Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Uganda Advanced Certificate of Education Resource Mock X Physics Paper 1 2 Hours 30 Minutes
Uploaded by
ssempijja jamesOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Uganda Advanced Certificate of Education Resource Mock X Physics Paper 1 2 Hours 30 Minutes
Uploaded by
ssempijja jamesCopyright:
Available Formats
P510/1
PHYSICS
Paper 1
July/Aug. 2019
1
2 hours
2
UGANDA ADVANCED CERTIFICATE OF EDUCATION
RESOURCE MOCK X
PHYSICS
Paper 1
2 hours 30 minutes
INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES:
Answer five questions, including at least one but not more than two from each of the sections
A, B, and C. Any additional question(s) attempted will not be marked.
Non- programmable scientific calculators may be used.
Assume where necessary:
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.81m s−2
Electronic charge, e = 1.6 x 10−19 C
Electron mass = 9.11 x 10−31kg
Mass of the earth = 5.97 x 1024 kg
Planck’s constant = 6.6 x 10−34 Js
Stefan’s – Boltzmann’s constant, σ = 5.67 x 10−8 Wm2 K −4
Radius of the earth = 6.4 x 106 m
UACE MOCK X 2019 Page 1
Speed of light in a vacuum, C = 3.0 x 108m s−1
Thermal conductivity of iron = 80 Wm−1 K−1
Universal gravitational constant, G = 6.67 x 10−11 Nm 2 kg−2
Avogadro’s number, NA = 6.02 x 1023mol-1
Density of water = 1000kgm−3
Density of mercury = 13600kgm−3
Gas constant = 8.31J mol -1K-1
SECTION A
1. ( a ) (i) State Bernoulli’s principle. (1 mark )
(ii) Explain why it is dangerous to stand close to a railway line on which a fast moving
train is passing. (3 marks )
(b) (i) Determine the dimensions of coefficient of viscosity. (1 mark )
( ii )Water of negligible viscosity flows through a horizontal pipe of varying
cross-sectional area. At a point A of cross-sectional area 10cm 2, the velocity is
0.2m s−1 . What is the pressure difference between A and B if the cross-sectional
area of point B is 2.5m s−1 ? (5 Marks)
(c) (i) Define coefficient of surface tension. (1 mark)
(ii) Explain the origin of surface tension. ( 3 marks)
(ii) Describe an experiment to measure the surface tension of a liquid by
Jaeger’s method. (5Marks)
2. (a) (i) State Kepler’s laws of planetary motion. (3 marks)
(ii) Distinguish between the gravitational constant, G and the acceleration due to
gravity, g. (2 marks)
UACE MOCK X 2019 Page 2
(b) (i) The moon moves in a circular orbit of radius, R about the earth of mass, M e with
period. If r e is the radius of the earth, and g, is the acceleration due to gravity on the
T 2 g r 2e
earth’s surface. Show that R3 = (3 Marks)
4 π2
(ii) The period of the moon round the earth is 670 hours. If the distance of the moon from
The earth is 3.8x108m, Calculate the acceleration due to gravity at the surface of the
earth. (3 Marks)
(c) (i) Describe an experiment to determine the acceleration due gravity ,g using a spiral
Spring of known force constant. (5 Marks)
(ii) Explain why a mass attached to the lower end of a clamped spiral spring comes to a
Stop after a short time when given a small displacement and then released.(2Marks)
(d) A body moving in a circular path of radius 0.5 m makes 40 revolutions per second. Find
The centripetal force if the mass of of the body is 1kg. (2 Marks)
3. (a) What is meant by the following terms?
(i) Elasticity. (1Mark)
(ii) Young’s modulus. (1Mark)
(iii) Plasticity. (1Marks)
(b) Derive an expression for the potential energy stored per unit volume in a stretched wire
in terms of stress and strain. (3Marks)
(c) A mass of 20g falls from a height of 2.0m to the top of a spring of force constant
100Nm-1. Calculate the resulting compression in the string if;
(i) The mass sticks on top of the spring. (3Marks)
(ii) The mass bounces off the spring with a speed of 2.0ms-1. (3Marks)
(d) A uniform rod AB weighing 100kg and 0.75m long is hinged to a vertical wall at end A and
UACE MOCK X 2019 Page 3
held horizontally by a stretched thin wire of diameter 0.8mm fixed at end B and C on the
vertical wall, 1.0m above A. If the wire was initially 1.23m long, find:
(i) The tension in the wire. (4Marks)
(ii) Young’s modulus for the wire. (4Marks)
4. (a) (i) What is simple harmonic motion? (1Mark)
(ii) Show that energy in simple harmonic motion is conserved. (4Marks)
(iii) Sketch a graph to show the variation of energy with displacement for a body
performing simple harmonic motion. (2Marks)
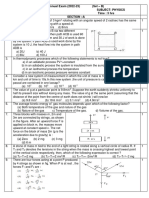
(b The figure 1 below shows a block of mass 0.1kg resting on a smooth horizontal surface
and attached to two springs A and B of spring constants 60Nm-1 and 100Nm-1
respectively. The block is pulled through a distance 4.0cm to the right and released.
A B
MM
Figure 1
(i) Find the frequency of oscillation. (3Marks)
(ii) Find the new amplitude of oscillation when a mass of 60.og is dropped vertically
on the block as the block passes the equilibrium position. Assume the mass sticks
to the block. (4Marks)
(c ) A piston in a car engine performs simple harmonic motion of frequency 12.5Hz. If the
Mass of the piston is 0.50kg and its amplitude of vibration is 45mm, find the maximum
force on the piston. (3Marks)
(d) Explain why the maximum speed of the car on a banked road is higher than that an
unbanked road. (3Marks)
UACE MOCK X 2019 Page 4
SECTION B
5. (a) (i) What is a black body? (1Mark)
(ii) Explain with the aid of a diagram, how a black body can be approximated.(3Marks)
(iii) With the aid of sketch graphs explain the salient features of the spectral distribution
of black body radiation. (4Marks)
(b) Give four properties of ultraviolet radiation. (2Marks)
(c ) Describe an experiment to compare the energy radiated by two surfaces of different
nature. (4Marks)
(d) (i) State Stefan’s law of black body radiation. (1Mark)
(ii) The earth receives energy from the sun at the rate of 1.4x10 3Wm-2. If the ratio of the
earth’s orbit to the sun’s radius is 216, calculate the surface temperature of the sun.
(5Marks)
6. (a) (i) State Charles’ law. (1Mark)
(ii) Describe an experiment to verify Charles’ law. (4Marks)
(b) (i) State Dalton’s law of partial pressures. (1Mark)
(ii) Two identical bulbs containing a gas at a pressure, P1 and temperature, T 1
are connected by a capillary tube. When one of the bulbs is immersed in a bath at
a temperature, T 2, the pressure becomes, P2.. Show that the temperature of the
P2 T
bath is given by T 2=
1
. (4Marks)
2 P1− P 2
(c) Define the specific heat capacity. (1Marks)
(d) In a continuous flow experiment on a liquid of specific heat capacity 4150JkgK -1 the
UACE MOCK X 2019 Page 5
following results were obtained:
Ammeter reading(A) Voltmeter reading(V) Mass of liquid collected
per minute(g)
2.00 25.2 75.0
2.52 30.0 115.9
If the inflow temperature was 15o C find
(i) The outflow temperature. (3Marks)
(ii) The rate of heat loss. (2Marks)
7. (a) (i) Define Specific heat capacity of a gas at constant volume and state its units.(2Marks)
(ii) Derive the relationship Cp – CV = R, where R is the universal molar gas constant. (3Marks)
(iii) Explain why CP is greater than CV . (2Marks)
(b) Using the kinetic theory of matter explain why change in volume of a saturated vapour at
constant temperature does not affect its pressure. (3Marks)
(c) One Kilo mole of an ideal gas is carried through the reversible cycle in the p-V diagram
below. p
1 2
In state (1) the gas has a pressure 1.0x105Nm-2 and a temperature of 0oC. The volume of the gas
in state (2) is four times that in state (1). Process (3) to (1) is a reversible isothermal
compression. Determine;
(i) The temperature of the gas in state (2). (2Marks)
(ii) The pressure of the gas in state (3). (2Marks)
UACE MOCK X 2019 Page 6
(iii)The work done by the gas in the cycle. (5Marks)
SECTION C:
8. (a) (i) Distinguish between X-rays and cathode rays. (2Marks)
(ii) In an X-ray tube explain the features adopted for the structure and material of the
anode. (3Marks)
(b) (i) State Bragg’s law. (1Mark)
(ii) What is the condition for obtaining many orders of X-ray diffraction? (1Mark)
(iii) A monochromatic beam of X-rays of wave length 1.10X10 -10mis incident on a set of
Cubic atomic planes in a potassium chloride crystal. First order diffraction maxima are
obverved at a glancing angle of 19o. Determine the density of potassium chloride if its
relative molecular mass is 75.5. (4Marks)
(c) (i) In photo electricity, what is meant by the work function? (1Marks)
(ii) Describe how you would determine Planck’s constant in a school. (4Marks)
(iii) When monochromatic light of frequency 6.0X1015Hz falls on a metal surface, the
stopping potential is 0.6V while when the same surface is irradiated by light of
frequency 1.0X1015Hz the stopping potential becomes 2.2V. Determine the work
function of the metal. (4Marks)
9. (a) State Bohr’s postulates of the hydrogen atom. (2Marks)
(b) Define the terms ionization energy and excitation energy. (2Marks)
( c) The energy levels of a mercury atom are; -10.4eV, -5.4eV, -3.7eV and -1.6eV.
(i) Find the ionization energy of mercury in joules. (2Marks)
(ii) What is likely to happen if a mercury atom in unexcited state is bombarded with an
Electron of energies of 4.0eV and 11.0eV? (4Marks)
UACE MOCK X 2019 Page 7
(d) (i) Explain the successes and failures of Rutherford’s model of an atom. (3Marks)
(ii) Show thaw he an alpha particle collides head on with an atom of atomic number Z,
Z e2
The closest distance of approach to the nucleus, x is given by; x = , where e is
π ε oM v
2
the electronic charge, M is the mass of an electron and v, the velocity of the alpha-
particle. (3Marks)
(e) Explain the emission spectrum of hydrogen. (4Marks)
10 (a)(i) Distinguish between radioactivity and nuclear fission. (2Marks)
(ii) Define binding energy of a nucleus. (1Marks)
(b) (i) What is half life of a radioactive substance? (1Marks)
(ii) Derive an expression relating half life and the decay constant of a radioactive
substance. (3Marks)
(C) A nucleus of uranium-238 disintegrates with emission of a nucleus X and an alpha particle.
(i) Write down the equation for the reaction. (1Marks)
(ii) Find the energy released in the reaction. (5Marks)
Mass of 238U =¿ 230.12492u ¿
Mass of X = 234.11650u
Mass of 4 He= 4.00387u
1u = 1.66x10-27kg = 1.494x10-12J.
(d) A beam of electrons is accelerated through a potential difference of 1800V and is directed
Mid-way between two horizontal plates of length 4.0cm and of separation 4.ocm. the
Potential difference across the plates is 90V.
(i) Calculate the speed of the electrons as they enter the region between the plates. (3mks)
(ii)Describe the motion of the electrons between the plates. (1Marks)
UACE MOCK X 2019 Page 8
(iii) Find the angle at which the electron emerges out of the field across the plates. (3marks).
END
UACE MOCK X 2019 Page 9
You might also like
- Lettice and Lovage PDFDocument1 pageLettice and Lovage PDFapi-2452366370% (2)
- Hadoop Course Content PDFDocument9 pagesHadoop Course Content PDFNaveen ElancersoftNo ratings yet
- Vibration in Pumps PDFDocument5 pagesVibration in Pumps PDFonspsnonsNo ratings yet
- White Lily - Ship's ParticularDocument1 pageWhite Lily - Ship's ParticularAYA ALHADITHEYNo ratings yet
- Shack Pre-Mock Examinations 2016 P510/1 Physics Paper 1Document9 pagesShack Pre-Mock Examinations 2016 P510/1 Physics Paper 1EfrataNo ratings yet
- S.6 Physics P1 Mock 1Document6 pagesS.6 Physics P1 Mock 1cyber secNo ratings yet
- Physics: Uace Mock Examinations 2015 Physics Paper 1 2 Hours 30 MinDocument5 pagesPhysics: Uace Mock Examinations 2015 Physics Paper 1 2 Hours 30 MinKitone A NdrewNo ratings yet
- A Level Seminar ReadyDocument16 pagesA Level Seminar ReadyOnesmus GumisirizaNo ratings yet
- s6 Physics p1 BugandaDocument7 pagess6 Physics p1 BugandaWafula EricNo ratings yet
- Physics Examinations S.6Document8 pagesPhysics Examinations S.6Ssensiiti JuliusNo ratings yet
- Namugongo A' Level Physics Seminar 2023Document18 pagesNamugongo A' Level Physics Seminar 2023abelcbucks06No ratings yet
- UACE Physics Paper 1 Set2Document5 pagesUACE Physics Paper 1 Set2mukembomeddie8No ratings yet
- Standard High School Zzana: P510/1 Physics Paper 1Document7 pagesStandard High School Zzana: P510/1 Physics Paper 1Kitone A NdrewNo ratings yet
- Form Six Aee 1 Examination. Physics 02: ST Peter Claver High SchoolDocument4 pagesForm Six Aee 1 Examination. Physics 02: ST Peter Claver High SchoolCharles GhatiNo ratings yet
- Physics Questions (A Level)Document4 pagesPhysics Questions (A Level)ojilongNo ratings yet
- Class XI Physics SP SET 1Document4 pagesClass XI Physics SP SET 1Dhivya.k Dhivya.kNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper 2 Uneb Question BankDocument116 pagesPhysics Paper 2 Uneb Question BankOnen-can Hendry Nyeko100% (1)
- Section A Physics Paper 1 Mechanics Revision Questions For A LevelDocument29 pagesSection A Physics Paper 1 Mechanics Revision Questions For A Levelalemorgan418No ratings yet
- BPhO Round 1 2017-2018 S2 PDFDocument12 pagesBPhO Round 1 2017-2018 S2 PDFWWTNo ratings yet
- 131 - Physics 2Document4 pages131 - Physics 2nassorussi9No ratings yet
- Phy 2 Tosa - 2023Document12 pagesPhy 2 Tosa - 2023sam2jbegNo ratings yet
- Phy F2Document12 pagesPhy F2Kimathi BundiNo ratings yet
- Phys F2Document9 pagesPhys F2Qiash JontezNo ratings yet
- 6.test Mix 2 (1h)Document4 pages6.test Mix 2 (1h)Duncan LinNo ratings yet
- S4 Physics P2Document5 pagesS4 Physics P2ivalryder3No ratings yet
- ICSE Class 11 Annual Exam Model Question Paper 2 - PHYSICSDocument3 pagesICSE Class 11 Annual Exam Model Question Paper 2 - PHYSICSArindam SardarNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes For Secondary Education of UgandaDocument11 pagesPhysics Notes For Secondary Education of UgandaMukiibi DuncanNo ratings yet
- Physics 1 - F6 - 2016Document6 pagesPhysics 1 - F6 - 2016Suhaila MbaroukNo ratings yet
- CAPE Physics 2003 U1 P1Document12 pagesCAPE Physics 2003 U1 P1Bob FridgeNo ratings yet
- NAME .ADM CLASS : 2022 Form 3 Term 1 Opener Exam - (April 2022)Document6 pagesNAME .ADM CLASS : 2022 Form 3 Term 1 Opener Exam - (April 2022)Benjamin mwanikiNo ratings yet
- Friction PPQsDocument18 pagesFriction PPQsolamide.odukunleNo ratings yet
- Class 11 PhysicsDocument4 pagesClass 11 PhysicsAlexis Ameen CruzerNo ratings yet
- Resource MockDocument8 pagesResource Mockgeorge willsNo ratings yet
- UACE PhY1 PDFDocument10 pagesUACE PhY1 PDFTRIPPLE KAYZ UGNo ratings yet
- Uganda Advanced Certificate of Education: Physics Paper Two P510/2Document9 pagesUganda Advanced Certificate of Education: Physics Paper Two P510/2ssempijja jamesNo ratings yet
- 11 Phy - Set B Ut-2Document4 pages11 Phy - Set B Ut-2dikshachoud44No ratings yet
- Physics 1 - F6 - 2015Document6 pagesPhysics 1 - F6 - 2015sam2jbegNo ratings yet
- Uce Physics Paper Two 3Document7 pagesUce Physics Paper Two 3Okiror GeorgeNo ratings yet
- +1 Physics: Adayar - Adambakkam - East Tambaram - Pallavaram - PammalDocument18 pages+1 Physics: Adayar - Adambakkam - East Tambaram - Pallavaram - Pammalvsivaraman94No ratings yet
- 1st Yr Hy 09Document4 pages1st Yr Hy 09Grezzju CauchiNo ratings yet
- Follow Up QsDocument8 pagesFollow Up QsVedant PapnejaNo ratings yet
- Dab Chemistry and MathematicsDocument3 pagesDab Chemistry and MathematicsRuth AlooNo ratings yet
- Mock Ext. P2 For S4 2017.Document6 pagesMock Ext. P2 For S4 2017.cyber secNo ratings yet
- Physics 1 - F6 - 2017Document6 pagesPhysics 1 - F6 - 2017sam2jbegNo ratings yet
- Trialstpm 2023 YUHUApaper 1 QuestionDocument6 pagesTrialstpm 2023 YUHUApaper 1 QuestionMathew Cheng Yu HaoNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Physics Sample Paper Set 2Document6 pagesCBSE Class 11 Physics Sample Paper Set 2Dheeraj KumarNo ratings yet
- UACE Physics Paper 1 Set1Document5 pagesUACE Physics Paper 1 Set1Ed Molson100% (1)
- s.3 Physics Paper 2 Term II 08Document2 pagess.3 Physics Paper 2 Term II 08joseph kunikinaNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Annual Qp2023-24Document8 pagesClass 11 Annual Qp2023-24prajittokdarNo ratings yet
- Turkish Light Academy Uganda Advanced Certificate of EducationDocument6 pagesTurkish Light Academy Uganda Advanced Certificate of EducationMutsyaba Victor JuniorNo ratings yet
- 2 Hours: P510/1 Physics Paper 1 Jul / Aug. 2019Document8 pages2 Hours: P510/1 Physics Paper 1 Jul / Aug. 2019ssempijja jamesNo ratings yet
- 11 PHY Set 2Document5 pages11 PHY Set 2dikshachoud44No ratings yet
- Sample Paper On Physics Grade 10Document3 pagesSample Paper On Physics Grade 10aadesh_mahatoNo ratings yet
- NECTA - Physics Paper 1 1994Document6 pagesNECTA - Physics Paper 1 1994GISCAR MINJANo ratings yet
- AP Physics 1 Practice Test 2Document18 pagesAP Physics 1 Practice Test 2John BoswellNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument5 pagesPhysicskaviraj.naidu848No ratings yet
- Mock 2023Document8 pagesMock 2023kinene richardNo ratings yet
- 1993-AL-Phy 1Document7 pages1993-AL-Phy 1chchppchchNo ratings yet
- S.6 Physics SeminarDocument15 pagesS.6 Physics SeminarKibudde StevenNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 2 August Holiday Assignment 2019Document10 pagesPhysics Form 2 August Holiday Assignment 2019frank kipkoechNo ratings yet
- 2018 Easter SAC Int LowersDocument5 pages2018 Easter SAC Int LowersSamantha GrechNo ratings yet
- Physics Practice Paper - IDocument3 pagesPhysics Practice Paper - Imehul yoNo ratings yet
- UACE Physics Paper 1 Set4Document5 pagesUACE Physics Paper 1 Set4na teumNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Uganda Advanced Certificate of Education: Physics Paper Two P510/2Document9 pagesUganda Advanced Certificate of Education: Physics Paper Two P510/2ssempijja jamesNo ratings yet
- Beginning of Term Ii 2019 Exam S.5 Physics P510/1 Time: 2 Hours Instructions Assume Where NecessaryDocument3 pagesBeginning of Term Ii 2019 Exam S.5 Physics P510/1 Time: 2 Hours Instructions Assume Where Necessaryssempijja jamesNo ratings yet
- 2 Hours: P510/1 Physics Paper 1 Jul / Aug. 2019Document8 pages2 Hours: P510/1 Physics Paper 1 Jul / Aug. 2019ssempijja jamesNo ratings yet
- Econ 2-1Document2 pagesEcon 2-1ssempijja jamesNo ratings yet
- P220/1 Paper 1 3 Hours: Economics Jul / Aug. 2019Document3 pagesP220/1 Paper 1 3 Hours: Economics Jul / Aug. 2019ssempijja jamesNo ratings yet
- Econ 1-2Document2 pagesEcon 1-2ssempijja jamesNo ratings yet
- © Naalya Schools Mock 2019 Page 1Document12 pages© Naalya Schools Mock 2019 Page 1ssempijja jamesNo ratings yet
- P220/1 Paper 1 3 Hours: Economics Jul / Aug. 2019Document3 pagesP220/1 Paper 1 3 Hours: Economics Jul / Aug. 2019ssempijja jamesNo ratings yet
- Name: . Stream : S 850/1 Subsidiary Information & Communication Technology Paper 1 2 HoursDocument6 pagesName: . Stream : S 850/1 Subsidiary Information & Communication Technology Paper 1 2 Hoursssempijja james100% (1)
- User Manual Product Description Rectifier DPR 6000B-48: Smarter. Greener. TogetherDocument14 pagesUser Manual Product Description Rectifier DPR 6000B-48: Smarter. Greener. Togethermoumen BoughraraNo ratings yet
- S. P. Rosenbaum (Auth.) - Edwardian Bloomsbury - The Early Literary History of The Bloomsbury Group Volume 2-Palgrave Macmillan UK (1994)Document573 pagesS. P. Rosenbaum (Auth.) - Edwardian Bloomsbury - The Early Literary History of The Bloomsbury Group Volume 2-Palgrave Macmillan UK (1994)HilmiNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Recruitment IN Aneja Training and Placement ServicesDocument25 pagesHuman Resource Recruitment IN Aneja Training and Placement ServicesHarnitNo ratings yet
- Article Review FormDocument2 pagesArticle Review FormdinarsyifaNo ratings yet
- Sachet MarketingDocument7 pagesSachet MarketingTom JohnNo ratings yet
- 2023 Global State of Digital Trust Infographic FinalDocument1 page2023 Global State of Digital Trust Infographic Finalhakkan meierNo ratings yet
- Wind Seismic CalculationsDocument4 pagesWind Seismic Calculationsumesh0% (1)
- 4.11 Radiation Protection - AHDocument112 pages4.11 Radiation Protection - AHGina RNo ratings yet
- Smart Goals Unit 2 BiologyDocument2 pagesSmart Goals Unit 2 Biologyapi-330056366No ratings yet
- Thesis Topics On Social EntrepreneurshipDocument6 pagesThesis Topics On Social EntrepreneurshipCollegePapersToBuySingapore100% (2)
- How To Product ManualDocument250 pagesHow To Product ManualAmith M DNo ratings yet
- Biosash Order Form Latest - 2019-9281576348996003Document3 pagesBiosash Order Form Latest - 2019-9281576348996003Amer Suhail ShareefNo ratings yet
- AC405 Assignment R185840RDocument3 pagesAC405 Assignment R185840RDiatomspinalcordNo ratings yet
- On Campus BA - Consultant JDDocument2 pagesOn Campus BA - Consultant JDSivaramakrishna SobhaNo ratings yet
- Design Calculation of Gantry GirderDocument7 pagesDesign Calculation of Gantry GirderKushal ChhetriNo ratings yet
- Hw-n300 ZP Fullmanual 00 Eng Spa 180713Document62 pagesHw-n300 ZP Fullmanual 00 Eng Spa 180713NIVARDO ÑAUPA MOROCCONo ratings yet
- AS 3 Mid-Year TestDocument2 pagesAS 3 Mid-Year TestМар'яна НагорнюкNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual: El SaadDocument184 pagesInstruction Manual: El SaadElias Rabbat100% (1)
- Leaf Area Estimation of Anacardium HumileDocument8 pagesLeaf Area Estimation of Anacardium HumileAngelita SoaresNo ratings yet
- Banasthali Vidyapith: Bachelor of Arts and Bachelor of LawsDocument172 pagesBanasthali Vidyapith: Bachelor of Arts and Bachelor of Lawssimranrai122002No ratings yet
- Clutch Bearing 2008-Application GuideDocument17 pagesClutch Bearing 2008-Application GuidemagdyfifaNo ratings yet
- Health Benefits of Financial Inclusion A Literature ReviewDocument7 pagesHealth Benefits of Financial Inclusion A Literature Reviewl1wot1j1fon3No ratings yet
- Automatic Summarization of Youtube Video Transcription Text Using Term Frequency-Inverse Document FrequencyDocument9 pagesAutomatic Summarization of Youtube Video Transcription Text Using Term Frequency-Inverse Document FrequencyKarunya ChavanNo ratings yet
- Hotels Review Classification FinalDocument34 pagesHotels Review Classification FinalPurvaNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument25 pagesSeminar ReportChethan kumar D NNo ratings yet
- Fermentación BatchDocument8 pagesFermentación BatchJennifer A. PatiñoNo ratings yet