Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Assessment and Intervention for Dehydration
Uploaded by
Kristil Chavez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views3 pagesThe document presents a nursing assessment and care plan for a 64-year-old female patient presenting with signs of dehydration such as delayed skin turgor and weakness, with a nursing diagnosis of deficient fluid volume related to vomiting. The plan is to administer IV fluids and replacement medications like cortisone to restore fluid volume and electrolyte balance, monitor vital signs and intake/output, and ensure the patient can maintain adequate hydration and health through diet and lifestyle changes after the intervention period.
Original Description:
Original Title
Untitled
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document presents a nursing assessment and care plan for a 64-year-old female patient presenting with signs of dehydration such as delayed skin turgor and weakness, with a nursing diagnosis of deficient fluid volume related to vomiting. The plan is to administer IV fluids and replacement medications like cortisone to restore fluid volume and electrolyte balance, monitor vital signs and intake/output, and ensure the patient can maintain adequate hydration and health through diet and lifestyle changes after the intervention period.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views3 pagesNursing Assessment and Intervention for Dehydration
Uploaded by
Kristil ChavezThe document presents a nursing assessment and care plan for a 64-year-old female patient presenting with signs of dehydration such as delayed skin turgor and weakness, with a nursing diagnosis of deficient fluid volume related to vomiting. The plan is to administer IV fluids and replacement medications like cortisone to restore fluid volume and electrolyte balance, monitor vital signs and intake/output, and ensure the patient can maintain adequate hydration and health through diet and lifestyle changes after the intervention period.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
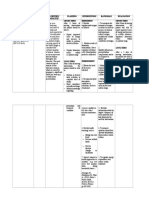
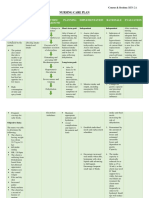
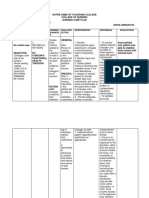
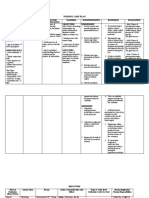
Assessment Nursing (Rationale) Desired Outcome Nursing Justification Evaluation
Cues Diagnosis Pathophysiologic / Schematic Diagram Intervention
Subjective:
Deficient Fluid Predisposing Precipitating After 8 hours of nursing Independent: Independent: SHORT TERM
“Halin pa gid sang Volume related to intervention the patient GOALS
vomiting as Factor Factor
kagina akon na suka, and family will be able: The patient will have
Nurse. Kaluya na gid evidenced by delay 64 YO HYPOTENSIVE Assess skin turgor and dry skin and mucous After 8 hours of
ka akon na in skin turgor. FEMALE DEHYDRATED 1. To maintain BP mucous membranes for signs membranes. Tenting of nursing
and skin turgor of dehydration. the skin will occur. The intervention, client
pamatyag".
within the normal tongue may have was able to:
range. longitudinal furrows.
Patient was weak and Definition: 1. Maintain BP
lethargic. within acceptable
HEALTH PROBLEMS 2. To demonstrates
Decreased lifestyle changes to Assess vital signs, especially A BP drop of more than range with V/S
intravascular, avoid progression noting BP and HR for 15 mm Hg when bp: 120/80 and
Delayed in skin interstitial and/or of dehydration. orthostatic changes. changing from supine to skin turgor of
Turgor was noted (6 sitting position, with a 2secs. GOAL
intracellular fluid.
seconds). concurrent elevation of MET.
This refers to
Adrenal glands not functioning due to After 3 days of nursing 15 beats per min in HR,
dehydration, indicates reduced 2. Demonstrate
autoimmune reasons intervention the patient
water loss alone circulating fluids. change of lifestyle
without change in and family will be able:
to avoid
sodium. Cortisol (hydrocortisone, cortisone dehydration by
acetatem prednisone, or dexmethasone) 1. To maintain and Encourage oral fluids as the As sodium loss verbalizing that
Objective: Patient is optimize overall
nonsmoker Reference: very low or absent. patient tolerates. increases, extracellular she needs to have
NANDA health status. fluid volume decreases. a healthy diet and
International, These interventions are maintain a healthy
Tried drinking alcohol
Nursing Glucocorticoid deficiency 2. To have adequate necessary to prevent lifestyle. GOAL
in her high school
Diagnoses, fluid and fluid volume deficit MET
years.
electrolyte because the kidneys are
Eleventh Edition
balance as unable to conserve LONG TERM
Patient had loss weight
Insulin sensitivity and disturbances in evidenced by sodium. GOALS:
according to her
husband carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism MIO. After 3 days of
nursing care, was
able to:
01/31/2023
Dependent: Dependent:
Vital signs 1. Maintain and
4:00 pm Hypoglycemia, decreased liver glycogen, Administer parenteral fluids Normal saline is infused optimize
BP: 80/60 weakness, trauma and circulatory failure as prescribed. Anticipate the initially to restore fluid overall health
HR: 106bpm need for an intravenous (IV) volume. Treatment are status as
fluid challenge with needed because of the evidenced by
RR: 24cpm
Deficient Fluid Volume related to immediate infusion of fluids high mortality with improvement
T: 36.0 C for patients with abnormal Addisonian crisis. in the V/S.
vomiting as evidenced by delay in skin
O2 sat: 98% vital signs. GOAL MET
turgor.
8:00 pm 2. Adequate
BP: 100/60 Source: Administer replacement Cortisone and prednisone fluid and
HR: 112bpm Nettina, Sandra M. (2003) Lippincott’s medications as prescribed or replace cortisol deficits, electrolyte
RR: 24cpm pocket manual of nursing practice. 2nd indicated: oral cortisone which will promote balance as
T: 36.1 C edition. (Cortone), hydrocortisone sodium resorption. evidenced by
O2 sat: 98% (Cortef), prednisone, or Fludrocortisone is a improvement
fludrocortisone (Florinef). mineralocorticoid for in MIO.
patients who require GOAL MET
Laboratories
aldosterone replacement
1/31/2023 to promote sodium and
WBC Count water replacement.
13.90 Acute adrenal
x10^9(elevated) insufficiency is a
Potassium medical emergency
5.9 mmol/L requiring immediate
(elevated) fluid and corticosteroid
ESR administration. If treated
55 mmol/L (elevated) for adrenal crisis, the
CRP patient requires IV
hydrocortisone initially;
16 mg/L (elevated)
usually by the second
TSH day, administration can
30 mIU/L (elevated) be converted to an oral
Cortisol form of replacement.
5mcg/dL (low)
ACTH
7 pg/mL (low) Collaborative:
Instruct the patient to inquire Collaborative:
a dietician with regards to
ingesting salt additives in Sweating increases
conditions of excess heat or sodium loss. A dietician
humidity. will help the patient with
regards to a healthy diet.
You might also like
- NCP - AgeDocument5 pagesNCP - Ageunsp3akabl386% (7)
- Pharmacology for Student and Pupil Nurses and Students in Associated ProfessionsFrom EverandPharmacology for Student and Pupil Nurses and Students in Associated ProfessionsNo ratings yet
- NCP Deficit Fluid VolumeDocument4 pagesNCP Deficit Fluid VolumeKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- NCP Peptic Ulcer DsDocument4 pagesNCP Peptic Ulcer Dsplug0650% (10)
- Assessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesAssessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationimnasNo ratings yet
- ROSABIA, Micaela Pauline J. .-BSN-2A-ISDH-GS-NURSERY-NCPDocument6 pagesROSABIA, Micaela Pauline J. .-BSN-2A-ISDH-GS-NURSERY-NCPkimberly quitonNo ratings yet
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: Sto: DX StoDocument2 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: Sto: DX StoBasema HashhashNo ratings yet
- Maintaining Fluid Balance in a Dehydrated PatientDocument9 pagesMaintaining Fluid Balance in a Dehydrated PatientTyn TynNo ratings yet
- NCP Assessment Fluid DeficitDocument2 pagesNCP Assessment Fluid DeficitBasema HashhashNo ratings yet
- NCP 3 - Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument4 pagesNCP 3 - Deficient Fluid VolumeKrishelle Kate PannigNo ratings yet
- Risk NCP - PESCADERO 4CDocument1 pageRisk NCP - PESCADERO 4COrlando VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Feedings Down": Subjective Short Term Goal After DX Short Term GoalDocument2 pagesFeedings Down": Subjective Short Term Goal After DX Short Term GoalTeddCamilingNo ratings yet
- NCP (Actual and Risk) ERESDocument7 pagesNCP (Actual and Risk) ERESKAROL MARIAE LUZ ERESNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument7 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationpamelaideaNo ratings yet
- Gi-Rle - NCP For Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument2 pagesGi-Rle - NCP For Deficient Fluid VolumeEvangeline Villa de Gracia100% (1)
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument2 pagesDecreased Cardiac OutputALEKS MONTECINO JIMENEZNo ratings yet
- NCP For HypoDocument5 pagesNCP For HypoCecil MonteroNo ratings yet
- NCP - Activity IntoleranceDocument4 pagesNCP - Activity IntoleranceRoyce Vincent TizonNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background and Knowledge Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention and Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Background and Knowledge Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention and Rationale EvaluationKristiene Kyle AquinoNo ratings yet
- Dengue NCPDocument3 pagesDengue NCPingridNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Fluid Volume DeficitDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Fluid Volume Deficitnj_pink08179456% (9)
- NCP Case Analysis GastritisDocument7 pagesNCP Case Analysis GastritisSteffi GolezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Hypertension with Occipital HeadacheDocument7 pagesNursing Care Plan for Hypertension with Occipital HeadacheMarie joy CortezNo ratings yet
- Salva, R.D NCP & Drug Study (Isph - Gs Pediaward)Document7 pagesSalva, R.D NCP & Drug Study (Isph - Gs Pediaward)Rae Dominick Aquino SalvaNo ratings yet
- NURSING Nursing Care Plan for Diabetes MellitusDocument3 pagesNURSING Nursing Care Plan for Diabetes MellitusYsun Espino100% (1)
- Assessment Diagnosi S Scientific Analysis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation PE Short Term Dependent Short TermDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosi S Scientific Analysis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation PE Short Term Dependent Short Termjamie carpioNo ratings yet
- Name: Olusegun-Obiwusi, Olufunke DATE: - : Subjective: DXDocument4 pagesName: Olusegun-Obiwusi, Olufunke DATE: - : Subjective: DXJemimah MejiaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Fatigue ManagementDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan for Fatigue ManagementJhasmine MocnanganNo ratings yet
- NCP Post PartumDocument2 pagesNCP Post PartumsteffiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationNelly CruzNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Deficit Related To Loose Watery Stool Diarrhea)Document2 pagesFluid Volume Deficit Related To Loose Watery Stool Diarrhea)Jesse James Advincula Edjec100% (15)
- College of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanPrince Juzzel Banag100% (1)
- Oraa, Jamie - NCPDocument3 pagesOraa, Jamie - NCPJamie LeeNo ratings yet
- Subjective Data: Long Term Goal: Diagnostic:: "I Was Trying To Vomit in The Emergency Department."Document5 pagesSubjective Data: Long Term Goal: Diagnostic:: "I Was Trying To Vomit in The Emergency Department."Erle Gray CadangenNo ratings yet
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Intervention Rationale Expected Outcome Subjective: Objective: Sto: DX Sto: (Goal Met)Document2 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Intervention Rationale Expected Outcome Subjective: Objective: Sto: DX Sto: (Goal Met)Basema HashhashNo ratings yet
- Sign and SymptomsDocument5 pagesSign and Symptomsmadras meditationNo ratings yet
- VILLAHERMOSA - Anorexia NCPDocument9 pagesVILLAHERMOSA - Anorexia NCPJv Jore VillahermosaNo ratings yet
- Villahermosa - GDM NCPDocument9 pagesVillahermosa - GDM NCPJv Jore VillahermosaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan, DeficientDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan, Deficientimee15No ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Noc: NIC: Fluid ManagementDocument10 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Noc: NIC: Fluid ManagementSkyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- Deficient Fluid Volume (Vanene)Document7 pagesDeficient Fluid Volume (Vanene)jajalerNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Background Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Background Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationMelrhean GraceNo ratings yet
- HydroceleDocument10 pagesHydroceleRyan ReNo ratings yet
- Risk for Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument3 pagesRisk for Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalancerod navales100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: IndependentDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: IndependentAdhaNo ratings yet
- Managing Overweight through Diet and ExerciseDocument17 pagesManaging Overweight through Diet and ExerciseMarie Ashley CasiaNo ratings yet
- NCP 3rd YearDocument6 pagesNCP 3rd YearTotoro AblogNo ratings yet
- Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation: Nursing Care Plan 3Document2 pagesCues Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation: Nursing Care Plan 3JP2001No ratings yet
- NCP Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument3 pagesNCP Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceVitha100% (1)
- Specific nursing interventions for Pernicious AnemiaDocument7 pagesSpecific nursing interventions for Pernicious AnemiaLeni YulisNo ratings yet
- Silliman University: Nursing Care Plan During DeliveryDocument12 pagesSilliman University: Nursing Care Plan During DeliveryShandle Dynne BaenaNo ratings yet
- NCP DHFDocument3 pagesNCP DHFjsdc_14No ratings yet
- Risk For Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument3 pagesRisk For Deficient Fluid VolumeALEKS MONTECINO JIMENEZNo ratings yet
- NCP LeptospirosisDocument6 pagesNCP LeptospirosisJean Marie DavidNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Submitted byDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Submitted byKarl Angelo MontanoNo ratings yet
- NCP & DSDocument4 pagesNCP & DSKyla Marie TejadaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Fluid Volume DeficitDocument7 pagesNursing Care Plan for Fluid Volume DeficitDan Dan ManaoisNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Fluid Volume DeficitDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Fluid Volume DeficitDan Dan ManaoisNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Nursing Care PlanjamieboyRN91% (32)
- Medical Abbreviations and Drug Calculations Practice ListDocument3 pagesMedical Abbreviations and Drug Calculations Practice ListKristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- Calendula (Pot Marigolds) : Kristil Marie E. Chavez BN3ADocument1 pageCalendula (Pot Marigolds) : Kristil Marie E. Chavez BN3AKristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- Gerd HTP Bn3aDocument4 pagesGerd HTP Bn3aKristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- Presenting Complaints (As Applicable)Document2 pagesPresenting Complaints (As Applicable)Kristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- Addison DiseaseDocument22 pagesAddison DiseaseKristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- Calendula (Pot Marigolds) : Kristil Marie E. Chavez BN3ADocument1 pageCalendula (Pot Marigolds) : Kristil Marie E. Chavez BN3AKristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- Intravenous/Parenteral Fluid Sheet: 01/31/2023 4:00pm 2 Pnss KMCDocument1 pageIntravenous/Parenteral Fluid Sheet: 01/31/2023 4:00pm 2 Pnss KMCKristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- Medication Sheet: Complete Name and Initials of Medication NurseDocument1 pageMedication Sheet: Complete Name and Initials of Medication NurseKristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation:: Kristil Chavez and Christiana Cruz BN3ADocument21 pagesCase Presentation:: Kristil Chavez and Christiana Cruz BN3AKristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledKristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- Gloves GRDDocument1 pageGloves GRDKristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- Case PresDocument2 pagesCase PresKristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- Student NursesDocument2 pagesStudent NursesKristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- LT 1 Charting (CHAVEZ BSN2A)Document2 pagesLT 1 Charting (CHAVEZ BSN2A)Kristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- Barangay Health Center Services and DOH ProgramsDocument7 pagesBarangay Health Center Services and DOH ProgramsKristil Chavez100% (1)
- GRAPHIC CHART TRACKS PATIENT'S VITAL SIGNSDocument2 pagesGRAPHIC CHART TRACKS PATIENT'S VITAL SIGNSKristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- Assignment 8Document1 pageAssignment 8Kristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- Draftt News ArticleeeeDocument1 pageDraftt News ArticleeeeKristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- IV-Sheet-MW2-Case 1Document1 pageIV-Sheet-MW2-Case 1Kristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- Nurse's Notes-MW2-Case 1Document1 pageNurse's Notes-MW2-Case 1Kristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- History of Arnis in <40 CharactersDocument16 pagesHistory of Arnis in <40 CharactersKristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- Task2 DrugStudy Penicillin-G-BenzathineDocument1 pageTask2 DrugStudy Penicillin-G-BenzathineKristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study-MW2-Case 1Document4 pagesDrug Study-MW2-Case 1Kristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- Breast Mini Case Study (Chavez - BSN1A)Document4 pagesBreast Mini Case Study (Chavez - BSN1A)Kristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Chavez BSN 2H)Document2 pagesDrug Study (Chavez BSN 2H)Kristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- Assignment 6Document1 pageAssignment 6Kristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- MIO-Sheet-MW2-Case 1Document1 pageMIO-Sheet-MW2-Case 1Kristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- 3.2.1 EINC1 Task 1 - Interview (Chavez BSN2H)Document2 pages3.2.1 EINC1 Task 1 - Interview (Chavez BSN2H)Kristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper (Chavez BSN1A)Document1 pageReaction Paper (Chavez BSN1A)Kristil ChavezNo ratings yet