Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosis Goals Adnd Desired Outcome Nursing Intervention Implementation Evaluation
Uploaded by
Nur Sanaani0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
239 views5 pagesOriginal Title
Nursing Care Plan
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
239 views5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosis Goals Adnd Desired Outcome Nursing Intervention Implementation Evaluation
Uploaded by
Nur SanaaniCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
Nursing Care Plan
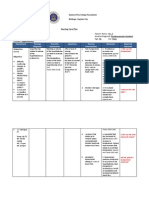
CUES NURSING GOALS ADND NURSING INTERVENTION IMPLEMENTATION EVALUATION
DIAGNOSIS DESIRED
OUTCOME
Objective Cues: Fatigue related The patient’s Hgb Check oximetry; inform physician 02 saturation 92% Monitor hemoglobin,
Inability to maintain to anemia and and Hct level are or less. hematocrit, RBC counts,
usual level of diminished normal. Rationale: This will determine the need for and reticulocyte counts.
supplementary oxygen if 02 saturation 92% or less.
physical activity oxygen-carrying Patient will Check oximetry; inform
such as self-care capacity of the verbalize use of Assess the specific cause of fatigue.
physician 02 saturation
activity as evidence blood. energy conservation Rationale: The specific cause of fatigue is due to 92% or less.
by difficulty in principles. tissue hypoxia from normocytic anemia; Other related Give Health Teaching on
eating independently Patient will medical problems can also compromise activity the medication given,
and drinking water. verbalize reduction tolerance. contraindication,
Drowsy and restless of fatigue, as indication and do’s and
facial expression evidenced by Monitor hemoglobin, hematocrit, RBC counts, and don’ts when given the
reports of increased reticulocyte counts. medication.
Pale lips, lower Rationale: Decreased RBC indexes are associated
extremities and as energy and ability Instruct the client about
with decreased oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood.
well as her lips and to perform desired It is critical to compare serial laboratory values to medications that may
palms. activities. evaluate progression or deterioration in the client and stimulate RBC production
Report of fatigue and Patient will regain to identify changes before they become potentially in the bone marrow and
lack of energy as energy as evidence life-threatening. Elemental iron
evidenced by by independency on Educate energy-conservation techniques. supplement.
performing self- Rationale: Clients and caregivers may need to learn Give Health Teaching on
difficulty in turning
care without skills for delegating task to others, setting priorities, energy-conservation
to sides. and clustering care to use available energy to complete
Low-Hematocrit assistance. techniques.
desired activities. Organization and time management
(34.10) and can help the client conserve energy and reduce Set up proper
Hemoglobin (10.8) fatigue. working
as evidenced by Instruct the client about medications that may conditions
latest CBC count stimulate RBC production in the bone marrow and Avoid
(taken on 12-13- Elemental iron supplement. unnecessary
Rationale: Recombinant human erythropoietin, a motions
2019 7:15 am)
hematological growth factor, increases hemoglobin Avoid rushing
and decreases the need for RBC transfusions.
Vital Signs: Provide supplemental oxygen therapy, as needed. Never hold your
T: 36.5˚c Rationale: Oxygen saturation should be kept at 90% breath during
BP 140/100 mmHg or greater. activity
RR: 24 bpm Anticipate the need for the transfusion of packed Inhale when
PR: 70 bpm RBCs. lifting your
Rationale: Packed RBCs increase oxygen-carrying arms up or
Subjective Cues: capacity of the blood. when extending
. the trunk
The patient expresses her Exhale when
need of increased rest bringing arms
requirements as verbalize down & when
“human daon (surgery) bending the
kinahanglan man mag trunk
pahuway nako. ” Exhale also
(After surgery, I necessarily during any
need to rest…”) physical
exertion (don’t
hold your
breath)
Hygienic measures
(showering rather than
bathe in a tub).
Avoid wearing tight-
fitting or constricting
undergarments made of
non-breathing materials.
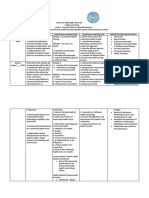
CUES NURSING GOALS ADND NURSING INTERVENTION IMPLEMENTATION EVALUATION
DIAGNOSIS DESIRED
OUTCOME
Objective cues: Risk For Client will have a Assess for local or systemic signs of Assess for local or
A surgical incision Infection reduced risk of infection, such as fever, chills, swelling, systemic signs of
is present in the related to infection as pain, and body malaise. infection, such as fever,
abdomen region. anemia evidenced by an Rationale: Opportunistic infections can chills, swelling, pain,
The patient’s absence of fever, easily develop, especially in and body malaise.
Neutrophils (84%) normal white immunocompromised clients. Monitor WBC count.
and White Blood blood cell count, Monitor WBC count. Instruct the client to
Cells (12.88) are and Rationale: A low white blood cell count report signs and
elevated. implementation of (leukopenia) is a decrease in disease- symptoms of infection
The patient’s preventive fighting cells (leukocytes) in your blood. In immediately.
family is not measures such as general, for adults a count lower than 4,000 Instruct the client to
practicing a proper proper hand white blood cells per microliter of blood is avoid contact with
hand washing washing. considered a low white blood cell count. people with existing
technique. Client will have Instruct the client to report signs and infections.
vital signs within symptoms of infection immediately. Instruct the client to
Vital Signs: the normal limit. Rationale: A simple fever is significant avoid eating raw fruits
The patient’s enough not to pay attention to. A need for and vegetables and
T: 36.5˚c white blood cells antibiotic therapy may be indicated. uncooked meat.
BP 140/100 mmHg and neutrophil Instruct the client to avoid contact with Stress the importance
RR: 24 bpm level are normal. people with existing infections. of daily hygiene,
PR: 70 bpm Rationale: These can be a source of mouth care, wound
infection for the immunocompromised dressing and perineal
Subjective cues: client. Children, 12 years of age or younger care.
are at risk because they can be carriers of Teach the client and
infection, especially upper respiratory visitors the proper hand
infection. washing.
Instruct the client to avoid eating raw fruits
and vegetables and uncooked meat.
Rationale: These food items can harbor
bacteria. A low bacterial diet protects the
client from exposure to pathogens.
Stress the importance of daily hygiene,
mouth care, wound dressing, and perineal
care.
Rationale: These preventive measures help
avoid skin breakdown and lessen the risk of
infection.
Teach the client and visitors the proper
hand washing.
Rationale: Practicing hand hygiene is an
effective way to prevent infections.
Washing hands can prevent the spread of
germs, including those that are resistant to
antibiotics.
You might also like
- 6 Nursing Care Plan 1Document2 pages6 Nursing Care Plan 1Denise Louise PoNo ratings yet
- NCP Imbalanced NutritionDocument7 pagesNCP Imbalanced NutritionNora VarshavskiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleTrysna Ayu SukardiNo ratings yet
- Healthcare - Nursing Care Plan - Excess Fluid VolumeDocument4 pagesHealthcare - Nursing Care Plan - Excess Fluid VolumeBenjamin CañalitaNo ratings yet
- Jake Yvan Dizon Case Study, Chapter 49, Assessment and Management of Patients With Hepatic DisordersDocument8 pagesJake Yvan Dizon Case Study, Chapter 49, Assessment and Management of Patients With Hepatic DisordersJake Yvan DizonNo ratings yet
- Health-Perception-Health-Management PatternDocument3 pagesHealth-Perception-Health-Management PatternBela MillenaNo ratings yet
- Content: Outline Form Only Make A Separate Sheet For The Content. The Health Teaching Plan Should Focus On Home Care For Patients With Mood DisorderDocument4 pagesContent: Outline Form Only Make A Separate Sheet For The Content. The Health Teaching Plan Should Focus On Home Care For Patients With Mood DisorderRaffy Sebastian Seballos100% (1)
- Idoc - Pub Nursing Care Plan For Seizure NCPDocument2 pagesIdoc - Pub Nursing Care Plan For Seizure NCPACERET, IVAN LAURENTINE G.No ratings yet
- NCP PainDocument2 pagesNCP PainApril_Ivy_Raga_3835No ratings yet
- Activity IntoleranceDocument1 pageActivity IntoleranceAndrea Francesca SantosNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluationkristel_nicole18yahoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation: Mechanism of ActionDocument2 pagesAssessment Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation: Mechanism of ActionNicole CalpoturaNo ratings yet
- NCP Blood Glucose Imbalance 4thDocument2 pagesNCP Blood Glucose Imbalance 4thRainier IbarretaNo ratings yet
- RLEFand ECSDocument3 pagesRLEFand ECSPaul JacksonNo ratings yet
- A Client With Cushing's Syndrome: Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageA Client With Cushing's Syndrome: Nursing Care PlanJulius Caesar ColladoNo ratings yet
- Case # 1: Nursing Diagnosis Goal Interventions Expected OutcomeDocument3 pagesCase # 1: Nursing Diagnosis Goal Interventions Expected Outcomejoyrena ochondraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan. HypertensionDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan. HypertensionKiara Shanelle Posadas AbrioNo ratings yet
- Cu 4Document3 pagesCu 4Paul SahagunNo ratings yet
- Thalassemia Nursing Diagnosis and CareDocument1 pageThalassemia Nursing Diagnosis and CareHannah Clarisse Monge IgniNo ratings yet
- Actual NCPDocument2 pagesActual NCPbaki0146No ratings yet
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPmftaganasNo ratings yet
- Propranolol, Prophylactic Warfarin, Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH), Furosemide, AntibioticsDocument8 pagesPropranolol, Prophylactic Warfarin, Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH), Furosemide, AntibioticsArlyn MarcelinoNo ratings yet
- Case CHFDocument10 pagesCase CHFAgnes Erlita Distriani Patade50% (2)
- Abbreviations For Nursing StudentsDocument7 pagesAbbreviations For Nursing StudentssodiwoNo ratings yet
- NCP - Activity Intolerance & Excess Fluid VolumeDocument2 pagesNCP - Activity Intolerance & Excess Fluid VolumeCindy MariscotesNo ratings yet
- NCP Sa Sinus Tachycardia FinalDocument13 pagesNCP Sa Sinus Tachycardia FinalMYKRISTIE JHO MENDEZNo ratings yet
- Papillary Thyroid Ca: Group. 1 B Grand CaseDocument16 pagesPapillary Thyroid Ca: Group. 1 B Grand CaseAdora Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- NCP Active SeizureDocument4 pagesNCP Active SeizureAngelica CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Hildegard Peplau's Interpersonal Relations 101Document85 pagesHildegard Peplau's Interpersonal Relations 101Ynaffit Alteza Untal100% (1)
- Medication ThalassemiaDocument3 pagesMedication ThalassemiaDivya ToppoNo ratings yet
- Internet Tools For Advanced Nursing PracticeDocument9 pagesInternet Tools For Advanced Nursing Practicesprescott01No ratings yet
- Clinical Objectives of PHN 5 SmesterDocument3 pagesClinical Objectives of PHN 5 SmesterHafiz Muhammad Awais QadriNo ratings yet
- Course in The WardDocument1 pageCourse in The WardGeevee Naganag VentulaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Group 4-Open Wound Head Injury After Debris FallDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Group 4-Open Wound Head Injury After Debris FallNicole Villanueva, BSN - Level 3ANo ratings yet
- Ngo 2bsn1 Ncm109 Prelim NCPDocument7 pagesNgo 2bsn1 Ncm109 Prelim NCPAMIEL SIMON NGONo ratings yet
- Nursing of The Childbearing FamilyDocument3 pagesNursing of The Childbearing Familyroby sorianoNo ratings yet
- NCP CvaDocument4 pagesNCP CvaMariquita BuenafeNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationMonica RamboyongNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk For InjuryDocument2 pagesNCP Risk For Injurycristina_galang_2No ratings yet
- Valdez Reflective-Questions PDFDocument3 pagesValdez Reflective-Questions PDFDexel Lorren ValdezNo ratings yet
- A.) 62 Yo Male, S/P (Status Post) Exploratory Laparotomy Secondary Intestinal ObstructionDocument4 pagesA.) 62 Yo Male, S/P (Status Post) Exploratory Laparotomy Secondary Intestinal ObstructionKate Aenyle AgsoyNo ratings yet
- Diabetes InsipidusDocument48 pagesDiabetes InsipidusAhmed Fraz MamoonNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objective Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Short Term: Short TermDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objective Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Short Term: Short TermGensen Cu RoxasNo ratings yet
- NCP - Hygiene and ComfortDocument3 pagesNCP - Hygiene and ComfortJaella EpeNo ratings yet
- NCP PpwardDocument15 pagesNCP PpwardKarl Vincent Soso100% (1)
- Laryngeal Cancer Concept MapDocument1 pageLaryngeal Cancer Concept MapTessa Claire JaranowskiNo ratings yet
- NCP Fluid Vol Excess AgnDocument3 pagesNCP Fluid Vol Excess AgnArbie JacintoNo ratings yet
- Scribd 020922 Case Study-Oncology A&kDocument2 pagesScribd 020922 Case Study-Oncology A&kKellie DNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument3 pagesHypertensionkarl de guzmanNo ratings yet
- Management For Acute Lymphocytic LeukemiaDocument3 pagesManagement For Acute Lymphocytic LeukemiamarivohNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument10 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyChris CHris ChRis100% (1)
- Example of Drug StudyDocument2 pagesExample of Drug Studydonna mae junioNo ratings yet
- Case Studies On Major Concepts: NeurologicalDocument37 pagesCase Studies On Major Concepts: NeurologicalJek Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Case Report On Bipolar Affective Disorder: Mania With Psychotic SymptomsDocument2 pagesCase Report On Bipolar Affective Disorder: Mania With Psychotic SymptomskslhfwoiebvNo ratings yet
- Premenstrual Dysphoric DisorderDocument11 pagesPremenstrual Dysphoric Disorderapi-3764215No ratings yet
- Anemia Nursing Care PlanDocument21 pagesAnemia Nursing Care PlanbhavanaNo ratings yet
- NCP AnemiaDocument3 pagesNCP AnemiaJadeNo ratings yet
- NCP AnemiaDocument2 pagesNCP AnemiaAriaNo ratings yet
- NCP A Utoimmune H Emolytic A Nemia: NIC-Health System GuidanceDocument7 pagesNCP A Utoimmune H Emolytic A Nemia: NIC-Health System GuidanceEmmeline Dycangchon-GarmaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Subjective: IndependentDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Subjective: Independentmark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- OB Nursing NotesDocument101 pagesOB Nursing NotesNur Sanaani100% (1)
- Code of Ethics For Filipino NursesDocument22 pagesCode of Ethics For Filipino NursesNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Answer Key.Document4 pagesAnswer Key.Nur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Notes THE SETTINGDocument2 pagesNotes THE SETTINGNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Code of Ethics For Filipino NursesDocument22 pagesCode of Ethics For Filipino NursesNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- PediaDocument9 pagesPediaNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Nursing Research - InitialDocument25 pagesNursing Research - InitialNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease NursingDocument22 pagesCommunicable Disease NursingNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Management Quiz 1Document10 pagesManagement Quiz 1Reema100% (1)
- Management Quiz 1Document10 pagesManagement Quiz 1Reema100% (1)
- Management Quiz 1Document10 pagesManagement Quiz 1Reema100% (1)
- Module Content CHN113Document6 pagesModule Content CHN113Nur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Answer Key.Document4 pagesAnswer Key.Nur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For SCIDocument10 pagesNursing Care Plan For SCINur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Course Title Course Code Course Description Prerequisites Course Credit Placement Program OutcomeDocument10 pagesCourse Title Course Code Course Description Prerequisites Course Credit Placement Program OutcomeNur Sanaani100% (1)
- Answer Key.Document4 pagesAnswer Key.Nur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- 3 Reflection Paper in One WordDocument3 pages3 Reflection Paper in One WordNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- 3 Reflection Paper in One WordDocument3 pages3 Reflection Paper in One WordNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Rationale: Answer: C. If A Patient HasDocument12 pagesRationale: Answer: C. If A Patient HasNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Neurologic System Disorders: Ateneo de Zamboanga UniversityDocument2 pagesNeurologic System Disorders: Ateneo de Zamboanga UniversityNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- A-Module 2 - EVP, CommunicationRecords Mgt.Document7 pagesA-Module 2 - EVP, CommunicationRecords Mgt.Nur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- 3 Reflection Paper in One WordDocument3 pages3 Reflection Paper in One WordNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Date/Week Learning Objectives Asynchronous Learning Topic Synchronous Learning TopicDocument6 pagesDate/Week Learning Objectives Asynchronous Learning Topic Synchronous Learning TopicNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- MultisystemDocument19 pagesMultisystemNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Nso Topics: INSTRUCTION: Using The Format Provided, Please Report On ThursdayDocument1 pageNso Topics: INSTRUCTION: Using The Format Provided, Please Report On ThursdayNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Sanaani Nso AngioplastyDocument14 pagesSanaani Nso AngioplastyNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Emergency NursingDocument56 pagesEmergency NursingNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Nephrons (Functional Unit)Document44 pagesNephrons (Functional Unit)Nur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument121 pagesUntitled DocumentNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- RRL Mental Health Adjustment and Perceived Academic Performance of Senior Highschool StudentsDocument19 pagesRRL Mental Health Adjustment and Perceived Academic Performance of Senior Highschool StudentsNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- NCLEX Questions and RationaleDocument19 pagesNCLEX Questions and RationaleLarissa SabsayNo ratings yet
- Nutrition - Nursing Test QuestionsDocument9 pagesNutrition - Nursing Test QuestionsRNStudent1100% (1)
- CiullahemaDocument60 pagesCiullahemaMariel AbatayoNo ratings yet
- Pernicious AnemiaDocument24 pagesPernicious AnemiaArthadian De PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Very Important SMLE NotesDocument38 pagesVery Important SMLE NotesHassan Al SinanNo ratings yet
- Journal of Internal Medicine - 2019 - Cappellini - Iron Deficiency Anaemia RevisitedDocument18 pagesJournal of Internal Medicine - 2019 - Cappellini - Iron Deficiency Anaemia RevisitedRaúl Joaquín Espinoza del CarmemNo ratings yet
- Case Base Discussion: Advisor: Dr. H. M. Saugi Abduh, SP - PD, KKV, FINASIM By: Andini Rizky Budiati (30101407134)Document38 pagesCase Base Discussion: Advisor: Dr. H. M. Saugi Abduh, SP - PD, KKV, FINASIM By: Andini Rizky Budiati (30101407134)Andini RizkyNo ratings yet
- Case Report - Anemia Ec Cervical Cancer Stages 2bDocument71 pagesCase Report - Anemia Ec Cervical Cancer Stages 2bAnna ListianaNo ratings yet
- Fileshare - Ro - The Complete Hematology GuideDocument113 pagesFileshare - Ro - The Complete Hematology Guidemaurice_ejw100% (2)
- Done2019!12!12 Answered EmreeDocument36 pagesDone2019!12!12 Answered EmreeDependoQueen-independentNo ratings yet
- 7anemia Caused by Defects of DNA MetabolismDocument30 pages7anemia Caused by Defects of DNA MetabolismanonacadsNo ratings yet
- Nutritional AnemiaDocument20 pagesNutritional AnemianadNo ratings yet
- Akshay A Patra CSR Proposal 202223Document25 pagesAkshay A Patra CSR Proposal 202223suresh kumarNo ratings yet
- Definition: Anemic Syndrome:: Semiotics of Basic Diseases of The Blood SystemDocument4 pagesDefinition: Anemic Syndrome:: Semiotics of Basic Diseases of The Blood SystemSagar KhairwalNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation of AnemiaDocument71 pagesCase Presentation of AnemiaJessica Esther Canlas100% (2)
- Anemia in PregnancyDocument4 pagesAnemia in PregnancyDheyaa A. SabahNo ratings yet
- Sickle Cell PresentationDocument11 pagesSickle Cell PresentationibtiNo ratings yet
- Sysmex XT 2000iDocument2 pagesSysmex XT 2000iMunawwar AweNo ratings yet
- Lab Normal Value S&Sof S&Sof : Loma Linda University School of Nursing Accepted Lab Values Adapted From KaplanDocument3 pagesLab Normal Value S&Sof S&Sof : Loma Linda University School of Nursing Accepted Lab Values Adapted From KaplanGiacen100% (3)
- 4-Morphology Based Detection of Abnormal Red Blood Cells in Peripheral Blood Smear ImagesDocument2 pages4-Morphology Based Detection of Abnormal Red Blood Cells in Peripheral Blood Smear ImagesAli M. RiyathNo ratings yet
- The Micronutrients & Water: Roxana Dev Omar DevDocument36 pagesThe Micronutrients & Water: Roxana Dev Omar Deverwan berhanNo ratings yet
- DIBDDocument11 pagesDIBDKabirNo ratings yet
- CH 044 Megaloblastic AnemiaDocument6 pagesCH 044 Megaloblastic AnemiaGshshNo ratings yet
- National Health ProgramsDocument19 pagesNational Health ProgramsSANANo ratings yet
- MSN I 12.6.2020 FN Unit V Megaloblastic Anemia & Aplastic AnemiaDocument44 pagesMSN I 12.6.2020 FN Unit V Megaloblastic Anemia & Aplastic AnemiaHariniNo ratings yet
- AnemiaDocument13 pagesAnemiaAnnisa HarumNo ratings yet
- SYMBBS ALL SUBJECTS IMPS (Hngu Mbbs Students Union)Document77 pagesSYMBBS ALL SUBJECTS IMPS (Hngu Mbbs Students Union)afijdnldoNo ratings yet
- Anemia NCPDocument5 pagesAnemia NCPMel Christian Baldoz100% (2)
- Oet 2.0 Listening Task 1: British Academy British AcademyDocument6 pagesOet 2.0 Listening Task 1: British Academy British AcademyKrishna Ramas-Maddi0% (1)
- USMLE STEP 1 CHECKLIST @lifeinwhitecoatDocument23 pagesUSMLE STEP 1 CHECKLIST @lifeinwhitecoatGlorivy E. Mora Gonzalez100% (3)
- Clean: Overcoming Addiction and Ending America’s Greatest TragedyFrom EverandClean: Overcoming Addiction and Ending America’s Greatest TragedyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (18)
- The Bodies of Others: The New Authoritarians, COVID-19 and The War Against the HumanFrom EverandThe Bodies of Others: The New Authoritarians, COVID-19 and The War Against the HumanRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (12)
- The Wisdom of Plagues: Lessons from 25 Years of Covering PandemicsFrom EverandThe Wisdom of Plagues: Lessons from 25 Years of Covering PandemicsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- Epic Measures: One Doctor. Seven Billion Patients.From EverandEpic Measures: One Doctor. Seven Billion Patients.Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (13)
- Deaths of Despair and the Future of CapitalismFrom EverandDeaths of Despair and the Future of CapitalismRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (30)
- Uncontrolled Spread: Why COVID-19 Crushed Us and How We Can Defeat the Next PandemicFrom EverandUncontrolled Spread: Why COVID-19 Crushed Us and How We Can Defeat the Next PandemicNo ratings yet
- Summary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)
- Do You Believe in Magic?: The Sense and Nonsense of Alternative MedicineFrom EverandDo You Believe in Magic?: The Sense and Nonsense of Alternative MedicineNo ratings yet
- The Hair Color Mix Book: More Than 150 Recipes for Salon-Perfect Color at HomeFrom EverandThe Hair Color Mix Book: More Than 150 Recipes for Salon-Perfect Color at HomeRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (7)
- The Atlas of Disease: Mapping Deadly Epidemics and Contagion from the Plague to the CoronavirusFrom EverandThe Atlas of Disease: Mapping Deadly Epidemics and Contagion from the Plague to the CoronavirusRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- The Price of Health: The Modern Pharmaceutical Industry and the Betrayal of a History of CareFrom EverandThe Price of Health: The Modern Pharmaceutical Industry and the Betrayal of a History of CareRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Nutritional and Therapeutic Interventions for Diabetes and Metabolic SyndromeFrom EverandNutritional and Therapeutic Interventions for Diabetes and Metabolic SyndromeNo ratings yet
- Epidemics and Society: From the Black Death to the PresentFrom EverandEpidemics and Society: From the Black Death to the PresentRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- The Invisible Rainbow: A History of Electricity and LifeFrom EverandThe Invisible Rainbow: A History of Electricity and LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Getting Pregnant Naturally: Healthy Choices To Boost Your Chances Of Conceiving Without Fertility DrugsFrom EverandGetting Pregnant Naturally: Healthy Choices To Boost Your Chances Of Conceiving Without Fertility DrugsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- The HPV Vaccine On Trial: Seeking Justice For A Generation BetrayedFrom EverandThe HPV Vaccine On Trial: Seeking Justice For A Generation BetrayedRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- Development of Questionnaires for Quantitative Medical ResearchFrom EverandDevelopment of Questionnaires for Quantitative Medical ResearchNo ratings yet
- A Good Time to Be Born: How Science and Public Health Gave Children a FutureFrom EverandA Good Time to Be Born: How Science and Public Health Gave Children a FutureRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mercury, Mining, and Empire: The Human and Ecological Cost of Colonial Silver Mining in the AndesFrom EverandMercury, Mining, and Empire: The Human and Ecological Cost of Colonial Silver Mining in the AndesNo ratings yet
- The Wuhan Cover-Up: And the Terrifying Bioweapons Arms RaceFrom EverandThe Wuhan Cover-Up: And the Terrifying Bioweapons Arms RaceNo ratings yet
- Coronary: A True Story of Medicine Gone AwryFrom EverandCoronary: A True Story of Medicine Gone AwryRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- The Varicose Veins Mastery Bible: Your Blueprint for Complete Varicose Veins ManagementFrom EverandThe Varicose Veins Mastery Bible: Your Blueprint for Complete Varicose Veins ManagementNo ratings yet
- Public Health and the Environment - Second Edition: Uncovering Key Social, Ecological, and Economic ConnectionsFrom EverandPublic Health and the Environment - Second Edition: Uncovering Key Social, Ecological, and Economic ConnectionsNo ratings yet
- Inflamed: Deep Medicine and the Anatomy of InjusticeFrom EverandInflamed: Deep Medicine and the Anatomy of InjusticeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (12)