Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Overview of The Current State of Technology in The Philippines
Uploaded by
Jonel NaquitaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Overview of The Current State of Technology in The Philippines
Uploaded by
Jonel NaquitaCopyright:
Available Formats
Overview of the current state of technology in the Philippines
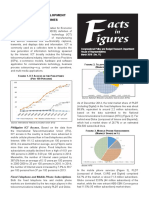
The Philippines adopts the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD)
definition of information and communications technology (ICT) which refers to a combination of
manufacturing and service industries that electronically captures, transmits, and displays data and
information. According to the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), ICT access in the
Philippines is much more advanced in mobile cellular phones than in fixed telephones and the Internet.
It also said that every Filipino’s owned one or more cellular phone. In terms of broadband connection,
broadband services in the Philippines is poor. It is reported that the Philippines has the slowest average
download speed in Asia. The factors affecting the poor broadband connection in the country are lack of
competition due to the presence of barriers to the entry, lack of infrastructure such as national
broadband network and the weak and ineffective regulation.
Reference:https://cpbrd.congress.gov.ph/images/PDF%20Attachments/Facts%20in
%20Figures/FF2016-11_ICT.pdf
In terms of preparedness for technological change in the next few years, the Philippines
improved. According to the article “Philippines climbs in technological readiness ranking” by Ian
Nicholas Cigaral (2018), the Philippines climbed to the 55 th spot out of 82 economies tracked in
the latest Technological Readiness Ranking published by the Economist Intelligence Unit. The
Philippines is the 4th most tech-ready economy in Southeast Asia.
Reference:https://www.philstar.com/headlines/2018/06/06/1822109/philippines-climbs-
technological-readiness-ranking
You might also like
- Project Proposal - Zero Plastic Waste AdvocacyDocument7 pagesProject Proposal - Zero Plastic Waste Advocacygrace budumo mosqueda71% (7)
- A Study On The Internet Connectivity in The PhilippinesDocument22 pagesA Study On The Internet Connectivity in The PhilippinesXyrelle OrmitaNo ratings yet
- The Development of Telecommunications Industry in The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesThe Development of Telecommunications Industry in The PhilippinesHubert SemenianoNo ratings yet
- CS111 IM Week 3Document63 pagesCS111 IM Week 3Jonel NaquitaNo ratings yet
- BJMP Case AnalysisDocument25 pagesBJMP Case AnalysisJonel NaquitaNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Economics (Internet Service Provider)Document20 pagesEconomics (Internet Service Provider)romelyn xygnetsNo ratings yet
- Abarcar ArticleDocument2 pagesAbarcar Articleapi-267763690No ratings yet
- GRP7 - IMPROVEMENTS IN INTERNET CONNECTIVITY - TanA - Canillo - Castaneda - Cortero - DelaRoDocument4 pagesGRP7 - IMPROVEMENTS IN INTERNET CONNECTIVITY - TanA - Canillo - Castaneda - Cortero - DelaRoAngelo CorteroNo ratings yet
- GW01 F Industry Analysis Globe Telecom Inc. 1Document31 pagesGW01 F Industry Analysis Globe Telecom Inc. 1Lara FloresNo ratings yet
- Intern Et Connectivi Ty in TH e Philippin Es: TH e Asi An Persp Ecti VeDocument8 pagesIntern Et Connectivi Ty in TH e Philippin Es: TH e Asi An Persp Ecti VeCharm BoquirenNo ratings yet
- Casev Study - Austria, Maria Fe C.Document10 pagesCasev Study - Austria, Maria Fe C.maria fe austriaNo ratings yet
- What Is Happening in ICT in Ethiopia: UnderstandingDocument58 pagesWhat Is Happening in ICT in Ethiopia: Understandingabey134175No ratings yet
- National ICT Ecosystem Framework PDFDocument144 pagesNational ICT Ecosystem Framework PDFMaryrose GestosoNo ratings yet
- Philippine Electronic IndustryDocument2 pagesPhilippine Electronic Industryrico onrubiaNo ratings yet
- Ict in The PhilippinesDocument1 pageIct in The Philippinesapi-532539634No ratings yet
- What Do ICT Stats Say About The Philippines?: Jose Ramon G. Albert and Raymond E. GasparDocument35 pagesWhat Do ICT Stats Say About The Philippines?: Jose Ramon G. Albert and Raymond E. Gasparrmateo_caniyasNo ratings yet
- Nictef PDFDocument140 pagesNictef PDFZhel DianingNo ratings yet
- Reaction PaperDocument12 pagesReaction PaperJill_xyinz1458975% (4)
- Iv. Information and Communication Technology Infrastructure: A. IntroductionDocument18 pagesIv. Information and Communication Technology Infrastructure: A. IntroductionMuhammad Usman SaeedNo ratings yet
- Unciano - MODULE EXAM - 1Document2 pagesUnciano - MODULE EXAM - 1Matthew TumaliwanNo ratings yet
- Duterte Vows Faster Internet, Free Wi-Fi: Maime Autida July 27,2016 IT-14 (Computer Networks 2) WednesdayDocument2 pagesDuterte Vows Faster Internet, Free Wi-Fi: Maime Autida July 27,2016 IT-14 (Computer Networks 2) WednesdayKim CasabayNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document29 pagesModule 4Justine MonteroNo ratings yet
- 2015 Sep ITU Regional Workshop On Policy and Regulatory Landscape v2Document21 pages2015 Sep ITU Regional Workshop On Policy and Regulatory Landscape v2myownme2022No ratings yet
- Technology and Automation As Sources of 21 - Century Firm Productivity: The Economics of Slow Internet Connectivity in The PhilippinesDocument5 pagesTechnology and Automation As Sources of 21 - Century Firm Productivity: The Economics of Slow Internet Connectivity in The PhilippinesCholo Marcus GetesNo ratings yet
- PLDT Company Portfolio AnalysisDocument13 pagesPLDT Company Portfolio AnalysisMary Bernadette VillaluzNo ratings yet
- The Sorry State of Internet Service in The PhilippinesDocument5 pagesThe Sorry State of Internet Service in The PhilippinesAnthony Tamayosa Del AyreNo ratings yet
- Philippine Digital Strategy 2011-2016Document154 pagesPhilippine Digital Strategy 2011-2016tonyocruzNo ratings yet
- Serrano, Franz Jezreel M.Document1 pageSerrano, Franz Jezreel M.Franz JezreelNo ratings yet
- Phil Lip Pine National Observatory On The Information SocietyDocument23 pagesPhil Lip Pine National Observatory On The Information SocietyAllan Ore CruzNo ratings yet
- The Philippine IT Plan: Prospects and Problems: Claro V. ParladeDocument10 pagesThe Philippine IT Plan: Prospects and Problems: Claro V. ParladeLGS A RO12-05No ratings yet
- E-Government and Philippine Development: Francisco A. MagnoDocument15 pagesE-Government and Philippine Development: Francisco A. MagnoKristine RGNo ratings yet
- SSRN 2882313Document88 pagesSSRN 2882313Kobie Loraine PonioNo ratings yet
- Bernardo Villegas PDFDocument2 pagesBernardo Villegas PDFrmateo_caniyasNo ratings yet
- Bernardo VillegasDocument2 pagesBernardo VillegasJaiDomeyegNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument4 pagesCase StudyWild CatNo ratings yet
- Internet Adoption and Usage in Bangladesh: Md. Shah AzamDocument12 pagesInternet Adoption and Usage in Bangladesh: Md. Shah AzamSandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Protecting Children in Cyberspace-NaumanDocument20 pagesProtecting Children in Cyberspace-Naumannmafzal70No ratings yet
- Philippines - Information and Communications TechnologyDocument11 pagesPhilippines - Information and Communications Technologypeach ParkNo ratings yet
- Philippines - Information and Communications Technology - Export - GovDocument11 pagesPhilippines - Information and Communications Technology - Export - Govrmateo_caniyasNo ratings yet
- VILORIA, BRYAN - Topic 1 (Internet Penetration and Broadband Subscription On Economic Growth)Document3 pagesVILORIA, BRYAN - Topic 1 (Internet Penetration and Broadband Subscription On Economic Growth)BB ViloriaNo ratings yet
- Serrano, Franz Jezreel M.Document1 pageSerrano, Franz Jezreel M.Franz JezreelNo ratings yet
- FF2016-11 IctDocument2 pagesFF2016-11 IctEdelyn CuriosoNo ratings yet
- Fatih Muflih - BahasaInggrisTeknikDocument9 pagesFatih Muflih - BahasaInggrisTeknikFatih MuflihNo ratings yet
- Input 1 QuizDocument49 pagesInput 1 QuizMay Pearl BernaldezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Ict State in The PhilippinesDocument37 pagesLesson 3 Ict State in The PhilippinesRence Matthew AustriaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Research RevisedDocument6 pagesChapter 2 Research RevisedChristian BarandaNo ratings yet
- Digital TechnologyDocument33 pagesDigital TechnologystanfordmarindaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document8 pagesActivity 1Grace Nagpiing CasabarNo ratings yet
- Last Published: 7/18/2019: Information Technology (IT)Document3 pagesLast Published: 7/18/2019: Information Technology (IT)lez2No ratings yet
- Philippines Current Real State in ICTDocument7 pagesPhilippines Current Real State in ICTRay Jay PacatangNo ratings yet
- (An Update Report) : Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Development in The PhilippinesDocument27 pages(An Update Report) : Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Development in The PhilippinesJaiDomeyegNo ratings yet
- Commission On Information and Communications TechnologyDocument3 pagesCommission On Information and Communications TechnologySly VeranoNo ratings yet
- Emtech Week 1.0 NotesDocument57 pagesEmtech Week 1.0 NotesGakusei AkagamiNo ratings yet
- Dict 2022Document16 pagesDict 2022GHEIST INC.No ratings yet
- Infrastructure Asia Conference 2010 - 13 April2010Document22 pagesInfrastructure Asia Conference 2010 - 13 April2010Marina NatsirNo ratings yet
- Philippines - Information TechnologyDocument12 pagesPhilippines - Information TechnologyBianca YssabelNo ratings yet
- Pakistan FOTN2011Document12 pagesPakistan FOTN2011arzakNo ratings yet
- E-Government and Philippine Development: Francisco A. MagnoDocument15 pagesE-Government and Philippine Development: Francisco A. MagnoKorean Drama 2019No ratings yet
- Internet ConnectivityDocument6 pagesInternet ConnectivityMaria Theresa RabuyaNo ratings yet
- Princess Ann Malinao Emptechq1m1l3Document12 pagesPrincess Ann Malinao Emptechq1m1l3Cookie MonsterNo ratings yet
- ICT's Societal and Economic Impact: TransactionsDocument6 pagesICT's Societal and Economic Impact: Transactionsdeka degan AliNo ratings yet
- 6-Business Analysis PlanningDocument11 pages6-Business Analysis PlanningJonel NaquitaNo ratings yet
- Week 5-Needs AssessmentDocument11 pagesWeek 5-Needs AssessmentJonel NaquitaNo ratings yet
- Week 8-Requirements Elicitation & AnalysisDocument7 pagesWeek 8-Requirements Elicitation & AnalysisJonel NaquitaNo ratings yet
- Week 4-Creating Charts in Microsoft ExcelDocument10 pagesWeek 4-Creating Charts in Microsoft ExcelJonel NaquitaNo ratings yet
- Psystat Lecture Asynchronous Task 3Document1 pagePsystat Lecture Asynchronous Task 3Jonel NaquitaNo ratings yet
- Psystat Lecture Asynchronous Task 3Document1 pagePsystat Lecture Asynchronous Task 3Jonel NaquitaNo ratings yet
- Wondershare Filmora9 Review and Tutorial #1 - What's NewDocument5 pagesWondershare Filmora9 Review and Tutorial #1 - What's NewJonel NaquitaNo ratings yet
- Central TendencyDocument31 pagesCentral TendencyJonel NaquitaNo ratings yet
- 7 QueeniePearlV TomaroDyahMutiarin90-104Document26 pages7 QueeniePearlV TomaroDyahMutiarin90-104Jonel NaquitaNo ratings yet
- Batangas State University Jplpc-Malvar: Budget Summary Total Cost: - 000.00Document7 pagesBatangas State University Jplpc-Malvar: Budget Summary Total Cost: - 000.00Jonel NaquitaNo ratings yet
- Amelita Sari PDFDocument13 pagesAmelita Sari PDFJonel NaquitaNo ratings yet
- Wondershare Filmora9 Review and Tutorial #1 - What's NewDocument5 pagesWondershare Filmora9 Review and Tutorial #1 - What's NewJonel NaquitaNo ratings yet
- Attachment PDFDocument5 pagesAttachment PDFVanessa NatanNo ratings yet
- Was Was: (COOP Project), l,2Document12 pagesWas Was: (COOP Project), l,2Jonel NaquitaNo ratings yet
- 2013 Bookmatter BetweenEmpires PDFDocument29 pages2013 Bookmatter BetweenEmpires PDFJonel NaquitaNo ratings yet
- Web-Based Billing and Collection System For A Municipal Water and Services UnitDocument30 pagesWeb-Based Billing and Collection System For A Municipal Water and Services UnitJonel NaquitaNo ratings yet
- Si112 PDFDocument6 pagesSi112 PDFAmanual EngdawNo ratings yet
- 7 The Impact of Reform: Par Excellence The Teleological View of History, and Bristle WithDocument2 pages7 The Impact of Reform: Par Excellence The Teleological View of History, and Bristle WithJonel NaquitaNo ratings yet
- Smart Goods Billing Management and Payment System: March 2018Document7 pagesSmart Goods Billing Management and Payment System: March 2018Jonel NaquitaNo ratings yet
- Attachment PDFDocument5 pagesAttachment PDFVanessa NatanNo ratings yet
- PI 100 Position PaperDocument2 pagesPI 100 Position PaperAngel Rose TrocioNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1605536585231 6734108521583470594Document3 pagesOrca Share Media1605536585231 6734108521583470594Jonel NaquitaNo ratings yet
- Database System in Automatic Billing For SupermarketDocument4 pagesDatabase System in Automatic Billing For SupermarketEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- C++ Super Market Billing SystemDocument42 pagesC++ Super Market Billing SystemTribhuwan Kumar68% (114)