Professional Documents
Culture Documents
He Patient's Level of Anxiety Will Significantl y Drop
Uploaded by
Mia GarciaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
He Patient's Level of Anxiety Will Significantl y Drop
Uploaded by
Mia GarciaCopyright:
Available Formats
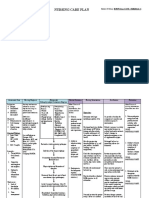
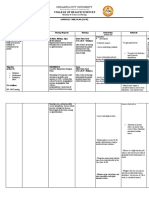
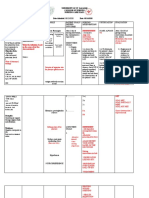
NURSING EVALUATION
ASSESSMENT/ BACKGROUND
NURSING DIAGNOSIS GOALS AND OBJECTIVES INTERVENTIONS
CUES KNOWLEDGE
AND RATIONALE
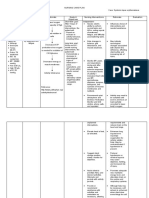
SUBJECTIVE: Fatigue related to decreased Fatigue is one of the most
-39-year-old hemoglobin and hematocrit common symptoms of iron NOC: Endurance NIC: Energy Enhancement
-Post op from count secondary to anemia deficiency anemia. It occurs as a Partially Goal met:
cesarean section result of your body’s inability to The patient reports
- 36+2 weeks twin make sufficient amounts of Goal: The patient will report improved sense of energy
intrauterine hemoglobin, a protein that improve sense of energy and and exhibited improved
pregnancy carries oxygen to tissues exhibit improve symptoms of symptoms of fatigue as
throughout your body. fatigue as evidenced by increase evidenced by hgb of 13
OBJECTIVE: counts of hgb and hct. g/dl and hct of 38 counts.
-BP 100/80 In mild cases of iron deficiency
he
-HR 102 bpm anemia, the client is
-RR 24 bpm asymptomatic; in more severe -
-FHR B1=110; B2 cases, assessment reveals the Short-term Objectives:
After an hour of nursing
patient’s
90 general manifestations of anemia
-HGB 6g/dl including fatigue; headache; interventions, the patient:
-HCT 32 dyspnea; palpitations; pallor in ---
level of
-Ruptured the face, palm of the hand, nail
Membrane bed and mucous membranes of Establish rapport and Verbalized 2
understandings of
- Emergency low the mouth and conjunctiva; therapeutic communication. causative factors for
anxiety
transverse angular stomatitis, glossitis, and (To gain the trust of the pt. fatigue:
cesarean section cheilitis; and brittle nails. involved.) - Lifestyle factors
(e.g., Lack of
will
(Medical-Surgical Nursing: Assess for possible reasons for sleep, , Not eating
Clinical Management for Positive fatigue. (Fatigue can be nutritious diet and
outcomes by Joyce M. Black and caused by physical, mental, or etc.)
Jane Hokanson Hawks, 8th edition)
significantl emotional stressors. Knowing
the exact reason and
contributing factors helps in
- Physical Health
Conditions
(Anemia)
y the planning of care.)
Assess the nutritional status.
drop, (Adequate calorie intake from
good sources can affect
accompani
someone’s level of fatigue.
Inadequate food intake can
lead to deficiencies that can
ed by cause fatigue. Deficient
vitamins and iron can lead to
feeling tired.)
her Evaluate the patient’s sleeping
pattern, such as Difficulty
verbalizati falling asleep and Difficulty
staying asleep. (Inadequate
on of
amounts of sleep can lead to
fatigue.)
Consider the chief complaint
such and review the past medical
history. (The patient’s current
improvem condition may contribute to
feeling tired. Comorbidities
and other illnesses could also
ents and play a role in the patient’s
symptoms of lack of energy.)
demonstrat ---
Provide a quiet environment. Identified 3 ways to
ion of (Additional stressors can
intensify the pt. perception
and tolerance of anxiety)
relieve fatigue.
- Rule out health
effective
problems
Allow the patient to express - Eat a balanced
feelings about fatigue. (The diet or Prioritize
relaxation patient’s point of view can iron-rich foods
give valuable insight into his and Stay Hydrated
or her awareness and - Get enough sleep
motivation to improve fatigue
techniques
symptoms.)
a Assist the patient in
nd demonstration of effective developing fatigue-reducing
relaxation techniques skills. (Using fatigue-
reduction strategies enhances
patient's sense of personal
mastery and confidence.)
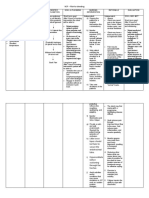
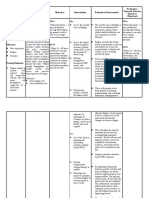
Short-term Objectives: Collaborate with the attending
After an hour of nursing physician about optimizing
interventions, the patient will be medications. (Certain
able to: medications such as sleep
medications, sedatives, pain
Verbalize 3 understandings medications, and others can
of causative factors for contribute to fatigue.
fatigue: Adjustments in frequency and
- Lifestyle factors (e.g.,. dosing could improve
Lack of sleep, Physical symptoms of fatigue.)
exertion, Not eating
nutritious diet and etc.)
- Physical Health Long-term Objectives:
Conditions (e.g.,. After 3 days of nursing
Anemia, Cancer, interventions, the patient:
Diabetes, Chronic
fatigue syndrome and
etc.) ---
- Mental health issues
(e.g.,. anxiety, depression Monitor patient’s vital signs. Exhibited normal vital
and seasonal affective (To detect any changes or signs as evidenced by
disorder.) deterioration on vital signs.) no hypotension; no
tachycardia; no
Teach family members and hypoxemia.
caregivers signs of
overexertion. (Increased heart
rate, Increased blood pressure,
increased respiratory rate,
increased oxygen demand)
(Regular checks of vital signs
and an overall observation of
the patient’s general
appearance will reveal their
activity level.)
---
Observe physiological
reaction to activities such as Reported increased
any alterations in BP, energy.
respiratory rate, or heart rate.
(Tolerance varies
significantly, depending on the
phase of the disease
progression, nutrition
condition, fluid balance, and
quantity or sort of
opportunistic diseases that
patient has been subjected to.
Identify 4 ways to relieve ---
fatigue. Displayed an
- Rule out health problems Review the patient’s lab acceptable range of
- Eat a balanced diet or values. (Hemoglobin, laboratory values of
Prioritize iron-rich foods hematocrit, Blood glucose and Hgb and Hct.
and Stay Hydrated etc.) (Anemia, low blood
- Get enough sleep sugar, and other physiological
- Manage stress (e.g., deep changes due to underlying
breathing techniques,
disease can cause fatigue.)
meditation)
Long-term Objectives:
After 3 days of nursing
interventions, the patient will be
able to:
Exhibit normal vital signs.
Reports increased energy.
Display an acceptable range
of laboratory values of Hgb
and Hct.
You might also like
- How A Diagnosis of Asperger's Transformed A Marriage: The Journal of Best Practices by David FinchDocument24 pagesHow A Diagnosis of Asperger's Transformed A Marriage: The Journal of Best Practices by David FinchSimon and Schuster100% (10)
- Nursing Care Plan For HypertensionDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For HypertensionKathleen Dimacali100% (2)
- NCP. Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument5 pagesNCP. Decreased Cardiac OutputJillian AmponinNo ratings yet
- NCP Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument3 pagesNCP Rheumatoid ArthritisJanieross Lamboso100% (1)
- Decreased Cardiac Output EclampsiaDocument6 pagesDecreased Cardiac Output EclampsiaNursesLabs.com100% (7)
- NCP FatigueDocument3 pagesNCP FatigueKateLayaog100% (2)
- "Mayroong Namuong Dugo Sa Utak Niya Kaya Hindi Maayos Ang Daloy NG Dugo Rito" As Verbalized by The Patient'sDocument4 pages"Mayroong Namuong Dugo Sa Utak Niya Kaya Hindi Maayos Ang Daloy NG Dugo Rito" As Verbalized by The Patient'sAllisson BeckersNo ratings yet
- Fatigue NCPDocument2 pagesFatigue NCPclydell joyce masiar100% (6)
- KISSD: Ketamine Intramuscular Stepped System for Depression: The Holy Grail of Depression Is Our 100 Days of Freedom from DepressionFrom EverandKISSD: Ketamine Intramuscular Stepped System for Depression: The Holy Grail of Depression Is Our 100 Days of Freedom from DepressionNo ratings yet
- Part III Internal Medicine Examination AnswersDocument91 pagesPart III Internal Medicine Examination AnswersFırat GüllüNo ratings yet
- CCU NCP Week 2Document4 pagesCCU NCP Week 2April Kate BanagodosNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment: Partially Met AsDocument1 pagePhysical Assessment: Partially Met AsPaolo UyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - Activity IntoleranceDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan - Activity IntoleranceChezka Orton Swift Bolintiam100% (3)
- Name: Olusegun-Obiwusi, Olufunke DATE: - : Subjective: DXDocument4 pagesName: Olusegun-Obiwusi, Olufunke DATE: - : Subjective: DXJhasmine MocnanganNo ratings yet
- Name: Olusegun-Obiwusi, Olufunke DATE: - : Subjective: DXDocument4 pagesName: Olusegun-Obiwusi, Olufunke DATE: - : Subjective: DXJemimah MejiaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Cues Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcome Nursing Intervention Justification EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Cues Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcome Nursing Intervention Justification EvaluationKristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- Name: Olusegun-Obiwusi, Olufunke DATE: - : Subjective: DXDocument4 pagesName: Olusegun-Obiwusi, Olufunke DATE: - : Subjective: DXGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- Nueva Ecija University of Science and TechnologyDocument7 pagesNueva Ecija University of Science and TechnologyKym RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Medina, Joanna BN3C - NCP FormatDocument7 pagesMedina, Joanna BN3C - NCP FormatJOANNA MARIE MEDINANo ratings yet
- NCP - Activity IntoleranceDocument4 pagesNCP - Activity IntoleranceRoyce Vincent TizonNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionDocument4 pagesIneffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionLeticia ElricNo ratings yet
- Subjective: " " Sto: Diagnostics: Sto:Goal MET: VitalDocument3 pagesSubjective: " " Sto: Diagnostics: Sto:Goal MET: VitalKarl KiwisNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related To Interruption of Blood Flow Secondary To Hemorrhage As Evidenced by GCS of 7Document2 pagesIneffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related To Interruption of Blood Flow Secondary To Hemorrhage As Evidenced by GCS of 7dana100% (4)
- NCP FinDocument4 pagesNCP FinDivine LavaNo ratings yet
- NCP SGH DianaDocument2 pagesNCP SGH Dianadaniloabautista44No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Interventions Rationale Evaluation Sto: Diagnostic: StoDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Interventions Rationale Evaluation Sto: Diagnostic: StoNelly CruzNo ratings yet
- Name: DATE: - Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesName: DATE: - Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationRJ JOHNNo ratings yet
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument2 pagesDecreased Cardiac OutputHope TomeNo ratings yet
- Copy of NCP Format)Document4 pagesCopy of NCP Format)shai raNo ratings yet
- NCP NeuroDocument20 pagesNCP NeuroNica Gaborne Navarro100% (3)
- NCP SGHDocument2 pagesNCP SGHdaniloabautista44No ratings yet
- Data Nursing Diagnos IS Scientific Backgrou ND Goal/Objective Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesData Nursing Diagnos IS Scientific Backgrou ND Goal/Objective Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDienizs LabiniNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan About ANEMIA by Payongayong, Chielee Anne A.Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan About ANEMIA by Payongayong, Chielee Anne A.Chielee Anne PayongayongNo ratings yet
- NCP Mugar Icu3 Batch2 GRP3Document2 pagesNCP Mugar Icu3 Batch2 GRP3FRANZI ALYANNA MUGARNo ratings yet
- NCP Updated Aug312022Document2 pagesNCP Updated Aug312022Mariella BadongenNo ratings yet
- Kami Kagina, Gulpiyada Lang Siya Nadulaan Kusog Kag Gapukol Iya Hambalanon, Kag Nagakiwi Iya Nga Itsura." As VerbalizedDocument4 pagesKami Kagina, Gulpiyada Lang Siya Nadulaan Kusog Kag Gapukol Iya Hambalanon, Kag Nagakiwi Iya Nga Itsura." As VerbalizedKoleen Lhyte T. UYNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN Grand CaseDocument6 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN Grand CaseDaniel Andre S. SomorayNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Artery Blockage May BeDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Artery Blockage May BeDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Group 9Document8 pagesNursing Care Plan Group 9Joan Antonate MonterolaNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanPrince Juzzel Banag100% (1)
- NCP 2 MiDocument16 pagesNCP 2 MiWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- DLW NCPDocument8 pagesDLW NCPNurse NotesNo ratings yet
- Revised NCP 1-3Document6 pagesRevised NCP 1-3MarcieNo ratings yet
- PathophysiologyDocument1 pagePathophysiologyArt Lemuel LotereñaNo ratings yet
- Metoprolol Drug StudyDocument4 pagesMetoprolol Drug StudyCrisha Ann Billones BacutaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Cues Nursing Diagnosis (Rationale) Pathophysiologic/Schematic Diagram Desired Outcome Nursing Intervention Justification EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Cues Nursing Diagnosis (Rationale) Pathophysiologic/Schematic Diagram Desired Outcome Nursing Intervention Justification EvaluationTrishaNo ratings yet
- College of Health Sciences: Urdaneta City UniversityDocument7 pagesCollege of Health Sciences: Urdaneta City UniversityMarie joy CortezNo ratings yet
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument5 pagesDecreased Cardiac Outputshuang81No ratings yet
- Sign and SymptomsDocument5 pagesSign and Symptomsmadras meditationNo ratings yet
- Case Study Myocardial InfarctionDocument23 pagesCase Study Myocardial InfarctionJester GalayNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Age: 60 Years OldDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan Age: 60 Years OldLouise GudmalinNo ratings yet
- NCP LupusDocument5 pagesNCP LupusMarwin OditaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationNelly CruzNo ratings yet
- Final Drug Study MeropenemalbendazoleDocument10 pagesFinal Drug Study MeropenemalbendazoleLuis WashingtonNo ratings yet
- Paloayen Mod12 NCPDocument4 pagesPaloayen Mod12 NCPAyen PaloNo ratings yet
- Nanda NCP BasedDocument14 pagesNanda NCP Baseddeliejoyce100% (1)
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals & Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals & Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationMiggy SikatNo ratings yet
- FATIGUEDocument4 pagesFATIGUEArian May MarcosNo ratings yet
- Related To Vomiting As Evidence by Muscle Weakness and FatigueDocument3 pagesRelated To Vomiting As Evidence by Muscle Weakness and FatiguejuiceNo ratings yet
- NCP - Tissue Perfusion (Cerebral)Document2 pagesNCP - Tissue Perfusion (Cerebral)moodlayers50% (6)
- Okir A DatuDocument6 pagesOkir A DatuRonel FillomenaNo ratings yet
- Health and H BehaviorDocument69 pagesHealth and H BehaviorDawud AsnakewNo ratings yet
- Ulcerative ColitisDocument30 pagesUlcerative ColitisAndika SulistianNo ratings yet
- Journal Reading (Heat Stroke)Document24 pagesJournal Reading (Heat Stroke)Adinda WidyantidewiNo ratings yet
- Toxoplasma GondiiDocument7 pagesToxoplasma GondiiDedy SavradinataNo ratings yet
- 756 1754 1 PBDocument2 pages756 1754 1 PBmiayt2006No ratings yet
- Let's Talk Game CardsDocument4 pagesLet's Talk Game CardssycagurlNo ratings yet
- Natiomal Plan of ActionDocument36 pagesNatiomal Plan of Actiontendai precious nyamadzaoNo ratings yet
- Jadwal Pir MalangDocument4 pagesJadwal Pir MalangAbraham BayuNo ratings yet
- Liver CancerDocument16 pagesLiver CancerMark James MelendresNo ratings yet
- Clinical Presentation of Abdominal TuberculosisDocument4 pagesClinical Presentation of Abdominal TuberculosisRizky AmaliahNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan NutritionDocument7 pagesLesson Plan NutritionPraveenNo ratings yet
- Using Master Tung's Gallbladder Points For Diseases of The Head and NeckDocument2 pagesUsing Master Tung's Gallbladder Points For Diseases of The Head and NeckTrần Hồ Thạnh Phú100% (1)
- LVS Chronic Pain WsDocument49 pagesLVS Chronic Pain WsdtncorreoNo ratings yet
- 2.6. Curved Mirrors Calculations & Applications LessonDocument32 pages2.6. Curved Mirrors Calculations & Applications Lesson6h4gxcf7jbNo ratings yet
- Neurology II 6.04 Traumatic Brain Injury Dr. TanDocument10 pagesNeurology II 6.04 Traumatic Brain Injury Dr. TanAbi IgsNo ratings yet
- Urinary Retention PostpartumDocument5 pagesUrinary Retention PostpartumpaswordnyalupaNo ratings yet
- Antihypnotics and AnxiolyticsDocument12 pagesAntihypnotics and AnxiolyticsSabreena NordinNo ratings yet
- H1 User Manual (H1E02G10)Document69 pagesH1 User Manual (H1E02G10)Hồng Vân PhạmNo ratings yet
- The Human Heart: © 2014 Pearson Education, IncDocument45 pagesThe Human Heart: © 2014 Pearson Education, IncSafee HaiderNo ratings yet
- SIgE Conjugate 02.17Document4 pagesSIgE Conjugate 02.17Clodagh WhelanNo ratings yet
- Patofisiologi Kanker RahimDocument98 pagesPatofisiologi Kanker RahimOjo Nesu100% (1)
- Physiology Paper 1 Question BankDocument8 pagesPhysiology Paper 1 Question BankVeshalinee100% (1)
- Complication of Enteral Nutrition PDFDocument3 pagesComplication of Enteral Nutrition PDFIndra WijayaNo ratings yet
- Management of PPHDocument24 pagesManagement of PPHMutabazi SharifNo ratings yet
- Background: NIA Adverse Event and Serious Adverse Event GuidelinesDocument10 pagesBackground: NIA Adverse Event and Serious Adverse Event GuidelinesAndreia MonteiroNo ratings yet
- Journal Neuropediatri PDFDocument8 pagesJournal Neuropediatri PDFHalimah PramudiyantiNo ratings yet
- Giannopoulos PC - AlDocument54 pagesGiannopoulos PC - AlNikosNo ratings yet