
Other:
Patient Data Collection Form
American Medical Academy School of Nursing
Patient Data Collection Form
American Medical Academy School of Nursing
Revised September 18, 2018
NURSING CAREPLAN TEMPLATE
Urinalysis Normal Value Client’s Date
Color Yellow Yellow 10/28/2020
Turbidity Clear Clear 10/28/2020
Specific Gravity 1.016 to 1.022 1.020 10/28/2020
Leukocytes Negative Negative 10/28/2020
Nitrite Negative Negative 10/28/2020
Urobilinogen 0.2-1.0 1.0 10/28/2020
Protein Negative Negative 10/28/2020
pH 4.5 to 7.8 5.5 10/28/2020
Blood Negative Negative 10/28/2020
Ketones Negative Negative 10/28/2020
Bilirubin Negative Negative 10/28/2020
Glucose >0.5g/day Negative 10/28/2020
Revised September 18, 2018
NURSING CAREPLAN TEMPLATE
Patient Data Collection Form
American Medical Academy School of Nursing
Chemistry No Client’s Date Hematol No Clie Date
rm ogy rm nt’s
al al Val
Val Val ue
ue ue
Blood Osmolali 280 to 290 10/28/20
ty 300 20
Protein 6 to 8 g/dL 8 10/28/202 RDW
0
Bilirubin 0.3-1.0 1.0 10/28/202 MPV
0
Urobilinog 0.2-1.0 1.0 10/28/202 AIC-Hgb 11.6-16.4 15 10/28/20
en 0 20
Nitrate ALT 7-30 9 10/28/20
(SGPT) 20
Leukocytes AST 9-25 15 10/28/20
(SGOT) units/L 20
Cast 0-2 hyaline 1 10/28/202 PT 11-13 12 10/28/20
0 20
RBC 4.5-5.0 4.7 10/28/202 PTT 25-35 28 10/28/20
0 20
Crystals HDL 30-70 50 10/28/20
20
WBC 4,500 to 4,700 10/28/202 LDL Less 110 10/28/20
0 than130 20
Epithl 0-4 p,v,f 3p.v.f 10/28/202 VLDL
ial
Cells
0
CHOL/
HDL
Miscellane
ous
Vitamin D
TSH
Revised September 18, 2018
NURSING CAREPLAN TEMPLATE
LDH
Relate the clinical signiDicance of abnormal lab values above:
Patient Data Collection Form
American Medical Academy School of Nursing
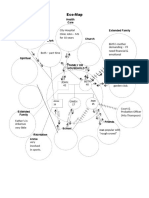
Psychosocial Assessment: Describe the client’s coping processes using the tenets of
Madeleine Leininger’s Culture Care Theory.
Revised September 18, 2018
NURSING CAREPLAN TEMPLATE
Culture Care Diversity and Commonalities
1. What are the commonalities between the patient’s cultural health
practices and the dominant cultural practices seen in the region? The
commonalities between the patient’s cultural health practices and the
dominant cultural practices seen in the region as both focus on the
healing and caring process. It includes the understanding of the cause,
preventive methods as well as promotion of the health. Both indulge in
perspective of improving the health conditions of the patients. There
are several similarities such as implementation of health elevation,
analyzing the cause and remove the factors and health disparities.
2. What are the observed DIFFERENCES between the patient’s cultural
health practices and the dominant cultural practices seen in the
region?In some communities fast for 18 hours, that will be a cultural
practice for them and mandatory for them, if the patient is suffering
from diabetes mellitus or gastric ulcers it will adversely affects the
treatment and the condition may worse, so the patient cultural health
practices and the dominant cultural practices inDluences the treatment.
Cultural & Social Structure
1. Economics impacting health:Social and economic factors such as education,
employment, income, social support and community safety inDluence the well and
how long we live, these factors affects our healthy decision in selecting food,
medical care and housing and living standards. The social and cultural
environment variables on health involves dimensions of both time as well as place.
2. Religious beliefs related to health: The religious beliefs sometimes affects the
health care system because some communities reject the medical treatment
including preventive measures like vaccinations, it will adversely affect the health
care systems groups reject some kind of foods that will also affects the health of
the individual.
3. Structure of support that may inDluence health: The government bodies helps the
health care system works effectively, the medical insurance and the other schemes of the
government policies also help the citizens get effective medical treatment.
Revised September 18, 2018
NURSING CAREPLAN TEMPLATE
Culture Care Preservation or Maintenance
1. Cultural Values that impact health:Cultural values are principles on which the
community exists. Culture is 4th pillar of sustainable development by UNESCO.
Culture values affects the beliefs and perceptions about causes of death, health
promotion, how illness and pain experienced and expressed.
2. Cultural Practices that impact health:Cultural practices lead to difference in
habitual conception of certain foods, differences in preparation and in some cultures milk
and meat are exempted from diet. Medical treatment like some cultures are against blood
transfusions.
Patient Data Collection Form
American Medical Academy School of Nursing
Assessment of Behavior
Non-Observable (Subjective):DifDiculty Breathing Chest tightness patient stated "I can’t
breathe”
Observable (Objective): : Wheezing patients oxygen saturation level is down Blue/Gray
lips/Dingernails
Cultural Assessment:
Nursing Diagnosis #1 (Label, R/T and EB):Patient is showing decreased oxygen content,
decreased oxygen saturation Acute COPD exacerbation.
Revised September 18, 2018
NURSING CAREPLAN TEMPLATE
Goals/ Outcomes (include timeframes):
Short Term
1. Prevent disease progression
2. Prevent and treat complications
3.Relieve COPD symptoms
Long Term
1.Ongoing and reinforced education of the patient and lifestyle changes
2.Prevent & manage complications/exacerbations
3.Improve exercise tolerance/ health status
Nursing Interventions and Rationales (include citation):
1.Observe sign and symptoms of infections
2.Encourage abdominal or pursed-lip breathing exercises.
3.Assess and monitor respirations and breath sounds, noting rate and sounds (tachypnea,
stridor, crackles, wheezes). Note inspiratory and expiratory ratio.
4.Increase Dluid intake to 3000 mL per day within cardiac tolerance
Evaluation: Met/Not Met
Short Term:
1.Met
2.Met
3.Met
Long Term:
1.Met
2.Not Met
3.Met
Nursing Diagnosis #2 (Label, R/T and EB): Patient has elevated blood pressure exceeding
140 over 90 mmHg and has severe headaches Hypertension.
Revised September 18, 2018
NURSING CAREPLAN TEMPLATE
Goals/ Outcomes (include timeframes):
Short Term
1. Patient will verbalized his understanding of never stopping a medication
without the advice of a doctor.
2. Patient states they are no longer suffering from a headache
3.Patient appear comfortable and pain-free.
Long Term
1. Patient will maintain BP within individually acceptable range.
2. Patient will demonstrate stable cardiac rhythm and rate within patient’s normal range.
3. Patient will participate in activities that reduce BP/cardiac workload.
Nursing Interventions and Rationales (include citation):
1. Monitor and record BP. Measure in both arms and thighs three times, 3–5 min
apart while patient is at rest, then sitting, then standing for initial evaluation
2. Observe skin color, moisture, temperature, and capillary reDill time.
3. Monitor response to medications to control blood pressure.
4. Auscultate heart tones and breath sounds.
Revised September 18, 2018
NURSING CAREPLAN TEMPLATE
Evaluation: Met/ Not Met
Short Term:
1.Met
2.Met
3.Met
Long Term:
1.Met
2.Met
3.Met
Nursing Diagnosis #3 (Label, R/T and EB): Patient has high levels of lipids (fats) in the
blood, including cholesterol and triglycerides and has been diagnosis with
Hyperlipidemia
Goals/ Outcomes (include timeframes):
Short Term
1. Eating a heart-healthy diet
2. Eat more Diber-rich foods, such as oatmeal, apples, bananas, pears, prunes,
kidney beans, chickpeas, lentils, and lima beans
3. Avoid sugary drinks and added sugars
Long Term
1.Losing excess weight
2.Quitting smoking
3.Becoming more physically
Revised September 18, 2018
NURSING CAREPLAN TEMPLATE
Nursing Interventions and Rationales (include citation):
1. lower elevated blood cholesterol
2.Educate patient on hyperlipidemia
3. promotion of behavioral change,
4. monitoring dietary change and patient outcomes
Evaluation: Met/ Not Met (Provide rationale for evaluation outcome)
Short Term:
1.Met
2.Met
3.Met
Long Term:
1.Met
2.Met
3.Not Met
Patient Data Collection Form
American Medical Academy School of Nursing
References
(Must include at least three; including the book)
https://www.webmd.com/hypertension-high-blood-pressure/default.htm
https://medlineplus.gov/copd.html https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-
conditions/hyperglycemia/symptoms-causes/syc- 20373631
Ignatavicius, D. D., & Workman, M. L. (2010). Medical-surgical
nursing: Hypertension, pg.720 Saunders.
Ignatavicius, D. D., & Workman, M. L. (2010). Medical-surgical
nursing: COPD pg.13 Saunders.
Revised September 18, 2018
NURSING CAREPLAN TEMPLATE
Revised September 18, 2018
You might also like
- Nurse Practitioner Board ReviewFrom EverandNurse Practitioner Board ReviewRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Case Study FinalDocument77 pagesCase Study FinalMacey Malonzo100% (1)
- ACLS Simulation ScenariosDocument14 pagesACLS Simulation ScenariosVanessa HermioneNo ratings yet
- COPD Case StudyDocument14 pagesCOPD Case StudyNita Gopinath100% (1)
- J.S Case Study 1 PDFDocument2 pagesJ.S Case Study 1 PDFania ojedaNo ratings yet
- Pentagon NLE Review NotesDocument33 pagesPentagon NLE Review NotesChieChay Dub93% (123)
- Final Practicum - Soap Note 3Document17 pagesFinal Practicum - Soap Note 3api-494643478100% (2)
- Peripheral Vascular Disease Arteries NHSDocument10 pagesPeripheral Vascular Disease Arteries NHSAdahl HetheringtonNo ratings yet
- Managing Breathlessness in the CommunityFrom EverandManaging Breathlessness in the CommunityRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Case Study HPTDocument16 pagesCase Study HPTIQmah RamliNo ratings yet
- COPD Case StudyDocument4 pagesCOPD Case StudyPj Declarador100% (4)
- Case Study Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocument11 pagesCase Study Acute Myocardial InfarctionChristine Elaine Batusin Ilagan91% (23)
- Fast Facts: Hyperlipidemia: Bringing clarity to lipid managementFrom EverandFast Facts: Hyperlipidemia: Bringing clarity to lipid managementNo ratings yet
- Plab 2 MaterialDocument24 pagesPlab 2 MaterialradugaNo ratings yet
- Case Study NSTEMIDocument26 pagesCase Study NSTEMIHomework Ping100% (1)
- Clinical Case Report on Dengue FeverDocument16 pagesClinical Case Report on Dengue FeverAimanazrul ZainudinNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 Health LAS PDFDocument31 pagesGrade 4 Health LAS PDFLey Domingo Villafuerte GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Bronchial Asthma (Case Study)Document12 pagesBronchial Asthma (Case Study)Adriane Coma100% (1)
- Case Report on Diabetes MellitusDocument30 pagesCase Report on Diabetes MellitusMochamad Badar WigunaNo ratings yet
- Acute Pancreatitis Case StudyDocument39 pagesAcute Pancreatitis Case StudyJm Bernardo100% (1)
- Toprank Midterms Post TestDocument79 pagesToprank Midterms Post TestTony ReyesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Board Exam ReviewerDocument32 pagesNursing Board Exam ReviewerRose Anne Mückl100% (9)
- Heart Failure Case StudyDocument8 pagesHeart Failure Case StudyDavid PayosNo ratings yet
- ASD Internship ReportingDocument14 pagesASD Internship ReportingPernel Jose Alam MicuboNo ratings yet
- Of PHL Deaths Due To Heart Vascular Disease 25 7 of Pinoys Hypertensive#Sthash - Fbqnsdso.DpufDocument41 pagesOf PHL Deaths Due To Heart Vascular Disease 25 7 of Pinoys Hypertensive#Sthash - Fbqnsdso.Dpufzozorina21No ratings yet
- PROCEDUREDocument10 pagesPROCEDURESabrina ReyesNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Septic Shock ManagementDocument37 pagesPaediatric Septic Shock ManagementJauhari DesloNo ratings yet
- Diabetic EmergenciesDocument9 pagesDiabetic EmergenciesIlyes FerenczNo ratings yet
- (KASUS-ENDOKRIN) (2023-10-24) A HYPEROSMOLAR HYPERGLYCEMIC STATE (HHS) PATIENT WITH NEUROLOGICAL MANIFESTATION INVOLUNTARY MOVEMENT (Biyan Maulana)Document11 pages(KASUS-ENDOKRIN) (2023-10-24) A HYPEROSMOLAR HYPERGLYCEMIC STATE (HHS) PATIENT WITH NEUROLOGICAL MANIFESTATION INVOLUNTARY MOVEMENT (Biyan Maulana)ANo ratings yet
- CC 2 Mei 2017 PneumoniaDocument37 pagesCC 2 Mei 2017 PneumoniaAhimsa Yoga AninditaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document5 pagesAssignment 3api-577583685No ratings yet
- Untitled Document - EditedDocument4 pagesUntitled Document - EditedchebetNo ratings yet
- Case Study:: Breathe ShortnessDocument6 pagesCase Study:: Breathe ShortnessAsifa SafdarNo ratings yet
- Tgs Askep Bhs InggrisDocument10 pagesTgs Askep Bhs InggrisSri YantiNo ratings yet
- Acute Disease Case Study: Metabolism - HypothermiaDocument8 pagesAcute Disease Case Study: Metabolism - HypothermiaRegina PerkinsNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia-COPD Case Study SolutionsDocument10 pagesPneumonia-COPD Case Study Solutionskmills876No ratings yet
- دراسة حالة مريضDocument14 pagesدراسة حالة مريضKhalid233No ratings yet
- C. Liver Function Test (Child Pugh Criteria-To See Albumin and Bilirubin)Document26 pagesC. Liver Function Test (Child Pugh Criteria-To See Albumin and Bilirubin)Nadhirah ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Ru For CVD BleesDocument30 pagesRu For CVD BleesKaye LeNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument38 pagesHypertensionmariatheressamercadoNo ratings yet
- Soap Notes HypertensionDocument6 pagesSoap Notes HypertensionCHRISTINE KARENDINo ratings yet
- BAIAE in Pregnancy.Document6 pagesBAIAE in Pregnancy.Mark Arthur MartinezNo ratings yet
- 13 Levels of AssessmentDocument11 pages13 Levels of AssessmentCatherine Cayda dela Cruz-BenjaminNo ratings yet
- Patient Scenario Chapter 20answer SheetDocument6 pagesPatient Scenario Chapter 20answer SheetcalliemozartNo ratings yet
- 001 ICU Case CoyocaDocument9 pages001 ICU Case CoyocaMiguel Kelly CataneNo ratings yet
- GeronDocument54 pagesGeronL Rean Carmelle MAGALLONESNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Disease Case StudiesDocument6 pagesCardiovascular Disease Case StudiesShanica Paul-RichardsNo ratings yet
- Anexa 5 - Cerere de Acordare A Vizei AnualeDocument11 pagesAnexa 5 - Cerere de Acordare A Vizei AnualecosminNo ratings yet
- NCMB312 - : Bachelor of Science in Nursing: Communicable Disease NursingDocument7 pagesNCMB312 - : Bachelor of Science in Nursing: Communicable Disease NursingMichelle Gliselle Guinto MallareNo ratings yet
- Case 2Document6 pagesCase 2Maryam Shoukat AliNo ratings yet
- Managing Diabetes with Lifestyle Changes and MedicationDocument9 pagesManaging Diabetes with Lifestyle Changes and MedicationCalingalan Hussin CaluangNo ratings yet
- Ujian Tulis Ipd Grup C AnswerDocument10 pagesUjian Tulis Ipd Grup C AnswerHartantoRezaGazaliNo ratings yet
- MR Moray BluntDocument7 pagesMR Moray Bluntbri ngNo ratings yet
- Tugas Penilaian Status GiziDocument12 pagesTugas Penilaian Status GiziZahra ZahiraNo ratings yet
- NUR 611 Case Study: Group DDocument17 pagesNUR 611 Case Study: Group DSheryl KumarNo ratings yet
- D2-Milla - Telemed Written Report 4Document5 pagesD2-Milla - Telemed Written Report 4Gabriel MillaNo ratings yet
- Lopez, Lovelle Nmd-ClerkDocument11 pagesLopez, Lovelle Nmd-ClerkLovelle LopezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Process of A Client With CholelithiasisDocument21 pagesNursing Process of A Client With Cholelithiasisapi-3822508100% (6)
- Hypoglycemia in Diabetes: Pathophysiology, Prevalence, and PreventionFrom EverandHypoglycemia in Diabetes: Pathophysiology, Prevalence, and PreventionNo ratings yet
- Abnormal High Fever (Malignant Hyperthermia), A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandAbnormal High Fever (Malignant Hyperthermia), A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Man with GI Bleed and Alcoholism Admitted to ICUDocument4 pagesMan with GI Bleed and Alcoholism Admitted to ICUania ojedaNo ratings yet
- Madeleine Leininger Careplan Template PDFDocument19 pagesMadeleine Leininger Careplan Template PDFania ojedaNo ratings yet
- ASN 11 Handout Case Study PDFDocument4 pagesASN 11 Handout Case Study PDFania ojedaNo ratings yet
- Case Study Assignment 11:02:2020 PDFDocument6 pagesCase Study Assignment 11:02:2020 PDFania ojedaNo ratings yet
- Care Plan 1 Med SurgeDocument25 pagesCare Plan 1 Med Surgeania ojedaNo ratings yet
- Hypothyroidism PDFDocument2 pagesHypothyroidism PDFania ojedaNo ratings yet
- Case Study PDFDocument4 pagesCase Study PDFania ojedaNo ratings yet
- Case Study ASN 11 PDFDocument3 pagesCase Study ASN 11 PDFania ojedaNo ratings yet
- Ecomap PDFDocument1 pageEcomap PDFania ojedaNo ratings yet
- Case Study 1 ASN 11:30:2020 PDFDocument3 pagesCase Study 1 ASN 11:30:2020 PDFania ojedaNo ratings yet
- HPV PDFDocument2 pagesHPV PDFania ojedaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Nurse Clinical-CARE PLAN SHEET PDFDocument2 pagesAdvanced Nurse Clinical-CARE PLAN SHEET PDFania ojedaNo ratings yet
- Video Response Worksheet-S PDFDocument2 pagesVideo Response Worksheet-S PDFania ojedaNo ratings yet
- Casa Study 2 11:30:2020 PDFDocument3 pagesCasa Study 2 11:30:2020 PDFania ojedaNo ratings yet
- CARE PLAN Case Study #2 PDFDocument2 pagesCARE PLAN Case Study #2 PDFania ojedaNo ratings yet
- Group Handout Medical Terminology Worksheet PDFDocument2 pagesGroup Handout Medical Terminology Worksheet PDFania ojedaNo ratings yet
- 47-year-old female admitted to rule out GERD vs PUDDocument2 pages47-year-old female admitted to rule out GERD vs PUDania ojedaNo ratings yet
- NUR209 WK7 Group Handout Case Study Assessment of Urinary Tract Infection Patient ProfileDocument4 pagesNUR209 WK7 Group Handout Case Study Assessment of Urinary Tract Infection Patient Profileania ojedaNo ratings yet
- Care Plan 1 Med SurgeDocument25 pagesCare Plan 1 Med Surgeania ojedaNo ratings yet
- Case Study on Effects of Drugs on Blood PressureDocument6 pagesCase Study on Effects of Drugs on Blood Pressureania ojedaNo ratings yet
- Asn 11 Clinical Case Study PDFDocument5 pagesAsn 11 Clinical Case Study PDFania ojedaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Nurse Clinical-CARE PLAN SHEET PDFDocument3 pagesAdvanced Nurse Clinical-CARE PLAN SHEET PDFania ojedaNo ratings yet
- Care Plan 2 PDFDocument16 pagesCare Plan 2 PDFania ojedaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Nurse Clinical-CARE PLAN SHEET PDFDocument2 pagesAdvanced Nurse Clinical-CARE PLAN SHEET PDFania ojedaNo ratings yet
- Gout PDFDocument4 pagesGout PDFania ojedaNo ratings yet
- Case Study ASN 11 PDFDocument3 pagesCase Study ASN 11 PDFania ojedaNo ratings yet
- Skin Study PDFDocument7 pagesSkin Study PDFania ojedaNo ratings yet
- Hypothyroidism PDFDocument2 pagesHypothyroidism PDFania ojedaNo ratings yet
- Case Study Assignment 11:02:2020 PDFDocument6 pagesCase Study Assignment 11:02:2020 PDFania ojedaNo ratings yet
- Introduction Case StudyDocument5 pagesIntroduction Case StudySheryl Ann Barit PedinesNo ratings yet
- Circadian Mechanisms in Medicine: Review ArticleDocument12 pagesCircadian Mechanisms in Medicine: Review ArticleNhien TranNo ratings yet
- SFH MCQ 2Document5 pagesSFH MCQ 2Shamanth MNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease: Mary Anne M. Baquing, MDDocument3 pagesPelvic Inflammatory Disease: Mary Anne M. Baquing, MDBob IrsanNo ratings yet
- Acid-Fast Stain (Ziehl-Neelsen Stain)Document15 pagesAcid-Fast Stain (Ziehl-Neelsen Stain)ASHUTOSH KHADANGANo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Three Men in A Boat - We Start To Make PlansDocument3 pagesChapter 2 Three Men in A Boat - We Start To Make PlansMawar Sani NainggolanNo ratings yet
- Trags In-House Safety Induction TrainingDocument14 pagesTrags In-House Safety Induction TrainingRajesh MNo ratings yet
- 1399 SericultureDocument21 pages1399 SericultureAkshat sharmaNo ratings yet
- Report of Field Visit To National Centre For Disease ControlDocument12 pagesReport of Field Visit To National Centre For Disease ControlVaishali JainarainNo ratings yet
- Icha 1Document5 pagesIcha 1kadek ayu ichaNo ratings yet
- Concept Map PT 1Document1 pageConcept Map PT 1api-657741346No ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis of Bipolar II Disorder and Borderline Personality DisorderDocument11 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of Bipolar II Disorder and Borderline Personality DisorderManu Cortes OsorioNo ratings yet
- Almitrine Bismesylate Drug OverviewDocument6 pagesAlmitrine Bismesylate Drug OverviewjeremyescaraNo ratings yet
- Prognosis and Outcomes Following Sudden Cardiac Arrest in AdultsDocument24 pagesPrognosis and Outcomes Following Sudden Cardiac Arrest in AdultsAnca StanNo ratings yet
- Newborn Screening For Critical Congenital Heart Disease Using Pulse OximetryDocument20 pagesNewborn Screening For Critical Congenital Heart Disease Using Pulse OximetryHardian RakhmawardanaNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary DisordersDocument53 pagesPulmonary DisordersAhmad Makhlouf100% (1)
- DraftDocument6 pagesDraftyayammNo ratings yet
- Pulm HTN WilcoxDocument11 pagesPulm HTN WilcoxyersiniapestismorNo ratings yet
- Kyphosis Physiotherapy From Childhood To Old Age: Jean Claude de MauroyDocument26 pagesKyphosis Physiotherapy From Childhood To Old Age: Jean Claude de MauroyromanciviNo ratings yet
- Physical Therapy For Low Back PainDocument6 pagesPhysical Therapy For Low Back PainCharles LimbuNo ratings yet
- Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology II: Topic: Soft Tissue TumorsDocument123 pagesOral & Maxillofacial Pathology II: Topic: Soft Tissue TumorsDorina MalanceaNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Guidance During Recovery From Covid 19Document27 pagesNutritional Guidance During Recovery From Covid 19eny widiyantiNo ratings yet
- Herpes Zoster OticusDocument12 pagesHerpes Zoster Oticusraghad.bassalNo ratings yet
- Surveillance System in The PhilippinesDocument38 pagesSurveillance System in The PhilippinesFred C. MirandaNo ratings yet
- Pao NCPDocument3 pagesPao NCPJay VillasotoNo ratings yet
- Pil 2425Document6 pagesPil 2425Gabriela ChiritoiuNo ratings yet