Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Uploaded by
Nelly Cruz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesOriginal Title
BSN-3-B-GROUP-3-NCP-final
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Uploaded by
Nelly CruzCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
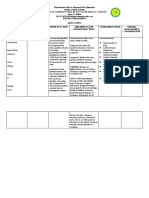
Don Mariano Marcos Memorial State
University South La Union Campus
COLLEGE OF COMMUNITY HEALTH AND ALLIED
MEDICAL SCIENCES
Agoo, La Union
Tel. 072.682.0663/ichams.dmmmsu-sluc.com
Embracing World Class Standards Nursing Department Care to learn, Learn to care
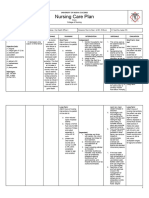
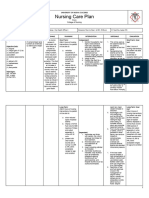
NURSING CARE PLAN
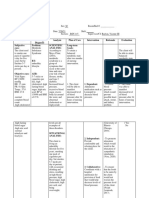
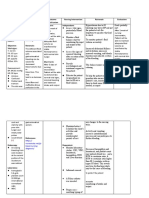
ASSESSMENT EXPLANATION OF OBJECTIVES INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
THE PROBLEM
Objective: STO: STO:
If blood pressure After 2 hours of THERAPEUTIC After 2 hours of
Vital Signs: drops too low, the nursing Administer oxygen by To maximize nursing
BP: 86/50 mmHg body's vital organs do intervention, the appropriate route. oxygenation of tissues. intervention, the
MAP: 58 mmHg not get enough oxygen patient’s blood patient’s blood
HR: 122 bpm and nutrients. pressure will Administer fluids, To rapidly restore or pressure did not
CVP: 4 bpm return to normal electrolytes, colloids, sustain circulating return to normal
RR: 32 bpm When sepsis occur, values blood or blood products volume, electrolyte values
SVR: 640 a systemic response as indicated. balance and prevent
dynes/sec/m-5 takes place and all the shock state. GOAL UNMET.
SpO2 :90% on blood vessels dilate
Room Air causing the blood to Provide nutrition by best To provide foods rich in
drop. If it gets too low, means (oral, enteral or nutrients, vitamins and
Laboratory Results: it can become life- LTO: parenteral feeding) or minerals needed to LTO:
WBC: threatening, leading to After 2 days of refer to nutritionist or promote healing and After 2 days of
22,000/mcL shock. nursing dietitian. support immune system nursing
Lactic Acid: 3.6 intervention, the health. intervention, the
mmol/L patient will patient was able
Urine: cloudy with a) display to
sediment hemodynamic For timely evaluation and a) display
Identify reportable signs
stability as and symptoms, including intervention. hemodynamic
ABGs evidenced by vital unrelieved pain, stability as
pH: 7.22 signs within unresolved bleeding, evidenced by vital
pCO2 :30 mmHg normal range for excessive fluid loss, signs within
HCO3 :16 mEq/L client; persistent fever and chills, normal range for
pO2 :64 mmHg b) prompt capillary change in skin color client;
*Metabolic Acidosis, refill; accompanied by chest b) prompt capillary
partially compensated c) adequate urinary output pain. refill;
with normal specific gravity; c) adequate
usual level of mentation. To reduce risk of urinary output with
Nursing Diagnosis: anaphylactic shock state normal specific
Risk for shock gravity; usual level
related to of mentation.
hypotension
GOAL MET.
You might also like
- Pharmacology for Student and Pupil Nurses and Students in Associated ProfessionsFrom EverandPharmacology for Student and Pupil Nurses and Students in Associated ProfessionsNo ratings yet
- Nursing Department: Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Department: Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Interventions Rationale EvaluationNelly CruzNo ratings yet
- NCP 3 - Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument4 pagesNCP 3 - Deficient Fluid VolumeKrishelle Kate PannigNo ratings yet
- Deficit Fluid VolumeDocument2 pagesDeficit Fluid VolumeALEKS MONTECINO JIMENEZNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury W/ Hyperkalemia NCPDocument5 pagesAcute Kidney Injury W/ Hyperkalemia NCPMyrvic Ortiz La OrdenNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan SampleDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Samplez6cc9vgg6nNo ratings yet
- Log Book Case Debriefing With The Preceptor Name of The Trainee: SCFHS Reference No: Year: D D Case Category: Date: AreaDocument3 pagesLog Book Case Debriefing With The Preceptor Name of The Trainee: SCFHS Reference No: Year: D D Case Category: Date: AreaS DNo ratings yet
- Assessment Cues Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcome Nursing Intervention Justification EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Cues Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcome Nursing Intervention Justification EvaluationKristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- Medina, Joanna BN3C - NCP FormatDocument7 pagesMedina, Joanna BN3C - NCP FormatJOANNA MARIE MEDINANo ratings yet
- Scientific Analysis Goal: Goal:: Subjective CuesDocument3 pagesScientific Analysis Goal: Goal:: Subjective CuesChloie Marie RosalejosNo ratings yet
- NCP Ca 3Document3 pagesNCP Ca 3Lalaine LocsinNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume ExcessDocument4 pagesFluid Volume Excessaudreyann.acobNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan NCPDocument24 pagesNursing Care Plan NCPRosemarie R. Reyes100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanMariel GamaloNo ratings yet
- Name: Olusegun-Obiwusi, Olufunke DATE: - : Subjective: DXDocument4 pagesName: Olusegun-Obiwusi, Olufunke DATE: - : Subjective: DXJemimah MejiaNo ratings yet
- Name: Olusegun-Obiwusi, Olufunke DATE: - : Subjective: DXDocument4 pagesName: Olusegun-Obiwusi, Olufunke DATE: - : Subjective: DXJhasmine MocnanganNo ratings yet
- Final NCP (Jannel)Document6 pagesFinal NCP (Jannel)Zed P. EstalillaNo ratings yet
- ROSABIA, Micaela Pauline J. .-BSN-2A-ISDH-GS-NURSERY-NCPDocument6 pagesROSABIA, Micaela Pauline J. .-BSN-2A-ISDH-GS-NURSERY-NCPkimberly quitonNo ratings yet
- SepsisDocument3 pagesSepsisPhilip Poerworahjono100% (3)
- College of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanPrince Juzzel Banag100% (1)
- Nursing Care Management of Client With Hypokalemia ACTUAL 1Document4 pagesNursing Care Management of Client With Hypokalemia ACTUAL 1Angel Nieto PengsonNo ratings yet
- Head Nursing TemplateDocument10 pagesHead Nursing TemplateBianca MaeNo ratings yet
- Geriatic Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalance NCPDocument4 pagesGeriatic Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalance NCPCA Candido JavierNo ratings yet
- NCP ElectrolyteImbalanceDocument2 pagesNCP ElectrolyteImbalancegerold m chuaNo ratings yet
- NCP With Eval Dewara BSN3FDocument2 pagesNCP With Eval Dewara BSN3FPrincess Faniega SugatonNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume ExcessDocument4 pagesFluid Volume Excessaudreyann.acobNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPSteffi MurielNo ratings yet
- NCP - Or-Rotation 2Document12 pagesNCP - Or-Rotation 2Vian RiveraNo ratings yet
- Care of A Client With Diabetic Ketoacidosis FDocument33 pagesCare of A Client With Diabetic Ketoacidosis FHananNo ratings yet
- "Nanghihina Ako Tsaka Wala Akong Ganang Kumain" As VerbalizedDocument3 pages"Nanghihina Ako Tsaka Wala Akong Ganang Kumain" As VerbalizedAnonymous JtOaXOE1No ratings yet
- CAMARISTACM - NCP (ULCERATIVE COLITIS) (Diarrhea)Document4 pagesCAMARISTACM - NCP (ULCERATIVE COLITIS) (Diarrhea)Coleen Mae Camarista0% (1)
- Facto NCPDocument3 pagesFacto NCPkkd nyleNo ratings yet
- Group 47 NCP Bicarbonate DisordersHyperbicarbonatemia and HypobicarbonatemiaDocument6 pagesGroup 47 NCP Bicarbonate DisordersHyperbicarbonatemia and HypobicarbonatemiaAngel Joyce MontezaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationMargareth DandanNo ratings yet
- NCP - AgeDocument5 pagesNCP - Ageunsp3akabl386% (7)
- NCP - Dela CruzDocument4 pagesNCP - Dela CruzChristine Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- NCP UTI (Artillo)Document3 pagesNCP UTI (Artillo)Al TheóNo ratings yet
- NCP - Activity IntoleranceDocument4 pagesNCP - Activity IntoleranceRoyce Vincent TizonNo ratings yet
- Cues/Needs Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term Independent Short TermDocument2 pagesCues/Needs Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term Independent Short TermLatrell GelacioNo ratings yet
- NCP GI EditedDocument4 pagesNCP GI EditednicoleNo ratings yet
- NCP Case 3Document3 pagesNCP Case 3boomer SeargeNo ratings yet
- NCP Post PartumDocument2 pagesNCP Post PartumsteffiNo ratings yet
- NCP and Drug Study (Isph-Gs Nursery)Document4 pagesNCP and Drug Study (Isph-Gs Nursery)Cristyl Shine BariaoNo ratings yet
- Gi-Rle - NCP For Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument2 pagesGi-Rle - NCP For Deficient Fluid VolumeEvangeline Villa de Gracia100% (1)
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background and Knowledge Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention and Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Background and Knowledge Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention and Rationale EvaluationKristiene Kyle AquinoNo ratings yet
- NCP-ABRUPTIO PLACENTAE - PeregrinoDocument5 pagesNCP-ABRUPTIO PLACENTAE - PeregrinoJOYCE ANN PEREGRINONo ratings yet
- Burns NCPDocument5 pagesBurns NCPSmileNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Interventions Rationale Evaluation Sto: Diagnostic: StoDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Interventions Rationale Evaluation Sto: Diagnostic: StoNelly CruzNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPNurhaifa MocademaNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related To Interruption of Blood Flow Secondary To Hemorrhage As Evidenced by GCS of 7Document2 pagesIneffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related To Interruption of Blood Flow Secondary To Hemorrhage As Evidenced by GCS of 7dana100% (4)
- A Case Study On AGE Part 3Document2 pagesA Case Study On AGE Part 3pangee489No ratings yet
- Chronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesChronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanRuva Oscass JimmyNo ratings yet
- Problem List: Vital SignsDocument13 pagesProblem List: Vital SignsRey Jean GarciaNo ratings yet
- HydroceleDocument10 pagesHydroceleRyan ReNo ratings yet
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationTedd CamilingNo ratings yet
- NCP - Excess Fluid Volume Related Compromised Regulatory Mechanism (Renal Failure) (Acute Renal Failure)Document3 pagesNCP - Excess Fluid Volume Related Compromised Regulatory Mechanism (Renal Failure) (Acute Renal Failure)Kian Herrera100% (1)
- Waiters PATIENT CARE PLAN 2020 For PPHDocument3 pagesWaiters PATIENT CARE PLAN 2020 For PPHmp1757No ratings yet
- NCP FdarDocument13 pagesNCP FdarJhaymee Pineda100% (1)
- NCP Decrease Cardiac OutputDocument2 pagesNCP Decrease Cardiac OutputAnonymous 2hJKVrNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Student Nurse: Diestro, Angela Mae BSN 2BDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Student Nurse: Diestro, Angela Mae BSN 2BAngela Mae DiestroNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity No. 9 The Evolution of Phil. ConstitutionDocument4 pagesLearning Activity No. 9 The Evolution of Phil. ConstitutionNelly CruzNo ratings yet
- Module IDocument34 pagesModule INelly CruzNo ratings yet
- 3-B FdarDocument1 page3-B FdarNelly CruzNo ratings yet
- LEARNING ACTIVITY NO. 8 The Tejeros ConventionDocument3 pagesLEARNING ACTIVITY NO. 8 The Tejeros ConventionNelly CruzNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity No. 7 The First Catholic MassDocument2 pagesLearning Activity No. 7 The First Catholic MassNelly CruzNo ratings yet
- Dela Cruz, J. M4 NCPDocument2 pagesDela Cruz, J. M4 NCPNelly CruzNo ratings yet
- Dela Cruz, J. M4Document8 pagesDela Cruz, J. M4Nelly CruzNo ratings yet
- Dela Cruz, J. L1Document1 pageDela Cruz, J. L1Nelly CruzNo ratings yet
- Dela Cruz, J. M3Document4 pagesDela Cruz, J. M3Nelly CruzNo ratings yet
- Dela Cruz, J. L2 MODULE 3Document1 pageDela Cruz, J. L2 MODULE 3Nelly CruzNo ratings yet
- Dela Cruz, J. L4Document1 pageDela Cruz, J. L4Nelly CruzNo ratings yet
- Dela Cruz, J. M3 Critical ThinkingDocument1 pageDela Cruz, J. M3 Critical ThinkingNelly CruzNo ratings yet
- Dela Cruz, J. M1Document7 pagesDela Cruz, J. M1Nelly CruzNo ratings yet
- Dela Cruz, J. L3Document1 pageDela Cruz, J. L3Nelly CruzNo ratings yet
- Dela Cruz, J. L2Document1 pageDela Cruz, J. L2Nelly CruzNo ratings yet
- Dela Cruz, J. ActivityDocument2 pagesDela Cruz, J. ActivityNelly CruzNo ratings yet
- Dela Cruz, J. M4 A3Document2 pagesDela Cruz, J. M4 A3Nelly CruzNo ratings yet
- Dela Cruz, J. MODULE 2 A1Document9 pagesDela Cruz, J. MODULE 2 A1Nelly CruzNo ratings yet
- Dela Cruz, J. M4 A1Document2 pagesDela Cruz, J. M4 A1Nelly CruzNo ratings yet
- Dela Cruz, J. M4 A2Document3 pagesDela Cruz, J. M4 A2Nelly CruzNo ratings yet
- Dela Cruz, J. M3 NCPDocument2 pagesDela Cruz, J. M3 NCPNelly CruzNo ratings yet
- Dela Cruz, J. ActivityDocument2 pagesDela Cruz, J. ActivityNelly CruzNo ratings yet
- Dela Cruz, J. Activity # 2Document2 pagesDela Cruz, J. Activity # 2Nelly CruzNo ratings yet
- Dela Cruz, J. ActivityDocument2 pagesDela Cruz, J. ActivityNelly CruzNo ratings yet
- Norepinephrine FinalDocument2 pagesNorepinephrine FinalNelly CruzNo ratings yet
- FDARfinalDocument2 pagesFDARfinalNelly CruzNo ratings yet
- DS VancomycinDocument2 pagesDS VancomycinNelly CruzNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Interventions Rationale Evaluation Sto: Diagnostic: StoDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Interventions Rationale Evaluation Sto: Diagnostic: StoNelly CruzNo ratings yet
- 37 - Acute Rheumatic FeverDocument1 page37 - Acute Rheumatic FevernasibdinNo ratings yet
- 1st Lecture (NCM106 ABC I) Care of Clients in Cellular Aberrations, ABC, Emergency and Disaster NursingDocument14 pages1st Lecture (NCM106 ABC I) Care of Clients in Cellular Aberrations, ABC, Emergency and Disaster NursingKamx Mohammed100% (1)
- What Is High Blood PressureDocument3 pagesWhat Is High Blood PressureShekarNo ratings yet
- Core Knowledge OrthopaedicsDocument2 pagesCore Knowledge OrthopaedicsIamTineshNo ratings yet
- Management of Tinea Corporis, Tinea CrurisDocument10 pagesManagement of Tinea Corporis, Tinea CrurisRansidelenta Vistaprila ElmardaNo ratings yet
- Demodex Infestation Requires Immediate, Aggressive Treatment by Doctor, Patient - Primary Care Optometry NewsDocument5 pagesDemodex Infestation Requires Immediate, Aggressive Treatment by Doctor, Patient - Primary Care Optometry NewsΔιονύσης ΦιοραβάντεςNo ratings yet
- S2-Epid - Main Disese (3) - Influenza - Student - 2023Document48 pagesS2-Epid - Main Disese (3) - Influenza - Student - 2023Syahrul SanmasNo ratings yet
- Algorithm in Hypertension-PduiDocument32 pagesAlgorithm in Hypertension-PduiMochamad BurhanudinNo ratings yet
- 4333445492022-10-25T16 28 16.773Document6 pages4333445492022-10-25T16 28 16.773Nina JordanNo ratings yet
- PRELIMINARY ACTIVITY of Module 1Document3 pagesPRELIMINARY ACTIVITY of Module 1Casio, Anthony MaryNo ratings yet
- Gastro POMDocument63 pagesGastro POMLionell Castillo100% (1)
- DialysisDocument20 pagesDialysisSiwani rai100% (1)
- Part B - Health Facility Briefing & Design 55Document15 pagesPart B - Health Facility Briefing & Design 55Mudita PiseNo ratings yet
- Evidence Based TKR RehabDocument24 pagesEvidence Based TKR RehabVardhman Jain IINo ratings yet
- S - "Sakit Ahong Tinahian" As Verbalized byDocument6 pagesS - "Sakit Ahong Tinahian" As Verbalized bylandilinoNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B6 Deficiency As A Cause of Polyneuropathy in POEMS Syndrome Rapid Recovery With Supplementation in Two CasesDocument7 pagesVitamin B6 Deficiency As A Cause of Polyneuropathy in POEMS Syndrome Rapid Recovery With Supplementation in Two CasesYaseen MohamnadNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord InjuryDocument28 pagesSpinal Cord InjuryLouie John AbilaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal MeiristaDocument8 pagesJurnal Meiristameirista deviNo ratings yet
- What It Takes To Be A Doctor?Document11 pagesWhat It Takes To Be A Doctor?Marion YaoNo ratings yet
- M-i-M For DME Matrix-In-A-Matrix Technique For Deep Margin ElevationDocument5 pagesM-i-M For DME Matrix-In-A-Matrix Technique For Deep Margin Elevationfernando vicente100% (1)
- REVISI (Adelita Setiawan 2)Document7 pagesREVISI (Adelita Setiawan 2)Adelita SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Lapsus - Asrarudin - BPHDocument18 pagesLapsus - Asrarudin - BPHAsrarudin HamidNo ratings yet
- Gonadal enDocument60 pagesGonadal enm7md TotiaNo ratings yet
- Essential Hypertension (Also Called Primary Hypertension or Idiopathic Hypertension) IsDocument6 pagesEssential Hypertension (Also Called Primary Hypertension or Idiopathic Hypertension) Isbeenish ashfaqNo ratings yet
- Typhoid PerforationDocument3 pagesTyphoid PerforationSaryia JavedNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Contamination of BlenderizedDocument23 pagesBacterial Contamination of BlenderizedAgnes Alulod BuenaaguaNo ratings yet
- 5 Malado Guillain Barre SyndromeDocument7 pages5 Malado Guillain Barre SyndromeAllan CastroNo ratings yet
- Advanced Trauma Life SupportDocument8 pagesAdvanced Trauma Life SupportazlanajaibNo ratings yet
- Donald L. Renfrew, MD: Spine PainDocument16 pagesDonald L. Renfrew, MD: Spine PainalmiraerickaiNo ratings yet
- DEAR YIN LING 2nd - CompressedDocument282 pagesDEAR YIN LING 2nd - CompressedSunn Ren TeeNo ratings yet