Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anchor Bolt Design For Shear and Tension PDF
Uploaded by
k.m.ariful islamOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anchor Bolt Design For Shear and Tension PDF
Uploaded by
k.m.ariful islamCopyright:
Available Formats
Anchor Bolt Design for Shear and Tension
UMESH J. KHAROD
When column base plates are subject to both uplift and very
large shear loads, two independent systems are normally used
to resist tension in the anchor bolts and shear at the level of
the base plate: (1) the length of embedment and the diameter
of the anchor bolts are determined on the basis of uplift
tension and (2) a shear key is welded to the column base
plate to resist shear.
If very large shear loads do not accompany the uplift, the
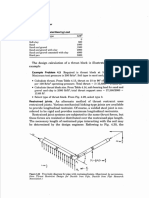
anchor bolts can be designed to resist both shear and tension, Figure 2
without using a shear key, as in the following example.
EXAMPLE Solution:
Given: Design anchor bolts for a column base plate for an Shear:
uplift of 100 kips, and a shear load of 40 kips due to See Fig. 2.
wind or seismic loading. Use 4 anchor bolts. (See
Fig. 1.) f'c = 3.0 ksi
Fp = 0.25f'c = 0.75 ksi
ls = 12D (assumed)
Ac = (lsD) = 12D2
Concrete resistance for shear:
S = ½FpAc = 6FpD2 = (6 × 0.75)D2
= 4.5D2
1/ 2 1/ 2
S 10
∴D = = = 49.1 in.
4.5 4.5
Use D = 2 in.
Figure 1 ls = 12D = 24 in.
Tension:
Design Data: Load per anchor bolt is as follows: For plain bars, u = 4.75 × 10−3/2(f'c)1/2/D
For D = 2:
100/4 = 25 kips u = 4.75 × 10−3/2 (3.0)1/2/2 = 0.13 ksi
∴use u = 0.13 ksi
40/4 = 10 kips T = u(π D) lt
T 25
lt = = = 30.61 in.
u(πD) 0.13(π × 2.0)
Umesh J. Kharod is Project Engineer, MikroPul Corp., Summit, New l = (ls + lt) = (24 + 30.61) = 54.61 in.
Jersey. Use l = 4 ft-6 in.
22
ENGINEERING JOURNAL / AMERICAN INSTITUTE OF STEEL CONSTRUCTION
Check Bolt Stresses:
(a) Ag = π D4 = 3.141in.2
2
At = 0.75Ag = 2.356 in.2 (AISC Spec. Sect. 1.5.2.1,
with n = 7)
Figure 3
For A307 bolts, Fy = 33 ksi; Fv = 0.3Fy = 10 ksi
Fnfnb = Ft = 0.6 Fy = 20 ksi
NOMENCLATURE
S 10
(b) f v = = = 3.188 ksi
Ag 3.141 Fy = Yield stress of anchor bolt material, ksi
Fv = Allowable shear stress in anchor bolt, ksi
Ft = Allowable tensile stress in anchor bolt, ksi
T 25
f t = = = 10.16 ksi Fb = Allowable bending stress in anchor bolt, ksi
At 2.356 Ac = Area of concrete in compression, in.2
D = Diameter of anchor bolt, in.
Ft = 28.0 – 1.6fv = 22.90 ksi ≤ 20 ksi (AISC Spec.
Ag = Gross area of anchor bolt, in.2
Sect. 1.6.3) At = Tensile stress area of anchor bolt, in.2
∴ Use Ft or Fb = 20 ksi Fp = Allowable bearing stress on concrete, ksi
f'c = Specified compressive strength of concrete at the end
(c) See Fig. 3. of 28 days, ksi
Bending moment due to shear S at the level of top of ls = Length of anchor bolt required for resisting shear
grout = m. force on bolt, in.
lt = Length of anchor bolt required for resisting tensile
m = (S × 1.0) = (10 × 1.0) = 10 kip-in. force on bolt, in.
m 10.0 l = Total length of embedment required, in.
fb = = = 12.73 ksi u = Allowable bond stress of concrete, ksi
(π / 32) D 3
(π / 32) × 2.0 3
fv = Actual shear stress in anchor bolt, ksi
(1/1.33) (ft + fb) = (1/1.33) (10.61 + 12.73) ft = Actual tensile stress in anchor bolt, ksi
= 17.55 ksi < Ft = 20 ksi o.k. n = Number of threads per inch for anchor bolt
23
FIRST QUARTER / 1980
You might also like
- Design of Footings: Foundation SystemDocument12 pagesDesign of Footings: Foundation SystemAbdirahman Ahmed IsseNo ratings yet
- Design of Multi-Storeyed Residential Building: MD Faruk Ansari 26301318059Document72 pagesDesign of Multi-Storeyed Residential Building: MD Faruk Ansari 26301318059Faruk AnsariNo ratings yet
- 16MST0038 Thesis Final PDFDocument54 pages16MST0038 Thesis Final PDFSrivatsanHariharanNo ratings yet
- Planning Analysis and Design of Steel Structures in Commercial BuildingDocument53 pagesPlanning Analysis and Design of Steel Structures in Commercial BuildingSriram Kumaran100% (1)
- 6 Design of Constant Dia RCC Chimney and Foundation 23052014 PDFDocument16 pages6 Design of Constant Dia RCC Chimney and Foundation 23052014 PDFbhargavramudu 2019No ratings yet
- Design of ColumnDocument8 pagesDesign of ColumnAfsar MansuriNo ratings yet
- Footings: General IntroductionDocument21 pagesFootings: General IntroductionMd Shafiul Alam FahadNo ratings yet
- Foundation 1 Design ReportDocument6 pagesFoundation 1 Design ReportDinesh RajaNo ratings yet
- Combined Footing (With Beam) - Excel - R0.0Document4 pagesCombined Footing (With Beam) - Excel - R0.0VIJAY PARMARNo ratings yet
- 15 - UT1 - AXC2 - 0010 - Concrete WorkDocument38 pages15 - UT1 - AXC2 - 0010 - Concrete Workhoang nguyen100% (1)
- "Rectbeam" - Rectangular Concrete Beam Analysis/Design: Program DescriptionDocument19 pages"Rectbeam" - Rectangular Concrete Beam Analysis/Design: Program DescriptionSandip SurNo ratings yet
- Designs A Crane Girder For Given Crane Loads, A Selected Section For Safe MD, Defln., Web Strength and Stiffeners, If Reqd.Document4 pagesDesigns A Crane Girder For Given Crane Loads, A Selected Section For Safe MD, Defln., Web Strength and Stiffeners, If Reqd.swapnilbhosale96No ratings yet
- Design of Combined Foundation For Column C7 & C8Document6 pagesDesign of Combined Foundation For Column C7 & C8Sneha RedkarNo ratings yet
- Restrained JointsDocument3 pagesRestrained JointsViswanathan NaraNo ratings yet
- Steel Column DesignDocument3 pagesSteel Column DesignGlenn TeNo ratings yet
- Connection Design:: SB NB Ub Yb Mo MB MFDocument1 pageConnection Design:: SB NB Ub Yb Mo MB MFSuman NakarmiNo ratings yet
- TowerDocument71 pagesTowerS. Chakrabarty MeconNo ratings yet
- Roof Truss DesignDocument44 pagesRoof Truss DesignEngr Gbadamosi NurudeenNo ratings yet
- Punch Typ C4Document10 pagesPunch Typ C4Suhail AhamedNo ratings yet
- Angular and Tubular Truss DifferenceDocument3 pagesAngular and Tubular Truss DifferenceKripasindhu BordoloiNo ratings yet
- Design of CW Channel For Section 'A-A'Document30 pagesDesign of CW Channel For Section 'A-A'Hemant SonawadekarNo ratings yet
- Hoisting FacilitiesDocument22 pagesHoisting FacilitiesArmie May RicoNo ratings yet
- Anchor Block CalculationDocument6 pagesAnchor Block CalculationChris Angelo G CaadlawonNo ratings yet
- Urban DrainageDocument26 pagesUrban Drainagesatria11No ratings yet
- Design Summary: Height of Compound Wall 2.4mDocument10 pagesDesign Summary: Height of Compound Wall 2.4mMa SrinuNo ratings yet
- Concepts Principles HydraulicsDocument34 pagesConcepts Principles HydraulicsVed DomaNo ratings yet
- B85 - Tie Beam Transverse TB-1Document8 pagesB85 - Tie Beam Transverse TB-1FrederickV.VelascoNo ratings yet
- ENCE 647 ENCE 647 Stability of Slopes Dr. Ahmet AydilekDocument23 pagesENCE 647 ENCE 647 Stability of Slopes Dr. Ahmet AydilekHoracioCruiseNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering Instructor: Dr. Nirmal Baran HuiDocument3 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering Instructor: Dr. Nirmal Baran HuiSatyajit SahuNo ratings yet
- XyzDocument64 pagesXyzP S HARSHITANo ratings yet
- Footing Spec As Per Is 456 - 2000Document4 pagesFooting Spec As Per Is 456 - 2000prabhu81No ratings yet
- Ctural: CLVLBL Structural. Design CalculationDocument70 pagesCtural: CLVLBL Structural. Design CalculationthakrarhitsNo ratings yet
- Selection of Spillways: 5.5 Energy Dissipation Below SpillwaysDocument4 pagesSelection of Spillways: 5.5 Energy Dissipation Below SpillwayshanoseNo ratings yet
- Design of Brick Wall For Ware House:-: 1 DataDocument3 pagesDesign of Brick Wall For Ware House:-: 1 DataSovan PramanickNo ratings yet
- Design Load Basis Report Tensile Canopy - Vedvan - Noida - R0Document27 pagesDesign Load Basis Report Tensile Canopy - Vedvan - Noida - R0Neeraj KumarNo ratings yet
- (Vinod Sharma, R.N. Agarwal) Planning Irrigation PDFDocument158 pages(Vinod Sharma, R.N. Agarwal) Planning Irrigation PDFRavi ValakrishnanNo ratings yet
- All Plumbing Design Calculation in One Excel Sheet: Engineering DiscoveriesDocument1 pageAll Plumbing Design Calculation in One Excel Sheet: Engineering Discoveriesfst manNo ratings yet
- 15a - Tabla de Deflexion para Vigas PDFDocument4 pages15a - Tabla de Deflexion para Vigas PDFKarla BonillaNo ratings yet
- Accounting Accidental Torsion STAADDocument3 pagesAccounting Accidental Torsion STAADmogustNo ratings yet
- For Axial Compressive Load & Biaxial Bending Moments, Including Slenderness Effect, As Per Is:456-2000Document43 pagesFor Axial Compressive Load & Biaxial Bending Moments, Including Slenderness Effect, As Per Is:456-2000Mohan BhalmeNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Intz Water Tank by Using Staad ProDocument8 pagesAnalysis and Design of Intz Water Tank by Using Staad ProEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Resistant StructuresDocument6 pagesEarthquake Resistant StructuresAmith KeshvtakarNo ratings yet
- Staircase Design 001Document18 pagesStaircase Design 001Er navneet jassiNo ratings yet
- Combined Footing For 2 Columns-1Document32 pagesCombined Footing For 2 Columns-1Wanda BeasleyNo ratings yet
- Water Resources Final Equation SheetDocument6 pagesWater Resources Final Equation SheetIBNo ratings yet
- 5-Ring Beam Design (For ArlIDocument6 pages5-Ring Beam Design (For ArlISher AfganNo ratings yet
- 38h-Racking of Timber Panels Type 02.PngDocument4 pages38h-Racking of Timber Panels Type 02.PngParthiban ArivazhaganNo ratings yet
- HP 1Document40 pagesHP 1pranavNo ratings yet
- Is-11682.1985 (Staging For Overhead Water Tanks) PDFDocument27 pagesIs-11682.1985 (Staging For Overhead Water Tanks) PDFamithcivil0% (1)
- 2.45M High Rubble Wall: Mila Feb-22Document4 pages2.45M High Rubble Wall: Mila Feb-22Nezza AriffNo ratings yet
- Computation Tool For Wind LoadDocument4 pagesComputation Tool For Wind LoadDr-Harshvadan PatelNo ratings yet
- Load Cal - Sheet - Ele 2, 3Document4 pagesLoad Cal - Sheet - Ele 2, 3ANJANA MPNo ratings yet
- 2395 CH 15Document19 pages2395 CH 15abdülkadir cebeciNo ratings yet
- Design of Concrete Linings of Pressure Tunnels and Shafts For External Water PressureDocument11 pagesDesign of Concrete Linings of Pressure Tunnels and Shafts For External Water PressureJUAN SEBASTIAN LOPEZ ZHINDONNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 5-Measurement of Water Yield From WatershedDocument23 pagesLECTURE 5-Measurement of Water Yield From WatershedChu DicksonNo ratings yet
- Partially Grouted Walls: B Effective Compressive Width Per Bar Min (S, 6t, 72 In) (5.1.2)Document18 pagesPartially Grouted Walls: B Effective Compressive Width Per Bar Min (S, 6t, 72 In) (5.1.2)Sky MoonNo ratings yet
- The Study of The Effects of Web Openings On The Concrete BeamsDocument10 pagesThe Study of The Effects of Web Openings On The Concrete BeamsChetan ToliaNo ratings yet
- ACI-350 P-M Interaction 2.1Document33 pagesACI-350 P-M Interaction 2.1corneliortizNo ratings yet
- Embedded Plates Calculation - Part 2Document8 pagesEmbedded Plates Calculation - Part 2Mai CNo ratings yet
- Base Plate Design - LRFD-1Document7 pagesBase Plate Design - LRFD-1k.m.ariful islamNo ratings yet
- AISC - EJ - Drake Elkin ERRATA 1 PDFDocument1 pageAISC - EJ - Drake Elkin ERRATA 1 PDFk.m.ariful islamNo ratings yet
- How To Develop High PerformanceDocument2 pagesHow To Develop High Performancek.m.ariful islamNo ratings yet
- Beam Web Opening - AnalysisDocument4 pagesBeam Web Opening - Analysisk.m.ariful islamNo ratings yet
- Frequently Addressed Topics in Fall Protection: PerspectivesDocument6 pagesFrequently Addressed Topics in Fall Protection: Perspectivesk.m.ariful islamNo ratings yet
- AISC EJ Drake-Elkin-ERRATADocument1 pageAISC EJ Drake-Elkin-ERRATAk.m.ariful islamNo ratings yet
- Steel Deck Institute Diaphragm Design Manual Second EditionDocument279 pagesSteel Deck Institute Diaphragm Design Manual Second EditionGeoffre14No ratings yet
- Mechanical Material PropertiesDocument10 pagesMechanical Material PropertiesDong HungNo ratings yet
- Snag List-Hyatt House Hvac and Chiller System Valve Pakage CD Fa Duct Rooms or Areas Fcu and Duct ConnectionDocument10 pagesSnag List-Hyatt House Hvac and Chiller System Valve Pakage CD Fa Duct Rooms or Areas Fcu and Duct ConnectionriyasudheenmhNo ratings yet
- Annex A - SpecificationsDocument5 pagesAnnex A - SpecificationsDesigners Eng'gConsultancyNo ratings yet
- Project-Diamond Green BuildingDocument41 pagesProject-Diamond Green BuildingIsabella WomsiworNo ratings yet
- Aramco Regulated Vendors List 2 15 PDFDocument684 pagesAramco Regulated Vendors List 2 15 PDFarslan0% (1)
- Fire Command Center - A5Document2 pagesFire Command Center - A5ΒΑΓΓΕΛΗΣ ΑΝΤΩΝΙΟΥNo ratings yet
- Gypsum Board Fire Rated ConstructionDocument5 pagesGypsum Board Fire Rated ConstructionphrishelNo ratings yet
- Keratek - Ventilated FacadesDocument22 pagesKeratek - Ventilated FacadesGuillermo Agustín Yáñez QuezadaNo ratings yet
- Catapang, John Walter C 3 CE-4 Assignment #1Document6 pagesCatapang, John Walter C 3 CE-4 Assignment #1Walter CatapangNo ratings yet
- Design For Maintenability-Guide-Non-ResidentialDocument61 pagesDesign For Maintenability-Guide-Non-ResidentialLaw Chee SeongNo ratings yet
- Final Bill For Toilet Works at Ulci Abstract of CostDocument6 pagesFinal Bill For Toilet Works at Ulci Abstract of Costsurendra_pangaNo ratings yet
- Brosur Baja Gunung Raja Paksi Roof & Wall SheetingDocument2 pagesBrosur Baja Gunung Raja Paksi Roof & Wall SheetingRobbi Shobri RakhmanNo ratings yet
- Cold and Cloudy Climate: 1. OrientationDocument3 pagesCold and Cloudy Climate: 1. OrientationmariyaNo ratings yet
- Technical Paper FinalDocument6 pagesTechnical Paper FinalMegha JJNo ratings yet
- Tek 14-07BDocument18 pagesTek 14-07BMuhammad ImranNo ratings yet
- On Grade Slab CJ Detail (NZ Notes)Document76 pagesOn Grade Slab CJ Detail (NZ Notes)Percre ChanNo ratings yet
- Stairwell PR SyDocument21 pagesStairwell PR SySameera GamageNo ratings yet
- Tabel Besi ProfilDocument27 pagesTabel Besi ProfilWildan PNo ratings yet
- YB22005 26-01-22 Mrs Chandra Chennai STR-01COLUMN AND CENTRELINEDocument1 pageYB22005 26-01-22 Mrs Chandra Chennai STR-01COLUMN AND CENTRELINEBoopathi YoganathanNo ratings yet
- Table 7d1.-U.S. Standard Reinforcing BarsDocument17 pagesTable 7d1.-U.S. Standard Reinforcing BarsHieu Huy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Investigating The Application of Waste Plastic Bottle As A Construction Material-A ReviewDocument14 pagesInvestigating The Application of Waste Plastic Bottle As A Construction Material-A ReviewYoi HNo ratings yet
- Code of Practice For Design Loads (Other Than Earthquake) For Buildings and StructuresDocument39 pagesCode of Practice For Design Loads (Other Than Earthquake) For Buildings and StructuresIshor ThapaNo ratings yet
- Final Project TRNSYSDocument2 pagesFinal Project TRNSYSAlex AutoconsumamosNo ratings yet
- Guideline For Specifying Steel Doors and Frames For Blast ResistanceDocument6 pagesGuideline For Specifying Steel Doors and Frames For Blast ResistanceГ. Баянмөнх100% (1)
- Dissertation Sustainable Facades MIKUS HERCSDocument34 pagesDissertation Sustainable Facades MIKUS HERCSRajat ChopraNo ratings yet
- Boilere Solare ELBI COMBIDocument4 pagesBoilere Solare ELBI COMBICsiszer RobertNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ConcreteDocument16 pagesIntroduction To ConcreteShehzad BachaniNo ratings yet
- Chiller Koolman CgakDocument8 pagesChiller Koolman Cgakfabieduarte440No ratings yet
- Arch II-9-lesson-THE ELEVATION PLAN PDFDocument5 pagesArch II-9-lesson-THE ELEVATION PLAN PDFUnica BaulosNo ratings yet
- Temp Humidity Control - FinalDocument97 pagesTemp Humidity Control - FinalAli HabibNo ratings yet