Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Feedings Down": Subjective Short Term Goal After DX Short Term Goal
Uploaded by
TeddCamiling0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views2 pagesThe patient was experiencing signs of dehydration including decreased skin turgor, dry mucous membranes, and lethargy. The nursing diagnosis was fluid volume deficit related to fluid and electrolyte loss from vomiting. The short term goal was for the patient to exhibit moist mucous membranes and good skin turgor after 8 hours of nursing intervention including fluid monitoring and IV fluids. The long term goal was for the patient to maintain fluid and electrolyte balance after 5 days. Nursing interventions included assessing vital signs, skin signs, behavior and activity level daily to monitor for dehydration and weigh the patient daily to monitor fluid status.
Original Description:
Original Title
NCP_RYAN_
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe patient was experiencing signs of dehydration including decreased skin turgor, dry mucous membranes, and lethargy. The nursing diagnosis was fluid volume deficit related to fluid and electrolyte loss from vomiting. The short term goal was for the patient to exhibit moist mucous membranes and good skin turgor after 8 hours of nursing intervention including fluid monitoring and IV fluids. The long term goal was for the patient to maintain fluid and electrolyte balance after 5 days. Nursing interventions included assessing vital signs, skin signs, behavior and activity level daily to monitor for dehydration and weigh the patient daily to monitor fluid status.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views2 pagesFeedings Down": Subjective Short Term Goal After DX Short Term Goal
Uploaded by
TeddCamilingThe patient was experiencing signs of dehydration including decreased skin turgor, dry mucous membranes, and lethargy. The nursing diagnosis was fluid volume deficit related to fluid and electrolyte loss from vomiting. The short term goal was for the patient to exhibit moist mucous membranes and good skin turgor after 8 hours of nursing intervention including fluid monitoring and IV fluids. The long term goal was for the patient to maintain fluid and electrolyte balance after 5 days. Nursing interventions included assessing vital signs, skin signs, behavior and activity level daily to monitor for dehydration and weigh the patient daily to monitor fluid status.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
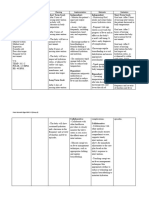
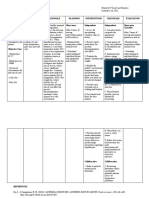
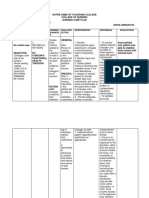
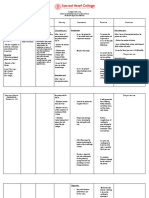
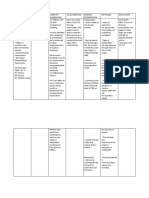
ASSESSMENT EXPLANATION PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
Subjective An imbalance in fluids and Short term goal; After Dx
“Ryan’s not keeping his electrolytes can result in 8 hours of Nursing Short term goal;
feedings down” excessive amounts of fluids intervention: The 1. Assess skin turgor, - Fluid loss occurs first in extracellular
in the body or dehydration. mucous membrane spaces, resulting in poor skin turgor
as verbalized by the patient be able to Goal met
This can happen as a result every shift. and dry mucous membrane.
patient’s mother. of an alteration in body After 8 hours of
systems, chronic disease, -Exhibit moist mucous nursing intervention
certain medications, or an membrane and good The patient was able
Objective Data 2. Monitor vital signs ate
underlying illness. skin turgor. to exhibit moist
-Decreased skin turgor every four hours. - Increased temperature and
mucous membrane
-Decreased tongue turgor Reference: respiratory rate contribute to fluid
-Refrain feeding without and skin turgor turns
-Lethargic loss, weak pulse and low blood
experiencing vomiting back normally.
-Warm to touch pressure may indicate dehydration.
(Nurse Labs, 2019)
-Sunken Fontanels
Long term goal After 5
-Dry mucous membrane days of Nursing
intervention: The patient Long term goal;
3. Assess the
VS taken as ff: will be able to: - A child with dehydration may
child behavior and activity. develop anorexia, decreased
-T- 100 F Goal met
activity level and general malaise.
-PR-180 BPM -Exhibit fluid and After 5 days of
-RR- 45/ min electrolyte balance. nursing intervention
Tx
-Weight- 7 lbs. the patient was able
-Maintain normal to exhibit fluid
4. Weigh the patient daily. - Provides the best assessment for
NURSING DIAGNOSIS weight. current fluid status and adequacy of electrolyte balance
fluid replacement. as manifested on his
Fluid volume deficit related latest laboratory
to loss of result.
fluids and - Fluid balance is less stable in young
electrolytes as manifested by 5. Monitor IV fusion every children, infusing too rapidly or too
vomiting. hour. slowly can lead to fluid imbalance.
6. Secure the IV site by - To protect the site and allow the
wrapping it with a soft child to move his hand and arm
bandage. freely.
7. Provide mouth care - The infant needs good mouth care
as the mucous membranes of the
mouth may be dry because of
dehydration and omission of oral
fluids before surgery; a pacifier can
satisfy the baby’s need for sucking
because of the interruption in
normal feeding and sucking habits.
Edx:
8. Educate the pt’s family - Enough knowledge aids the
member about possible patient’s family to take part in his or
cause and effect of fluid her plan of care.
losses or decreased fluid
intake.
- Include the caregivers in the
9. Promote family coping preparation for surgery and explain
the importance of added IV fluids,
the reason for ultrasonographic or
barium swallow examination, and
the function of the NG tube and
saline lavage; describe the surgical
procedure to be performed; and
explain what to expect and how
long the operation will last.
You might also like
- Leptin: Regulation and Clinical ApplicationsFrom EverandLeptin: Regulation and Clinical ApplicationsSam Dagogo-Jack, MDNo ratings yet
- NCP Peptic Ulcer DsDocument4 pagesNCP Peptic Ulcer Dsplug0650% (10)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanJobelyn TunayNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Specific Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective Cues: IndependentDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Specific Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective Cues: IndependentRap De la CruzNo ratings yet
- NCP Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument3 pagesNCP Deficient Fluid VolumeDoneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- NCP LeptospirosisDocument2 pagesNCP LeptospirosisLouise Anne Asuncion OclimaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Nursing Care PlanSheenaGuinoCullaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Cues Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcome Nursing Intervention Justification EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Cues Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcome Nursing Intervention Justification EvaluationKristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- FHP - NCP - Kidney FailureDocument9 pagesFHP - NCP - Kidney FailureFrancis AdrianNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument7 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationpamelaideaNo ratings yet
- Jessica Quiane Nursing Care PlanDocument11 pagesJessica Quiane Nursing Care PlanQuiane IcaNo ratings yet
- Franz - NCP (Pedia) - YeyyyyDocument7 pagesFranz - NCP (Pedia) - YeyyyyJohn Kenley FerryNo ratings yet
- NCP J2Document1 pageNCP J2jade abarillaNo ratings yet
- NCP AgeDocument1 pageNCP AgecaressmeNo ratings yet
- NCP For Acute PancreatitisDocument3 pagesNCP For Acute Pancreatitisrod navales100% (1)
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: Sto: DX StoDocument2 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: Sto: DX StoBasema HashhashNo ratings yet
- Oraa, Jamie - NCPDocument3 pagesOraa, Jamie - NCPJamie LeeNo ratings yet
- NCP Deficit Fluid VolumeDocument4 pagesNCP Deficit Fluid VolumeKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- NCP G7Document2 pagesNCP G7katt.edlessNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageAssessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationEiLseLNo ratings yet
- NCP HomeworkDocument6 pagesNCP HomeworkAndrea Albester GarinoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Deficit Related To Loose Watery Stool Diarrhea)Document2 pagesFluid Volume Deficit Related To Loose Watery Stool Diarrhea)Jesse James Advincula Edjec100% (15)
- DiagnosisDocument5 pagesDiagnosisBel Cabading AgbunagNo ratings yet
- NCP No. 2Document2 pagesNCP No. 2Lorraine Tuesday BuenviajeNo ratings yet
- NCP DHFDocument3 pagesNCP DHFjsdc_14No ratings yet
- HydroceleDocument10 pagesHydroceleRyan ReNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPNicole_Santos_6836No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Diagnosis Justification: Sodium-132 Mmol/l (Low)Document3 pagesNursing Care Plan Cues Diagnosis Justification: Sodium-132 Mmol/l (Low)rei_alina75% (4)
- Diabetes Mellitus (DM)Document1 pageDiabetes Mellitus (DM)Bheru LalNo ratings yet
- Prio NCP NG Dka ByeDocument5 pagesPrio NCP NG Dka ByeMARIA HILARY TABLANTENo ratings yet
- AppendectomyDocument2 pagesAppendectomyDARLENE ROSE BONGCAWILNo ratings yet
- Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation: Nursing Care Plan 3Document2 pagesCues Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation: Nursing Care Plan 3JP2001No ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Deficit Related To Nausea and VomitDocument3 pagesFluid Volume Deficit Related To Nausea and VomitJakeNo ratings yet
- NCP (Actual and Risk) ERESDocument7 pagesNCP (Actual and Risk) ERESKAROL MARIAE LUZ ERESNo ratings yet
- NCP Diabetic NephropathyDocument10 pagesNCP Diabetic NephropathyBiway RegalaNo ratings yet
- IndependentDocument2 pagesIndependentR Hornilla ArcegaNo ratings yet
- NCP - NCM 109 High-Risk Mother - CORITANA & ROBLESDocument4 pagesNCP - NCM 109 High-Risk Mother - CORITANA & ROBLESKimberly Almacen RoblesNo ratings yet
- NCP & DSDocument4 pagesNCP & DSKyla Marie TejadaNo ratings yet
- NCP 3rd YearDocument6 pagesNCP 3rd YearTotoro AblogNo ratings yet
- NCP&SOAPIEDocument4 pagesNCP&SOAPIEMica OmotsosircNo ratings yet
- NCP JaundiceDocument9 pagesNCP JaundiceMeena Koushal100% (1)
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background and Knowledge Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention and Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Background and Knowledge Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention and Rationale EvaluationKristiene Kyle AquinoNo ratings yet
- NCP Dehydration (Fluid Volume Deficit)Document3 pagesNCP Dehydration (Fluid Volume Deficit)Charissa de LeonNo ratings yet
- NCP - Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument2 pagesNCP - Deficient Fluid VolumeFretzgine Lou ManuelNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interentions EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interentions EvaluationHønëy ÇøhNo ratings yet
- Deficient Fluid Volume (AGEDocument2 pagesDeficient Fluid Volume (AGENursesLabs.com83% (6)
- NCP For Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument2 pagesNCP For Deficient Fluid VolumeRedwing_Dc_854758% (12)
- NCP DehydrationDocument3 pagesNCP Dehydrationcheane_jaja67% (3)
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Sto: DX StoDocument2 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Sto: DX StoBasema HashhashNo ratings yet
- Final Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesFinal Nursing Care PlanKatherine BellezaNo ratings yet
- Short Term: Independent: Independent: Short TermDocument2 pagesShort Term: Independent: Independent: Short TermAndre ImperialNo ratings yet
- Burns NCPDocument8 pagesBurns NCPJM AsentistaNo ratings yet
- NCP FinalDocument5 pagesNCP FinalVenus BonglayNo ratings yet
- CS5 (AGE) Acute Gastroenteritis NCPDocument2 pagesCS5 (AGE) Acute Gastroenteritis NCPAudrie Allyson GabalesNo ratings yet
- Breast Mass Bilateral To Consider FibroadenomaDocument5 pagesBreast Mass Bilateral To Consider FibroadenomaYum CNo ratings yet
- THE WATER AND THE BREATH: A guide to using water and breathing towards a stress free and successful lifeFrom EverandTHE WATER AND THE BREATH: A guide to using water and breathing towards a stress free and successful lifeNo ratings yet
- Living Systems Information Therapy LSIT: Introduction to Quantum MedicineFrom EverandLiving Systems Information Therapy LSIT: Introduction to Quantum MedicineNo ratings yet
- Polarity Therapy: How Re-Polarizing Your Body Can Heal YouFrom EverandPolarity Therapy: How Re-Polarizing Your Body Can Heal YouRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- The Causes and Effects of Alzheimer's Disease: The Silent DiseaseDocument35 pagesThe Causes and Effects of Alzheimer's Disease: The Silent DiseaseNina Canares100% (2)
- Immune DisorderDocument37 pagesImmune DisorderJessica TieuNo ratings yet
- Motor Neurone Disease: J GormallyDocument14 pagesMotor Neurone Disease: J GormallyBambang SutrisnoNo ratings yet
- TMJ DislocationDocument56 pagesTMJ DislocationAlok BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis of Bipolar II Disorder and Borderline Personality DisorderDocument11 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of Bipolar II Disorder and Borderline Personality DisorderManu Cortes OsorioNo ratings yet
- What Causes Water in The LungsDocument1 pageWhat Causes Water in The LungsSakuraerikaNo ratings yet
- Ariana's Reasearch PaperDocument8 pagesAriana's Reasearch Paperapi-281014657No ratings yet
- Checklist Hip ExaminationDocument7 pagesChecklist Hip ExaminationJavednNo ratings yet
- Amethyst Biomat Far Infrared Rays Stimulate Permanent Weight LossDocument2 pagesAmethyst Biomat Far Infrared Rays Stimulate Permanent Weight LossJenNo ratings yet
- Sylvie Steinbach - The Secrets of The Lenormand OracleDocument70 pagesSylvie Steinbach - The Secrets of The Lenormand OracleΒασιλικη Νικα100% (1)
- Quiz On School Health NursingDocument7 pagesQuiz On School Health Nursingchoobi0% (2)
- Cmca Lec Prelim ReviewerDocument26 pagesCmca Lec Prelim ReviewerCrystal MiranaNo ratings yet
- PPTDocument61 pagesPPTRheal P EsmailNo ratings yet
- Developmental Right-Hemisphere Syndrome: Clinical Spectrum of The Nonverbal Learning DisabilityDocument7 pagesDevelopmental Right-Hemisphere Syndrome: Clinical Spectrum of The Nonverbal Learning DisabilityCharitini PetridouNo ratings yet
- DDX of Generalized OedemaDocument33 pagesDDX of Generalized Oedemazaw wai aungNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Comprehensive Case StudyDocument12 pagesPsychiatric Comprehensive Case Studyapi-544878035No ratings yet
- Cardio Exam Test BankDocument17 pagesCardio Exam Test BankPINKY CUARESMA0% (1)
- 18106B1030 Sheetal Dahibavkar Social Relevance-1Document52 pages18106B1030 Sheetal Dahibavkar Social Relevance-1varadNo ratings yet
- TASk 2 DS NCPDocument3 pagesTASk 2 DS NCPCHRISTIAN CALAMBANo ratings yet
- Stroke, Epidemiology: Virginia J Howard, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL, United StatesDocument7 pagesStroke, Epidemiology: Virginia J Howard, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL, United StateswidyadariNo ratings yet
- Sensory Organs: EYE EAR Tongue Skin NoseDocument101 pagesSensory Organs: EYE EAR Tongue Skin NoseSaba PathyNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Knowledge Check 2Document78 pagesUnit 3 Knowledge Check 2SH SNo ratings yet
- Meningitis: Neonates (65)Document5 pagesMeningitis: Neonates (65)Eugina Naiborhu08No ratings yet
- WHO - The Need For Strong Health Information Systems - Rationale For The HMN FrameworkDocument4 pagesWHO - The Need For Strong Health Information Systems - Rationale For The HMN FrameworkHarumNo ratings yet
- Folliculitis and TrichomycosisDocument4 pagesFolliculitis and TrichomycosisYolisNo ratings yet
- Myocarditis: Mark A. Fischione, M.D. Pathological Sciences School of Osteopathic Medicine in ArizonaDocument28 pagesMyocarditis: Mark A. Fischione, M.D. Pathological Sciences School of Osteopathic Medicine in ArizonaTony ZiherlNo ratings yet
- Association Between Anxiety and Depression With Irritable Bowel Syndrome in MosulDocument6 pagesAssociation Between Anxiety and Depression With Irritable Bowel Syndrome in Mosulsarhang talebaniNo ratings yet
- AtpdDocument48 pagesAtpddrkadiyala2100% (2)
- Neonatal TransportDocument19 pagesNeonatal TransportNeha OberoiNo ratings yet
- MetabolismDocument16 pagesMetabolismAdiShineNo ratings yet