Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Community Pharmacy Project
Uploaded by
api-5344101300 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
123 views2 pagesBR is a 23-year-old Caucasian female with chronic back pain, headaches, endometriosis, and scoliosis. Her medications include Leuprolide Acetate injections every 3 months, Norethindrone Acetate tablets daily, Methenamine Hippurate tablets twice daily, Amitriptyline Hydrochloride tablets at bedtime, Cyclobenzaprine Hydrochloride tablets at bedtime, Rizatriptan tablets as needed, and Aspirin-acetaminophen-caffeine or Meloxicam tablets as needed. The assistant expresses concern about interactions between alcohol and Cyclobenzaprine or Amitriptyline, as well as potential
Original Description:
Original Title
community pharmacy project
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBR is a 23-year-old Caucasian female with chronic back pain, headaches, endometriosis, and scoliosis. Her medications include Leuprolide Acetate injections every 3 months, Norethindrone Acetate tablets daily, Methenamine Hippurate tablets twice daily, Amitriptyline Hydrochloride tablets at bedtime, Cyclobenzaprine Hydrochloride tablets at bedtime, Rizatriptan tablets as needed, and Aspirin-acetaminophen-caffeine or Meloxicam tablets as needed. The assistant expresses concern about interactions between alcohol and Cyclobenzaprine or Amitriptyline, as well as potential
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
123 views2 pagesCommunity Pharmacy Project
Uploaded by
api-534410130BR is a 23-year-old Caucasian female with chronic back pain, headaches, endometriosis, and scoliosis. Her medications include Leuprolide Acetate injections every 3 months, Norethindrone Acetate tablets daily, Methenamine Hippurate tablets twice daily, Amitriptyline Hydrochloride tablets at bedtime, Cyclobenzaprine Hydrochloride tablets at bedtime, Rizatriptan tablets as needed, and Aspirin-acetaminophen-caffeine or Meloxicam tablets as needed. The assistant expresses concern about interactions between alcohol and Cyclobenzaprine or Amitriptyline, as well as potential
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
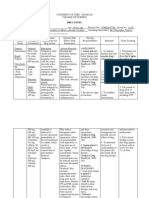
Name: Caitlyn Wegner
Community Pharmacy Project Part 1
Date: 02/16/2020
1. Patient’s initials, race, gender, and age: BR, Caucasian, Female, 23
2. List of patient’s medical problems:
Chronic back pain
Chronic tension headaches and migraines
Endometriosis
Scoliosis
3. List of Medications:
a. Leuprolide Acetate for Depot suspension IM Injections 11.25mg – Every three
months (pg. 922)
i. Directions: Administered by a healthcare provider
ii. MOA: A luteinizing hormone-releasing and GnRH agonist, acts as a
potent inhibitor of gonadotropin secretion when given continuously in
therapeutic doses
iii. SE: injection site reaction/pain, hot flashes/sweats, decreased libido,
nausea, constipation, headache, weight gain, bone pain,
fatigue/weakness.
iv. AE: pulmonary embolism, MI, bone loss, osteoporosis
b. Norethindrone Acetate Tablets 5mg orally– QD – nightly ~ 2300 (pg. 1156)
i. Directions: Take one pill orally once a day – used for add-back therapy
in conjunction with leuprolide acetate for depot suspension.
ii. MOA: Synthetic progestation hormone with androgenic, anabolic, and
estrogenic properties. Progestin-only contraceptives alter cervical
mucous, exert progestational effect on endometrium, interfere with
implantation, and, in some cases, suppress ovulation.
iii. SE: weight changes, breast tenderness, abnormal bleeding.
iv. AE: cerebral thrombosis or hemorrhage, pulmonary embolism.
c. Methenamine Hippurate 1g tablet orally – BID 0800/2300 (pg. 1021)
i. Directions: Take one tablet orally twice a day.
ii. MOA: Tertiary amine that liberates formaldehyde in an acid medium,
which is a nonspecific antibiotic agent with bactericidal activity.
iii. SE: Nausea, upset stomach, diarrhea, abdominal cramps.
iv. AE: N/A
d. Amitriptyline Hydrochloride 10 mg tablets orally – QD 2300 (pg. 80)
i. Directions: Take on tablet orally at bedtime.
ii. MOA: Inhibits the reuptake of serotonin (5-HT) and norepinephrine
from the synaptic gap, also inhibits norepinephrine uptake to a moderate
degree. Restoration of the levels of these neurotransmitters is a proposed
mechanism of its antidepressant action.
iii. SE: drowsiness, sedation, dizziness, orthostatic hypotension, dry mouth,
constipation, urinary retention
iv. AE: Bone marrow depression
e. Cyclobenzaprine Hydrochloride 5 mg tablets orally – 2 tablets QD 2300 (pg. 410)
i. Directions: Take two tablets orally at bedtime.
ii. MOA: Relieves skeletal muscle spasm of local origin without
interfering with muscle function. Believed to act primarily within CNS
at brainstem. Depresses tonic somatic motor activity, although both
gamma and alpha motor neurons are affected.
iii. SE: dry mouth, drowsiness.
iv. AE: edema of the tongue
f. Rizatriptan 10mg tablet – 1 tablet PRN no more than 2/week sublingually
g. Aspirin-acetaminophen-caffeine 250-250-65 mg tablets – 2 tablets QD PRN
orally
h. Meloxicam 15mg orally– QD PRN
4. Upon review of this list of medications and considering the age and current circumstance
of you patient, are there any medication interactions that concern you?
a. Due to this patient’s age I am worrisome about some of these medications that can
have interactions with alcohol (cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride, amitriptyline
hydrochloride). Alcohol mixed with suppressants and antidepressants can enhance
the CNS depression. I would advise the patient to not drink alcohol or at least
drink less alcohol and drink plenty of water prior to taking the medications or
advise them to hold the medications when they are drinking heavily. In addition,
the common side effect of urinary retention from amitriptyline hydrochloride
while the patient is also on methenamine hippurate. The therapeutic use of
methenamine hippurate is to help prevent recurrent urinary tract infections (UTI)
and urinary retention can cause a UTI. I would advise the patient to carefully
watch any changes with their urinary help and possibly talk to their doctor about
alternative medications. Lastly, I would question the patient about the length of
time they would be on the leuprolide acetate with depot suspension due to the
possible adverse effects of bone loss and osteoporosis. At her age, that is not
something that one would want to acquire.
5. Source:
Shields, K. M., Fox, K. L., & Liebrecht, C. (2019). Pearson Nurses Drug Guide 2019. New
York: Pearson.
You might also like
- Drug StudyDocument15 pagesDrug StudyLene Derlene Gerona100% (2)
- Pharmacology Volume 1 Unit 5 CardioDocument138 pagesPharmacology Volume 1 Unit 5 CardioAkhilesh TiwariNo ratings yet
- All Meds ListDocument7 pagesAll Meds ListjackyNo ratings yet
- Drug Summary March 23,2012Document6 pagesDrug Summary March 23,2012Bloxx777No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyMenard VelascoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - ParacetamolDocument8 pagesDrug Study - Paracetamoldamtere71% (7)
- Drug StudiesDocument32 pagesDrug StudiesKelly ChanNo ratings yet
- Bumetanide MIMSDocument2 pagesBumetanide MIMSIndri WahyuniNo ratings yet
- MethylprednisoloneDocument4 pagesMethylprednisoloneadryananestesiNo ratings yet
- Name: - Date Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesName: - Date Nursing ResponsibilitiesSheryl Ann Barit PedinesNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology BY: Hermie M. Pueyo M.D., R.N. PharmacologyDocument30 pagesPharmacology BY: Hermie M. Pueyo M.D., R.N. PharmacologyjessieNo ratings yet
- Drug 25Document17 pagesDrug 25carol_gigliotti24100% (1)
- DS Drug METFORMINDocument4 pagesDS Drug METFORMINAlexandrea MayNo ratings yet
- Drug Card PhenytoinDocument5 pagesDrug Card PhenytoinGifther JohnNo ratings yet
- 02-04 2022 Pharm Mens and Womens Health 2022 R4Document86 pages02-04 2022 Pharm Mens and Womens Health 2022 R4Amira HelayelNo ratings yet
- No SpaDocument6 pagesNo SpaIlyes FerenczNo ratings yet
- 5th Draft DrugsDocument7 pages5th Draft DrugsShayne Jessemae AlmarioNo ratings yet
- 6 Gastric Carcinoma HTPDocument15 pages6 Gastric Carcinoma HTPDan Floyd FernandezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Format For RLEDocument2 pagesDrug Study Format For RLESheryl Ann Barit PedinesNo ratings yet
- PrednisoneDocument3 pagesPrednisoneShaira TanNo ratings yet
- Inflammation, PainDocument23 pagesInflammation, Painلوى كمالNo ratings yet
- Magnesium SulfateDocument6 pagesMagnesium SulfatePrincess Alane MorenoNo ratings yet
- AtropineDocument3 pagesAtropinegovind_soni_15No ratings yet
- MC CholecalciferolDocument2 pagesMC CholecalciferolCliff by the seaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Anthemether Lumefrantine and RifampincineDocument12 pagesDrug Study Anthemether Lumefrantine and RifampincineAnonymous K99UIf1No ratings yet
- CetirizineDocument2 pagesCetirizineAnonymous QqyLDoW1No ratings yet
- PharmaDocument20 pagesPharmaMary Roan RonatoNo ratings yet
- E Kart DrugsDocument3 pagesE Kart DrugsNichole CastleNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Magnesium SulfateDocument6 pagesDrug Study - Magnesium SulfatePrincess Alane MorenoNo ratings yet
- A Drug Study On MISOPROSTOLDocument6 pagesA Drug Study On MISOPROSTOLAlexandrea MayNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyXandra ArticuloNo ratings yet
- I. Nama Obat: (1R, 5S) - 3-Benzhydryloxy-8-Methyl-8-Azabicyclo (3.2.1) OctaneDocument5 pagesI. Nama Obat: (1R, 5S) - 3-Benzhydryloxy-8-Methyl-8-Azabicyclo (3.2.1) Octanesalsabilla hastuti dwi kustyoriniNo ratings yet
- Pharma 12Document16 pagesPharma 12Mary Roan RonatoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyJanielle Christine MonsaludNo ratings yet
- CortisoneDocument2 pagesCortisoneJulioNo ratings yet
- 1st Tetanus DSDocument2 pages1st Tetanus DSSheryl Ann Barit PedinesNo ratings yet
- 10b-Discussion of The DiseaseDocument7 pages10b-Discussion of The DiseaseApple MaeNo ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument33 pagesPharmacologyFreeNursingNotes90% (67)
- Prime Pharmacotherapy ProblemsDocument1 pagePrime Pharmacotherapy Problemsjp100% (3)
- Pharmacology: By: Jan Michael Khalid L. Macarambon, RNDocument164 pagesPharmacology: By: Jan Michael Khalid L. Macarambon, RNJan MacarambonNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Drugs Acting On The Immune SystemDocument30 pagesUnit 5 Drugs Acting On The Immune SystemBea Bianca Cruz100% (1)
- EpitoinDocument2 pagesEpitoinmahgadNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis DrugsDocument6 pagesAppendicitis DrugsCross0No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument24 pagesDrug StudyMc Joewell HudencialNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic AcidDocument6 pagesMefenamic AcidArisa VijungcoNo ratings yet
- CASE STUDY Chapter 59 (ANTIEMETIC AGENTS)Document4 pagesCASE STUDY Chapter 59 (ANTIEMETIC AGENTS)Kate Angelique RodriguezNo ratings yet
- ANA P. BACANI - Activity Assignment 1 Medication ReconciliationDocument5 pagesANA P. BACANI - Activity Assignment 1 Medication ReconciliationAna Paula Bacani-SacloloNo ratings yet
- Seminar Drug.... Mohan.sDocument28 pagesSeminar Drug.... Mohan.smOHAN.S0% (1)
- Autonomic Nervous System & Homeopathy: Personalized Nutrition Concept Depicted in Homeopathy & AyurvedaFrom EverandAutonomic Nervous System & Homeopathy: Personalized Nutrition Concept Depicted in Homeopathy & AyurvedaNo ratings yet
- Myasthenia Gravis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandMyasthenia Gravis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Complementary and Alternative Therapies and the Aging Population: An Evidence-Based ApproachFrom EverandComplementary and Alternative Therapies and the Aging Population: An Evidence-Based ApproachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- My Mifespristone and Misoprostol Story: How I used mifepristone and misoprostol for a successful medical abortion and all you must know about these abortion pillsFrom EverandMy Mifespristone and Misoprostol Story: How I used mifepristone and misoprostol for a successful medical abortion and all you must know about these abortion pillsNo ratings yet
- Translational Endocrinology of Bone: Reproduction, Metabolism, and the Central Nervous SystemFrom EverandTranslational Endocrinology of Bone: Reproduction, Metabolism, and the Central Nervous SystemGerard KarsentyNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B6 Deficiency, A Simple Guide to the Condition, its Treatment and Related DiseasesFrom EverandVitamin B6 Deficiency, A Simple Guide to the Condition, its Treatment and Related DiseasesNo ratings yet
- Natural Alternatives to Antibiotics – Revised and Updated: How to treat infections without antibioticsFrom EverandNatural Alternatives to Antibiotics – Revised and Updated: How to treat infections without antibioticsNo ratings yet
- Summary of Ana Claudia Domene's Multiple Sclerosis and (lots of) Vitamin DFrom EverandSummary of Ana Claudia Domene's Multiple Sclerosis and (lots of) Vitamin DNo ratings yet
- The Best Practice Is The Lowest Effective Dose Your Third Psychiatric Consultation: Diet, Exercise, and Sleep Trump Medications Medication is the Last Option Your Fourth Psychiatric ConsultationFrom EverandThe Best Practice Is The Lowest Effective Dose Your Third Psychiatric Consultation: Diet, Exercise, and Sleep Trump Medications Medication is the Last Option Your Fourth Psychiatric ConsultationNo ratings yet
- QsenDocument17 pagesQsenapi-534410130No ratings yet
- Wegner Caitlyn - ResumeDocument1 pageWegner Caitlyn - Resumeapi-534410130No ratings yet
- Caitlyn Wegner Ob Clinical Skills Check SheetDocument1 pageCaitlyn Wegner Ob Clinical Skills Check Sheetapi-534410130No ratings yet
- Ob - Ebp ProjectDocument11 pagesOb - Ebp Projectapi-534410130No ratings yet
- My Nursing PhilosophyDocument4 pagesMy Nursing Philosophyapi-534410130No ratings yet
- Tuberculosis QsenDocument22 pagesTuberculosis Qsenapi-534410130No ratings yet
- Caitlyn 211 CetDocument7 pagesCaitlyn 211 Cetapi-534410130No ratings yet
- Fundies QsenDocument9 pagesFundies Qsenapi-534410130No ratings yet
- Life Span - Aa - Puerto RicoDocument13 pagesLife Span - Aa - Puerto Ricoapi-534410130No ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy Nursing Care PlansDocument27 pagesEctopic Pregnancy Nursing Care Plansviper7967880% (20)
- FCPS SurgeryDocument106 pagesFCPS Surgeryrehan hayderNo ratings yet
- EMPANELEDHOSPITALLISTDocument12 pagesEMPANELEDHOSPITALLISTVsknNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Operative DentistryDocument11 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To Operative DentistryMariam AdnanNo ratings yet
- Hepatology Research - 2023 - Yoshiji - Management of Cirrhotic Ascites Seven Step Treatment Protocol Based On The JapaneseDocument12 pagesHepatology Research - 2023 - Yoshiji - Management of Cirrhotic Ascites Seven Step Treatment Protocol Based On The JapaneseSarah FaziraNo ratings yet
- 8 Cns StimulantsDocument46 pages8 Cns StimulantslouradelNo ratings yet
- CBD Spinal Infection: by Neoh Zhong NingDocument26 pagesCBD Spinal Infection: by Neoh Zhong NingJoni NeohNo ratings yet
- Liver BiopsyDocument3 pagesLiver BiopsyBiway RegalaNo ratings yet
- Abdul Malik Hassim Lecturer DMA Management & Science UniversityDocument21 pagesAbdul Malik Hassim Lecturer DMA Management & Science UniversitykimmgizelleNo ratings yet
- Giardia Duodenalis Affect Farmers Child Growth and DevelopmentDocument2 pagesGiardia Duodenalis Affect Farmers Child Growth and DevelopmentAnitaNo ratings yet
- 1000 Mcqs - Periodontics Plus September 2014 McqsDocument16 pages1000 Mcqs - Periodontics Plus September 2014 McqsSelvaArockiam86% (7)
- Abortion in CattleDocument6 pagesAbortion in CattlekumarpujariNo ratings yet
- Scale For Ranking Health Conditions and Problems According To PrioritiesDocument9 pagesScale For Ranking Health Conditions and Problems According To Prioritiescnvfiguracion100% (1)
- Chapter 17 Mood Disorders and SuicideDocument13 pagesChapter 17 Mood Disorders and Suicidemyer pasandalanNo ratings yet
- Cost Per Test PC400 2020Document10 pagesCost Per Test PC400 2020fischaNo ratings yet
- JaundiceDocument4 pagesJaundiceTaleb AbjiNo ratings yet
- Evaluasi Usg Dan Tatalaksana Pada Varises Vena Tungkai - DR RamziDocument31 pagesEvaluasi Usg Dan Tatalaksana Pada Varises Vena Tungkai - DR RamziMohamad ZulfikarNo ratings yet
- Contoh Soal Epilepsy and SeizureDocument4 pagesContoh Soal Epilepsy and SeizurejumasriNo ratings yet
- Day 1 - GynacologyDocument204 pagesDay 1 - GynacologyTingting GeNo ratings yet
- MLT MCQDocument6 pagesMLT MCQzubair farooq50% (2)
- March 2012Document28 pagesMarch 2012Bill5199No ratings yet
- REAL in Nursing Journal (RNJ)Document8 pagesREAL in Nursing Journal (RNJ)Anonymous 8hlR5KvNo ratings yet
- Exchange Blood Transfusion 2Document15 pagesExchange Blood Transfusion 2Sarah100% (1)
- Formularium 2017Document87 pagesFormularium 2017Venita AgustinaNo ratings yet
- Thesis Synopsis - Naveen ReddyDocument16 pagesThesis Synopsis - Naveen ReddyNaveen ReddyNo ratings yet
- Effects of Advanced Carbohydrate Counting On Glucose Control and QolDocument9 pagesEffects of Advanced Carbohydrate Counting On Glucose Control and QollloplNo ratings yet
- LabReportNew - 2023-06-23T171149.608Document1 pageLabReportNew - 2023-06-23T171149.608B AZAD SIMHANo ratings yet
- Opalescence Tooth Whitening Systems: At-Home Whitening InstructionsDocument1 pageOpalescence Tooth Whitening Systems: At-Home Whitening InstructionsPande NandaNo ratings yet
- Media Release - COVID-19Document2 pagesMedia Release - COVID-19Executive Director100% (2)
- Prostaglandins in Pregnancy: Scott W. Walsh, PHDDocument21 pagesProstaglandins in Pregnancy: Scott W. Walsh, PHDIrene AtimNo ratings yet