0% found this document useful (0 votes)
176 views4 pagesNursing Care Plan for Anemia Management
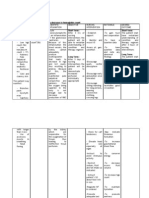
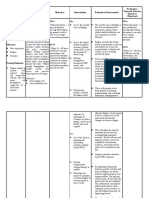
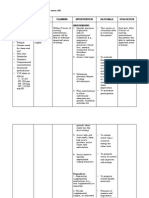
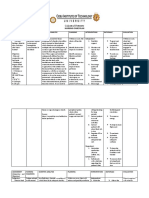
The patient presented with fatigue related to decreased hemoglobin level and diminished oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood secondary to anemia. The nursing interventions included assessing the cause of fatigue, monitoring vital signs and laboratory results, assisting with activities of daily living, administering prescribed medications and packed red cells, and educating the patient on energy conservation techniques. The objectives were for the patient to identify the basis of fatigue, understand energy conservation principles, and participate in recommended treatment within 30 minutes to 1 hour; and to report improved energy and independently perform ADLs within 24-48 hours.
Uploaded by
Jemimah MejiaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
176 views4 pagesNursing Care Plan for Anemia Management
The patient presented with fatigue related to decreased hemoglobin level and diminished oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood secondary to anemia. The nursing interventions included assessing the cause of fatigue, monitoring vital signs and laboratory results, assisting with activities of daily living, administering prescribed medications and packed red cells, and educating the patient on energy conservation techniques. The objectives were for the patient to identify the basis of fatigue, understand energy conservation principles, and participate in recommended treatment within 30 minutes to 1 hour; and to report improved energy and independently perform ADLs within 24-48 hours.
Uploaded by
Jemimah MejiaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd